Abstract
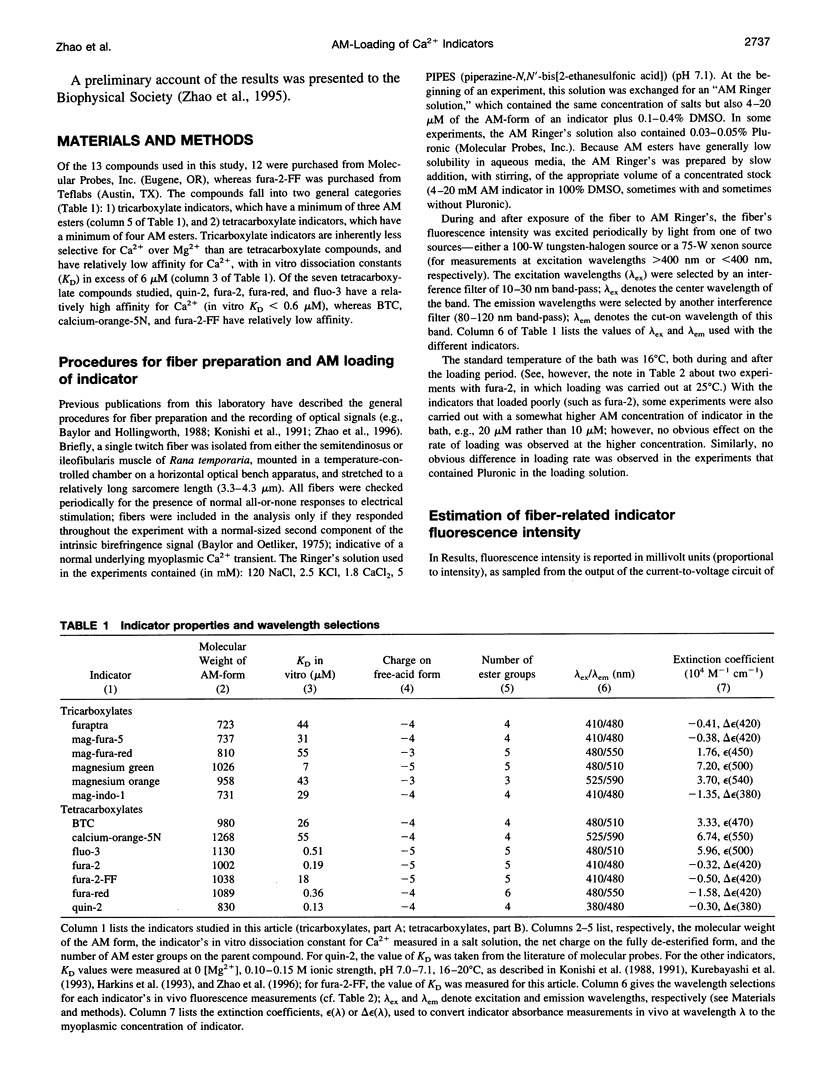
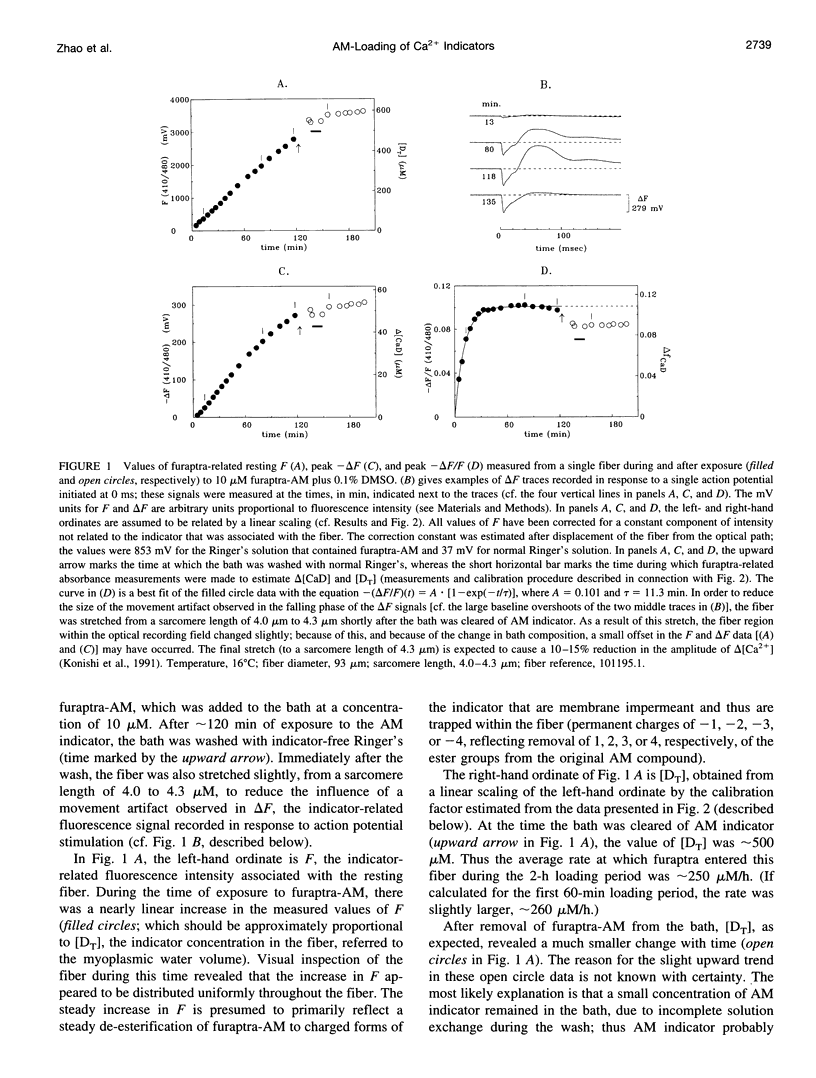
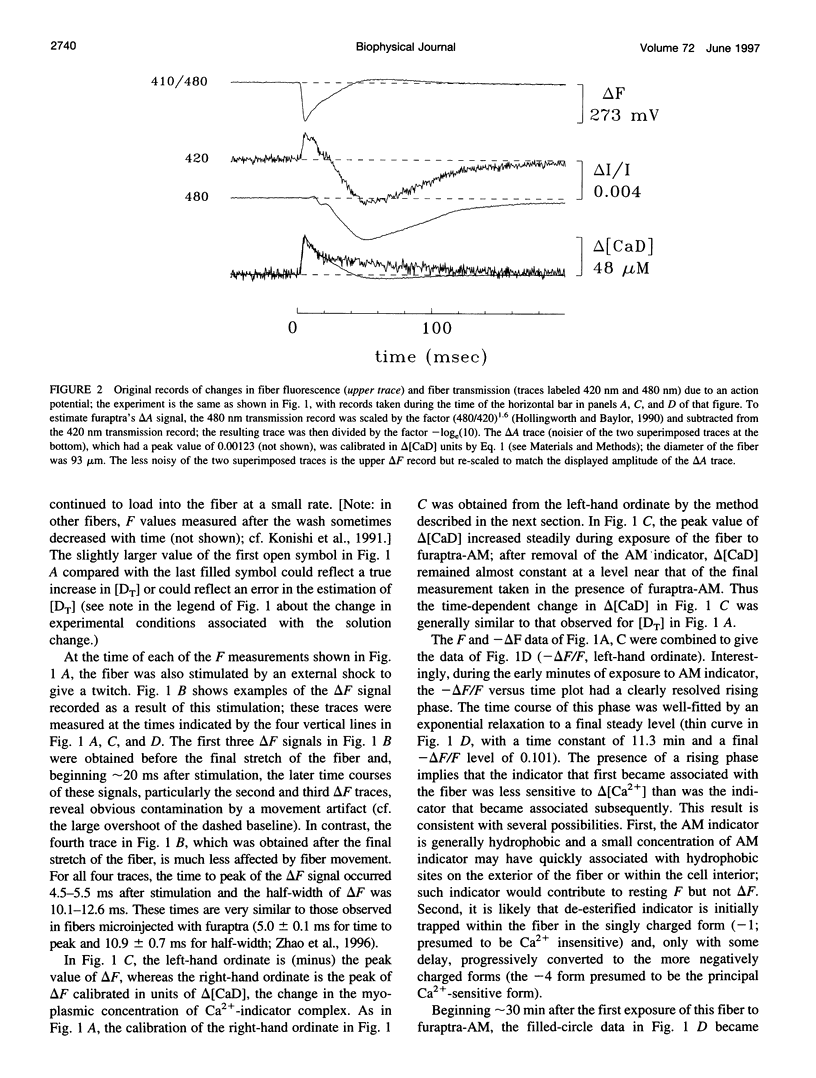
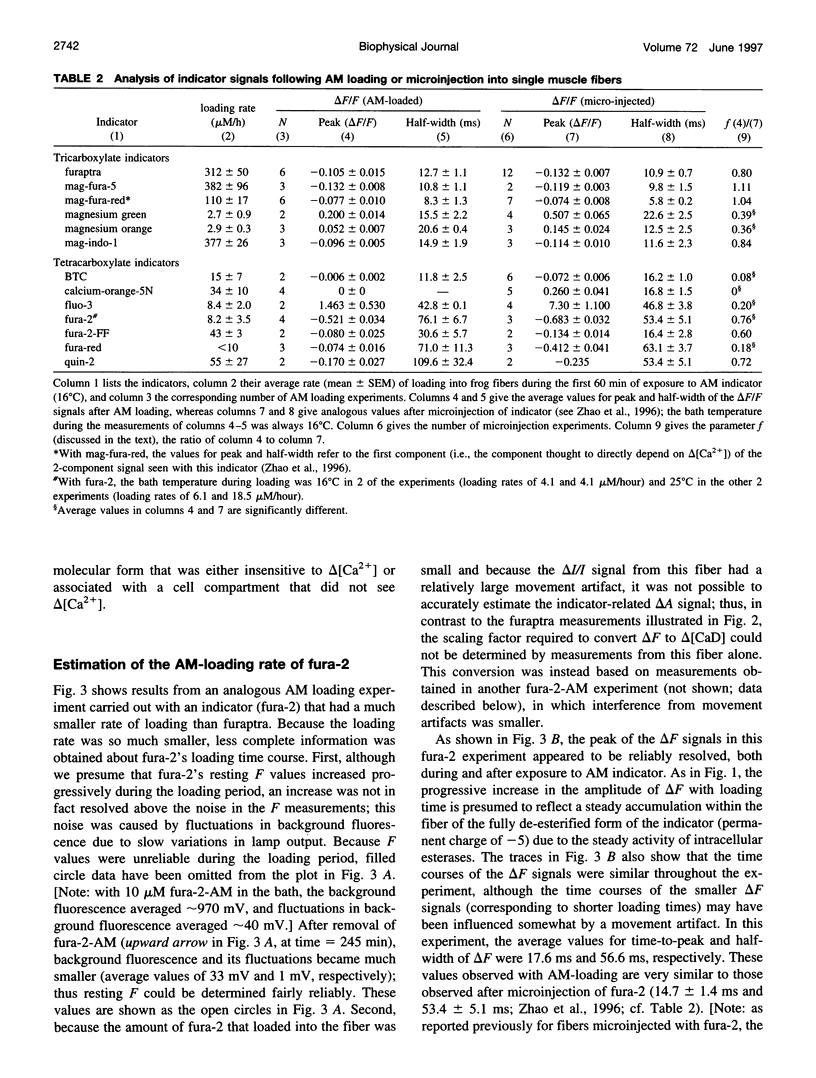
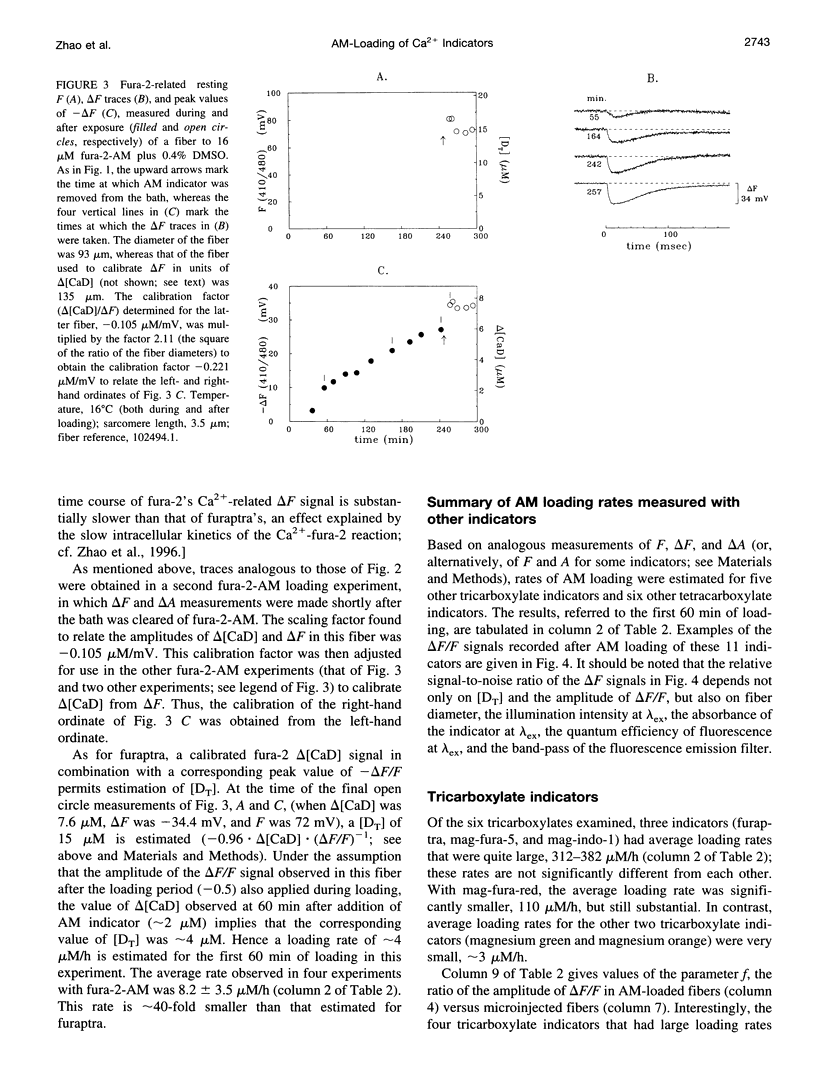
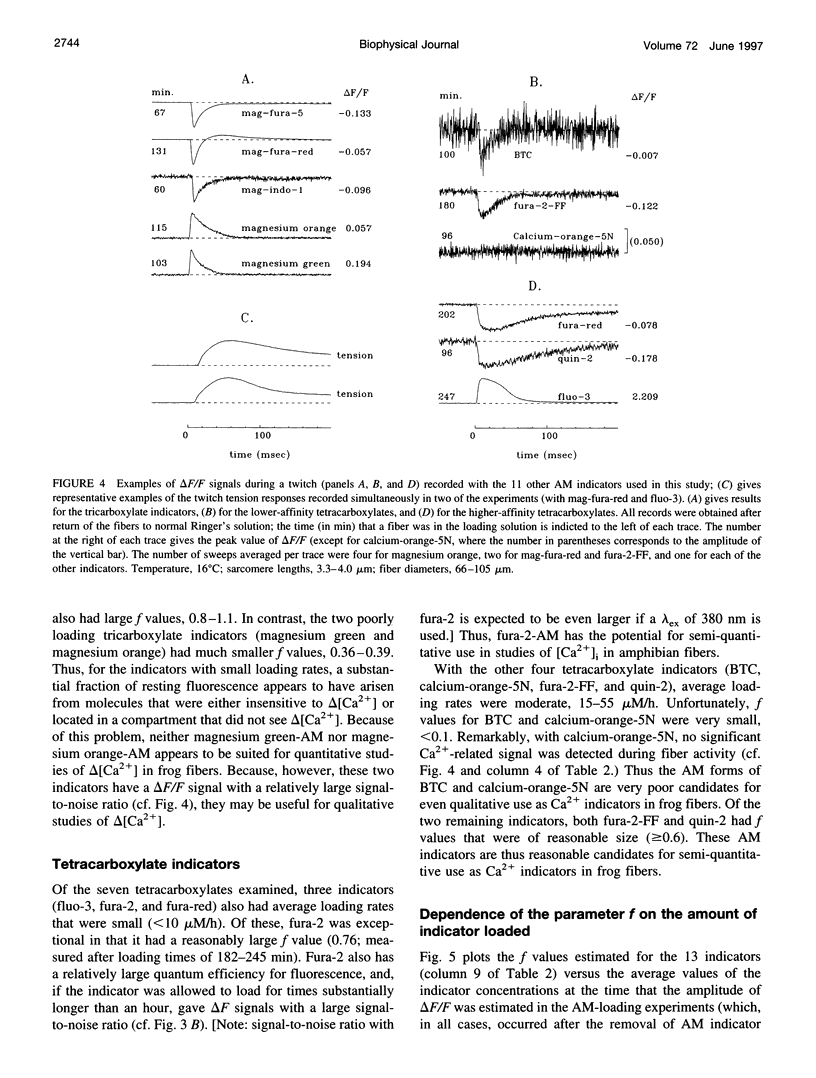
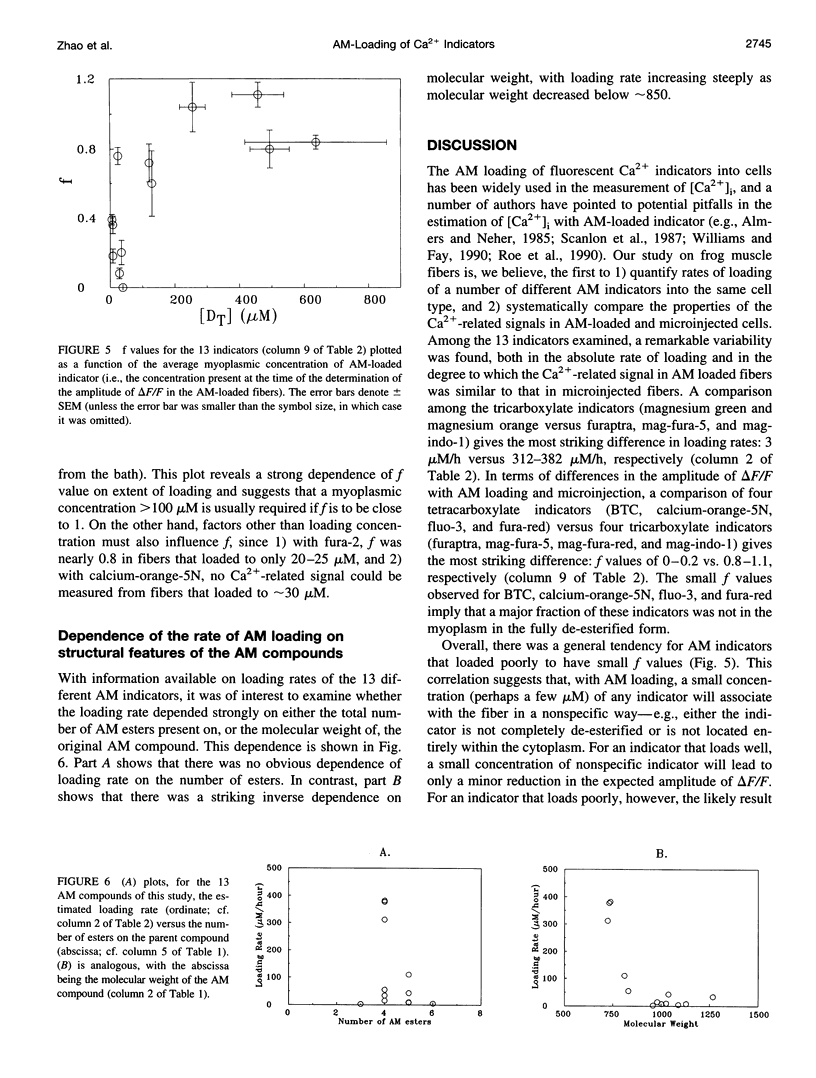
The AM loading of a number of different fluorescent Ca2+ indicators was compared in intact single fibers of frog muscle. Among the 13 indicators studied, loading rates (the average increase in the fiber concentration of indicator per first 60 min of loading) varied approximately 100-fold, from approximately 3 microM/h to >300 microM/h (16 degrees C). Loading rates were strongly dependent on the molecular weight of the AM compounds, with the rate increasing steeply as molecular weight decreased below approximately 850. Properties of delta F/F (the Ca2(+)-related fluorescence signal observed with fiber stimulation) were also measured in AM-loaded fibers and compared with those previously reported for fibers