Abstract
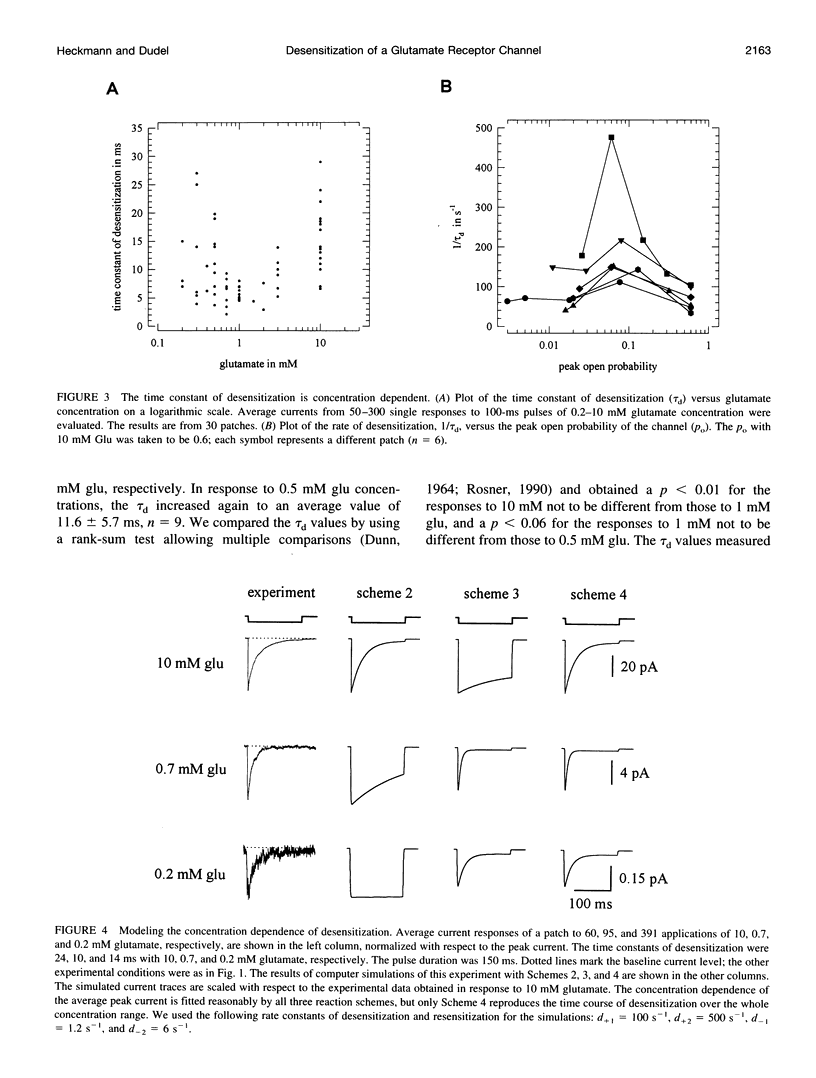
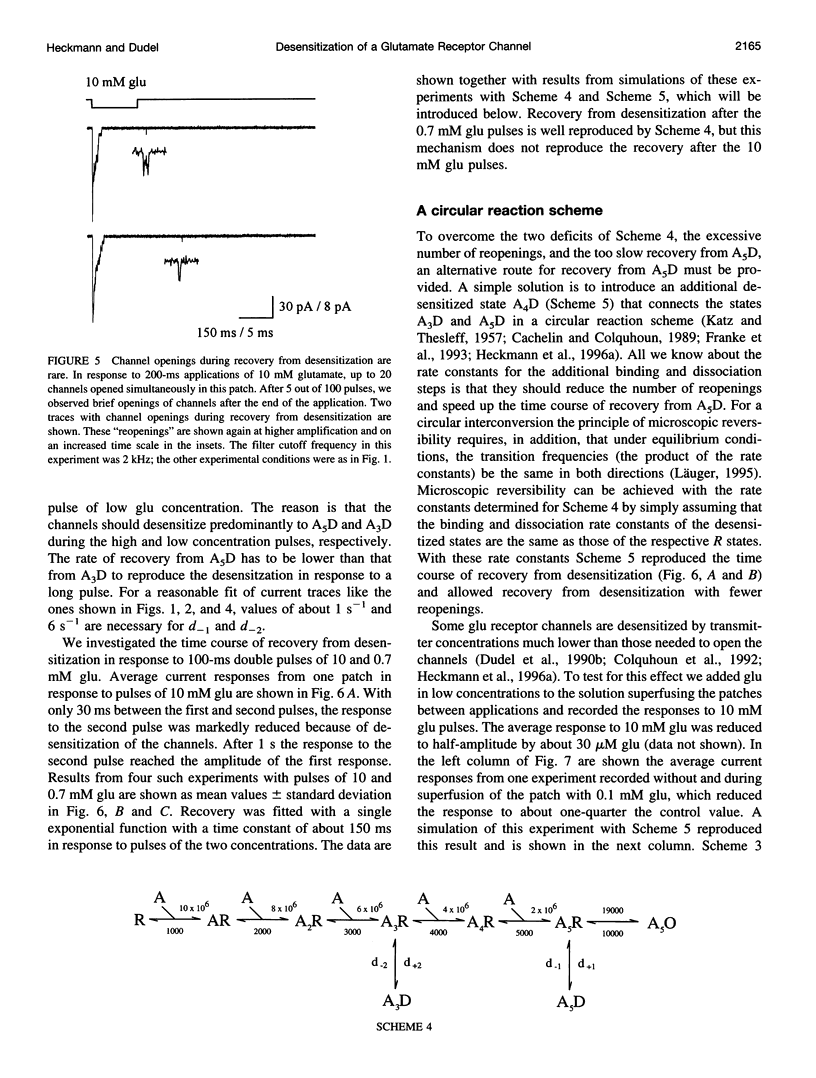
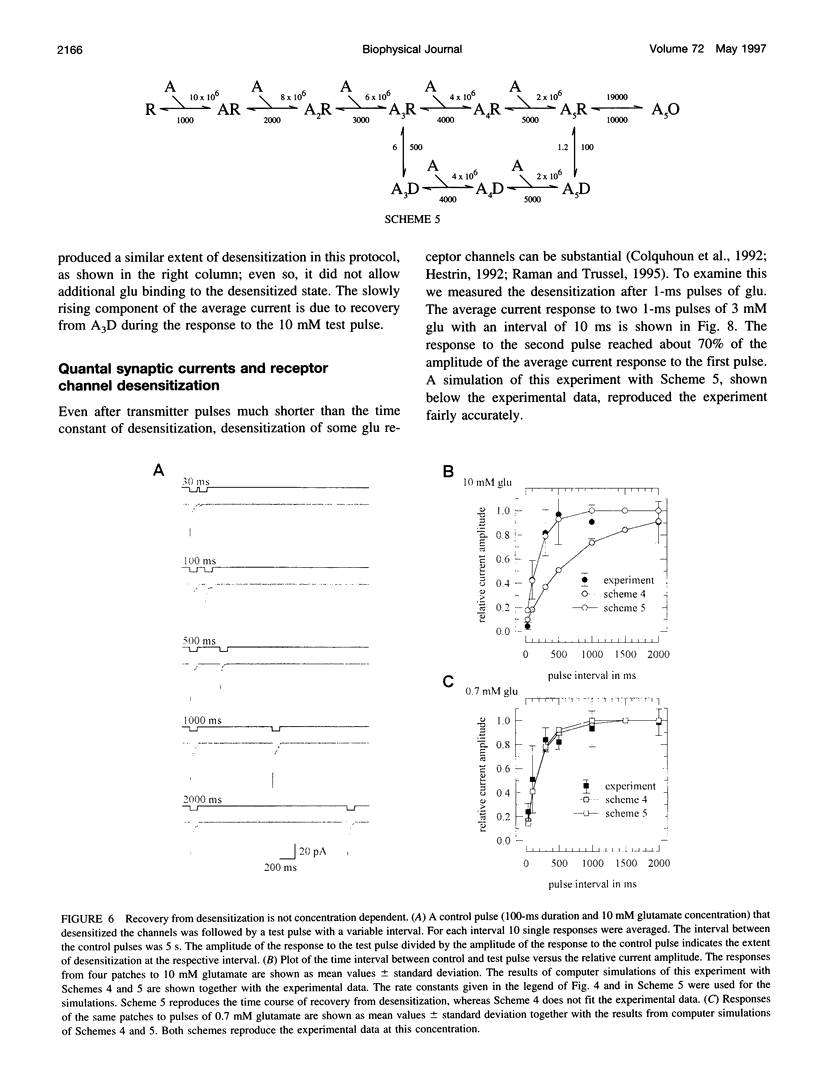
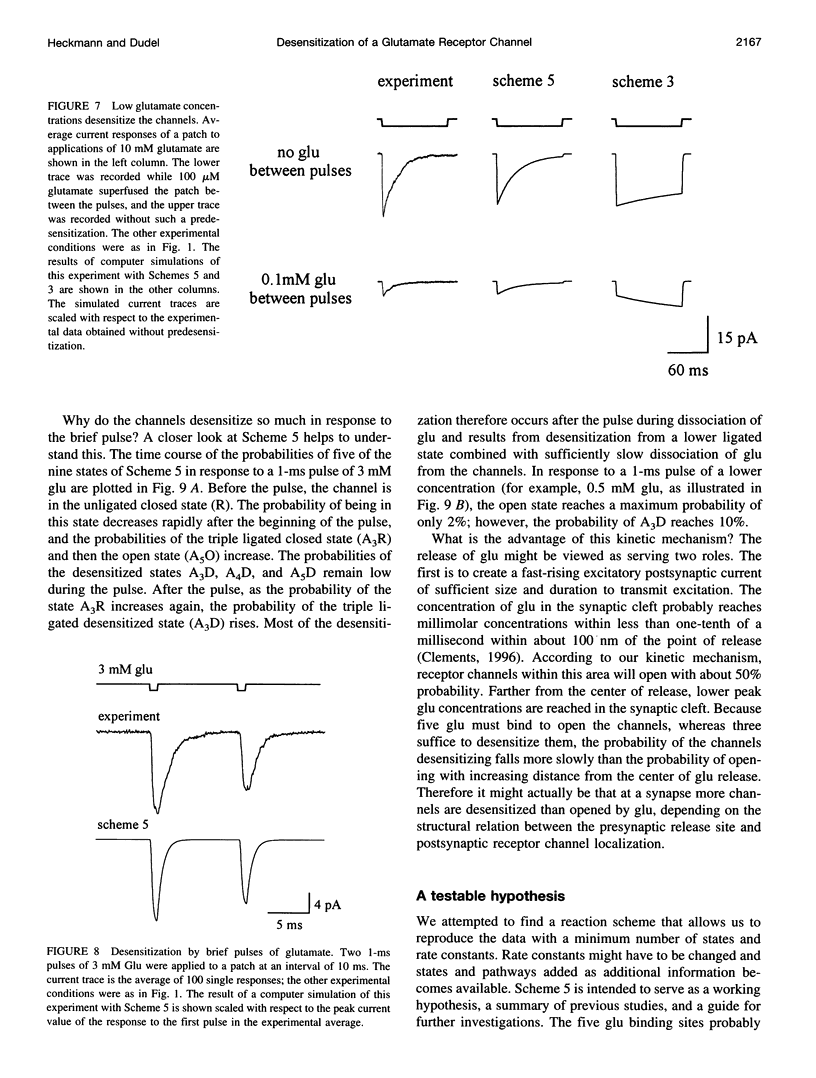
Outside-out patches from wild-type Drosophila larval muscle were exposed to L-glutamate (glu) using a piezo-driven application system. Glu receptor channels opened and desensitized in response to rapid applications of 10 mM glu. Desensitization was fitted with an exponential function with a mean time constant of desensitization (tau d) of 15 ms in response to 10 mM glu. The tau d was concentration dependent and decreased to 6 ms (on average) with 0.7 mM glu and increased again to 12 ms (on average) in response to 0.5 mM glu. Desensitization in response to longer applications of glu was almost complete, but surprisingly, even a 1-ms pulse of 3 mM glu produced about 30% desensitization. In the presence of low glu concentrations, the response to a pulse was reduced and was about halved by preequilibration with 30 microM glu. Recovery from desensitization was not concentration dependent and was fitted with an exponential function with a mean time constant of 150 ms. During recovery the channels rarely opened. Kinetic schemes were fitted to these results, and a circular reaction scheme was found to fit the data best. An important feature of the scheme is desensitization from a lower ligated closed state. This allows substantial desensitization of synaptic receptor channels in response to quantal release of transmitter, in part without opening of the channels. Desensitization reduces the probability of the channels opening in response to a subsequent release for a period of time determined by the rate of recovery from desensitization and might serve as a form of molecular short-term memory.
