Abstract
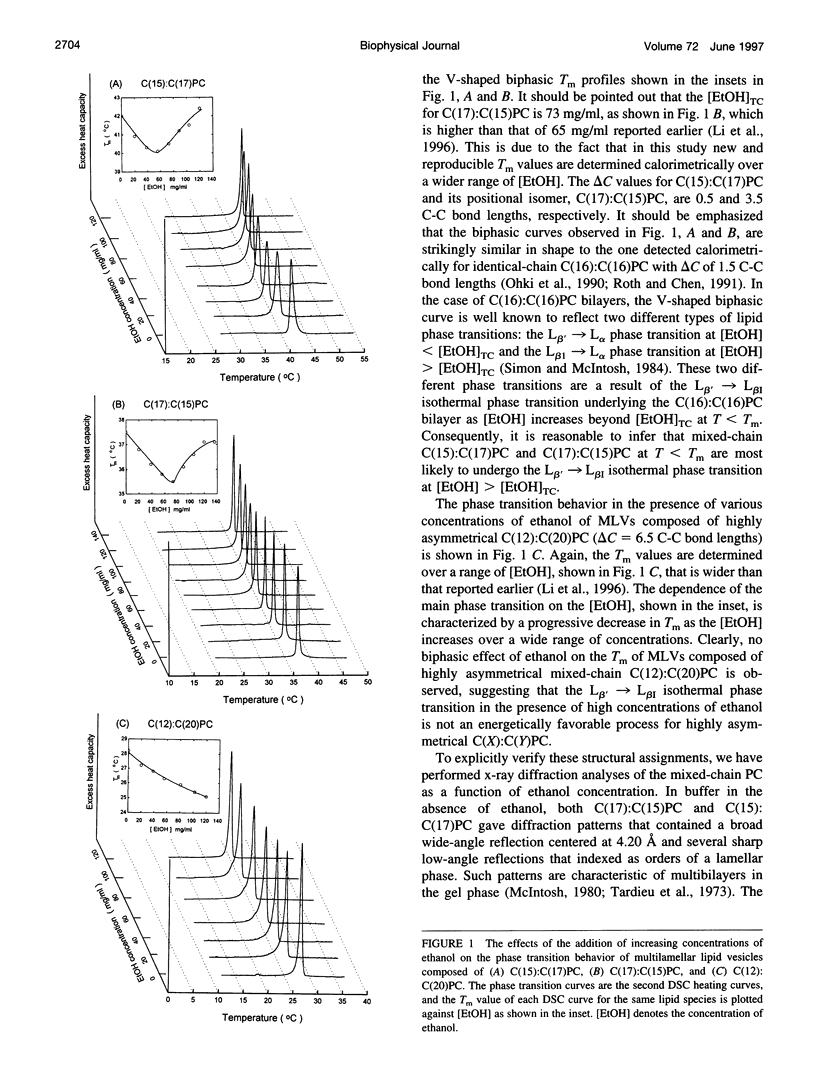
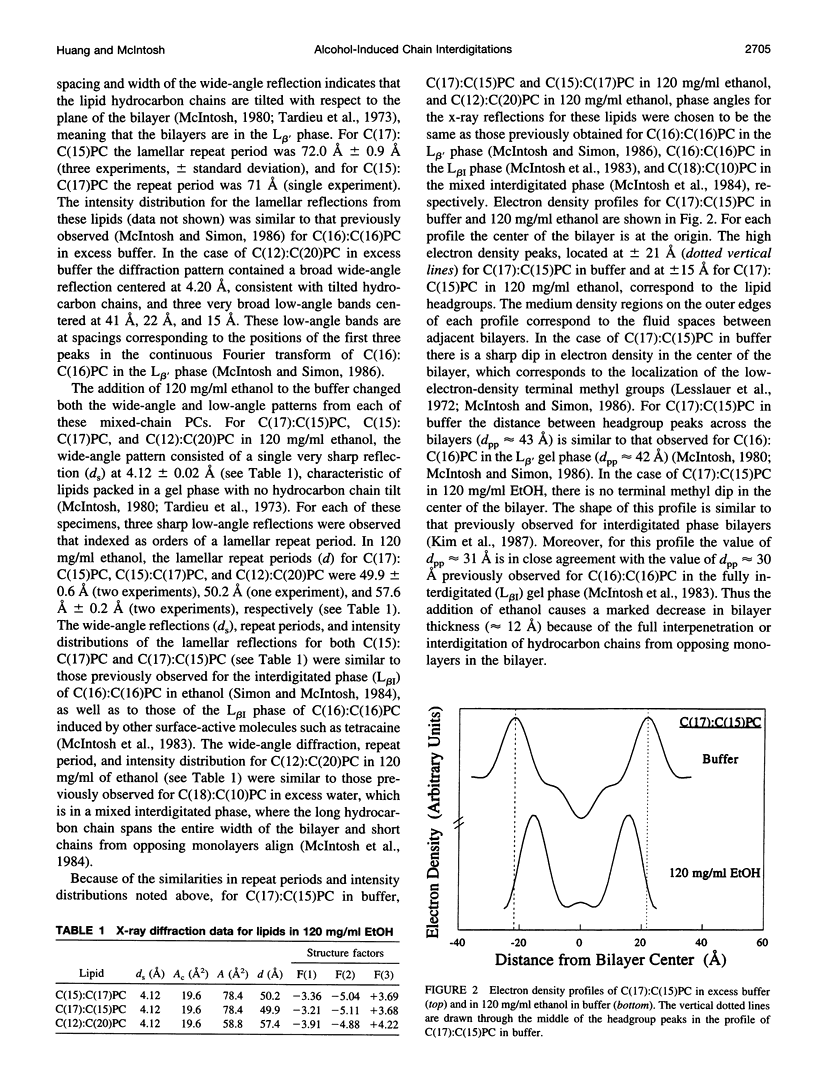
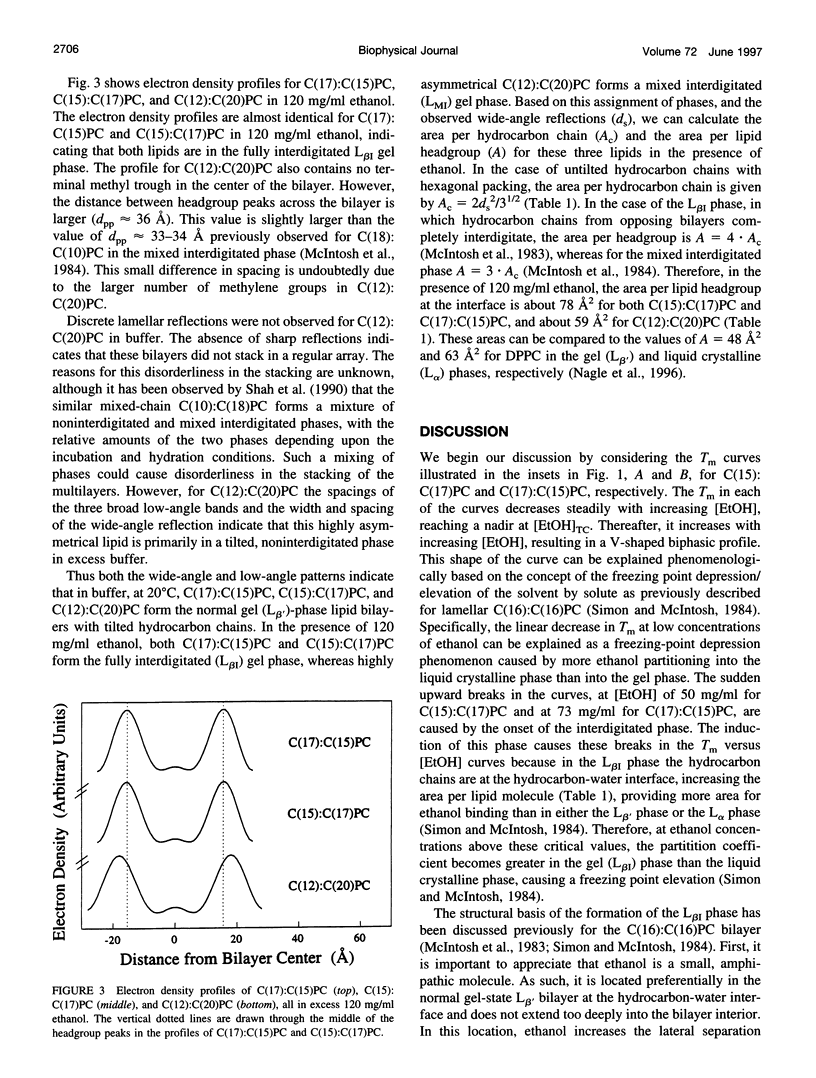
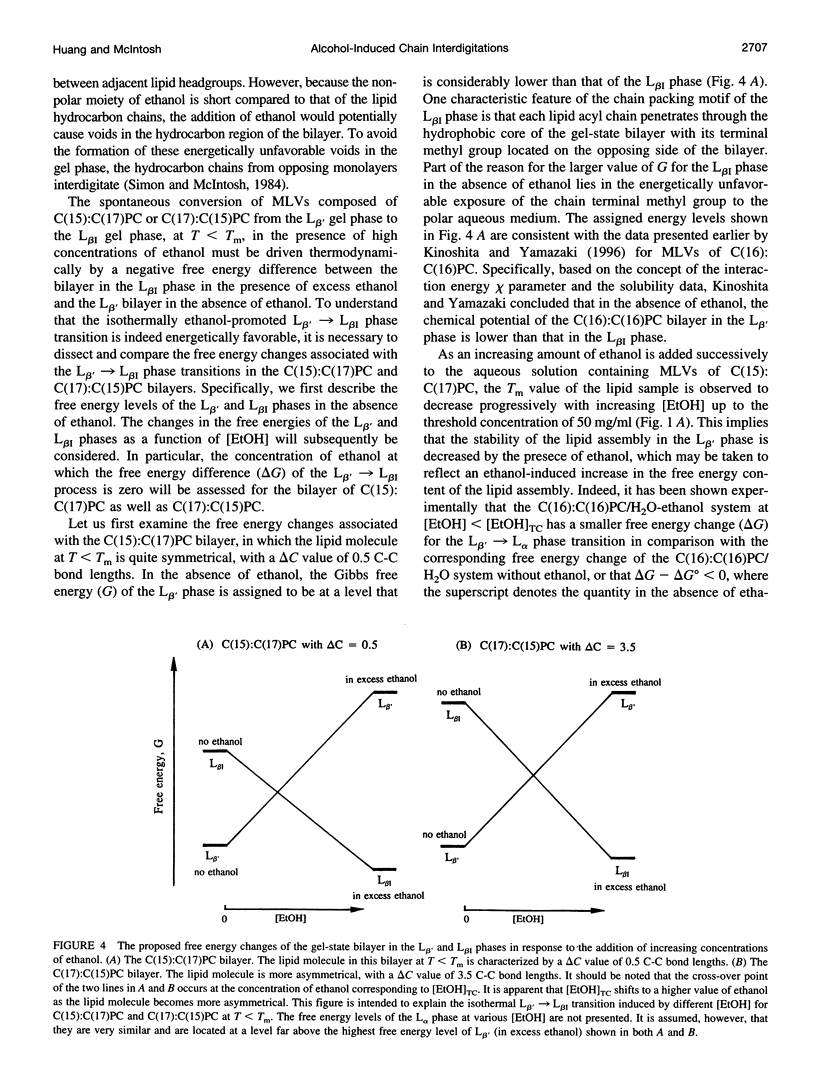
Using high-resolution differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), we have studied the effects of ethanol concentrations, [EtOH], on the main phase transition temperatures (T[m]) of the following mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines (PCs): C(15):C(17)PC, C(17):C(15)PC, and C(12):C(20)PC. These lipids have a common molecular weight; however, their apparent acyl chain-length differences between the sn-1 and sn-2 acyl chains, delta C, are distinctively different. The delta C values for these three mixed-chain PCs are, respectively, 0.5, 3.5, and 6.5 C-C bond lengths. DSC results show that the T(m) profiles for C(15):C(17)PC and C(17):C(15)PC bilayers in the plot of T(m) versus [EtOH] are V-shaped biphasic curves, with the minimum T(m) occurring at 50 and 73 mg/ml of ethanol, respectively. In contrast, the C(12):C(20)PC bilayer exhibits a nearly linear decrease in T(m) with increasing [EtOH]. In addition, x-ray diffraction experiments were also performed to assess the structural changes of these three mixed-chain PCs in the gel-state bilayers, at 20 degrees C, in response to high concentrations of ethanol. X-ray diffraction data indicate that, in the absence of ethanol, these three lamellar lipids are all packed in the normal (L beta') gel phase in aqueous media. In the presence of 120 mg/ml of ethanol, however, the C(15):C(17)PC and C(17):C(15)PC lamellae are packed in the fully interdigitated (L beta[I]) gel phase. The V-shaped T(m) curves detected