Abstract
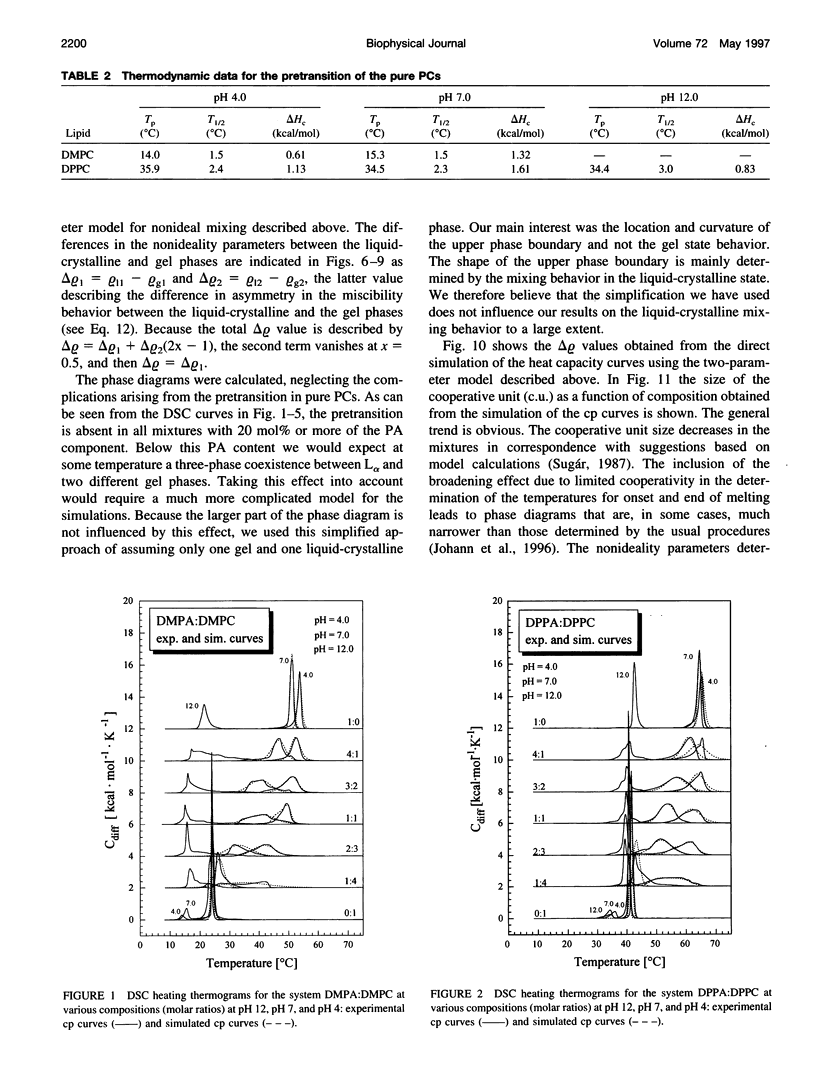
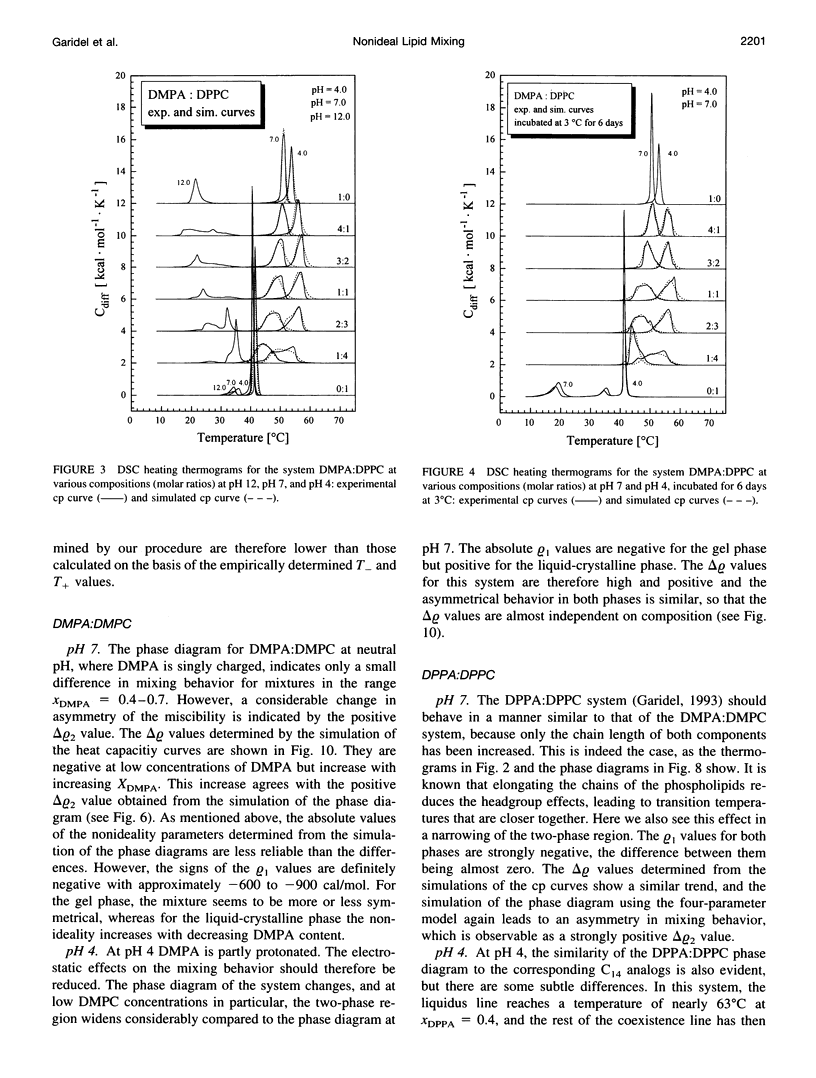
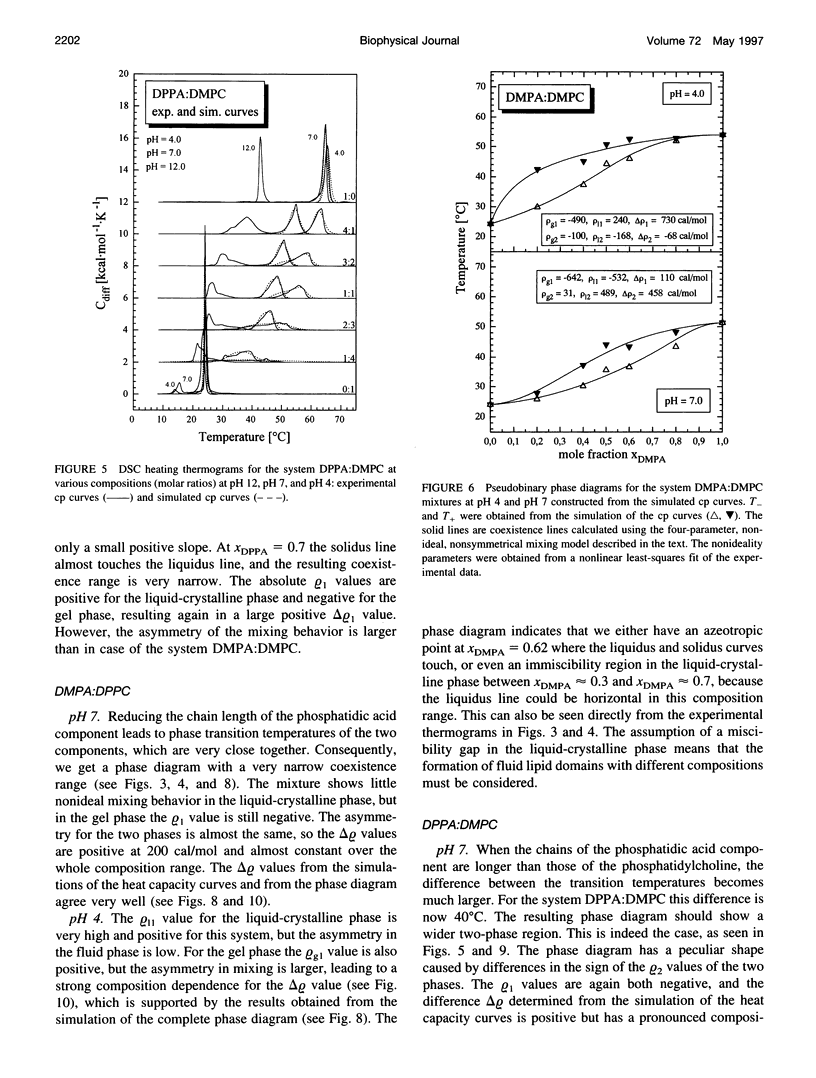
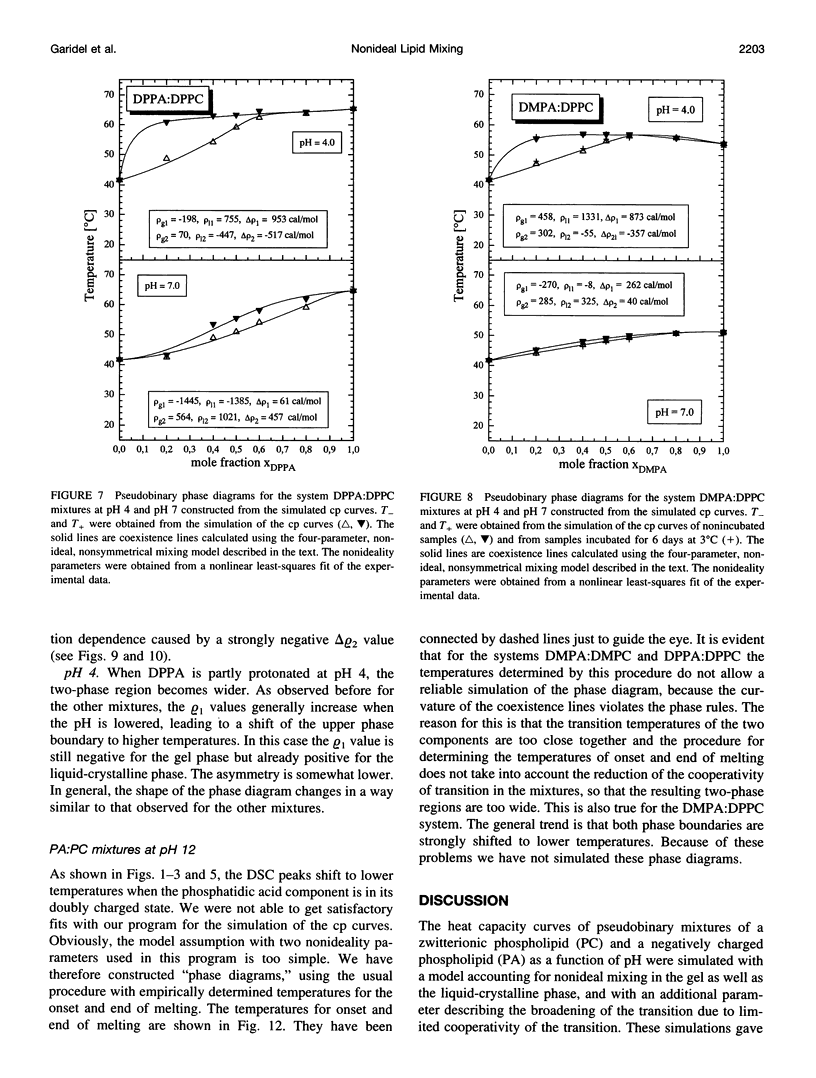
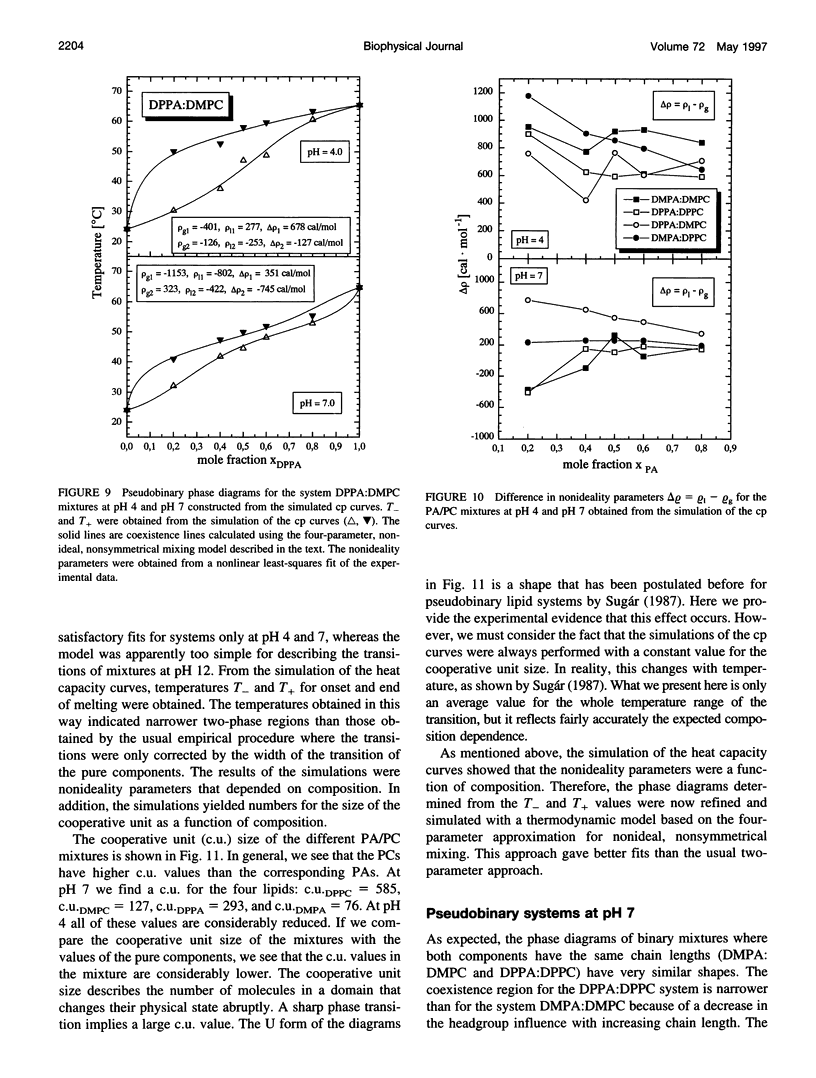
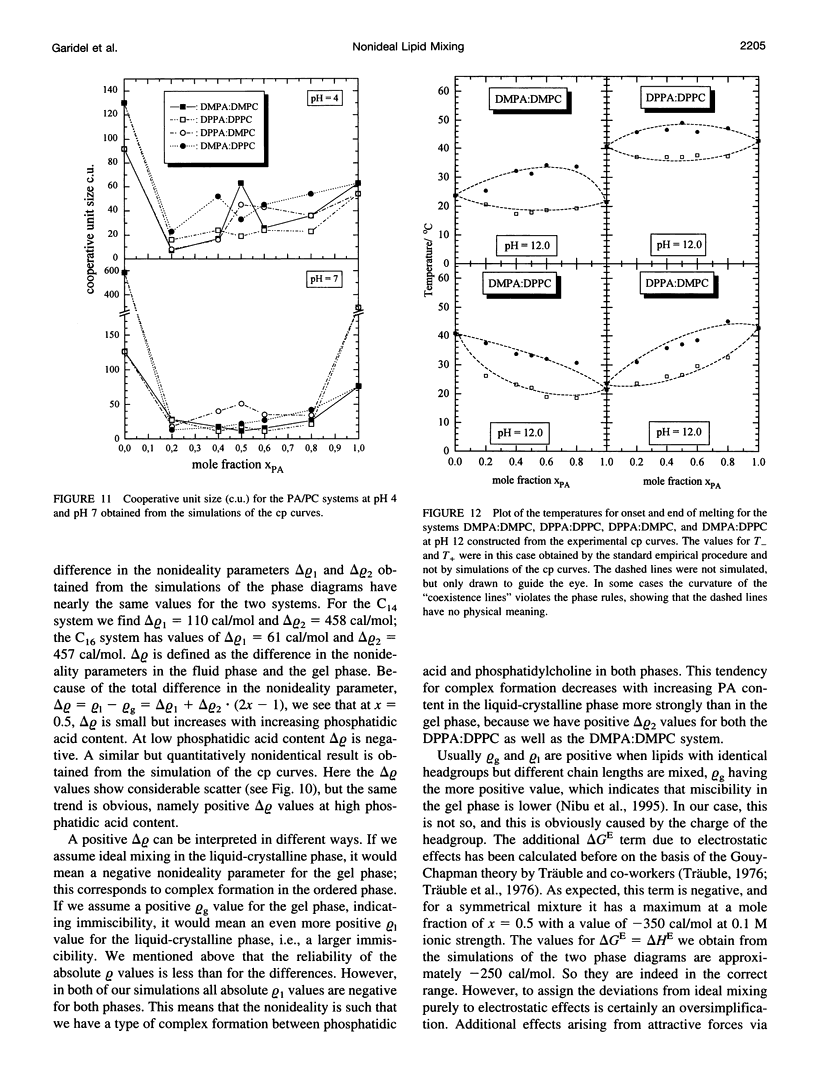
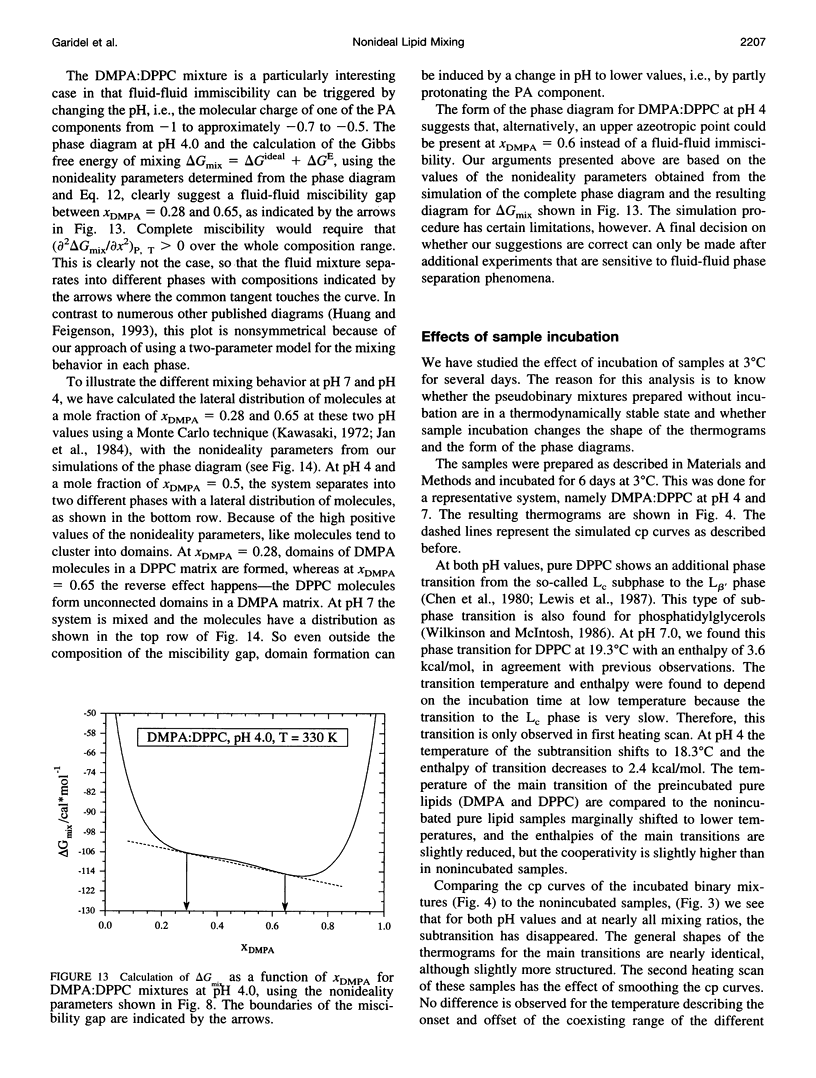
The miscibilities of phosphatidic acids (PAs) and phosphatidylcholines (PCs) with different chain lengths (n = 14, 16) at pH 4, pH 7, and pH 12 were examined by differential scanning calorimetry. Simulation of heat capacity curves was performed using a new approach that incorporates changes of cooperativity of the transition in addition to nonideal mixing in the gel and the liquid-crystalline phase as a function of composition. From the simulations of the heat capacity curves, first estimates for the nonideality parameters for nonideal mixing as a function of composition were obtained, and phase diagrams were constructed using temperatures for onset and end of melting, which were corrected for the broadening effect caused by a decrease in cooperativity. In all cases the composition dependence of the nonideality parameters indicated nonsymmetrical mixing behavior. The phase diagrams were therefore further refined by simulations of the coexistence curves using a four-parameter approximation to account for nonideal and nonsymmetrical mixing in the gel and the liquid-crystalline phase. The mixing behavior was studied at three different pH values to investigate how changes in headgroup charge of the PA influences the miscibility. The experiments showed that at pH 7, where the PA component is negatively charged, the nonideality