Full text
PDF



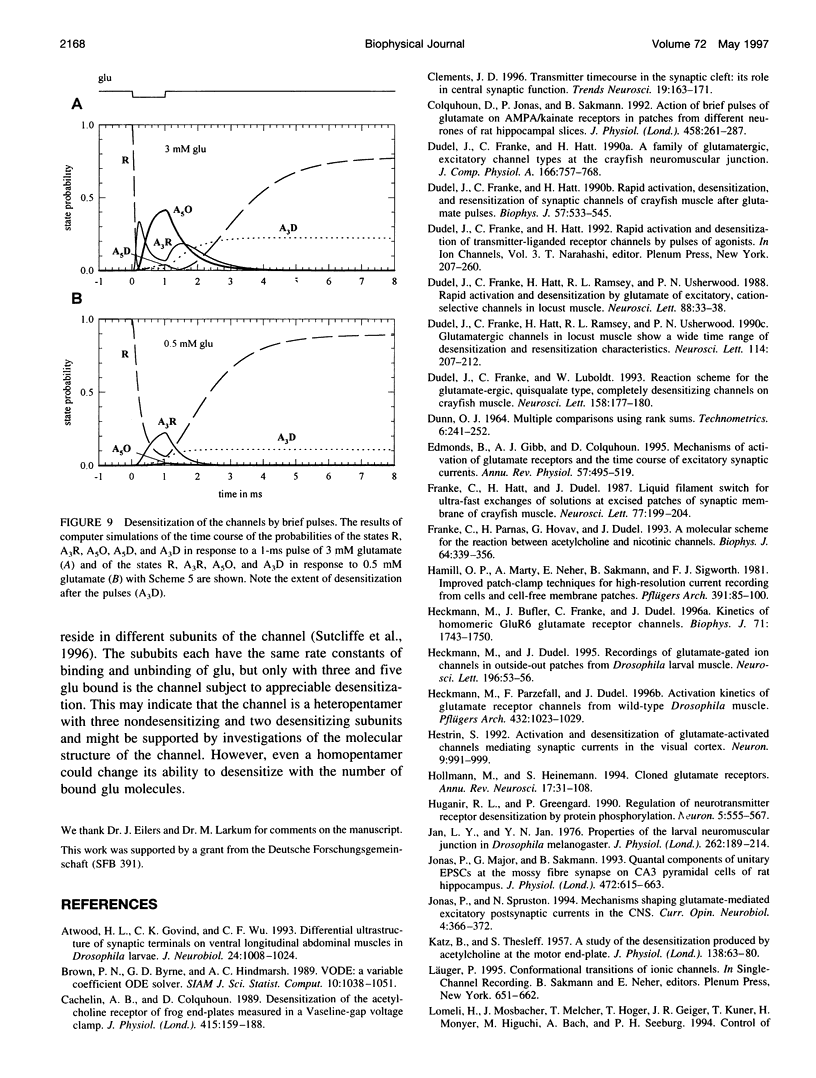

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwood H. L., Govind C. K., Wu C. F. Differential ultrastructure of synaptic terminals on ventral longitudinal abdominal muscles in Drosophila larvae. J Neurobiol. 1993 Aug;24(8):1008–1024. doi: 10.1002/neu.480240803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachelin A. B., Colquhoun D. Desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor of frog end-plates measured in a Vaseline-gap voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:159–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D. Transmitter timecourse in the synaptic cleft: its role in central synaptic function. Trends Neurosci. 1996 May;19(5):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(96)10024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Jonas P., Sakmann B. Action of brief pulses of glutamate on AMPA/kainate receptors in patches from different neurones of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:261–287. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H., Ramsey R. L., Usherwood P. N. Glutamatergic channels in locust muscle show a wide time range of desensitization and resensitization characteristics. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jul 3;114(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90073-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H., Ramsey R. L., Usherwood P. N. Rapid activation and desensitization by glutamate of excitatory, cation-selective channels in locust muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1988 May 16;88(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H. Rapid activation and desensitization of transmitter-liganded receptor channels by pulses of agonists. Ion Channels. 1992;3:207–260. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3328-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H. Rapid activation, desensitization, and resensitization of synaptic channels of crayfish muscle after glutamate pulses. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):533–545. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82569-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Luboldt W. Reaction scheme for the glutamate-ergic, quisqualate type, completely desensitizing channels on crayfish muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Aug 20;158(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90258-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds B., Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. Mechanisms of activation of glutamate receptors and the time course of excitatory synaptic currents. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:495–519. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H., Dudel J. Liquid filament switch for ultra-fast exchanges of solutions at excised patches of synaptic membrane of crayfish muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jun 15;77(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90586-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Parnas H., Hovav G., Dudel J. A molecular scheme for the reaction between acetylcholine and nicotinic channels. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):339–356. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81374-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann M., Bufler J., Franke C., Dudel J. Kinetics of homomeric GluR6 glutamate receptor channels. Biophys J. 1996 Oct;71(4):1743–1750. