Abstract
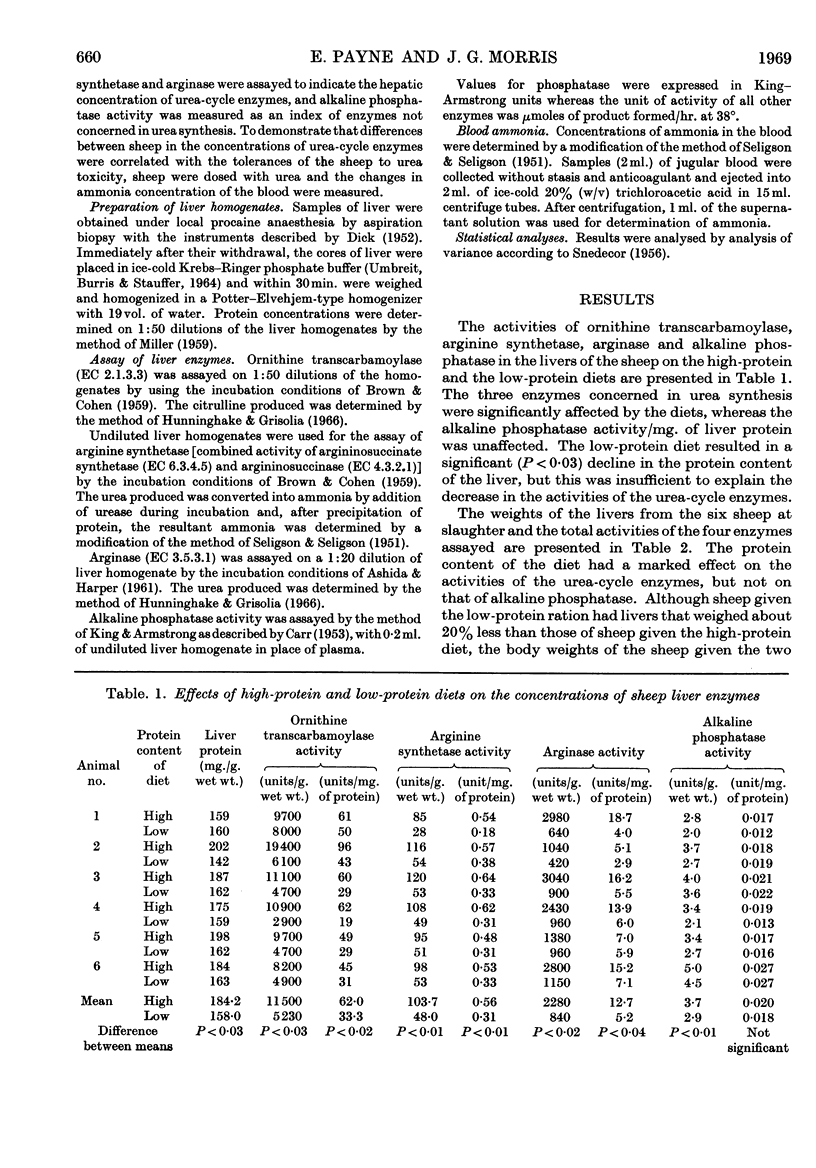
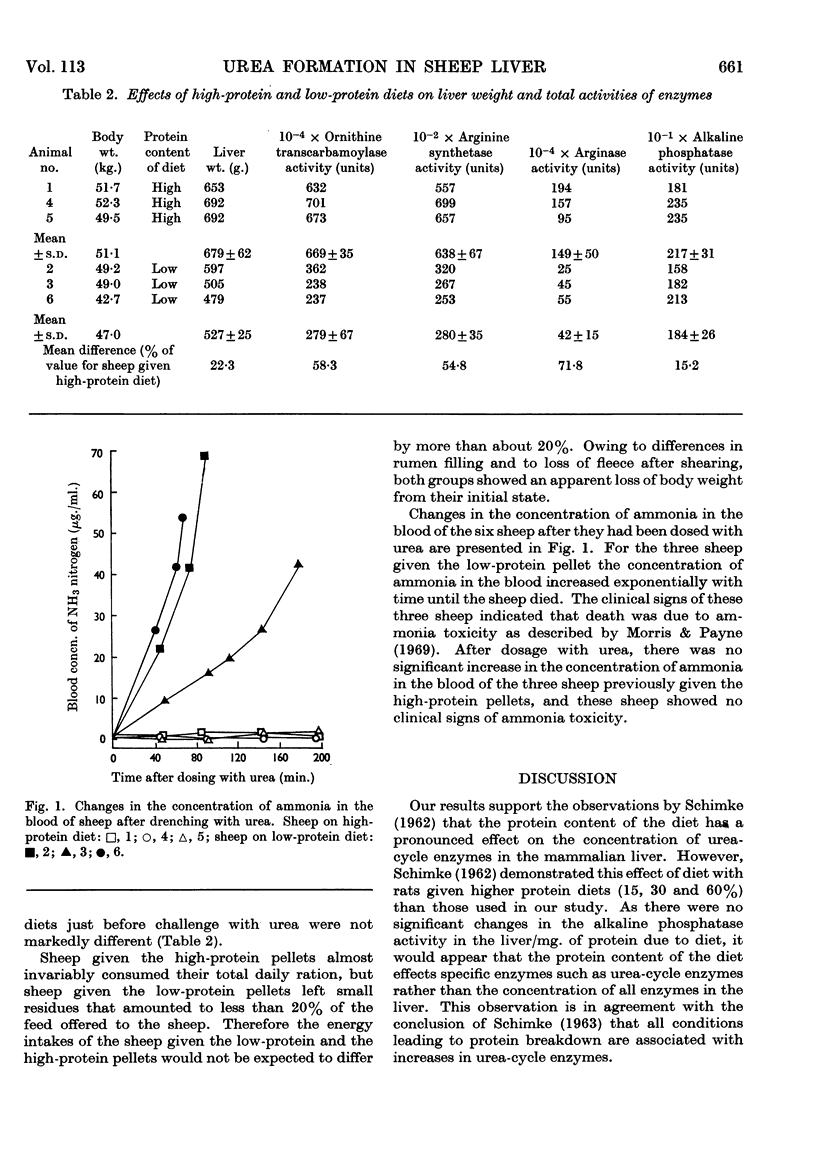
1. In the livers of six sheep given a high-protein diet, the concentrations of certain urea-cycle enzymes [ornithine transcarbamoylase, arginine synthetase (combined activity of argininosuccinate synthetase and argininosuccinase) and arginase] were significantly greater than when the sheep were given a low-protein diet. Alkaline phosphatase activity/mg. of liver protein was not significantly affected by diet. 2. Three sheep previously given the high-protein diet showed no significant rise in the concentration of ammonia in the blood after the administration of urea (0·5g./kg. body wt.). The concentration of ammonia in the blood of the three sheep given the low-protein diet rose exponentially with time after dosing with urea and all sheep died. 3. It is suggested that tolerance to ammonia toxicity in the sheep is at least partly a function of the activity of the urea-cycle enzymes in the liver.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHIDA K., HARPER A. E. Metabolic adaptations in higher animals. IV. Liver arginase activity during adaptation to high protein diet. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 May;107:151–156. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. W., Jr, COHEN P. P. Comparative biochemistry of urea synthesis. I. Methods for the quantitative assay of urea cycle enzymes in liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jul;234(7):1769–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake D., Grisolia S. A sensitive and convenient micromethod for estimation of urea, citrulline, and carbamyl derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1966 Aug;16(2):200–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNAN A. L., COHEN P. P. Ammonia detoxication in liver from humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jan;106:170–173. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald I. W. The absorption of ammonia from the rumen of the sheep. Biochem J. 1948;42(4):584–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. Adaptive characteristics of urea cycle enzymes in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. Studies on factors affecting the levels of urea cycle enzymes in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:1012–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGSON D., SELIGSON H. A microdiffusion method for the determination of nitrogen liberated as ammonia. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Aug;38(2):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