parameters are in most cases negative, indicating that electrostatic effects favor a mixing of the two components. Partial protonation of the PA component at pH 4 leads to strong changes in miscibility; the nonideality parameters for the liquid-crystalline phase are now in most cases positive, indicating clustering of like molecules. The phase diagram for 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidic acid:1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine mixtures at pH 4 indicates that a fluid-fluid immiscibility is likely. The results show that a decrease in ionization of PAs can induce large changes in mixing behavior. This occurs because of a reduction in electrostatic repulsion between PA headgroups and a concomitant increase in attractive hydrogen bonding interactions.
Full text
PDF




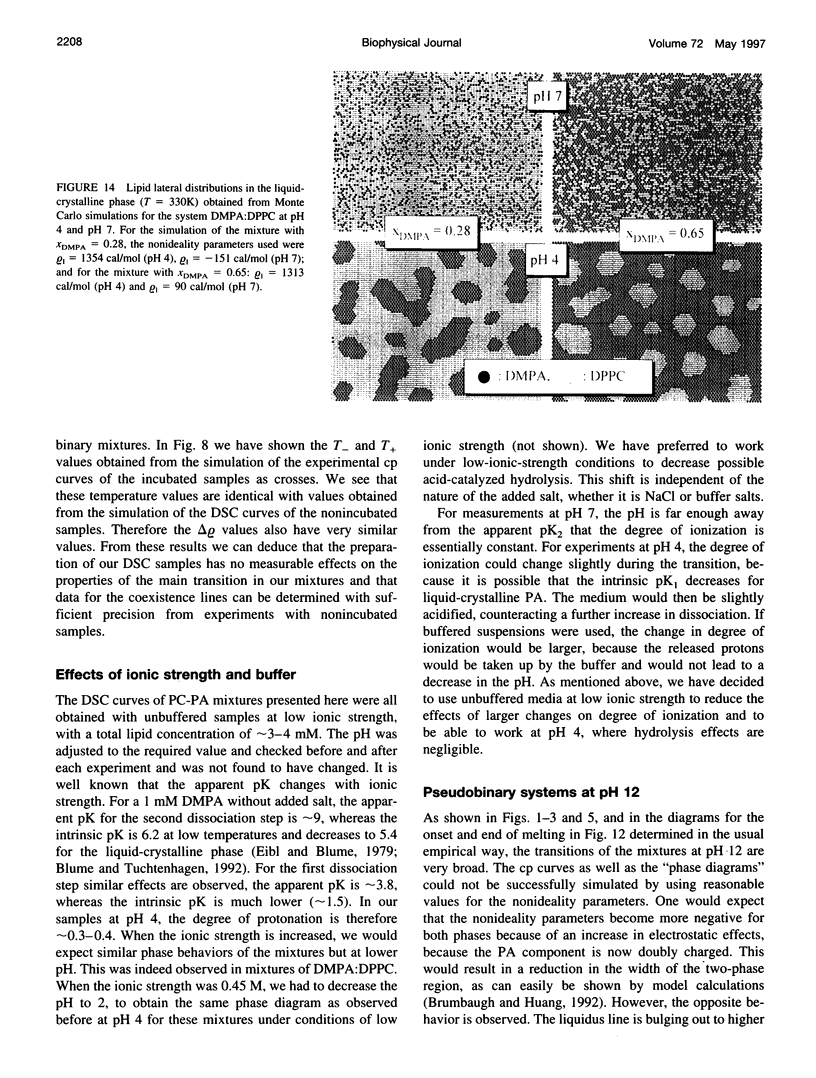


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S., Lin H. N., Bittman R., Huang C. H. Binary mixtures of saturated and unsaturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine. A differential scanning calorimetry study. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):522–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida P. F., Vaz W. L., Thompson T. E. Percolation and diffusion in three-component lipid bilayers: effect of cholesterol on an equimolar mixture of two phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):399–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81381-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benga G., Holmes R. P. Interactions between components in biological membranes and their implications for membrane function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;43(3):195–257. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berclaz T., Geoffroy M. Spin-labeling study of phosphatidylcholine-cardiolipin binary mixtures. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4033–4039. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Eibl H. The influence of charge on bilayer membranes. Calorimetric investigations of phosphatidic acid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 16;558(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90311-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Tuchtenhagen J. Thermodynamics of ion binding to phosphatidic acid bilayers. Titration calorimetry of the heat of dissociation of DMPA. Biochemistry. 1992 May 19;31(19):4636–4642. doi: 10.1021/bi00134a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh E. E., Huang C. Parameter estimation in binary mixtures of phospholipids. Methods Enzymol. 1992;210:521–539. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)10027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Sturtevant J. M., Gaffney B. J. Scanning calorimetric evidence for a third phase transition in phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5060–5063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr, Gelmann E. P. Physical properties of membrane lipids: biological relevance and regulation. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):232–256. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.232-256.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Blume A. The influence of charge on phosphatidic acid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):476–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Chemically induced phase separation in mixed vesicles containing phosphatidic acid. An optical study. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jul 9;97(14):4114–4120. doi: 10.1021/ja00847a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinderliter A. K., Huang J., Feigenson G. W. Detection of phase separation in fluid phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine mixtures. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1906–1911. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80673-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of Ca2+-induced phase separations in phosphatidylserine-containing lipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):1055–1061. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D. Role of lipid phase separations and membrane hydration in phospholipid vesicle fusion. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):2833–2840. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong-wei S., McConnell H. Phase separations in phospholipd membranes. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):847–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Feigenson G. W. Monte Carlo simulation of lipid mixtures: finding phase separation. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1788–1794. