Abstract
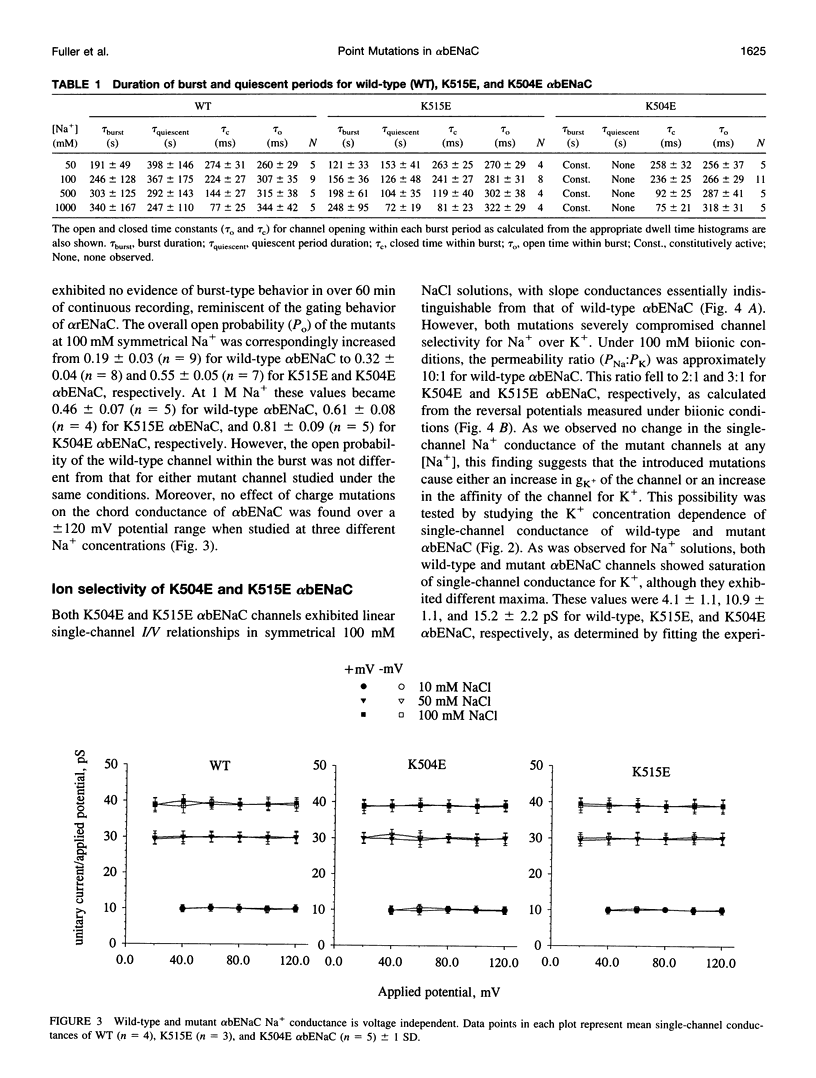
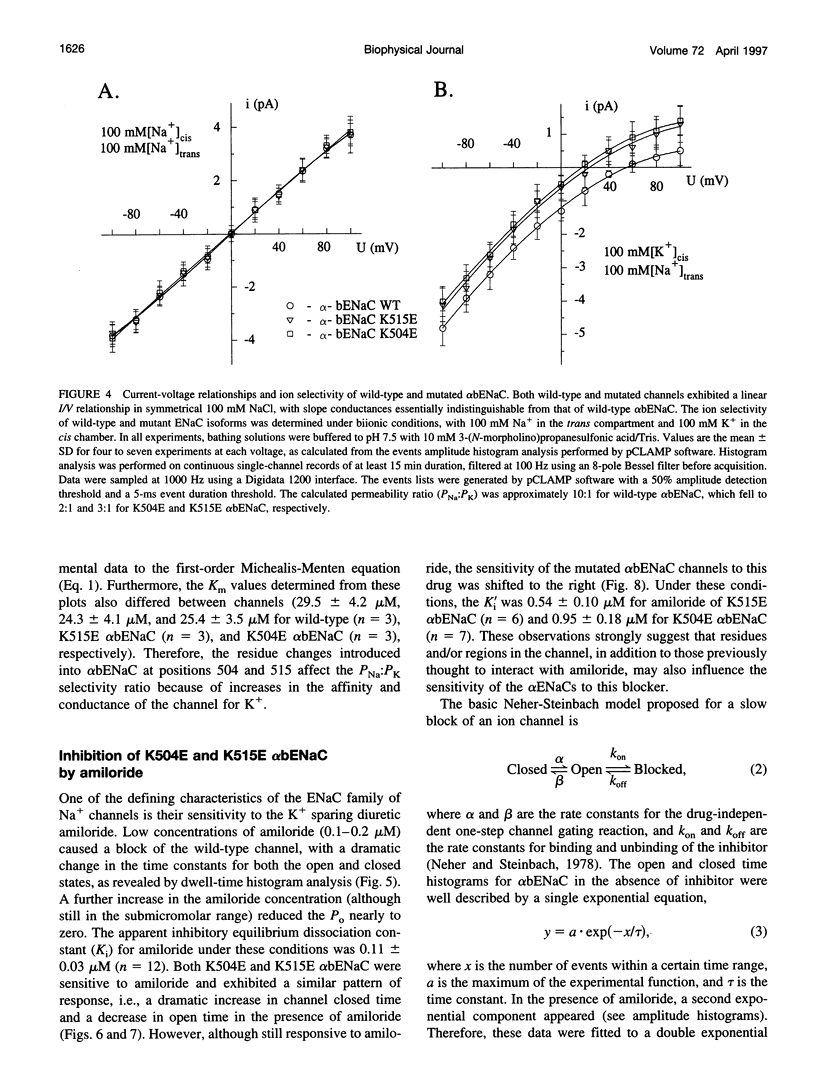
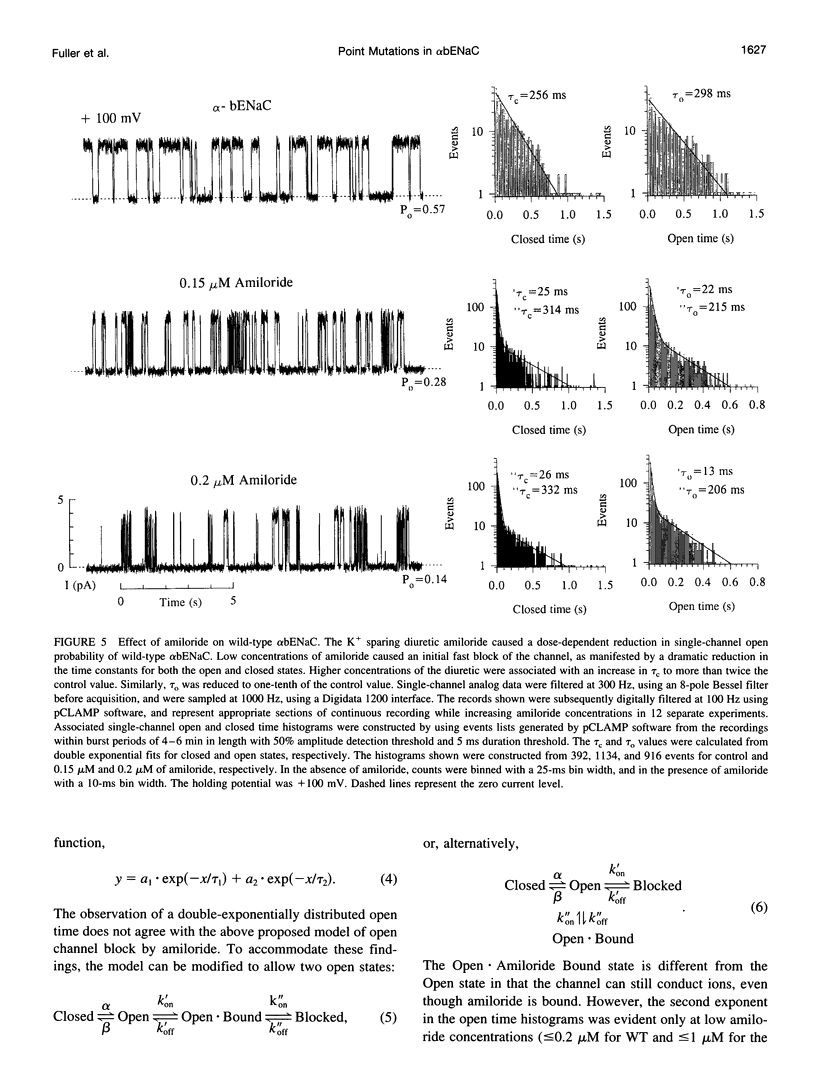
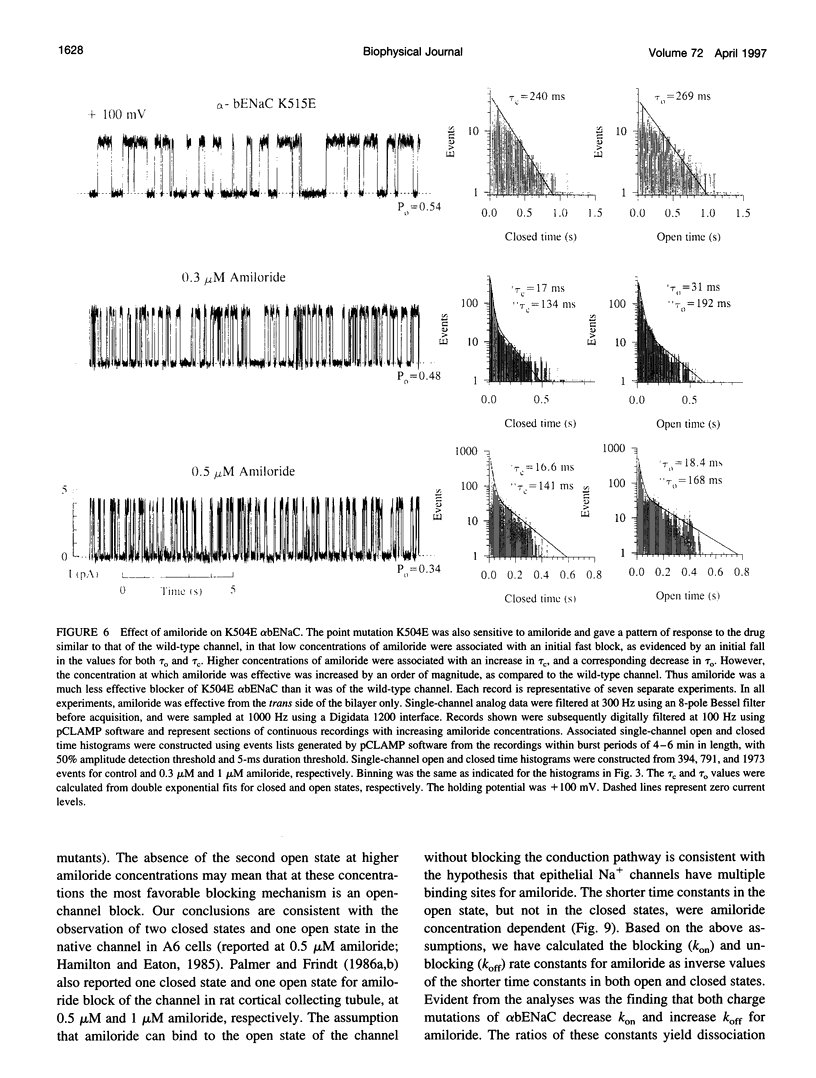
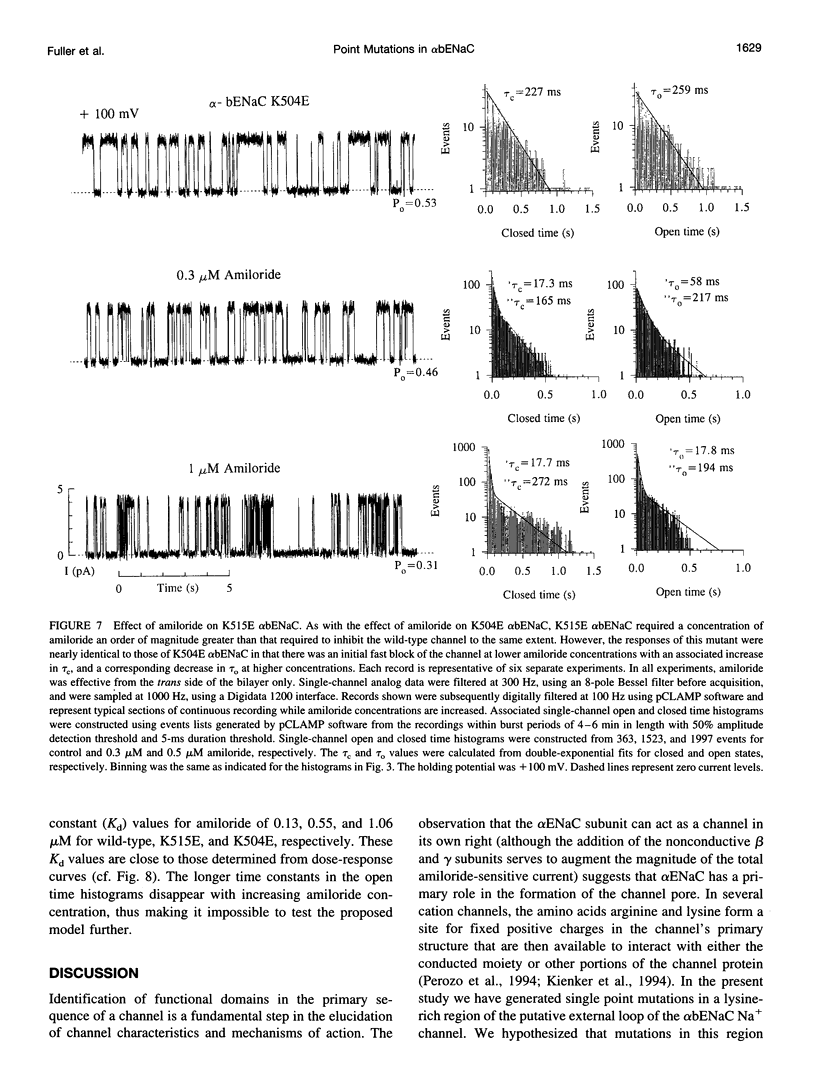
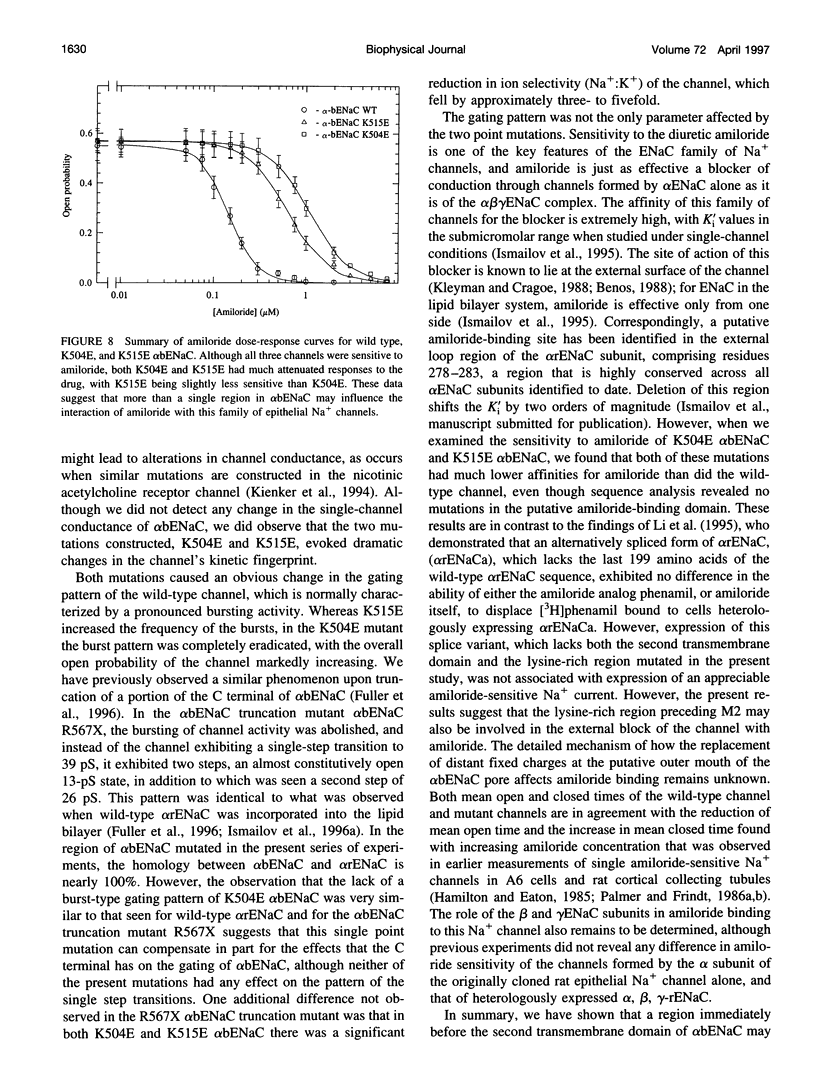
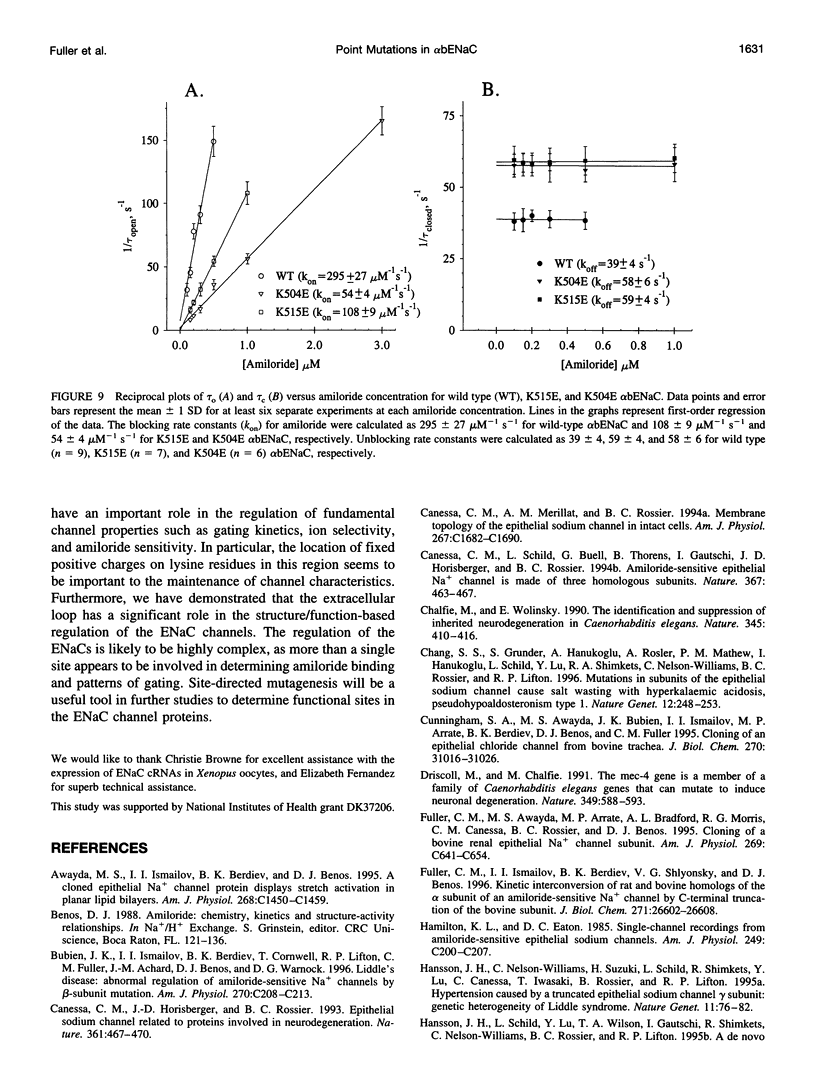
We have generated two site-directed mutants, K504E and K515E, in the alpha subunit of an amiloride-sensitive bovine epithelial Na+ channel, alpha bENaC. The region in which these mutations lie is in the large extracellular loop immediately before the second membrane-spanning domain (M2) of the protein. We have found that when membrane vesicles prepared from Xenopus oocytes expressing either K504E or K515E alpha bENaC are incorporated into planar lipid bilayers, the gating pattern, cation selectivity, and amiloride sensitivity of the resultant channel are all altered as compared to the wild-type protein. The mutated channels exhibit either a reduction or a complete lack of its characteristic burst-type behavior, significantly reduced Na+:K+ selectivity, and an approximately 10-fold decrease in the apparent inhibitory equilibrium dissociation constant (Ki) for amiloride. Single-channel conductance for Na+ was not affected by either mutation. On the other hand, both K504E and K515E alpha bENaC mutants were significantly more permeable to K+, as compared to wild type. These observations identify a lysine-rich region between amino acid residues 495 and 516 of alpha bENaC as being important to the regulation of fundamental channel properties.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awayda M. S., Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J. A cloned renal epithelial Na+ channel protein displays stretch activation in planar lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jun;268(6 Pt 1):C1450–C1459. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.6.C1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubien J. K., Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Cornwell T., Lifton R. P., Fuller C. M., Achard J. M., Benos D. J., Warnock D. G. Liddle's disease: abnormal regulation of amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels by beta-subunit mutation. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jan;270(1 Pt 1):C208–C213. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.1.C208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Merillat A. M., Rossier B. C. Membrane topology of the epithelial sodium channel in intact cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Dec;267(6 Pt 1):C1682–C1690. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.6.C1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Wolinsky E. The identification and suppression of inherited neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):410–416. doi: 10.1038/345410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. S., Grunder S., Hanukoglu A., Rösler A., Mathew P. M., Hanukoglu I., Schild L., Lu Y., Shimkets R. A., Nelson-Williams C. Mutations in subunits of the epithelial sodium channel cause salt wasting with hyperkalaemic acidosis, pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1. Nat Genet. 1996 Mar;12(3):248–253. doi: 10.1038/ng0396-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham S. A., Awayda M. S., Bubien J. K., Ismailov I. I., Arrate M. P., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J., Fuller C. M. Cloning of an epithelial chloride channel from bovine trachea. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 29;270(52):31016–31026. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.52.31016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M., Chalfie M. The mec-4 gene is a member of a family of Caenorhabditis elegans genes that can mutate to induce neuronal degeneration. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):588–593. doi: 10.1038/349588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller C. M., Awayda M. S., Arrate M. P., Bradford A. L., Morris R. G., Canessa C. M., Rossier B. C., Benos D. J. Cloning of a bovine renal epithelial Na+ channel subunit. Am J Physiol. 1995 Sep;269(3 Pt 1):C641–C654. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.3.C641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller C. M., Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Shlyonsky V. G., Benos D. J. Kinetic interconversion of rat and bovine homologs of the alpha subunit of an amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel by C-terminal truncation of the bovine subunit. J Biol Chem. 1996 Oct 25;271(43):26602–26608. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.43.26602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. L., Eaton D. C. Single-channel recordings from amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C200–C207. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson J. H., Nelson-Williams C., Suzuki H., Schild L., Shimkets R., Lu Y., Canessa C., Iwasaki T., Rossier B., Lifton R. P. Hypertension caused by a truncated epithelial sodium channel gamma subunit: genetic heterogeneity of Liddle syndrome. Nat Genet. 1995 Sep;11(1):76–82. doi: 10.1038/ng0995-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson J. H., Schild L., Lu Y., Wilson T. A., Gautschi I., Shimkets R., Nelson-Williams C., Rossier B. C., Lifton R. P. A de novo missense mutation of the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel causes hypertension and Liddle syndrome, identifying a proline-rich segment critical for regulation of channel activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11495–11499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Busch C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Konno T., Nakai J., Bujo H., Mori Y., Fukuda K., Numa S. Rings of negatively charged amino acids determine the acetylcholine receptor channel conductance. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):645–648. doi: 10.1038/335645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Awayda M. S., Berdiev B. K., Bubien J. K., Lucas J. E., Fuller C. M., Benos D. J. Triple-barrel organization of ENaC, a cloned epithelial Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):807–816. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J. Biochemical status of renal epithelial Na+ channels determines apparent channel conductance, ion selectivity, and amiloride sensitivity. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):1789–1800. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80049-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Fuller C. M., Bradford A. L., Lifton R. P., Warnock D. G., Bubien J. K., Benos D. J. Peptide block of constitutively activated Na+ channels in Liddle's disease. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jan;270(1 Pt 1):C214–C223. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.1.C214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kienker P., Tomaselli G., Jurman M., Yellen G. Conductance mutations of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor do not act by a simple electrostatic mechanism. Biophys J. 1994 Feb;66(2 Pt 1):325–334. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80781-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Busch C., Von Kitzing E., Imoto K., Wang F., Nakai J., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Rings of anionic amino acids as structural determinants of ion selectivity in the acetylcholine receptor channel. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 May 22;244(1310):69–79. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. J., Xu R. H., Guggino W. B., Snyder S. H. Alternatively spliced forms of the alpha subunit of the epithelial sodium channel: distinct sites for amiloride binding and channel pore. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;47(6):1133–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Champigny G., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Cloning of the amiloride-sensitive FMRFamide peptide-gated sodium channel. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):730–733. doi: 10.1038/378730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Functional modification of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel by trimethyloxonium. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8087–8092. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald F. J., Snyder P. M., McCray P. B., Jr, Welsh M. J. Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of a human amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L728–L734. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald F. J., Welsh M. J. Binding of the proline-rich region of the epithelial Na+ channel to SH3 domains and its association with specific cellular proteins. Biochem J. 1995 Dec 1;312(Pt 2):491–497. doi: 10.1042/bj3120491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Epithelial sodium channels: characterization by using the patch-clamp technique. Fed Proc. 1986 Nov;45(12):2708–2712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozo E., Santacruz-Toloza L., Stefani E., Bezanilla F., Papazian D. M. S4 mutations alter gating currents of Shaker K channels. Biophys J. 1994 Feb;66(2 Pt 1):345–354. