Abstract
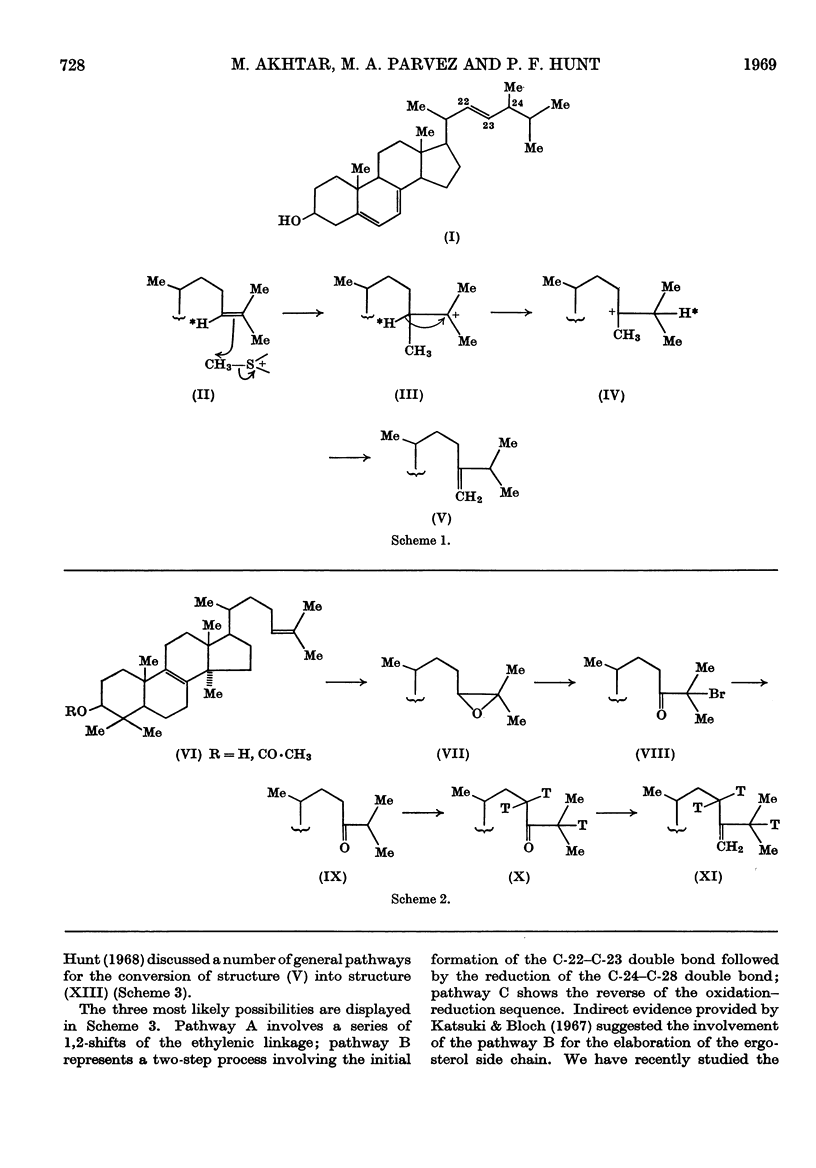
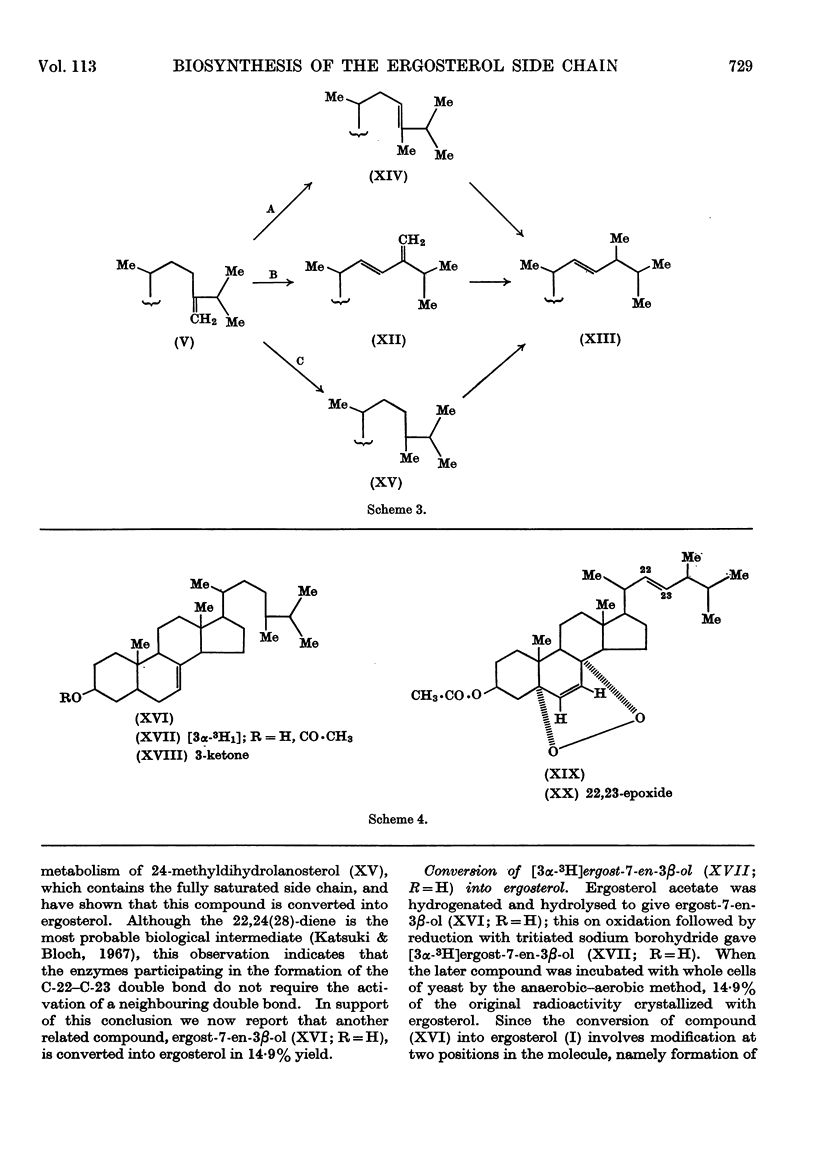
1. A convenient synthesis of 24-methylene[23,25-3H3]dihydrolanosterol is described. 2. A general anaerobic–aerobic method for the incorporation of sterols into whole yeast cells is also described and illustrated by experiments with 3H-labelled lanosterol. 3. The method was used to convert labelled 24-methylene-dihydrolanosterol into ergosterol, in good yield, by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 4. Degradation of the biosynthetic ergosterol provided confirmation of the conversion, which supports the proposed mechanism for the biosynthesis of the ergosterol side chain. 5. Mechanisms for the further conversion of the 24-methylene side chain into the ergosterol side chain are discussed and it was shown that a compound, [3α-3H1]-ergost-7-en-3β-ol, with a fully saturated side chain, can also be efficiently incorporated into ergosterol. 6. This result was confirmed by a procedure involving formation of the 5,8-epidioxide and subsequently the 5,8-epidioxy-22,23-epoxide of the biosynthetic ergosterol.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M., Hunt P. F., Parvez M. A. The transfer of hydrogen from C-24 to C-25 in ergosterol biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):616–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1030616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar M., Parvez M. A., Hunt P. F. The introduction of the C-22-C-23 ethylenic linkage in ergosterol biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):623–626. doi: 10.1042/bj1060623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle M., Blondin G. A., Nes W. R. The mechanism of introduction of alkyl groups at C-24 of sterols. I. The precursor of the C2 group. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 25;242(23):5796–5801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S. M., Akhtar M. The conversion of cholest-7-en-3beta-ol into cholesterol. General comments on the mechanism of the introduction of double bonds in enzymic reactions. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1187–1194. doi: 10.1042/bj1051187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad L. J., Hammam A. S., Dennis A., Goodwin T. W. Biosynthesis of the phytosterol side chain. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1322–1324. doi: 10.1038/2101322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN H. P., EATON N. R., MURPHY J. C. Net synthesis of sterols in resting cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Apr;13(4):591–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki H., Bloch K. Studies on the biosynthesis of ergosterol in yeast. Formation of methylated intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer E. The origin and function of some methyl groups in branched-chain fatty acids, plant sterols and quinones. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):449–468. doi: 10.1042/bj0930449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris L. J., Harris R. V., Kelly W., James A. T. The stereochemistry of desaturations of long-chain fatty acids in Chlorella vulgaris. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj1090673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab K. H., De Souza N. J., Nes W. R. The H-migration in the alkylation of sterols at C-24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 1;152(4):742–748. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. T., Van Aller R. T., Nes W. R. The mechanism of introduction of alkyl groups at C-24 of sterols. II. The necessity of the delta-24 bond. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 25;242(23):5802–5806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROEPFER G. J., Jr, BLOCH K. THE STEREOSPECIFIC CONVERSION OF STEARIC ACID TO OLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


