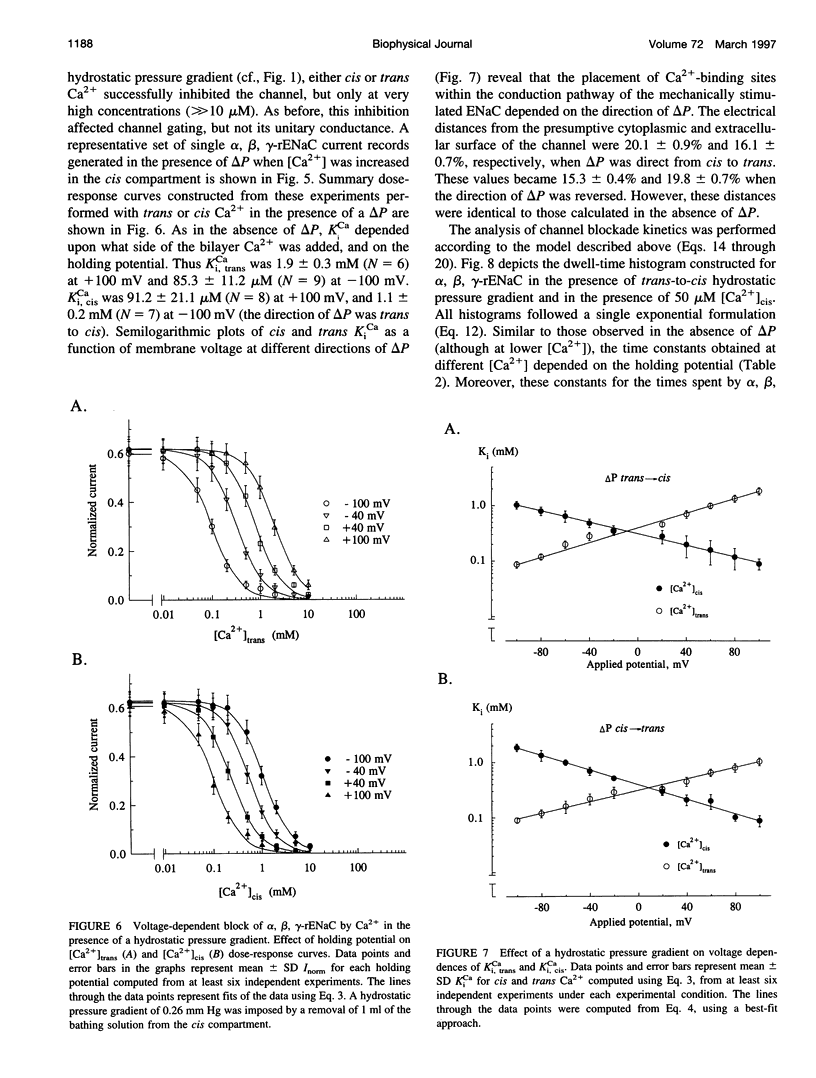
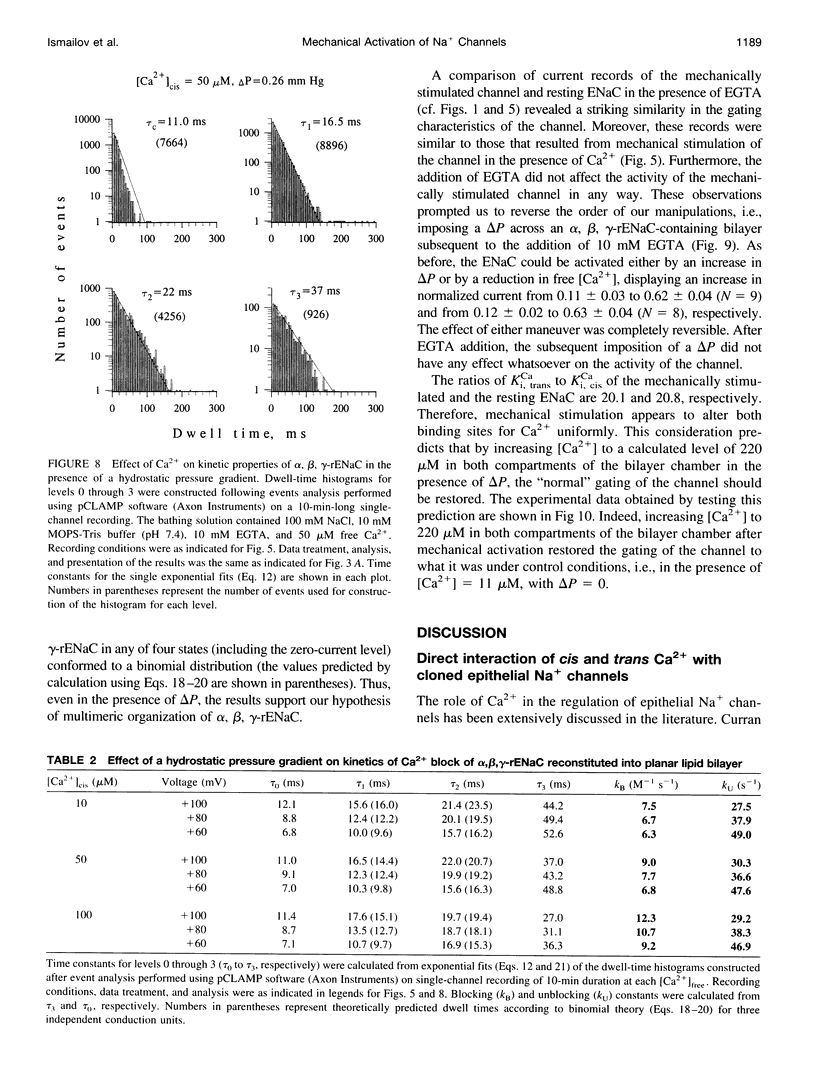
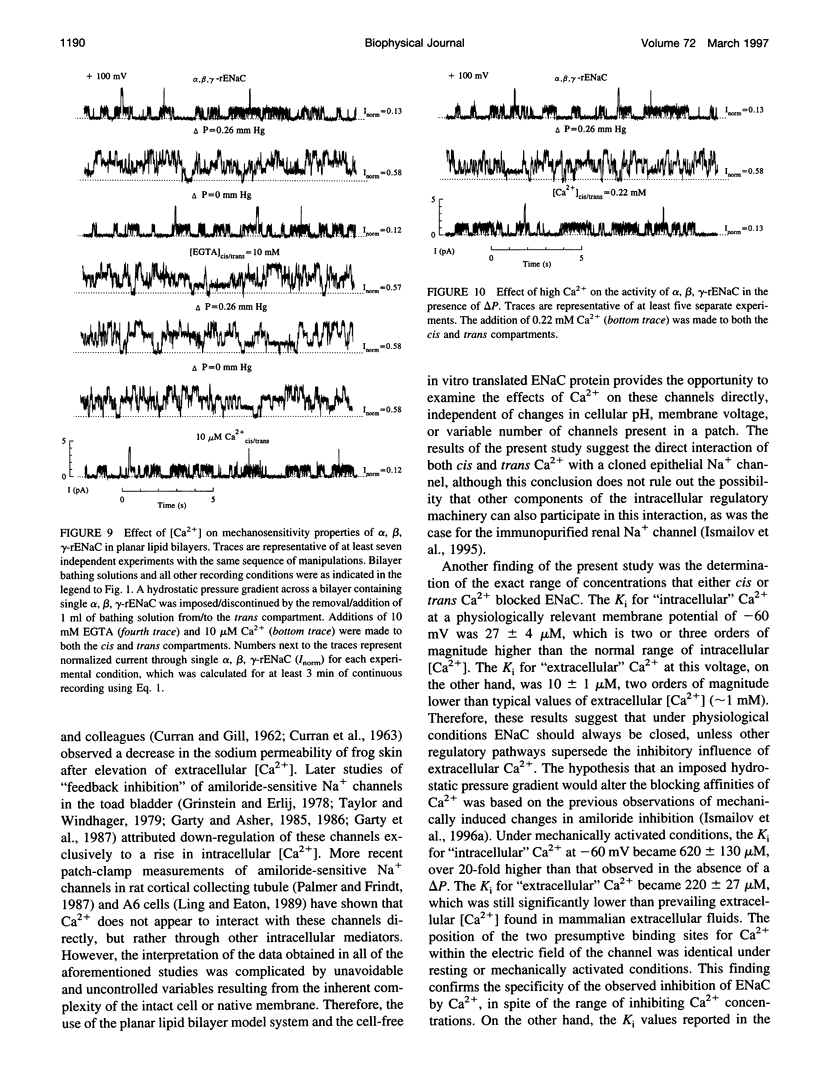
Abstract
A family of novel epithelial Na+ channels (ENaCs) have recently been cloned from several different tissues. Three homologous subunits (alpha, beta, gamma-ENaCs) from the core conductive unit of Na(+)-selective, amiloride-sensitive channels that are found in epithelia. We here report the results of a study assessing the regulation of alpha,beta,gamma-rENaC by Ca2+ in planar lipid bilayers. Buffering of the bilayer bathing solutions to [Ca2+] < 1 nM increased single-channel open probability by fivefold. Further investigation of this phenomenon revealed that Ca2+ ions produced a voltage-dependent block, affecting open probability but not the unitary conductance of ENaC. Imposing a hydrostatic pressure gradient across bilayers containing alpha,beta,gamma-rENaC markedly reduced the sensitivity of these channels to inhibition by [Ca2+]. Conversely, in the nominal absence of Ca2+, the channels lost their sensitivity to mechanical stimulation. These results suggest that the previously observed mechanical activation of ENaCs reflects a release of the channels from block by Ca2+.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awayda M. S., Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J. A cloned renal epithelial Na+ channel protein displays stretch activation in planar lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jun;268(6 Pt 1):C1450–C1459. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.6.C1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdiev B. K., Prat A. G., Cantiello H. F., Ausiello D. A., Fuller C. M., Jovov B., Benos D. J., Ismailov I. I. Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by short actin filaments. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 26;271(30):17704–17710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.30.17704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. P., Storey K. B. Bound and determined: a computer program for making buffers of defined ion concentrations. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 14;201(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., GILL J. R., Jr The effect of calcium on sodium transport by frog skin. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Mar;45:625–641. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., HERRERA F. C., FLANIGAN W. J. The effect of Ca and antidiuretic hormone on Na transport across frog skin. II. Sites and mechanisms of action. J Gen Physiol. 1963 May;46:1011–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., García-Añoveros J. Mechanosensation and the DEG/ENaC ion channels. Science. 1996 Jul 19;273(5273):323–324. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5273.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 1. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Oct;3(3):181–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Asher C. Ca2+-dependent, temperature-sensitive regulation of Na+ channels in tight epithelia. A study using membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8330–8335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Asher C. Ca2+-induced down-regulation of Na+ channels in toad bladder epithelium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7400–7406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Asher C., Yeger O. Direct inhibition of epithelial Na+ channels by a pH-dependent interaction with calcium, and by other divalent ions. J Membr Biol. 1987;95(2):151–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01869160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Benos D. J. Characteristics and regulatory mechanisms of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel. Physiol Rev. 1988 Apr;68(2):309–373. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Erlij D. Intracellular calcium and the regulation of sodium transport in the frog skin. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Jul 26;202(1148):353–360. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Awayda M. S., Berdiev B. K., Bubien J. K., Lucas J. E., Fuller C. M., Benos D. J. Triple-barrel organization of ENaC, a cloned epithelial Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):807–816. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Awayda M. S., Jovov B., Berdiev B. K., Fuller C. M., Dedman J. R., Kaetzel M., Benos D. J. Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):4725–4732. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J. Regulation by Na+ and Ca2+ of renal epithelial Na+ channels reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Sep;106(3):445–466. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Matsuzaki K. A stretch-activated cation channel in the apical membrane of A6 cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1993;43(6):817–832. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.43.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Eaton D. C. Effects of luminal Na+ on single Na+ channels in A6 cells, a regulatory role for protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1094–F1103. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markin V. S., Martinac B. Mechanosensitive ion channels as reporters of bilayer expansion. A theoretical model. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1120–1127. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82147-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Mechanosensitive ion channels of E. coli activated by amphipaths. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):261–263. doi: 10.1038/348261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Tohda H., Hagiwara N., Nakahari T. Antidiuretic hormone-responding nonselective cation channel in distal nephron epithelium (A6). Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):C1513–C1522. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.6.C1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Cruz J. dos S. Voltage-dependent block by internal Ca2+ ions of inwardly rectifying K+ channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:295–311. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H. Open-state substructure of inwardly rectifying potassium channels revealed by magnesium block in guinea-pig heart cells. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:237–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Effects of cell Ca and pH on Na channels from rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F333–F339. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Gating of Na channels in the rat cortical collecting tubule: effects of voltage and membrane stretch. J Gen Physiol. 1996 Jan;107(1):35–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.107.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G. Modulation of apical Na permeability of the toad urinary bladder by intracellular Na, Ca, and H. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):57–69. doi: 10.1007/BF01868738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J. L., Mathias R. T., Cooper K., Baldo G. Divalent cation effects on lens conductance and stretch-activated cation channels. Exp Eye Res. 1992 Jul;55(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90101-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. B., Frindt G., Windhager E. E., Palmer L. G. Feedback regulation of Na channels in rat CCT. I. Effects of inhibition of Na pump. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):F557–F564. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.3.F557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglietti V., Toselli M. A study of stretch-activated channels in the membrane of frog oocytes: interactions with Ca2+ ions. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:311–328. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Windhager E. E. Possible role of cytosolic calcium and Na-Ca exchange in regulation of transepithelial sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):F505–F512. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.6.F505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnheim K. Intrinsic regulation of apical sodium entry in epithelia. Physiol Rev. 1991 Apr;71(2):429–445. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Champigny G., Lazdunski M. Functional degenerin-containing chimeras identify residues essential for amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel function. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):11735–11737. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.11735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. C., Sachs F. Block of stretch-activated ion channels in Xenopus oocytes by gadolinium and calcium ions. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1068–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.2466333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]