Abstract
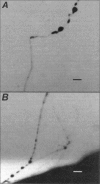
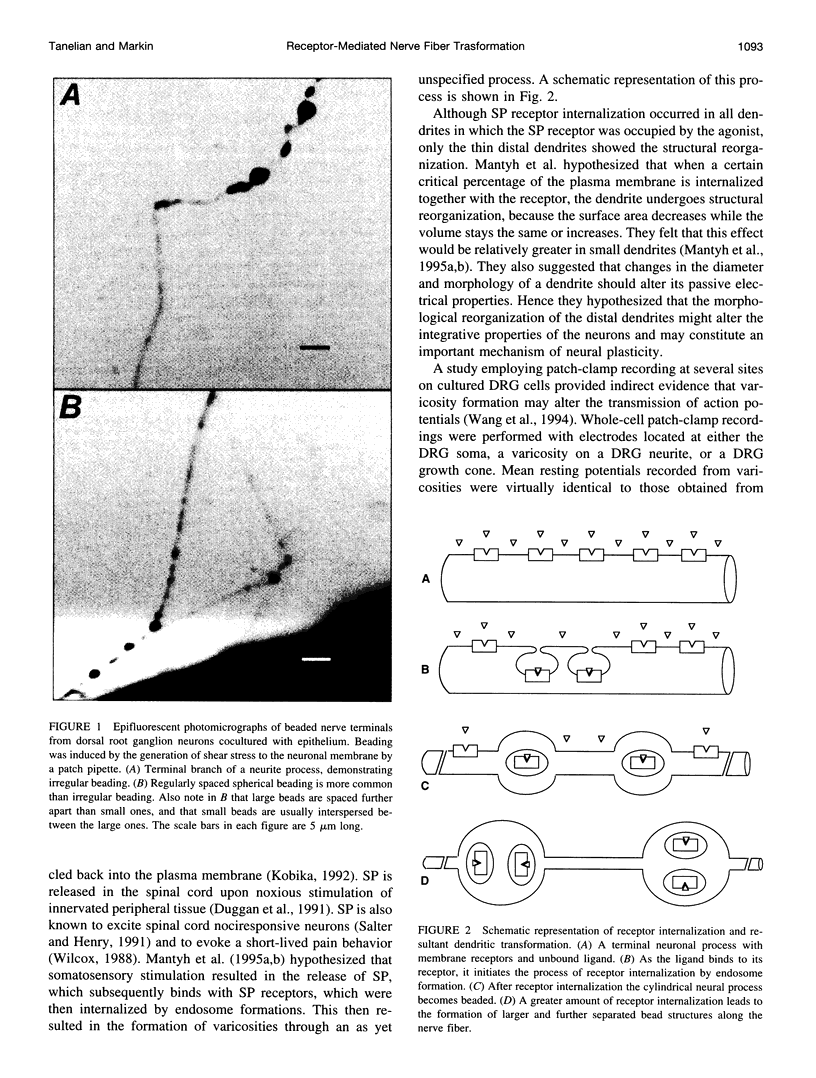
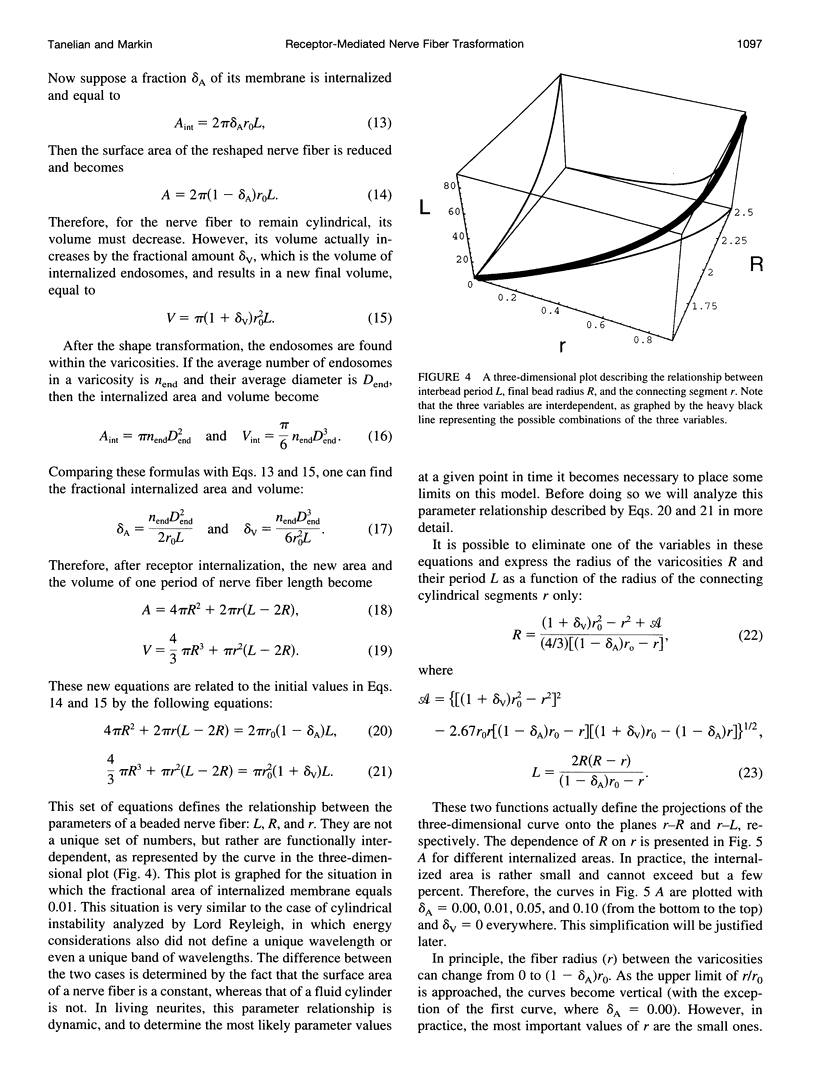
Stimulation of the nervous system by substance P, a G protein-coupled receptor, and subsequent receptor internalization causes dendrites to change their shape from homogeneous cylinders to a heterogeneous string of swollen varicosities (beads) connected by thin segments. In this paper we have analyzed this phenomenon and propose quantitative mechanisms to explain this type of physical shape transformation. We developed a mathematical solution to describe the relationship between the initial radius of a cylindrical nerve fiber and the average radii of the subsequently created varicosities and connecting segments, as well as the periodicity of the varicosities along the nerve fiber. Theoretical predictions are in good agreement with our own and published experimental data from dorsal root ganglion neurons, spinal cord, and brain. Modeling the electrical properties of these beaded fibers has led to an understanding of the functional biophysical consequences of nerve fiber transformation. Several hypotheses for how this shape transformation can be used to process information within the nervous system have been put forth.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. L., Bamburg J. R. Effects of local anesthetics on nerve growth in culture. Dev Neurosci. 1981;4(4):273–290. doi: 10.1159/000112767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. H., Chen M. Long-term memory in Aplysia modulates the total number of varicosities of single identified sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2373–2377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. H., Kandel E. R. Structural changes accompanying memory storage. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:397–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Ziv R, Moses E. Instability and "pearling" states produced in tubular membranes by competition of curvature and tension. Phys Rev Lett. 1994 Sep 5;73(10):1392–1395. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitel R. E., Dubner R. Fatigue and adaptation in unmyelinated (C) polymodal nociceptors to mechanical and thermal stimuli applied to the monkey's face. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):402–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitel R. E., Dubner R. Response of unmyelinated (C) polymodal nociceptors to thermal stimuli applied to monkey's face. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1160–1175. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknese S., Periasamy N., Shohet S. B., Verkman A. S. Cytoplasmic viscosity near the cell plasma membrane: measurement by evanescent field frequency-domain microfluorimetry. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1272–1282. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81179-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird M. M. Microsurgical transection of small nerve fibre bundles in vitro. Effects on axons, growth cones and glial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jul 10;190(3):525–538. doi: 10.1007/BF00219562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
