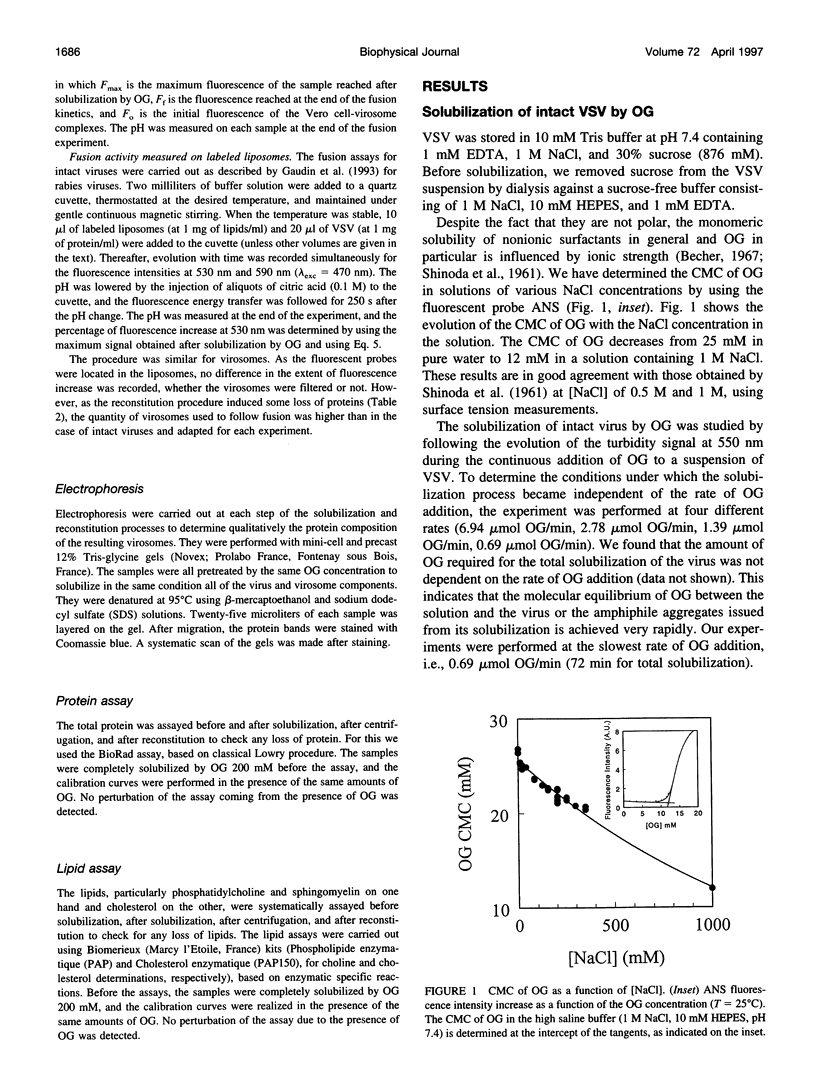
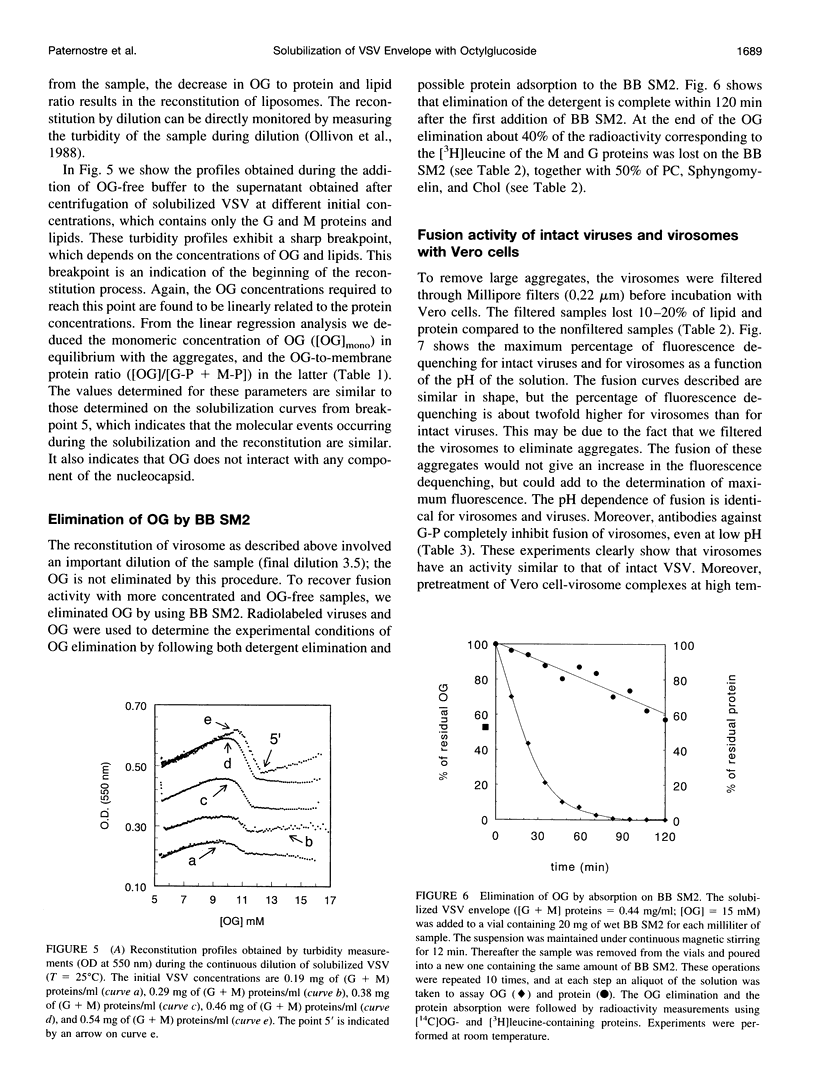
Abstract
Reconstituted vesicular stomatitis virus envelopes or virosomes are formed by detergent removal from solubilized intact virus. We have monitored the solubilization process of the intact vesicular stomatitis virus by the nonionic surfactant octylglucoside at various initial virus concentrations by employing turbidity measurements. This allowed us to determine the phase boundaries between the membrane and the mixed micelles domains. We have also characterized the lipid and protein content of the solubilized material and of the reconstituted envelope. Both G and M proteins and all of the lipids of the envelope were extracted by octylglucoside and recovered in the reconstituted envelope. Fusion activity of the virosomes tested either on Vero cells or on liposomes showed kinetics and pH dependence similar to those of the intact virus.
Full text
PDF





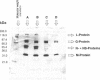
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenthal R., Bali-Puri A., Walter A., Covell D., Eidelman O. pH-dependent fusion of vesicular stomatitis virus with Vero cells. Measurement by dequenching of octadecyl rhodamine fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13614–13619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R., Loyter A. Reconstituted viral envelopes--'Trojan horses' for drug delivery and gene therapy? Trends Biotechnol. 1991 Feb;9(2):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(91)90184-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R., Sarkar D. P., Durell S., Howard D. E., Morris S. J. Dilation of the influenza hemagglutinin fusion pore revealed by the kinetics of individual cell-cell fusion events. J Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;135(1):63–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bron R., Ortiz A., Dijkstra J., Stegmann T., Wilschut J. Preparation, properties, and applications of reconstituted influenza virus envelopes (virosomes). Methods Enzymol. 1993;220:313–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)20091-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Schoch C., Zech L., Blumenthal R. Gating kinetics of pH-activated membrane fusion of vesicular stomatitis virus with cells: stopped-flow measurements by dequenching of octadecylrhodamine fluorescence. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1303–1308. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman O., Blumenthal R., Walter A. Composition of octyl glucoside-phosphatidylcholine mixed micelles. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2839–2846. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman O., Schlegel R., Tralka T. S., Blumenthal R. pH-dependent fusion induced by vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4622–4628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eytan G. D. Use of liposomes for reconstitution of biological functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 20;694(2):185–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin Y., Ruigrok R. W., Brunner J. Low-pH induced conformational changes in viral fusion proteins: implications for the fusion mechanism. J Gen Virol. 1995 Jul;76(Pt 7):1541–1556. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-7-1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin Y., Ruigrok R. W., Knossow M., Flamand A. Low-pH conformational changes of rabies virus glycoprotein and their role in membrane fusion. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1365–1372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1365-1372.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin Y., Tuffereau C., Segretain D., Knossow M., Flamand A. Reversible conformational changes and fusion activity of rabies virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4853–4859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4853-4859.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug P., Sleight R. G. Fusogenic virosomes prepared by partitioning of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein into preformed vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4050–4056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. L., Schmidt C. F., Lichtenberg D., Litman B. J., Albert A. D. Solubilization of phosphatidylcholine bilayers by octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4576–4582. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot M., Nussbaum O., Loyter A. Fusion of membrane vesicles bearing only the influenza hemagglutinin with erythrocytes, living cultured cells, and liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13736–13741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorge P., Cabiaux V., Long L., Ruysschaert J. M. Fusion of Newcastle disease virus with liposomes: role of the lipid composition of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 26;858(2):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90337-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., McKenzie M., Parce J. W. Subunit interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein stabilized by binding to viral matrix protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):349–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.349-358.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., van Meer G., Simons K. Reconstitution of the fusogenic activity of vesicular stomatitis virus. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3429–3435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer O., Ollivon M., Paternostre M. T. Solubilization steps of dark-adapted purple membrane by Triton X-100. A spectroscopic study. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 6;305(3):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80679-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Feuer B. I., Vanderoef R., Lenard J. Reconstituted G protein-lipid vesicles from vesicular stomatitis virus and their inhibition of VSV infection. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):421–429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Tobin G. J., McGowan J. J., Brown J. C. In vitro reassembly of vesicular stomatitis virus skeletons. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1055-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum O., Lapidot M., Loyter A. Reconstitution of functional influenza virus envelopes and fusion with membranes and liposomes lacking virus receptors. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2245–2252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2245-2252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollivon M., Eidelman O., Blumenthal R., Walter A. Micelle-vesicle transition of egg phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1695–1703. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Vesicular stomatitis virus membrane proteins and their interactions with lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 24;906(2):175–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Wiener J. R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Influence of the membrane glycoprotein and cholesterol of vesicular stomatitis virus on the dynamics of viral and model membranes: fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3624–3630. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paternostre M. T., Lowy R. J., Blumenthal R. pH-dependent fusion of reconstituted vesicular stomatitis virus envelopes with Vero cells. Measurement by dequenching of fluorescence. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paternostre M. T., Roux M., Rigaud J. L. Mechanisms of membrane protein insertion into liposomes during reconstitution procedures involving the use of detergents. 1. Solubilization of large unilamellar liposomes (prepared by reverse-phase evaporation) by triton X-100, octyl glucoside, and sodium cholate. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2668–2677. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paternostre M., Meyer O., Grabielle-Madelmont C., Lesieur S., Ghanam M., Ollivon M. Partition coefficient of a surfactant between aggregates and solution: application to the micelle-vesicle transition of egg phosphatidylcholine and octyl beta-D-glucopyranoside. Biophys J. 1995 Dec;69(6):2476–2488. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80118-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Glycoprotein micelles isolated from vesicular stomatitis virus spontaneously partition into sonicated phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Reconstitution into liposomes of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus by detergent dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4313–4316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri A., Clague M. J., Schoch C., Blumenthal R. Kinetics of fusion of enveloped viruses with cells. Methods Enzymol. 