Abstract
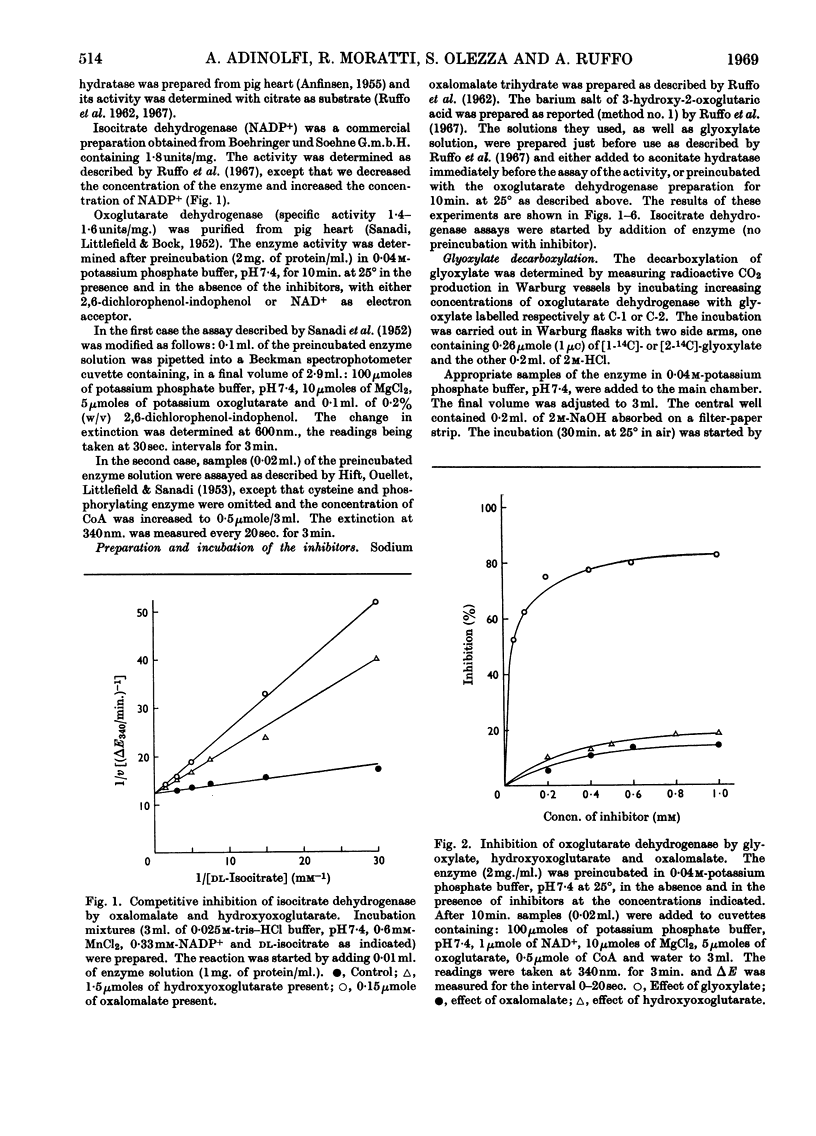