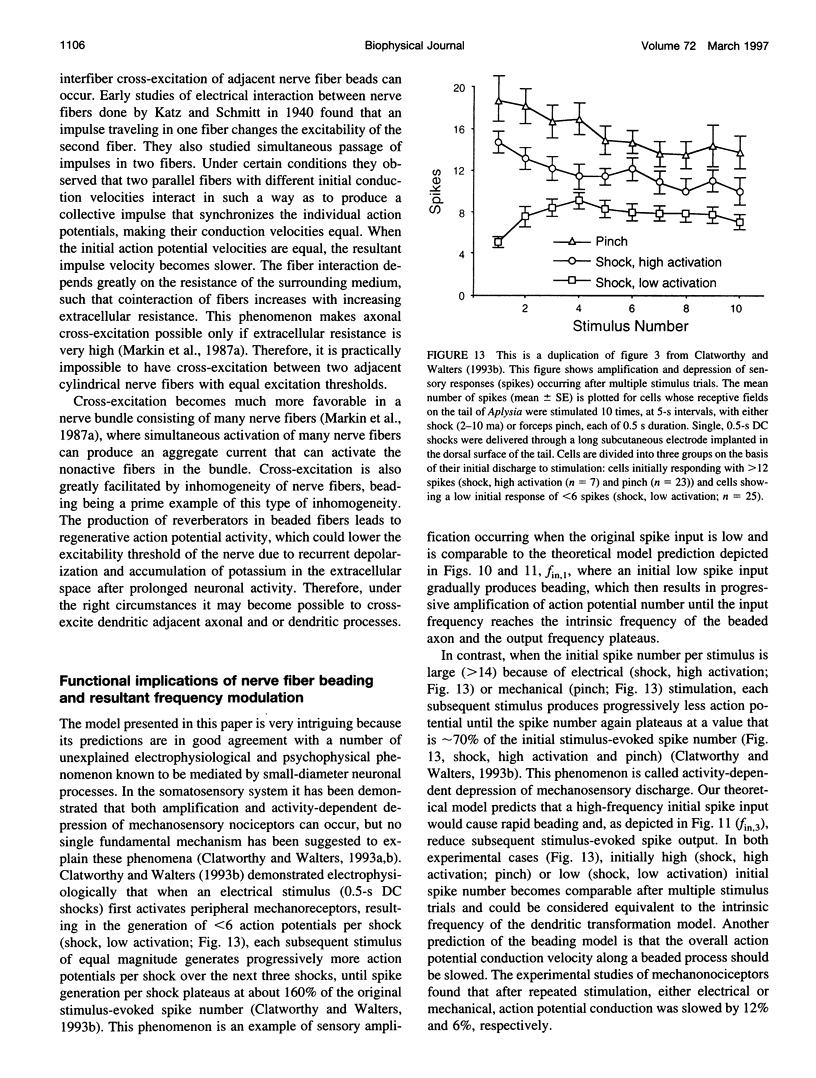
- Clatworthy A. L., Walters E. T. Activity-dependent depression of mechanosensory discharge in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Sep;70(3):1195–1209. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.3.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clatworthy A. L., Walters E. T. Rapid amplification and facilitation of mechanosensory discharge in Aplysia by noxious stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Sep;70(3):1181–1194. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.3.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hope P. J., Lang C. W., Williams C. A. Sustained isometric contraction of skeletal muscle results in release of immunoreactive neurokinins in the spinal cord of the anaesthetized cat. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 28;122(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90855-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. S., Rall W. Changes of action potential shape and velocity for changing core conductor geometry. Biophys J. 1974 Oct;14(10):731–757. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85947-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M. Intrinsic curvature hypothesis for biomembrane lipid composition: a role for nonbilayer lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M., Shyamsunder E. Is the mechanism of general anesthesia related to lipid membrane spontaneous curvature? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:685–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Zhang S. J. Action potential propagation and propagation block by GABA in rat posterior pituitary nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1995 Mar 15;483(Pt 3):597–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Euteneuer U., Traub P., Schliwa M. Viscoelastic properties of vimentin compared with other filamentous biopolymer networks. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):155–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. W., Schutzbach J. S. Modulation of dolichyl-phosphomannose synthase activity by changes in the lipid environment of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6315–6320. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. A note on interaction between nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1942 Mar 31;100(4):369–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1942.sp003948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Schmitt O. H. Electric interaction between two adjacent nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1940 Feb 14;97(4):471–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1940.sp003823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. Adrenergic receptors as models for G protein-coupled receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:87–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMotte R. H., Torebjörk H. E., Robinson C. J., Thalhammer J. G. Time-intensity profiles of cutaneous pain in normal and hyperalgesic skin: a comparison with C-fiber nociceptor activities in monkey and human. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1434–1450. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Allen C. J., Ghilardi J. R., Rogers S. D., Mantyh C. R., Liu H., Basbaum A. I., Vigna S. R., Maggio J. E. Rapid endocytosis of a G protein-coupled receptor: substance P evoked internalization of its receptor in the rat striatum in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2622–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., DeMaster E., Malhotra A., Ghilardi J. R., Rogers S. D., Mantyh C. R., Liu H., Basbaum A. I., Vigna S. R., Maggio J. E. Receptor endocytosis and dendrite reshaping in spinal neurons after somatosensory stimulation. Science. 1995 Jun 16;268(5217):1629–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.7539937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller K. Axoplasmic transport of horseradish peroxidase in single neurons of the dorsal root ganglion studied in vitro by microinjection. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Oct;270(1):139–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00381888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C., Lecar H. Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys J. 1981 Jul;35(1):193–213. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84782-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazif F. A., Byrne J. H., Cleary L. J. cAMP induces long-term morphological changes in sensory neurons of Aplysia. Brain Res. 1991 Jan 25;539(2):324–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91638-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P, Powers T, Seifert U. Dynamical Theory of the Pearling Instability in Cylindrical Vesicles. Phys Rev Lett. 1995 Apr 24;74(17):3384–3387. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.3384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy N., Armijo M., Verkman A. S. Picosecond rotation of small polar fluorophores in the cytosol of sea urchin eggs. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 24;30(51):11836–11841. doi: 10.1021/bi00115a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl E. R. Myelinated afferent fibres innervating the primate skin and their response to noxious stimuli. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):593–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón F., Joyner R. W., Moore J. W. Propagation of action potentials in inhomogeneous axon regions. Fed Proc. 1975 Apr;34(5):1357–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M. W., Henry J. L. Responses of functionally identified neurones in the dorsal horn of the cat spinal cord to substance P, neurokinin A and physalaemin. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90319-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Schwartz W. H., Selden S. C., Pollard T. D. Mechanical properties of brain tubulin and microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1205–1211. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltenburg-Didinger G., Boegner F., Grüning W., Wagner M., Marx P., Altenkirch H. Specific neurotoxic effects of different organic solvents on dissociated cultures of the nervous system. Neurotoxicology. 1992 Spring;13(1):161–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suneson A., Hansson H. A., Lycke E., Seeman T. Pressure wave injuries to rat dorsal root ganglion cells in culture caused by high-energy missiles. J Trauma. 1989 Jan;29(1):10–18. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198901000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. A., Frank R. S., Waugh R. E. Passive mechanical behavior of human neutrophils: power-law fluid. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2078–2088. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81238-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. T. Multiple sensory neuronal correlates of site-specific sensitization in Aplysia. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):408–417. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00408.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Van den Berg R. J., Ypey D. L. Resting membrane potentials and excitability at different regions of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in culture. Neuroscience. 1994 May;60(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann T. S., Pates R. D., Beach J. M., Salmon A., Brown M. F. Lipid-protein interactions mediate the photochemical function of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6469–6474. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox G. L. Pharmacological studies of grooming and scratching behavior elicited by spinal substance P and excitatory amino acids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;525:228–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb38608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]