microinjected with indicator. In general, the time course of delta F/F was very similar with AM-loading and microinjection; however, the amplitude of delta F/F was usually smaller with AM-loading. There was a strong correlation between the rate of indicator loading and the value of the parameter f (the ratio of the amplitude of delta F/F in AM-loaded versus microinjected fibers). For indicators with small loading rates (<10 microM/h, N = 5), f values were generally small (< or =0.4, N = 4); whereas with large loading rates (>100 microM/h, N = 4), f values were large (> or =0.8, N = 4). This suggests that, with any AM indicator, a small concentration may associate nonspecifically with the fiber (either the indicator is incompletely de-esterified or, if completely de-esterified, not located in the myoplasmic compartment). If the loaded concentration is small, the nonspecific indicator will present a significant source of error in the estimation of [Ca2+]i.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Absorbance signals from resting frog skeletal muscle fibers injected with the pH indicator dye, phenol red. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Sep;96(3):449–471. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S., Hui C. S., Quinta-Ferreira M. E. Properties of the metallochromic dyes Arsenazo III, Antipyrylazo III and Azo1 in frog skeletal muscle fibres at rest. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:89–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Oetliker H. Birefringence experiments on isolated skeletal muscle fibres suggest a possible signal from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1975 Jan 10;253(5487):97–101. doi: 10.1038/253097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Edman K. A., Lou F., Sun Y. B. Variation in myoplasmic Ca2+ concentration during contraction and relaxation studied by the indicator fluo-3 in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 1;478(Pt 1):137–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin D. R., Morgan D. L., Stephenson D. G., Julian F. J. The intracellular Ca2+ transient and tension in frog skeletal muscle fibres measured with high temporal resolution. J Physiol. 1994 Mar 1;475(2):319–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Changes in phenol red absorbance in response to electrical stimulation of frog skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Sep;96(3):473–491. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Kurebayashi N., Konishi M., Baylor S. M. Excitation-contraction coupling in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers injected with mmolar concentrations of fura-2. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):224–234. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81599-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic calcium transients in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers monitored with the fluorescent indicator furaptra. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):271–301. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Olson A., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic binding of fura-2 investigated by steady-state fluorescence and absorbance measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83045-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurebayashi N., Harkins A. B., Baylor S. M. Use of fura red as an intracellular calcium indicator in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1934–1960. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81564-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A., Westerblad H., Allen D. G. Changes in tetanic and resting [Ca2+]i during fatigue and recovery of single muscle fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:307–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe M. W., Lemasters J. J., Herman B. Assessment of Fura-2 for measurements of cytosolic free calcium. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon M., Williams D. A., Fay F. S. A Ca2+-insensitive form of fura-2 associated with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Assessment and accurate Ca2+ measurement. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6308–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):527–528. doi: 10.1038/290527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerblad H., Allen D. G. Changes of myoplasmic calcium concentration during fatigue in single mouse muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Sep;98(3):615–635. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fay F. S. Intracellular calibration of the fluorescent calcium indicator Fura-2. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao M., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Properties of tri- and tetracarboxylate Ca2+ indicators in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1996 Feb;70(2):896–916. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79633-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


