Abstract
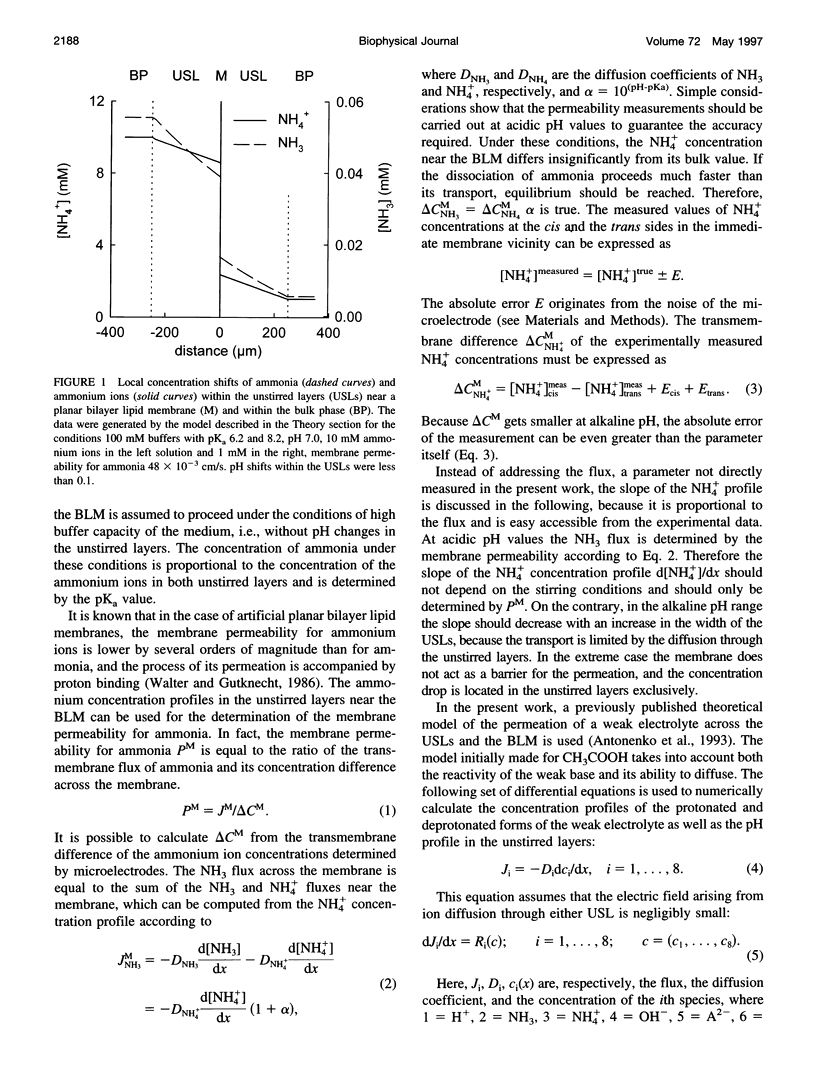
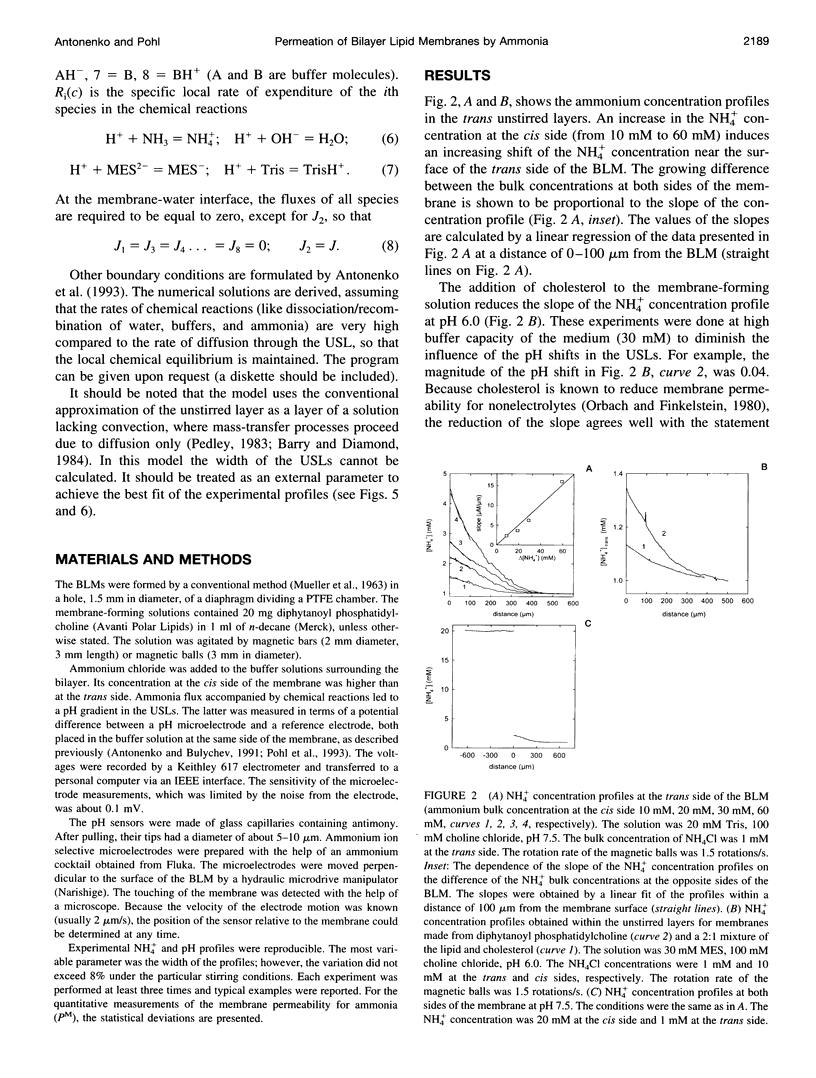
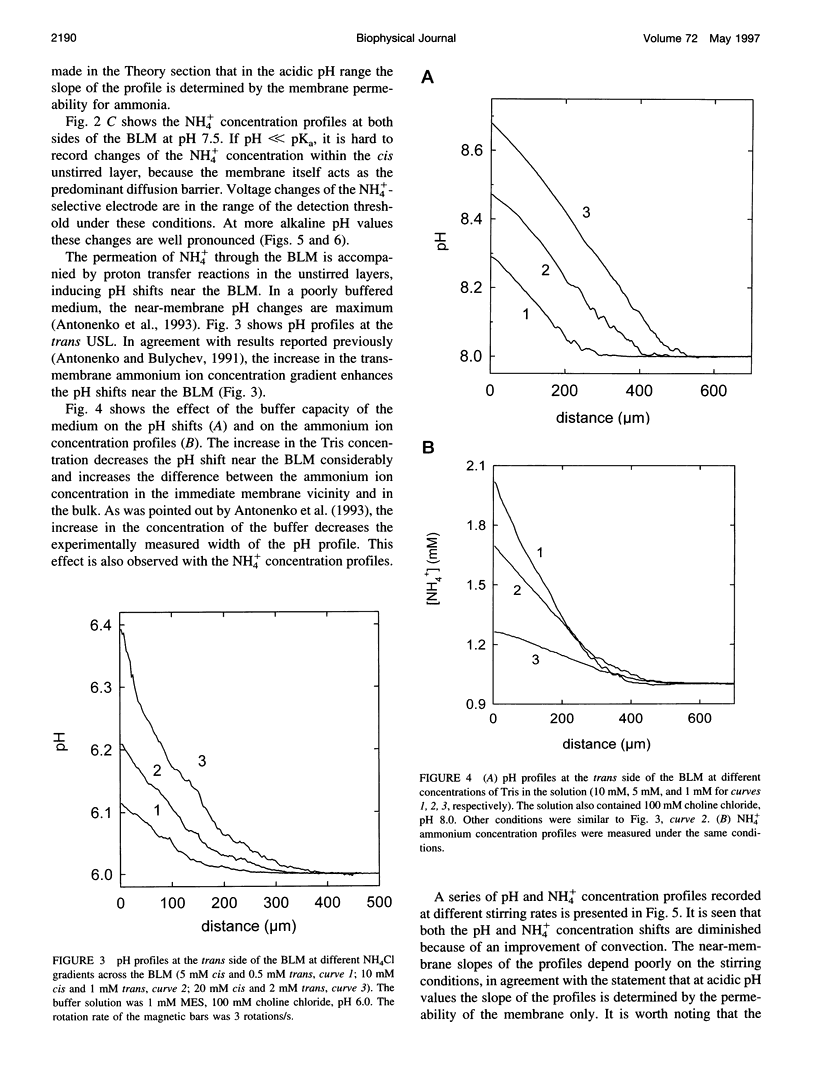
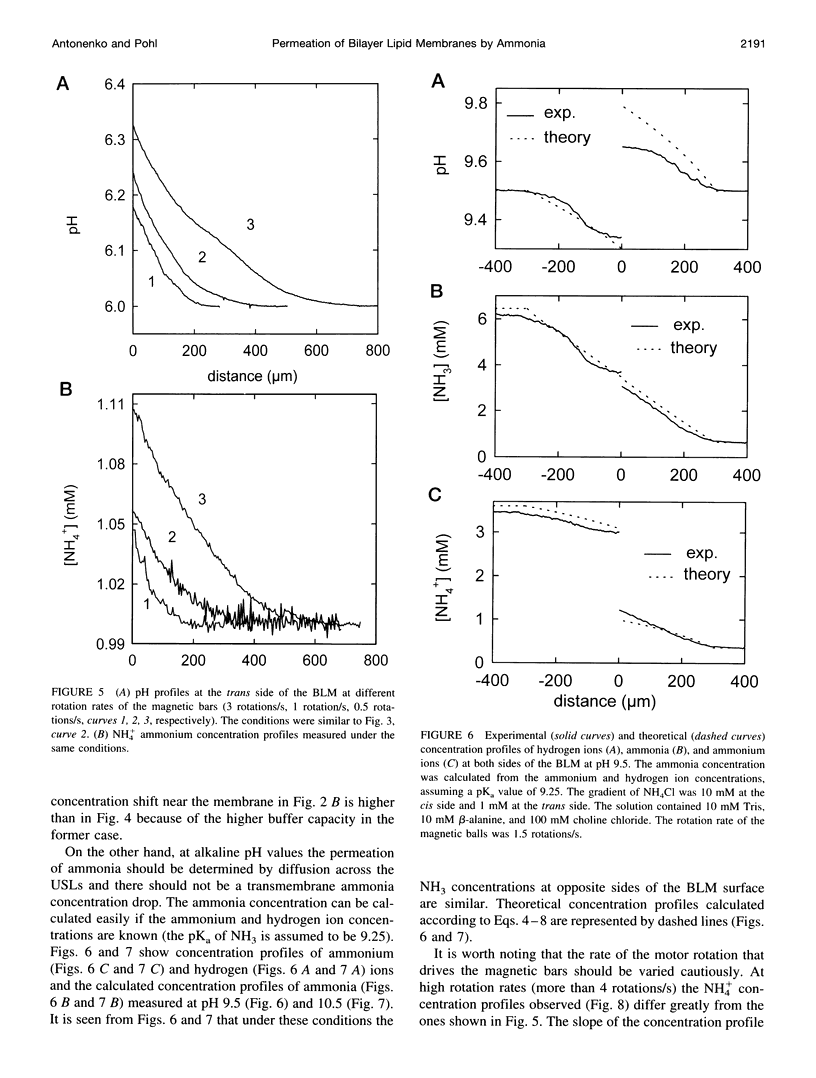
Ammonium ion and proton concentration profiles near the surface of a planar bilayer lipid membrane (BLM) generated by an ammonium ion gradient across the BLM are studied by means of microelectrodes. If the concentration of the weak base is small compared with the buffer capacity of the medium, the experimental results are well described by the standard physiological model in which the transmembrane transport is assumed to be limited by diffusion across unstirred layers (USLs) adjacent to the membrane at basic pH values (pH > pKa) and by the permeation across the membrane itself at acidic pH values. In a poorly buffered medium, however, these predictions are not fulfilled. A pH gradient that develops within the USL must be taken into account under these conditions. From the concentration distribution of ammonium ions recorded at both sides of the BLM, the membrane permeability for ammonia is determined for BLMs of different lipid composition (48 x 10(-3) cm/s in the case of diphytanoyl phosphatidylcholine). A theoretical model of weak electrolyte transport that is based on the knowledge of reaction and diffusion rates is found to describe well the experimental profiles under any conditions. The microelectrode technique can be applied for the study of the membrane permeability of other weak acids or bases, even if no microsensor for the substance under study is available, because with the help of the theoretical