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79375-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann M., Dudel J. Recordings of glutamate-gated ion channels in outside-out patches from Drosophila larval muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Aug 18;196(1-2):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11836-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann M., Parzefall F., Dudel J. Activation kinetics of glutamate receptor channels from wild-type Drosophila muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Oct;432(6):1023–1029. doi: 10.1007/s004240050230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S. Activation and desensitization of glutamate-activated channels mediating fast excitatory synaptic currents in the visual cortex. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):991–999. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90250-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. Regulation of neurotransmitter receptor desensitization by protein phosphorylation. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90211-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Properties of the larval neuromuscular junction in Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):189–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Major G., Sakmann B. Quantal components of unitary EPSCs at the mossy fibre synapse on CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:615–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Spruston N. Mechanisms shaping glutamate-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents in the CNS. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;4(3):366–372. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomeli H., Mosbacher J., Melcher T., Höger T., Geiger J. R., Kuner T., Monyer H., Higuchi M., Bach A., Seeburg P. H. Control of kinetic properties of AMPA receptor channels by nuclear RNA editing. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1709–1713. doi: 10.1126/science.7992055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman I. M., Trussell L. O. The mechanism of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate receptor desensitization after removal of glutamate. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80168-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster C. M., Ultsch A., Schloss P., Cox J. A., Schmitt B., Betz H. Molecular cloning of an invertebrate glutamate receptor subunit expressed in Drosophila muscle. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):112–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1681587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The TiPS/TINS lecture: the molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Aug;14(8):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90047-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standley C., Norris T. M., Ramsey R. L., Usherwood P. N. Gating kinetics of the quisqualate-sensitive glutamate receptor of locust muscle studied using agonist concentration jumps and computer simulations. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1379–1386. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81192-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe M. J., Wo Z. G., Oswald R. E. Three-dimensional models of non-NMDA glutamate receptors. Biophys J. 1996 Apr;70(4):1575–1589. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79724-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Zhang S., Raman I. M. Desensitization of AMPA receptors upon multiquantal neurotransmitter release. Neuron. 1993 Jun;10(6):1185–1196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90066-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Mammalian ionotropic glutamate receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90120-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Beckerath N., Adelsberger H., Parzefall F., Franke C., Dudel J. GABAergic inhibition of crayfish deep extensor abdominal muscle exhibits a steep dose-response relationship and a high degree of cooperativity. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Apr;429(6):781–788. doi: 10.1007/BF00374801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