1993;220:277–287. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)20089-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri A., Dimitrov D. S., Golding H., Blumenthal R. Interactions of CD4+ plasma membrane vesicles with HIV-1 and HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-expressing cells. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(9):915–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri A., Grimaldi S., Blumenthal R. Role of viral envelope sialic acid in membrane fusion mediated by the vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):10108–10113. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud J. L., Paternostre M. T., Bluzat A. Mechanisms of membrane protein insertion into liposomes during reconstitution procedures involving the use of detergents. 2. Incorporation of the light-driven proton pump bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2677–2688. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud J. L., Pitard B., Levy D. Reconstitution of membrane proteins into liposomes: application to energy-transducing membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Oct 10;1231(3):223–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(95)00091-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar D. P., Morris S. J., Eidelman O., Zimmerberg J., Blumenthal R. Initial stages of influenza hemagglutinin-induced cell fusion monitored simultaneously by two fluorescent events: cytoplasmic continuity and lipid mixing. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):113–122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoch C., Blumenthal R. Role of the fusion peptide sequence in initial stages of influenza hemagglutinin-induced cell fusion. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9267–9274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Morselt H. W., Booy F. P., van Breemen J. F., Scherphof G., Wilschut J. Functional reconstitution of influenza virus envelopes. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2651–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Nir S., Wilschut J. Membrane fusion activity of influenza virus. Effects of gangliosides and negatively charged phospholipids in target liposomes. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1698–1704. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainstein A., Hershkovitz M., Israel S., Rabin S., Loyter A. A new method for reconstitution of highly fusogenic Sendai virus envelopes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 27;773(2):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Membrane fusion. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):917–924. doi: 10.1126/science.1439803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. D., McKenzie M. O., Parce J. W., Lyles D. S. Subunit interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein influenced by detergent micelles and lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10458–10464. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilschut J., Corver J., Nieva J. L., Bron R., Moesby L., Reddy K. C., Bittman R. Fusion of Semliki Forest virus with cholesterol-containing liposomes at low pH: a specific requirement for sphingolipids. Mol Membr Biol. 1995 Jan-Mar;12(1):143–149. doi: 10.3109/09687689509038510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Ohnishi S. Vesicular stomatitis virus binds and fuses with phospholipid domain in target cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3703–3708. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yedgar S., Barenholz Y., Cooper V. G. Molecular weight, shape and structure of mixed micelles of Triton X-100 and sphingomyelin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 21;363(1):98–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Blumenthal R., Sarkar D. P., Curran M., Morris S. J. Restricted movement of lipid and aqueous dyes through pores formed by influenza hemagglutinin during cell fusion. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1885–1894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Foresta B., Merah Z., le Maire M., Champeil P. How to evaluate the distribution of an "invisible" amphiphile between biological membranes and water. Anal Biochem. 1990 Aug 15;189(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90044-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]