model the membrane permeability values can be estimated from pH profiles alone. The accuracy of such measurements is limited, however, because small changes in the equilibrium constants, diffusion coefficients, or concentrations used for computations create a systematic error.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoneko Y. N., Bulychev A. A. Measurements of local pH changes near bilayer lipid membrane by means of a pH microelectrode and a protonophore-dependent membrane potential. Comparison of the methods. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 18;1070(1):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonenko YuN, Yaguzhinsky L. S. Generation of potential in lipid bilayer membranes as a result of proton-transfer reactions in the unstirred layers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Dec;14(5-6):457–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00743071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonenko Y. N., Denisov G. A., Pohl P. Weak acid transport across bilayer lipid membrane in the presence of buffers. Theoretical and experimental pH profiles in the unstirred layers. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1701–1710. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81542-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. H., Diamond J. M. Effects of unstirred layers on membrane phenomena. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):763–872. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J., Tosteson D. C. Diffusion of weak acids across lipid bilayer membranes: effects of chemical reactions in the unstirred layers. Science. 1973 Dec 21;182(4118):1258–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4118.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm L. L., Trigg D., Martin D., Gillespie C., Buerkert J. Transport of ammonia in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):478–485. doi: 10.1172/JCI111723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikeri D., Sun A., Zeidel M. L., Hebert S. C. Cell membranes impermeable to NH3. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):478–480. doi: 10.1038/339478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D., Furne J. K., Levitt D. G. Shaking of the intact rat and intestinal angulation diminish the jejunal unstirred layer. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1460–1466. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91165-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach E., Finkelstein A. The nonelectrolyte permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Apr;75(4):427–436. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.4.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley T. J. Calculation of unstirred layer thickness in membrane transport experiments: a survey. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):115–150. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl P., Antonenko Y. N., Rosenfeld E. Effect of ultrasound on the pH profiles in the unstirred layers near planar bilayer lipid membranes measured by microelectrodes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 10;1152(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90242-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie R. J., Gibson J. Permeability of ammonia and amines in Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Bacillus firmus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 1;258(2):332–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90352-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. K., Binder H. J., Geibel J. P., Boron W. F. An apical permeability barrier to NH3/NH4+ in isolated, perfused colonic crypts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11573–11577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruoka S., Takeda M., Yoshitomi K., Imai M. Cellular heterogeneity of ammonium ion transport across the basolateral membrane of the hamster medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1881–1888. doi: 10.1172/JCI116780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter A., Gutknecht J. Monocarboxylic acid permeation through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):255–264. doi: 10.1007/BF01870573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter A., Gutknecht J. Permeability of small nonelectrolytes through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):207–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01870127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang T. X., Anderson B. D. Diffusion of ionizable solutes across planar lipid bilayer membranes: boundary-layer pH gradients and the effect of buffers. Pharm Res. 1993 Nov;10(11):1654–1661. doi: 10.1023/a:1018989107129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


