Abstract
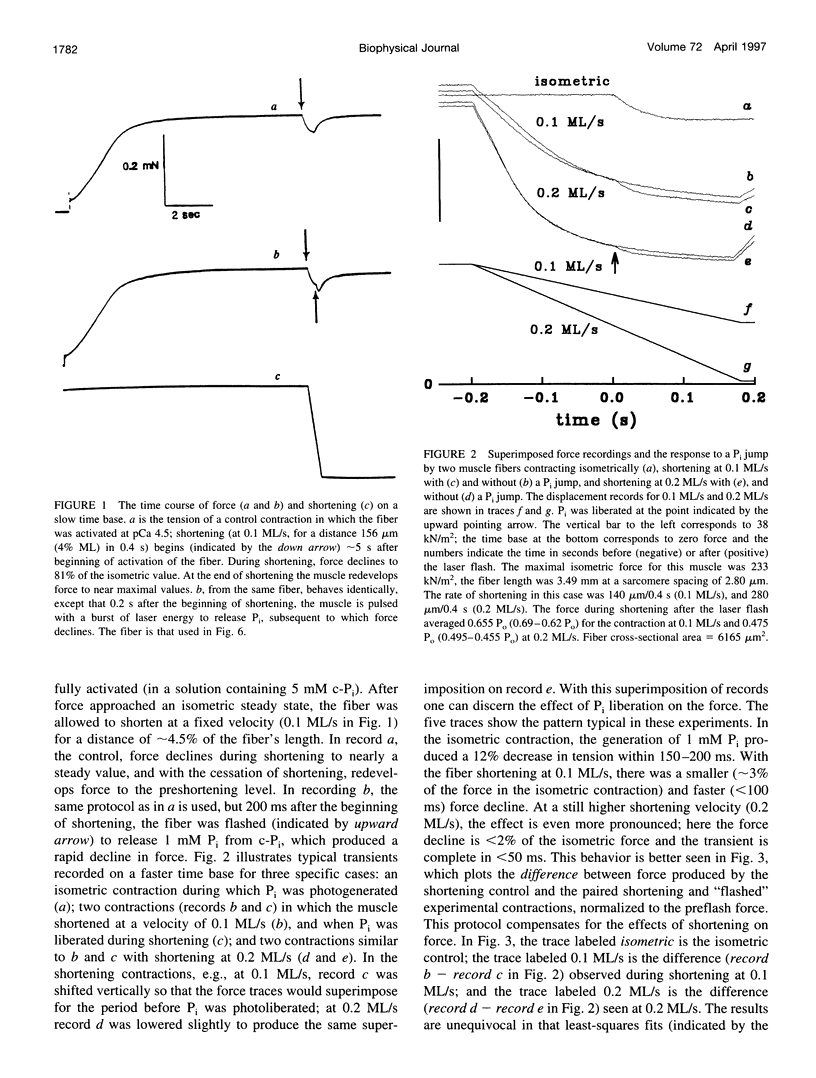
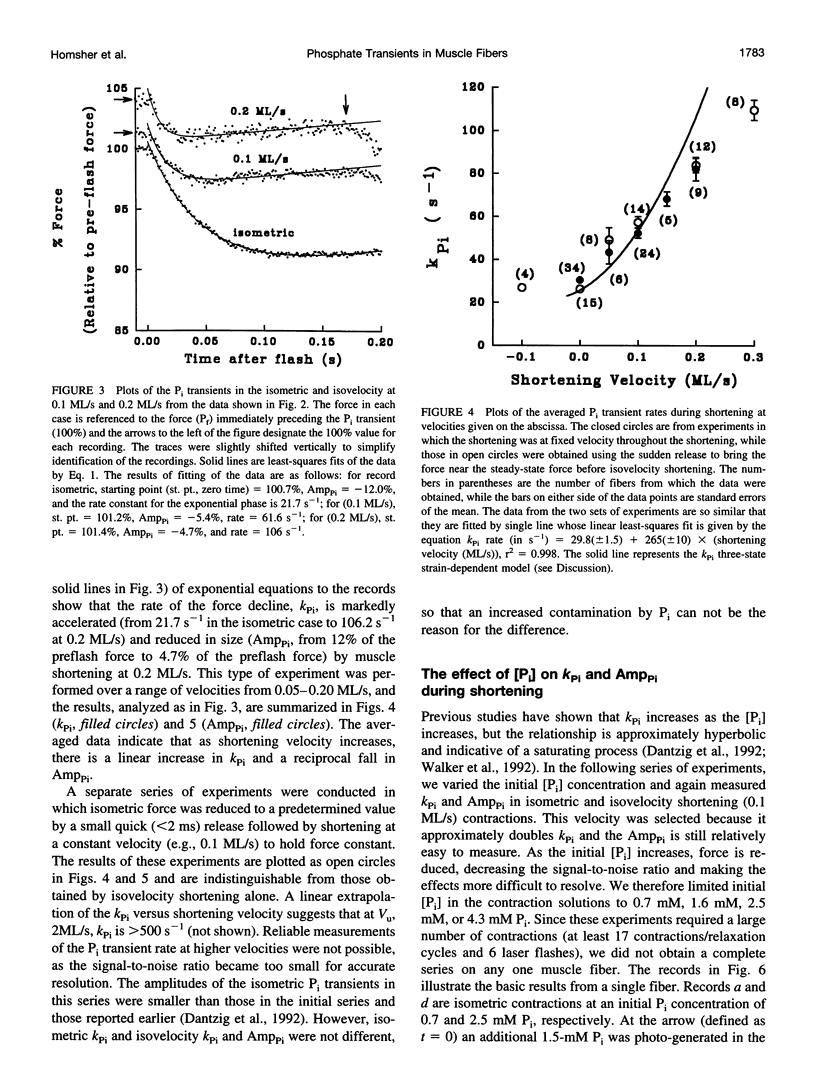
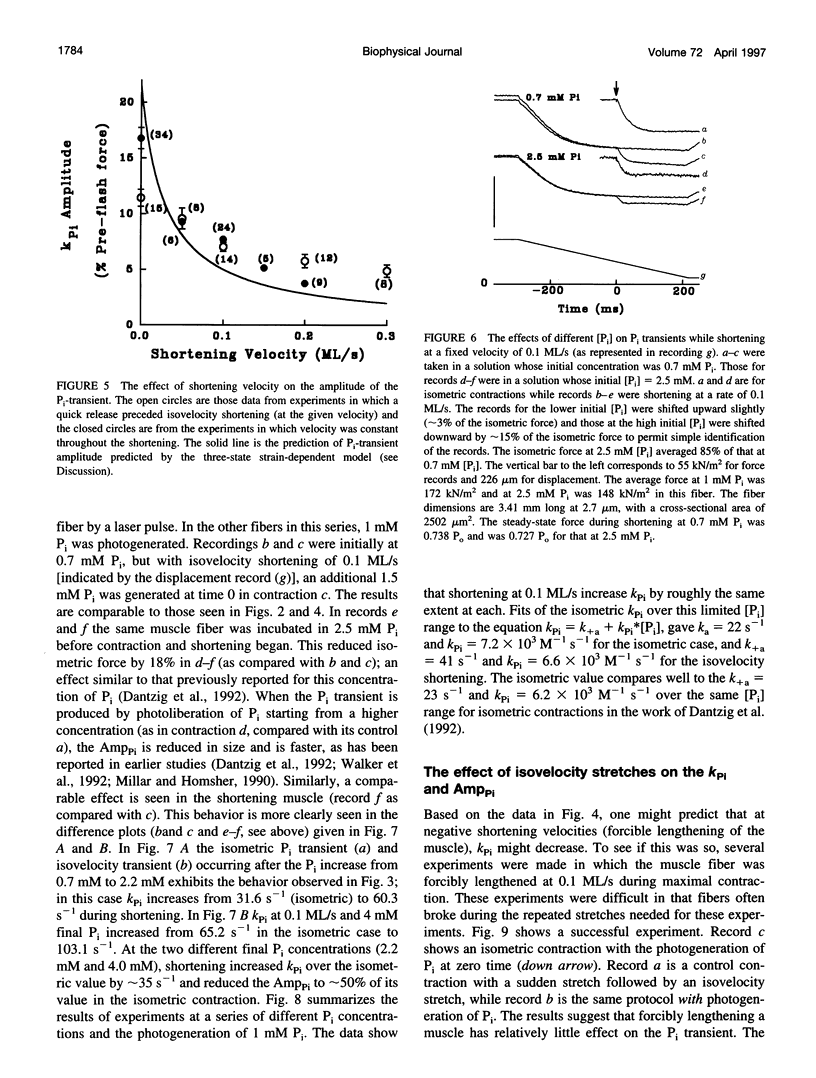
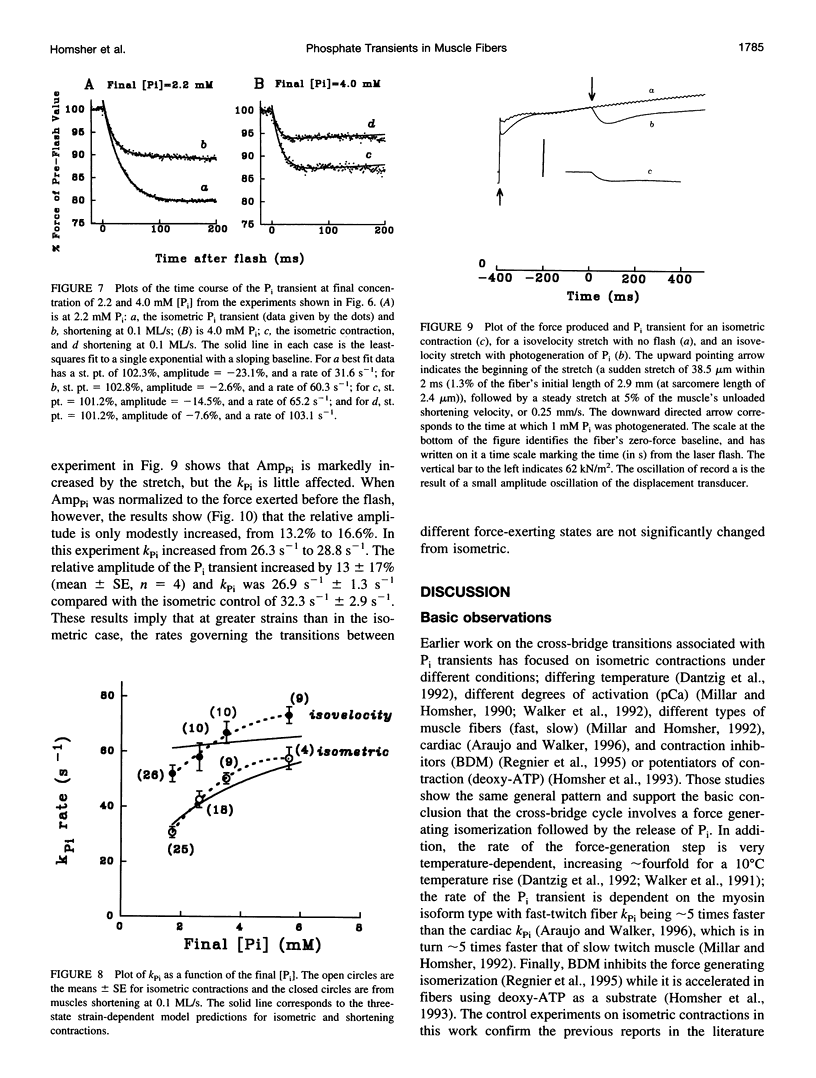
When inorganic phosphate (Pi) is photogenerated from caged Pi during isometric contractions of glycerinated rabbit psoas muscle fibers, the released Pi binds to cross-bridges and reverses the working stroke of cross-bridges. The consequent force decline, the Pi-transient, is exponential and probes the kinetics of the power-stroke and Pi release. During muscle shortening, the fraction of attached cross-bridges and the average strain on them decreases (Ford, L. E., A.F. Huxley, and R.M. Simmons, 1977. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibers near slack length. J. Physiol. (Lond.). 269:441-515; Ford, L. E., A. F. Huxley, and R.M. Simmons, 1985. Tension transients during steady state shortening of frog muscle fibers. J. Physiol. (Lond.). 361:131-150. To learn to what extent the Pi transient is strain dependent, muscle fibers were activated and shortened or lengthened at a fixed velocity during the photogeneration of Pi. The Pi transients observed during changes in muscle length showed three primary characteristics: 1) during shortening the Pi transient rate, Kpi, increased and its amplitude decreased with shortening velocity; Kpi increased linearly with velocity to > 110 s-1 at 0.3 muscle lengths per second (ML/s). 2) At a specific shortening velocity, increases in [Pi] produce increases in Kpi that are nonlinear with [Pi] and approach an asymptote. 3) During forced lengthening Kpi and the amplitude of the Pi transient are little different from the isometric contractions. These data can be approximated by a strain-dependent three-state cross-bridge model. The results show that the power stroke's rate is strain-dependent, and are consistent with biochemical studies indicating that the rate-limiting step at low strains is a transition from a weakly to a strongly bound cross-bridge state.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo A., Walker J. W. Phosphate release and force generation in cardiac myocytes investigated with caged phosphate and caged calcium. Biophys J. 1996 May;70(5):2316–2326. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79797-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on cross-bridge turnover kinetics in skinned single rabbit psoas fibers: implications for regulation of muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. The cross-bridge cycle in muscle. Mechanical, biochemical, and structural studies on single skinned rabbit psoas fibers to characterize cross-bridge kinetics in muscle for correlation with the actomyosin-ATPase in solution. Basic Res Cardiol. 1986;81 (Suppl 1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-11374-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by troponin-tropomyosin without blocking the binding of myosin to actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2432–2437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E., Millar N. C., Lacktis J., Homsher E. Reversal of the cross-bridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992;451:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman K. A. The velocity of unloaded shortening and its relation to sarcomere length and isometric force in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:143–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):195–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension transients during steady shortening of frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:131–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Contractile activation and force generation in skinned rabbit muscle fibres: effects of hydrostatic pressure. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 15;474(2):283–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Tension responses to rapid pressure release in glycerinated rabbit muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A., Goody R. S., Gutfreund H. Kinetics of acto-S1 interaction as a guide to a model for the crossbridge cycle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Aug;5(4):351–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00818255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relaxation of rabbit psoas muscle fibres from rigor by photochemical generation of adenosine-5'-triphosphate. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:577–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Dantzig J. A., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Phosphate release and force generation in skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.3159090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Yanagida T., Goldman Y. E. Compliance of thin filaments in skinned fibers of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):1000–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79975-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsher E., Rall J. A. Energetics of shortening muscles in twitches and tetanic contractions. I. A reinvestigation of Hill's concept of the shortening heat. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Dec;62(6):663–676. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.6.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Two step mechanism of phosphate release and the mechanism of force generation in chemically skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82227-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Zhao Y. Cross-bridge scheme and force per cross-bridge state in skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):638–651. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81109-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight P. J., Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A. Effects of pressure on equatorial x-ray fiber diffraction from skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):814–822. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81111-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Cooke R., Pate E. A model of stress relaxation in cross-bridge systems: effect of a series elastic element. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C279–C288. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y. Z., Taylor E. W. Kinetic mechanism of myofibril ATPase. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1542–1553. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80945-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Calcium-sensitive cross-bridge transitions in mammalian fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1088–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.2309121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. Kinetics of force generation and phosphate release in skinned rabbit soleus muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):C1239–C1245. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.5.C1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. A steady-state and transient kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20234–20240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. A model of crossbridge action: the effects of ATP, ADP and Pi. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Jun;10(3):181–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01739809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. Addition of phosphate to active muscle fibers probes actomyosin states within the powerstroke. Pflugers Arch. 1989 May;414(1):73–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00585629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnier M., Morris C., Homsher E. Regulation of the cross-bridge transition from a weakly to strongly bound state in skinned rabbit muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1995 Dec;269(6 Pt 1):C1532–C1539. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.6.C1532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleep J. A., Boyer P. D. Effect of actin concentration on the intermediate oxygen exchange of myosin; relation to the refractory state and the mechanism of exchange. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5417–5422. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. A., Geeves M. A. Strain-dependent cross-bridge cycle for muscle. Biophys J. 1995 Aug;69(2):524–537. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79926-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Lu Z., Moss R. L. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetics of phosphate release in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2459–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Taylor E. W. Energetics and mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5818–5826. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the cross-bridge cycle in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1655–1668. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80638-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