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80783-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M. P., Snyder P. M., Welsh M. J. Cloning and expression of a novel human brain Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 5;271(14):7879–7882. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.14.7879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez G., Lagrutta A., Adelman J. P., Toro L. Reconstitution of expressed KCa channels from Xenopus oocytes to lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1022–1027. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80883-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renard S., Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Biochemical analysis of the membrane topology of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12981–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Bar-Sagi D., O'Brodovich H., Merilainen J., Lehto V. P., Canessa C. M., Rossier B. C., Downey G. P. An SH3 binding region in the epithelial Na+ channel (alpha rENaC) mediates its localization at the apical membrane. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4440–4450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild L., Lu Y., Gautschi I., Schneeberger E., Lifton R. P., Rossier B. C. Identification of a PY motif in the epithelial Na channel subunits as a target sequence for mutations causing channel activation found in Liddle syndrome. EMBO J. 1996 May 15;15(10):2381–2387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets R. A., Warnock D. G., Bositis C. M., Nelson-Williams C., Hansson J. H., Schambelan M., Gill J. R., Jr, Ulick S., Milora R. V., Findling J. W. Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. M., McDonald F. J., Stokes J. B., Welsh M. J. Membrane topology of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24379–24383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub O., Dho S., Henry P., Correa J., Ishikawa T., McGlade J., Rotin D. WW domains of Nedd4 bind to the proline-rich PY motifs in the epithelial Na+ channel deleted in Liddle's syndrome. EMBO J. 1996 May 15;15(10):2371–2380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voilley N., Bassilana F., Mignon C., Merscher S., Mattéi M. G., Carle G. F., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Cloning, chromosomal localization, and physical linkage of the beta and gamma subunits (SCNN1B and SCNN1G) of the human epithelial amiloride-sensitive sodium channel. Genomics. 1995 Aug 10;28(3):560–565. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voilley N., Lingueglia E., Champigny G., Mattéi M. G., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. The lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel: biophysical properties, pharmacology, ontogenesis, and molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J., Krueger B. K. Trimethyloxonium modification of single batrachotoxin-activated sodium channels in planar bilayers. Changes in unit conductance and in block by saxitoxin and calcium. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Feb;87(2):327–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Restoration of inactivation in mutants of Shaker potassium channels by a peptide derived from ShB. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2122520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]