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81234-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phase transitions and phase separations in phospholipid membranes induced by changes in temperature, pH, and concentration of bivalent cations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan N., Lookman T., Pink D. A. On computer simulation methods used to study models of two-component lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3227–3231. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Temperature and compositional dependence of the structure of hydrated dimyristoyl lecithin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6068–6078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johann C., Garidel P., Mennicke L., Blume A. New approaches to the simulation of heat-capacity curves and phase diagrams of pseudobinary phospholipid mixtures. Biophys J. 1996 Dec;71(6):3215–3228. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79515-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Toon P. A., Warren G. B. Clusters in lipid bilayers and the interpretation of thermal effects in biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3699–3705. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Fluorescence studies of chlorophyll a incorporated into lipid mixtures, and the interpretation of "phase" diagrams. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 17;413(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Functional properties of biological membranes: a physical-chemical approach. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;29(1):3–56. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Lipid phase transitions and phase diagrams. II. Mictures involving lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 14;472(3-4):285–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., Mak N., McElhaney R. N. A differential scanning calorimetric study of the thermotropic phase behavior of model membranes composed of phosphatidylcholines containing linear saturated fatty acyl chains. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6118–6126. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separations in binary mixtures of phospholipids having different charges and different crystalline structures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 17;470(2):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. T. Mixing behavior of symmetric chain length and mixed chain length phosphatidylcholines in two-component multilamellar bilayers: evidence for gel and liquid-crystalline phase immiscibility. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4421–4429. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Brown J. Diffusion of calcium ions in retinal rods. A theoretical calculation. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Apr;77(4):475–487. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf T. N., Wang J. L., Schindler M. Lateral diffusion of phospholipids in the plasma membrane of soybean protoplasts: Evidence for membrane lipid domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibu Y., Inoue T., Motoda I. Effect of headgroup type on the miscibility of homologous phospholipids with different acyl chain lengths in hydrated bilayer. Biophys Chem. 1995 Nov;56(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(95)00041-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separation in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2351–2360. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. R. Solid- and liquid-phase equilibria in phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine mixtures. A calorimetric study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 28;857(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stier A., Sackmann E. Spin labels as enzyme substrates. Heterogeneous lipid distribution in liver microsomal membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocanne J. F., Cézanne L., Lopez A., Piknova B., Schram V., Tournier J. F., Welby M. Lipid domains and lipid/protein interactions in biological membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1994 Sep 6;73(1-2):139–158. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(94)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokutomi S., Ohki K., Ohnishi S. I. Proton-induced phase separation in phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 28;596(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Eibl H. Electrostatic effects on lipid phase transitions: membrane structure and ionic environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):214–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyäuble H., Teubner M., Woolley P., Eibl H. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. I. Effects of pH and univalent cations on membrane structure. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;4(4):319–342. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L. Diffusion and chemical reactions in phase-separated membranes. Biophys Chem. 1994 May;50(1-2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(94)85026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L. Percolation properties of two-component, two-phase phospholipid bilayers. Mol Membr Biol. 1995 Jan-Mar;12(1):39–43. doi: 10.3109/09687689509038493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J. Lipidic intramembranous particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 27;779(1):43–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., de Kruyff B., Ververgaert P. H., Tocanne J. F., van Deenen L. L. The influence of pH, Ca2+ and protein on the thermotropic behaviour of the negatively charged phospholipid, phosphatidylglycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 29;339(3):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. A., McIntosh T. J. A subtransition in a phospholipid with a net charge, dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):295–298. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Stephenson F. A., Huang C. H. Binary mixtures of asymmetric phosphatidylcholines with one acyl chain twice as long as the other. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5448–5453. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijck P. W., Kaper A. J., Oonk H. A., de Gier J. Miscibility properties of binary phosphatidylcholine mixtures. A calorimetric study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 3;470(1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Dreele P. H. Estimation of lateral species separation from phase transitions in nonideal two-dimensional lipid mixtures. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):3939–3943. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]