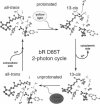
Abstract
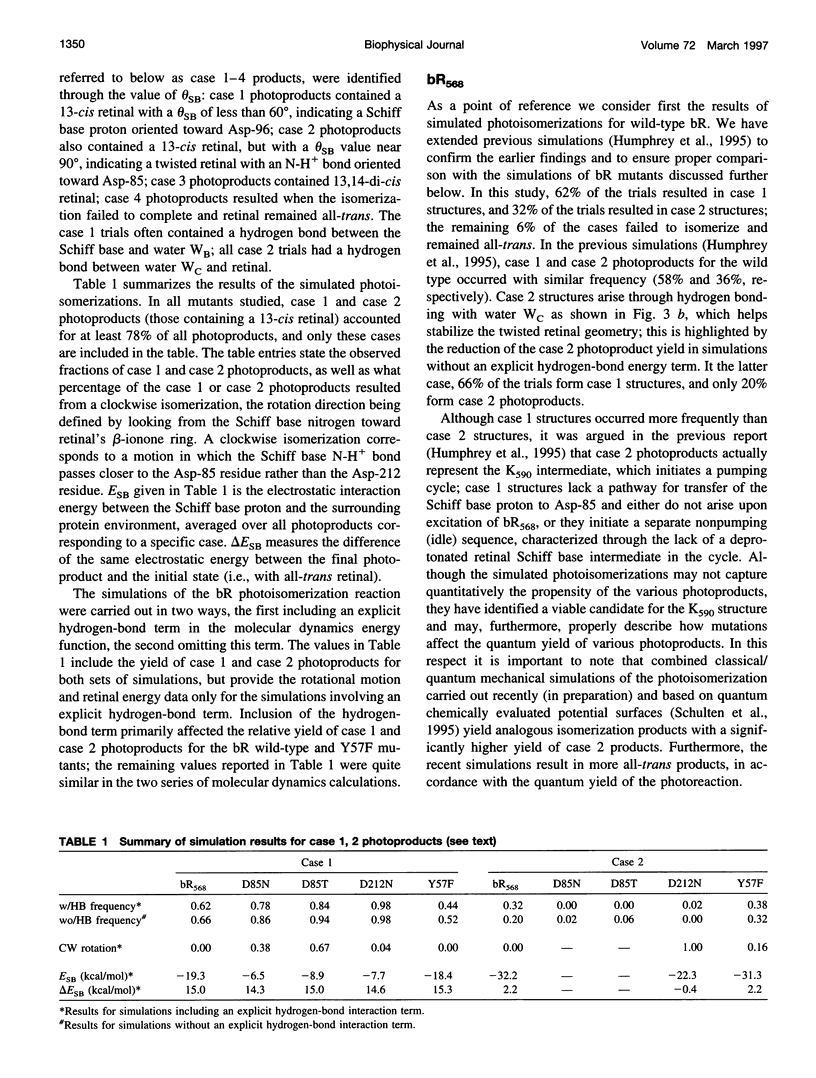
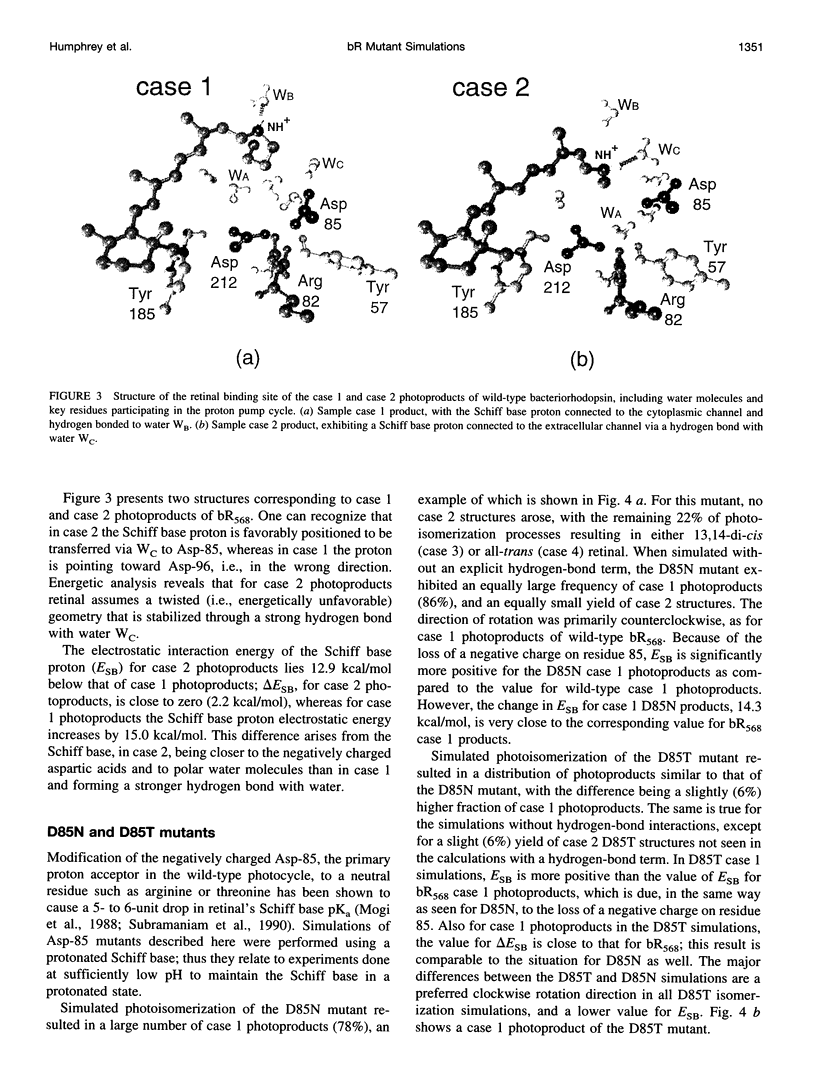
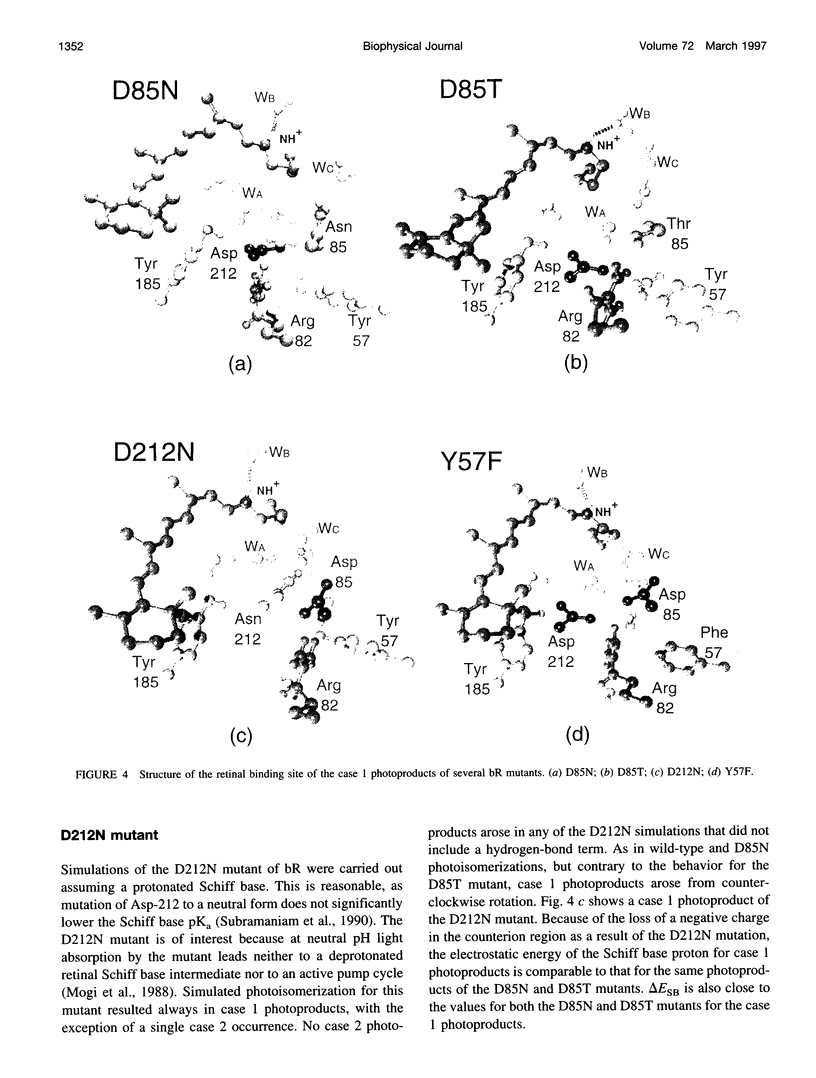
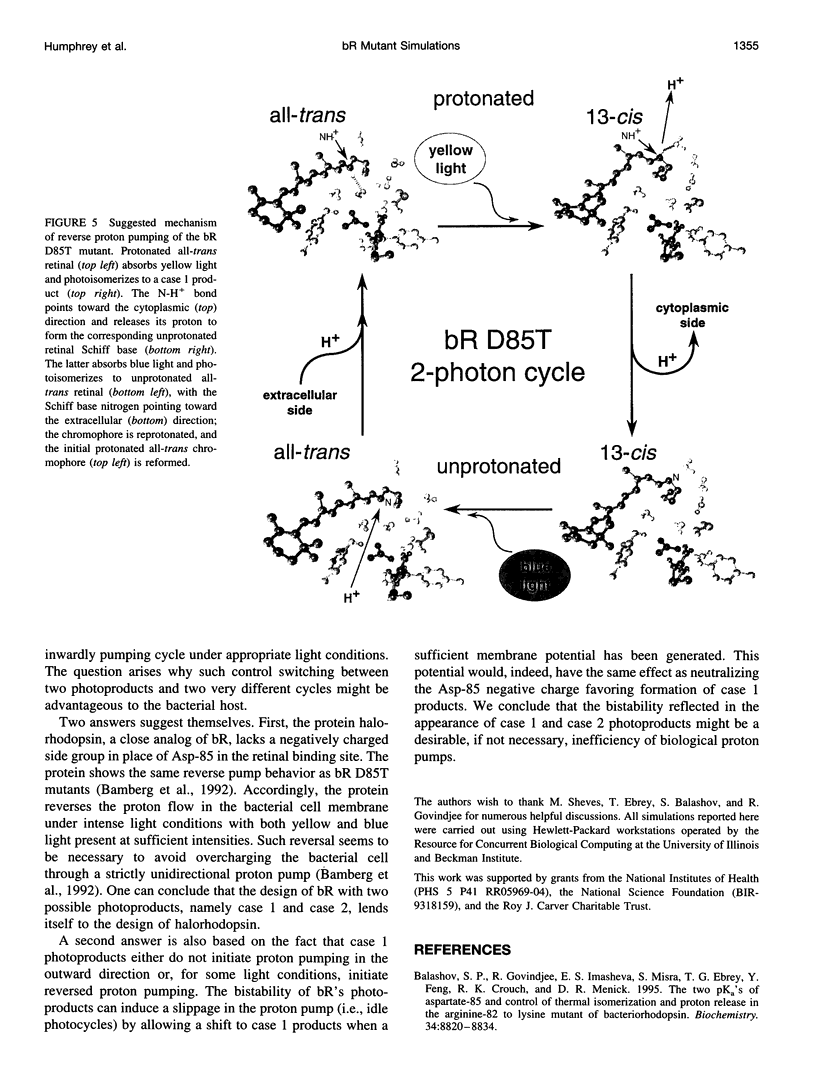
Molecular dynamics simulations of wild-type bacteriorhodopsin (bR) and of its D85N, D85T, D212N, and Y57F mutants have been carried out to investigate possible differences in the photoproducts of these proteins. For each mutant, a series of 50 molecular dynamics simulations of the photoisomerization and subsequent relaxation process were completed. The photoproducts can be classified into four distinct classes: 1) 13-cis retinal, with the retinal N-H+ bond oriented toward Asp-96; 2) 13-cis retinal, with the N-H+ oriented toward Asp-85 and hydrogen-bonded to a water molecule; 3) 13,14-di-cis retinal; 4) all-trans retinal. Simulations of wild-type bR and of its Y57F mutant resulted mainly in class 1 and class 2 products; simulations of D85N, D85T, and D212N mutants resulted almost entirely in class 1 products. The results support the suggestion that only class 2 products initiate a functional pump cycle. The formation of class 1 products for the D85N, D85T, and D212N mutants can explain the reversal of proton pumping under illumination by blue and yellow light.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balashov S. P., Govindjee R., Imasheva E. S., Misra S., Ebrey T. G., Feng Y., Crouch R. K., Menick D. R. The two pKa's of aspartate-85 and control of thermal isomerization and proton release in the arginine-82 to lysine mutant of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 11;34(27):8820–8834. doi: 10.1021/bi00027a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. S., Sasaki J., Kandori H., Maeda A., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. Glutamic acid 204 is the terminal proton release group at the extracellular surface of bacteriorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 10;270(45):27122–27126. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.45.27122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjec R., Kono M., Balashov S. P., Imasheva E., Sheves M., Ebrey T. G. Effects of substitution of tyrosine 57 with asparagine and phenylalanine on the properties of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 11;34(14):4828–4838. doi: 10.1021/bi00014a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Balashov S. P., Ebrey T. G. Quantum efficiency of the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):597–608. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82403-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Drachev L. A., Mogi T., Otto H., Kaulen A. D., Heyn M. P., Skulachev V. P., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic acid-96 by asparagine in bacteriorhodopsin slows both the decay of the M intermediate and the associated proton movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey W., Logunov I., Schulten K., Sheves M. Molecular dynamics study of bacteriorhodopsin and artificial pigments. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 29;33(12):3668–3678. doi: 10.1021/bi00178a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B. Hydration effects on cis--trans isomerization of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80874-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Proton transfer and energy coupling in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):169–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00762675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Sasaki J., Yamazaki Y., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. Interaction of aspartate-85 with a water molecule and the protonated Schiff base in the L intermediate of bacteriorhodopsin: a Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopic study. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 22;33(7):1713–1717. doi: 10.1021/bi00173a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Marti T., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G. Aspartic acid substitutions affect proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman R., Chang M., Ni B., Váró G., Fornés J., White S. H., Lanyi J. K. Properties of Asp212----Asn bacteriorhodopsin suggest that Asp212 and Asp85 both participate in a counterion and proton acceptor complex near the Schiff base. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11478–11484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J., Bamberg E. A unifying concept for ion translocation by retinal proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00762676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Engel F., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Substitution of amino acids Asp-85, Asp-212, and Arg-82 in bacteriorhodopsin affects the proton release phase of the pump and the pK of the Schiff base. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos G., Dencher N. A., Zaccai G., Büldt G. Water molecules and exchangeable hydrogen ions at the active centre of bacteriorhodopsin localized by neutron diffraction. Elements of the proton pathway? J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90140-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter H. T., Brown L. S., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. A linkage of the pKa's of asp-85 and glu-204 forms part of the reprotonation switch of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1996 Apr 2;35(13):4054–4062. doi: 10.1021/bi952883q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Protonation state of Asp (Glu)-85 regulates the purple-to-blue transition in bacteriorhodopsin mutants Arg-82----Ala and Asp-85----Glu: the blue form is inactive in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1013–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittor J., Oesterhelt D., Bamberg E. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants D85N, D85T and D85,96N as proton pumps. Biophys Chem. 1995 Sep-Oct;56(1-2):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(95)00027-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittor J., Schweiger U., Oesterhelt D., Bamberg E. Inversion of proton translocation in bacteriorhodopsin mutants D85N, D85T, and D85,96N. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1682–1690. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80642-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu D., Martin C., Schulten K. Molecular dynamics study of early picosecond events in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: dielectric response, vibrational cooling and the J, K intermediates. Biophys J. 1996 Jan;70(1):453–460. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79588-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu D., Sheves M., Schulten K. Molecular dynamics study of the M412 intermediate of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1995 Dec;69(6):2745–2760. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80146-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou F., Windemuth A., Schulten K. Molecular dynamics study of the proton pump cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2291–2306. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]