calorimetrically for these two lipids in response to [EtOH] can thus be explained by the ethanol-induced L beta' --> L beta[I] isothermal phase transition. Interestingly, the results of x-ray diffraction study reveal, for the first time, that an ethanol-induced L beta' --> L(MI) (mixed interdigitated phase) isothermal phase transition occurs in the gel-state bilayer of highly asymmetrical C(12):C(20)PC. Therefore, the chain asymmetry is recognized to play an important role in the ethanol-induced chain interdigitation at T < T(m).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Takahashi H., Ohki K., Hatta I. Interdigitated structure of phospholipid-alcohol systems studied by x-ray diffraction. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1850–1855. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80361-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Empirical estimation of the gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition temperatures for fully hydrated saturated phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):26–30. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Mason J. T. Structure and properties of mixed-chain phospholipid assemblies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 22;864(3-4):423–470. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Mason J. T., Huang C. Acyl chain interdigitation in saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayer dispersions. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5570–5577. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. T., Mattai J., Shipley G. G. Bilayer interactions of ether- and ester-linked phospholipids: dihexadecyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6599–6603. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita K., Yamazaki M. Organic solvents induce interdigitated gel structures in multilamellar vesicles of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Oct 23;1284(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(96)00136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesslauer W., Cain J. E., Blasie J. K. X-ray diffraction studies of lecithin bimolecular leaflets with incorporated fluorescent probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Lin H. N., Wang G., Huang C. Effects of alcohols on the phase transition temperatures of mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2784–2794. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79848-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. N., Wang Z. Q., Huang C. H. Differential scanning calorimetry study of mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines with a common molecular weight identical with diheptadecanoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7063–7072. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A., Ellington J. C., Jr, Porter N. A. New structural model for mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4038–4044. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Hydration force and bilayer deformation: a reevaluation. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4058–4066. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena P. L., Djerassi C. Synthesis of 5,9-hexacosadienoic acid phospholipids. 11. Phospholipid studies of marine organisms. Chem Phys Lipids. 1985 Jun-Jul;37(3):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(85)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Zhang R., Tristram-Nagle S., Sun W., Petrache H. I., Suter R. M. X-ray structure determination of fully hydrated L alpha phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1419–1431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79701-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki K., Tamura K., Hatta I. Ethanol induces interdigitated gel phase (L beta I) between lamellar gel phase (L beta') and ripple phase (P beta') in phosphatidylcholine membranes: a scanning density meter study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 19;1028(3):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90169-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranck J. L., Keira T., Luzzati V. A novel packing of the hydrocarbon chains in lipids. The low temperature phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl-glycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah J., Sripada P. K., Shipley G. G. Structure and properties of mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4254–4262. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J. Interdigitated hydrocarbon chain packing causes the biphasic transition behavior in lipid/alcohol suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90562-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng J. W., Chong P. L. Interactions between pressure and ethanol on the formation of interdigitated DPPC liposomes: a study with Prodan fluorescence. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 1;30(39):9485–9491. doi: 10.1021/bi00103a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


