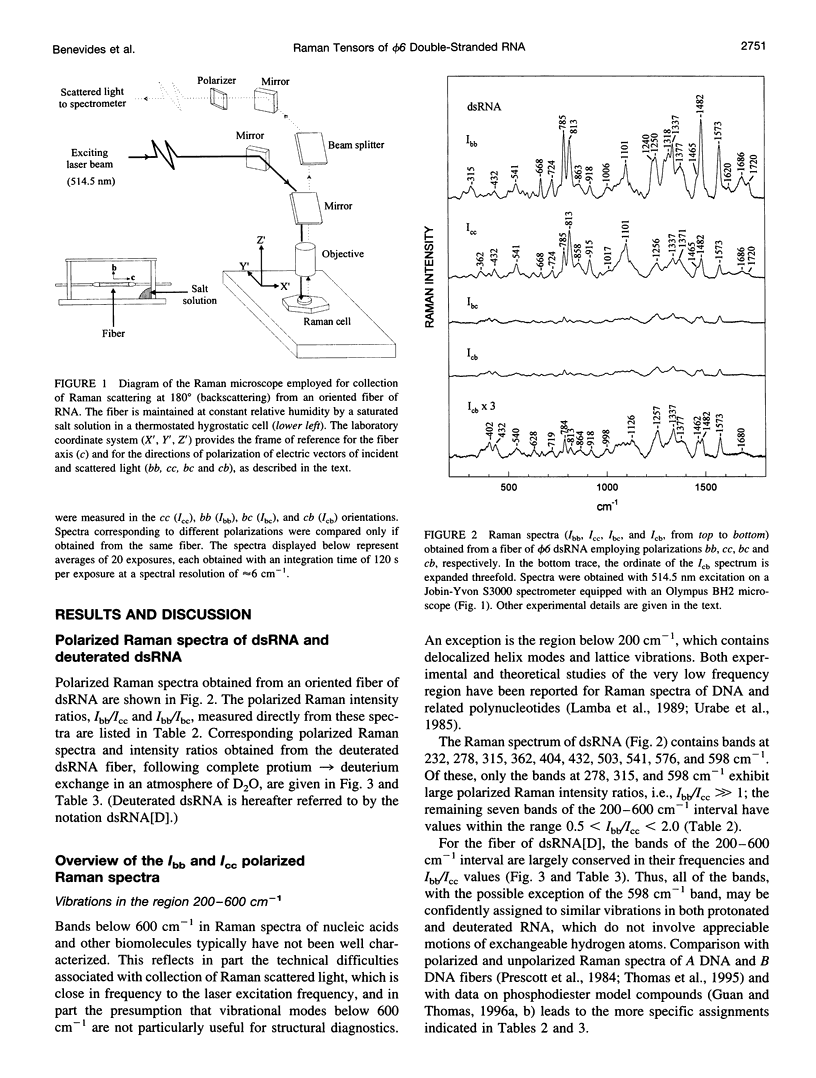
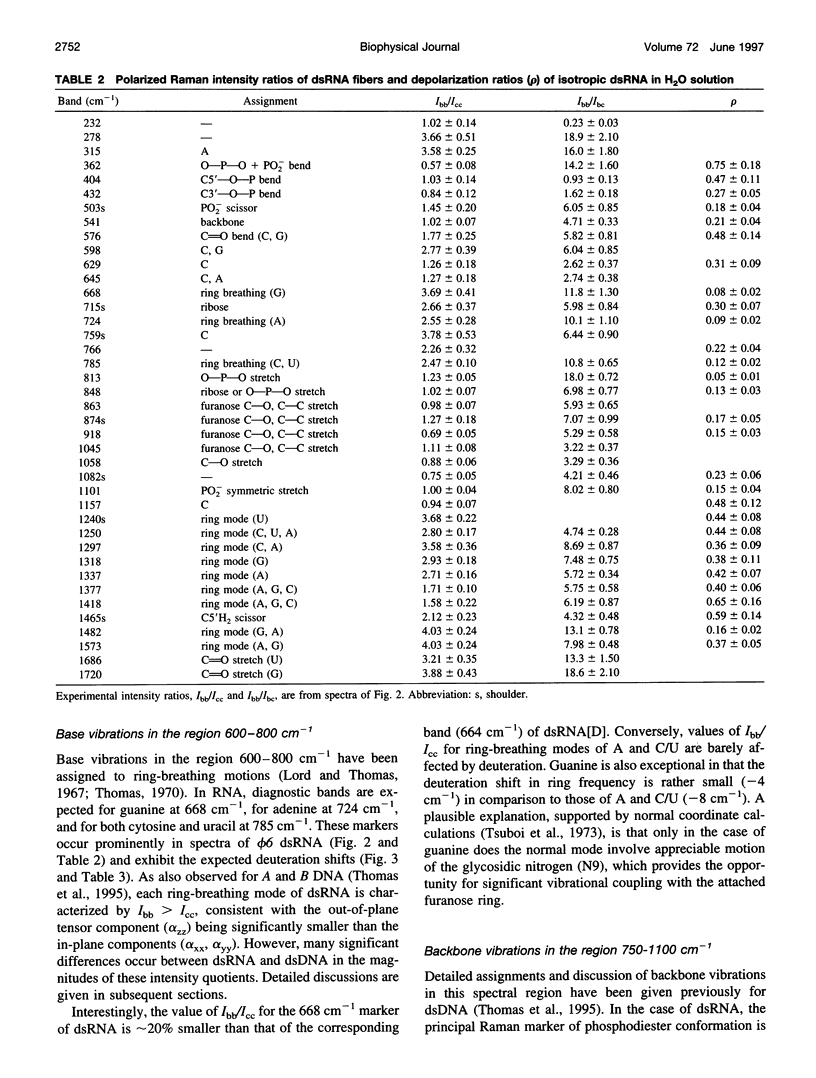
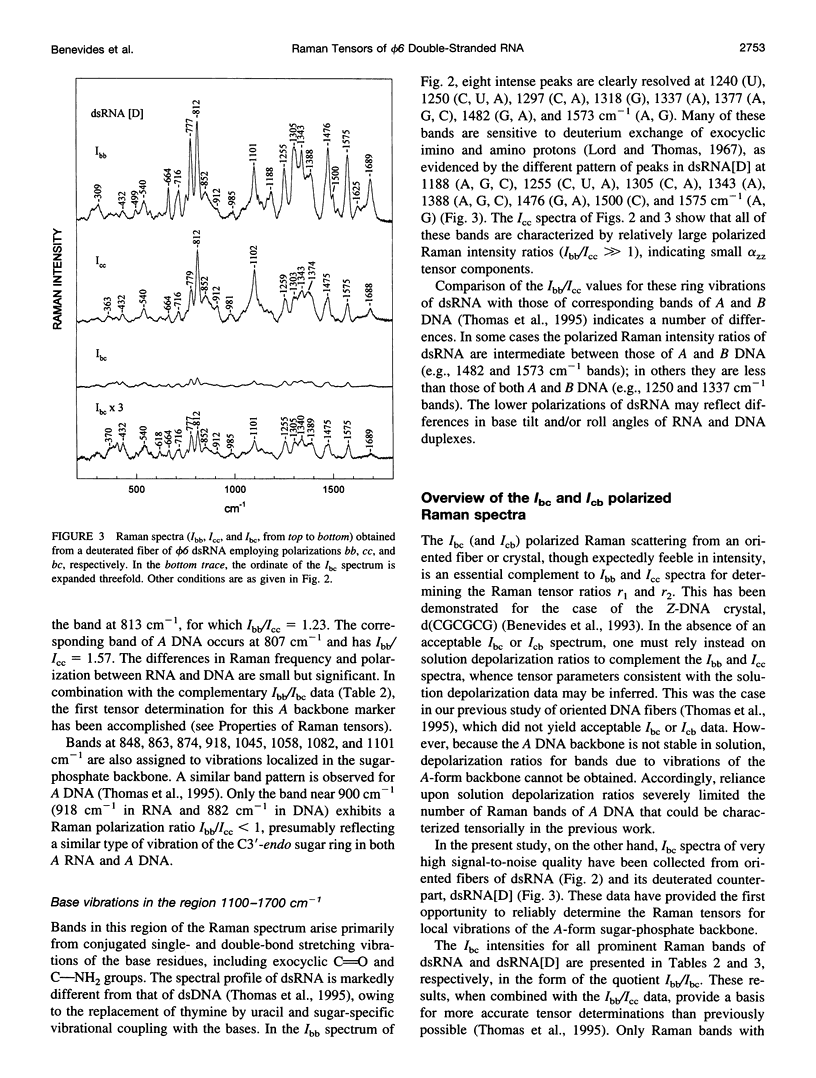
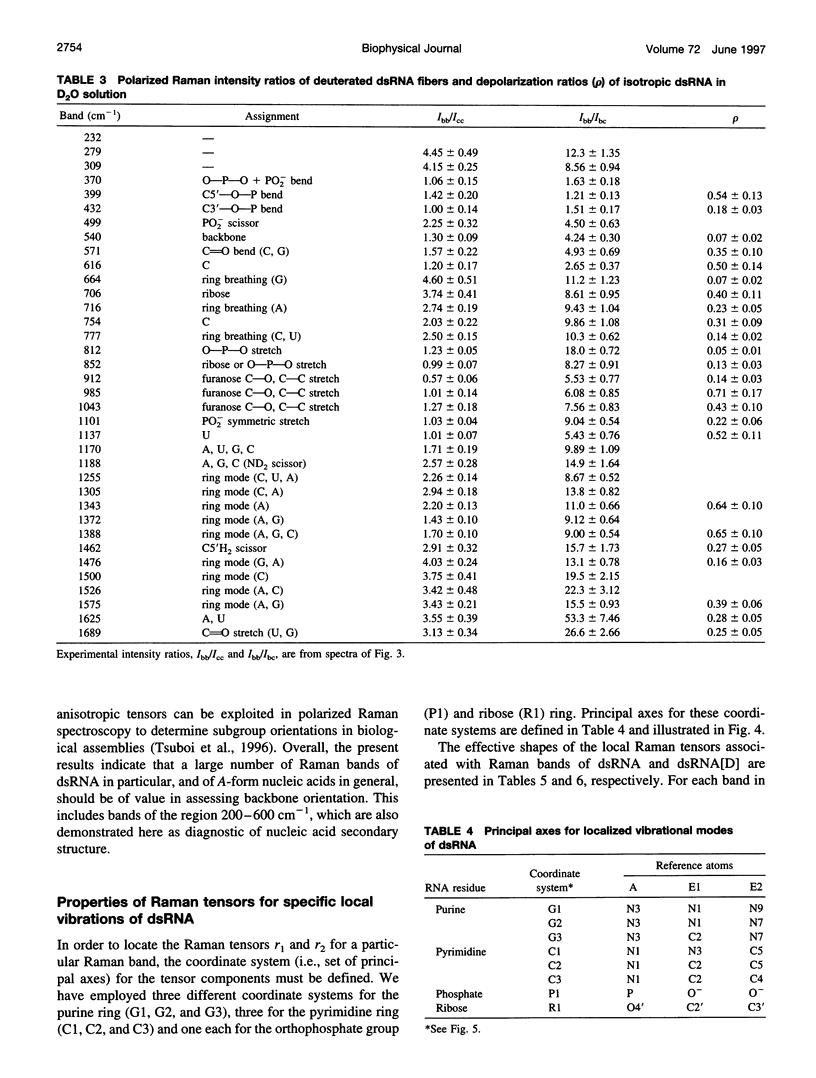
Abstract
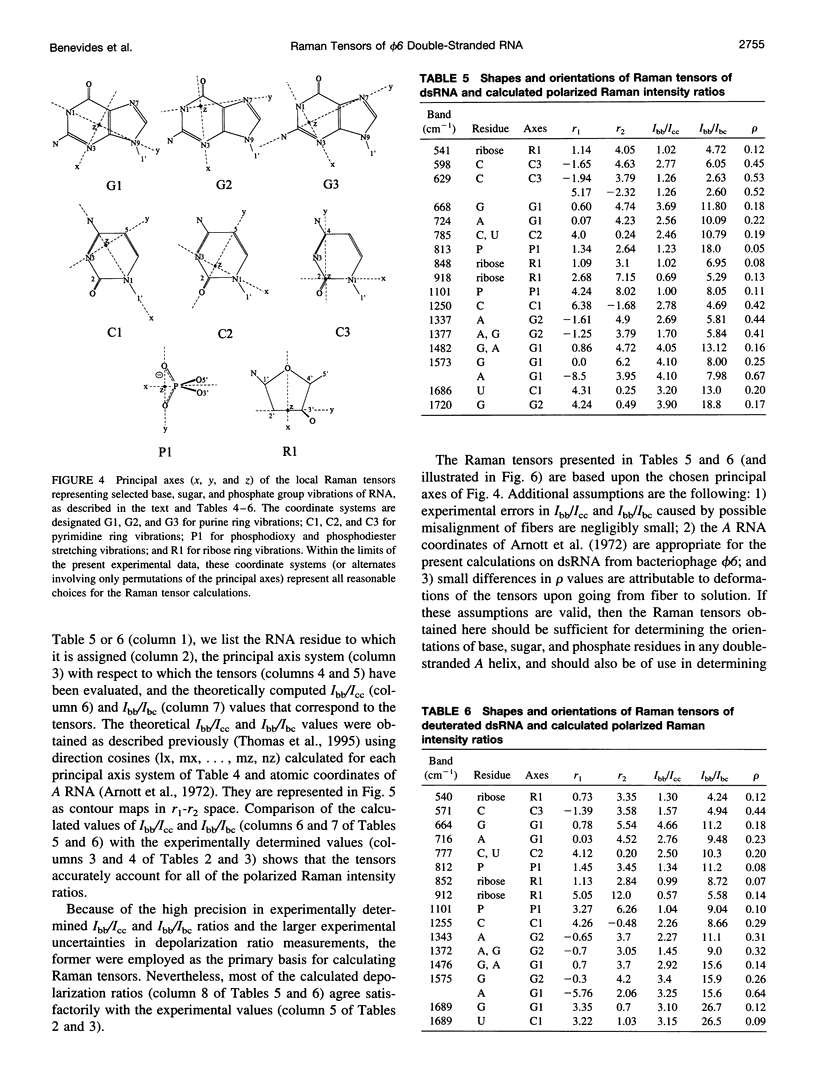
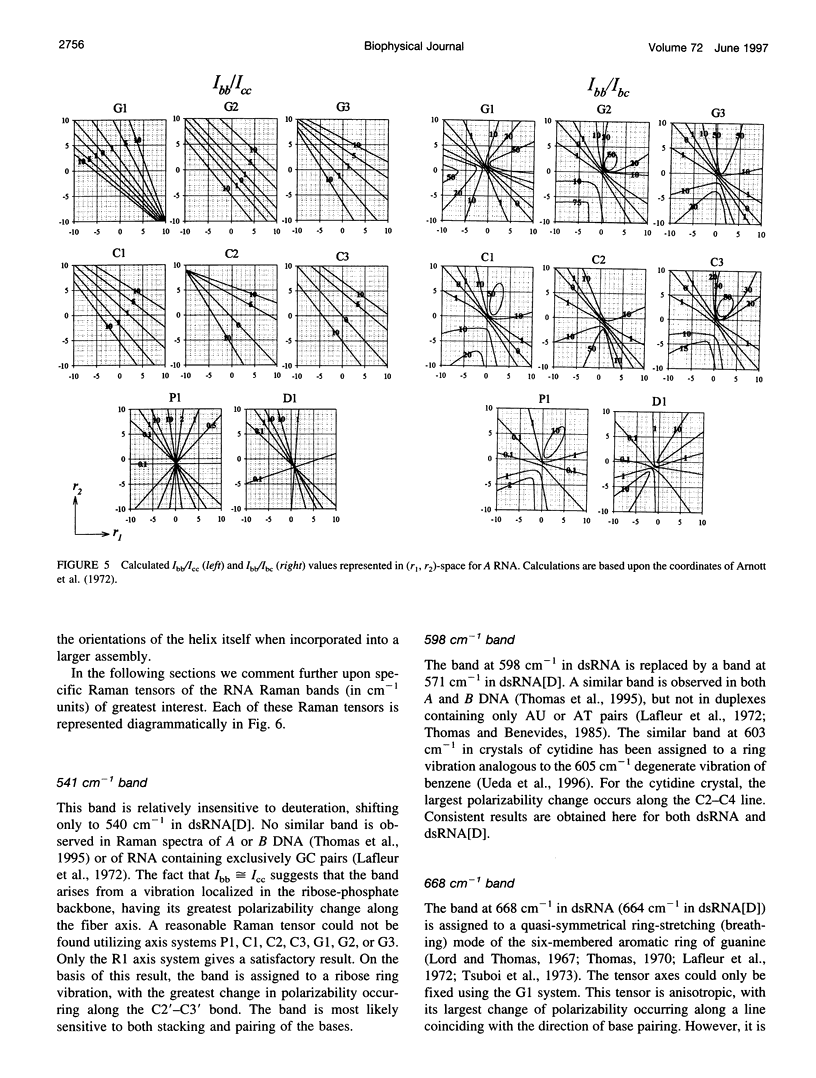
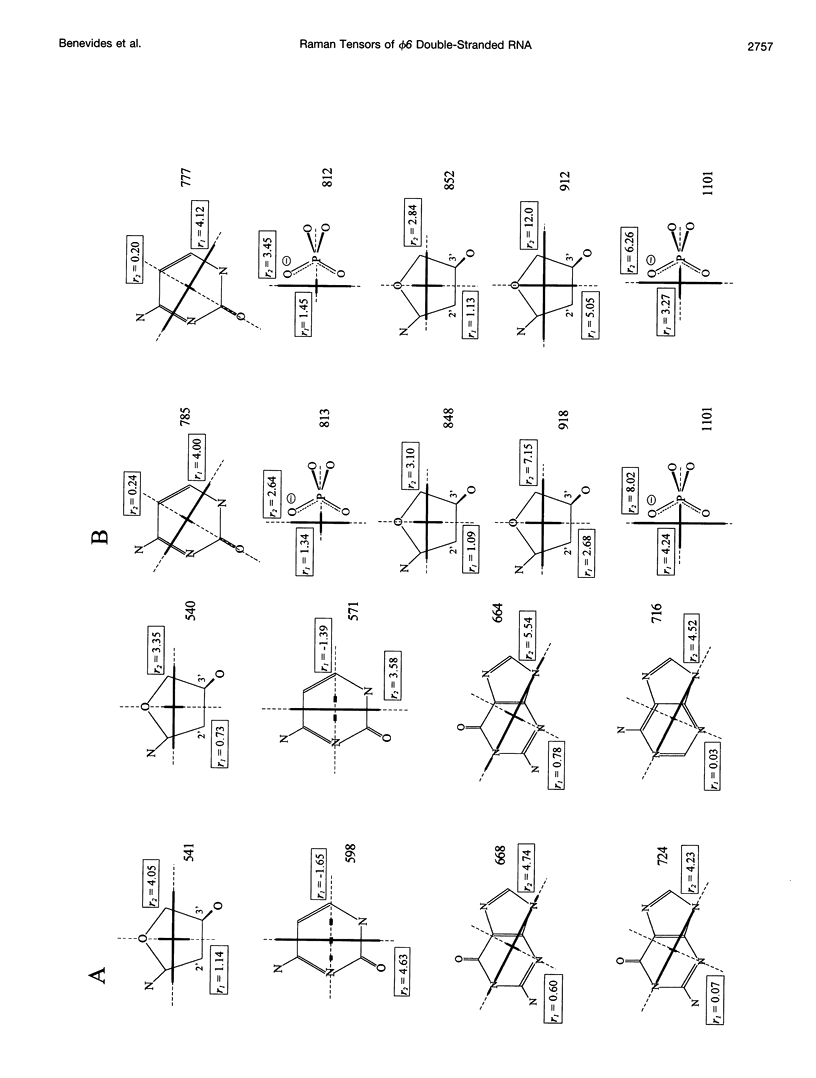
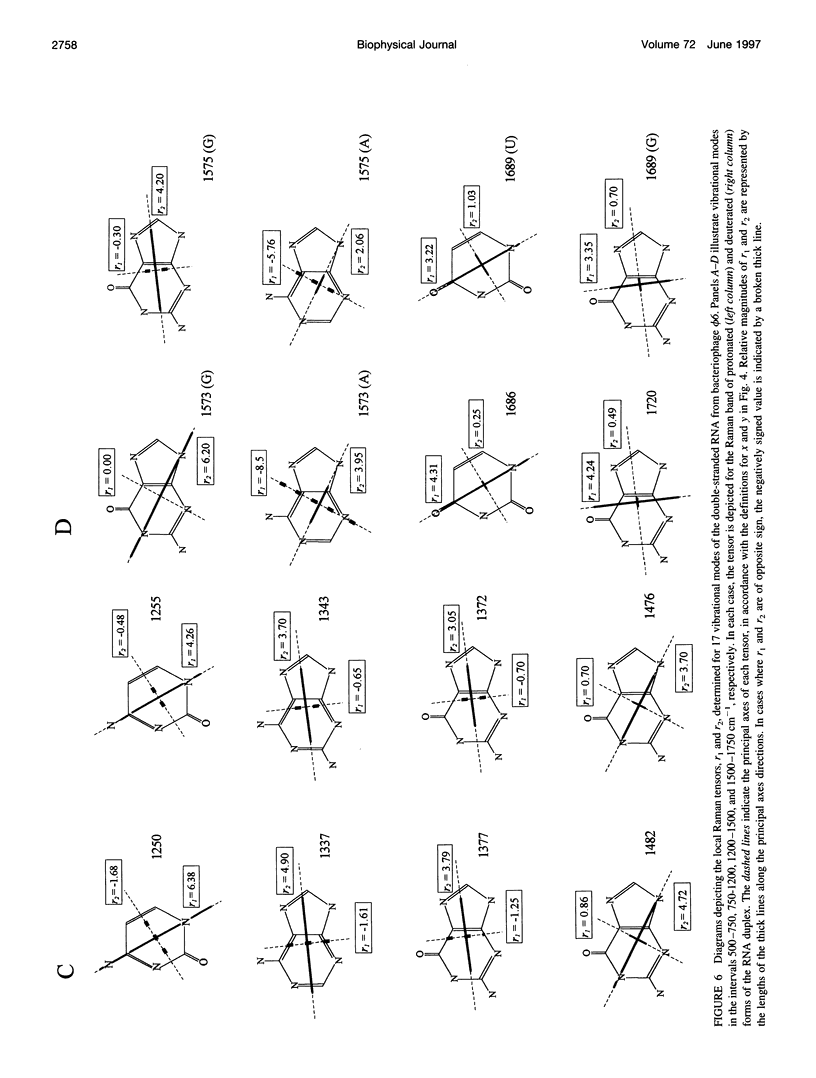
Raman tensors for localized vibrations of base (A, U, G, and C), ribose and phosphate groups of double-stranded RNA have been determined from polarized Raman measurements on oriented fibers of the genomic RNA of bacteriophage phi6. Polarized Raman intensities for which electric vectors of both the incident and scattered light are polarized either perpendicular (I[bb]) or parallel (I[cc]) to the RNA fiber axis have been obtained by Raman microspectroscopy using 514.5-nm excitation. Similarly, the polarized Raman components, I(bc) and I(cb), for which incident and scattered vectors are mutually perpendicular, have been obtained. Spectra collected from fibers maintained at constant relative humidity in both H2O and D2O environments indicate the effects of hydrogen-isotopic shifts on the Raman polarizations and tensors. Novel findings are the following: 1) the intense Raman band at 813 cm(-1), which is assigned to phosphodiester (OPO) symmetrical stretching and represents the key marker of the A conformation of double-stranded RNA, is characterized by a moderately anisotropic Raman tensor; 2) the prominent RNA band at 1101 cm(-1), which is assigned to phosphodioxy (PO2-) symmetrical stretching, also exhibits a moderately anisotropic Raman tensor. Comparison with results obtained previously on A, B, and Z DNA suggests that tensors for localized vibrations of backbone phosphodiester and phosphodioxy groups are sensitive to helix secondary structure and local phosphate group environment; and 3) highly anisotropic Raman tensors have been found for prominent and well-resolved Raman markers of all four bases of the RNA duplex. These enable the use of polarized Raman spectroscopy for the determination of purine and pyrimidine base residue orientations in ribonucleoprotein assemblies. The present determination of Raman tensors for dsRNA is comprehensive and accurate. Unambiguous tensors have been deduced for virtually all local vibrational modes of the 300-1800 cm(-1) spectral interval. The results provide a reliable basis for future evaluations of the effects of base pairing, base stacking, and sequence context on the polarized Raman spectra of nucleic acids.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W., Dover S. D. Optimised parameters for RNA double-helices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1392–1399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90867-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benevides J. M., Kukolj G., Autexier C., Aubrey K. L., DuBow M. S., Thomas G. J., Jr Secondary structure and interaction of phage D108 Ner repressor with a 61-base-pair operator: evidence for altered protein and DNA structures in the complex. Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 6;33(35):10701–10710. doi: 10.1021/bi00201a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benevides J. M., Lemeur D., Thomas G. J., Jr Molecular conformations and 8-CH exchange rates of purine ribo- and deoxyribonucleotides: investigation by Raman spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1984 Jun;23(6):1011–1024. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benevides J. M., Weiss M. A., Thomas G. J., Jr An altered specificity mutation in the lambda repressor induces global reorganization of the protein-DNA interface. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10869–10878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes R., Rupprecht A., Kearns D. R. Interaction of water with oriented DNA in the A- and B-form conformations. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):683–691. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82715-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Y., Thomas G. J., Jr Vibrational analysis of nucleic acids. IV. Normal modes of the DNA phosphodiester structure modeled by diethyl phosphate. Biopolymers. 1996 Dec;39(6):813–835. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(199612)39:6%3C813::AID-BIP7%3E3.0.CO;2-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Y., Thomas G. J., Jr Vibrational analysis of nucleic acids. V. Force field and conformation-dependent modes of the phosphodiester backbone modeled by diethyl phosphate. Biophys J. 1996 Nov;71(5):2802–2814. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79474-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafleur L., Rice J., Thomas G. J., Jr Raman studies of nucleic acids. VII. Poly A-poly U and poly G-poly C. Biopolymers. 1972;11(12):2423–2437. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360111205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamba O. P., Wang A. H., Thomas G. J., Jr Low-frequency dynamics and Raman scattering of crystals, of B-, A-, and Z-DNA, and fibers of C-DNA. Biopolymers. 1989 Feb;28(2):667–678. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. S., Chen Z. G., Johnson J. E., Thomas G. J., Jr Structural studies of bean pod mottle virus, capsid, and RNA in crystal and solution states by laser Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 May 29;29(21):5018–5026. doi: 10.1021/bi00473a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T., Bamford D. H., Bamford J. K., Thomas G. J., Jr Structural studies of the enveloped dsRNA bacteriophage phi 6 of Pseudomonas syringae by Raman spectroscopy. I. The virion and its membrane envelope. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):461–472. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T., Johnson J. E., Thomas G. J., Jr Raman dynamic probe of hydrogen exchange in bean pod mottle virus: base-specific retardation of exchange in packaged ssRNA. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1963–1972. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81272-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Thomas G. J., Jr, Fuller M., King J. Investigations of bacteriophage P22 by laser Raman spectroscopy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;64:271–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Thomas G. J., Jr Structure and dynamics of interstrand guanine association in quadruplex telomeric DNA. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 25;34(29):9645–9654. doi: 10.1021/bi00029a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olkkonen V. M., Ojala P. M., Bamford D. H. Generation of infectious nucleocapsids by in vitro assembly of the shell protein on to the polymerase complex of the dsRNA bacteriophage phi 6. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):569–581. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90702-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overman S. A., Tsuboi M., Thomas G. J., Jr Subunit orientation in the filamentous virus Ff(fd, f1, M13). J Mol Biol. 1996 Jun 14;259(3):331–336. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott B., Steinmetz W., Thomas G. J., Jr Characterization of DNA structures by laser Raman spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1984 Feb;23(2):235–256. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly K. E., Thomas G. J., Jr Hydrogen exchange dynamics of the P22 virion determined by time-resolved Raman spectroscopy. Effects of chromosome packaging on the kinetics of nucleotide exchanges. J Mol Biol. 1994 Aug 5;241(1):68–82. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Benevides J. M. An A-helix structure for poly(dA-dT) X poly(dA-dT). Biopolymers. 1985 Jun;24(6):1101–1105. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Benevides J. M., Overman S. A., Ueda T., Ushizawa K., Saitoh M., Tsuboi M. Polarized Raman spectra of oriented fibers of A DNA and B DNA: anisotropic and isotropic local Raman tensors of base and backbone vibrations. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):1073–1088. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80282-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr Raman spectral studies of nucleic acids. 3. Laser-excited spectra of ribosomal RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 8;213(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi M., Overman S. A., Thomas G. J., Jr Orientation of tryptophan-26 in coat protein subunits of the filamentous virus Ff by polarized Raman microspectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1996 Aug 13;35(32):10403–10410. doi: 10.1021/bi9527707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma R., Bamford J. H., Bamford D. H., Russell M. P., Thomas G. J., Jr Structure, interactions and dynamics of PRD1 virus I. Coupling of subunit folding and capsid assembly. J Mol Biol. 1996 Mar 22;257(1):87–101. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma R., Bamford J. H., Bamford D. H., Thomas G. J., Jr Structure, interactions and dynamics of PRD1 virus II. Organization of the viral membrane and DNA. J Mol Biol. 1996 Mar 22;257(1):102–115. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma R., Prevelige P. E., Jr, Thomas G. J., Jr Structural transitions in the scaffolding and coat proteins of P22 virus during assembly and disassembly. Biochemistry. 1996 Apr 9;35(14):4619–4627. doi: 10.1021/bi952793l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Ushizawa K., Tsuboi M. Depolarization of Raman scattering from some nucleotides of RNA and DNA. Biopolymers. 1993 Dec;33(12):1791–1802. doi: 10.1002/bip.360331205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