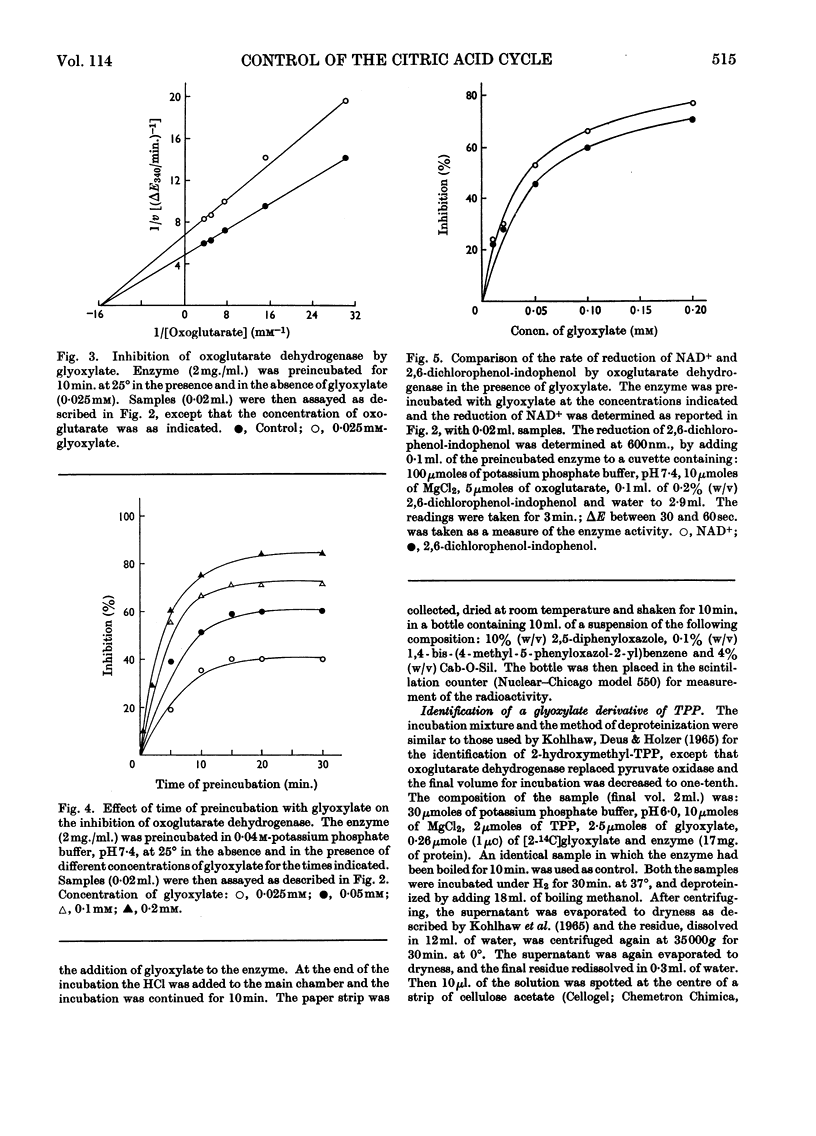
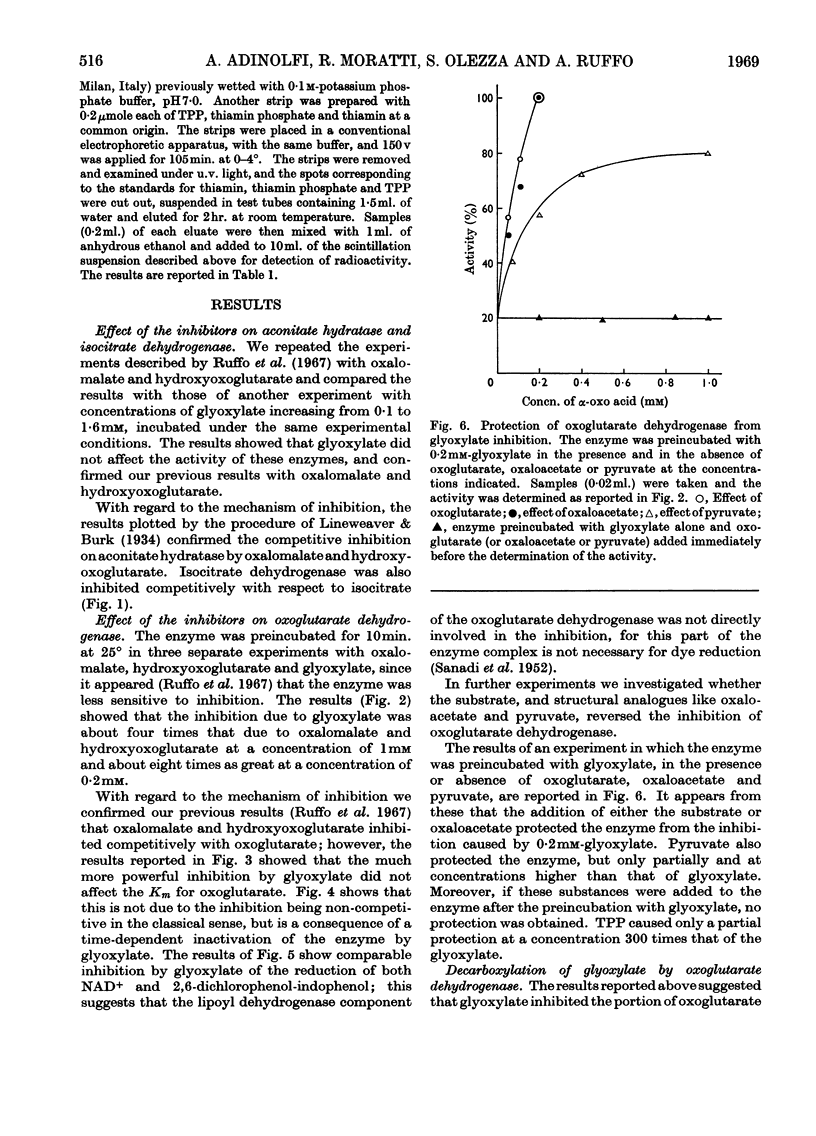
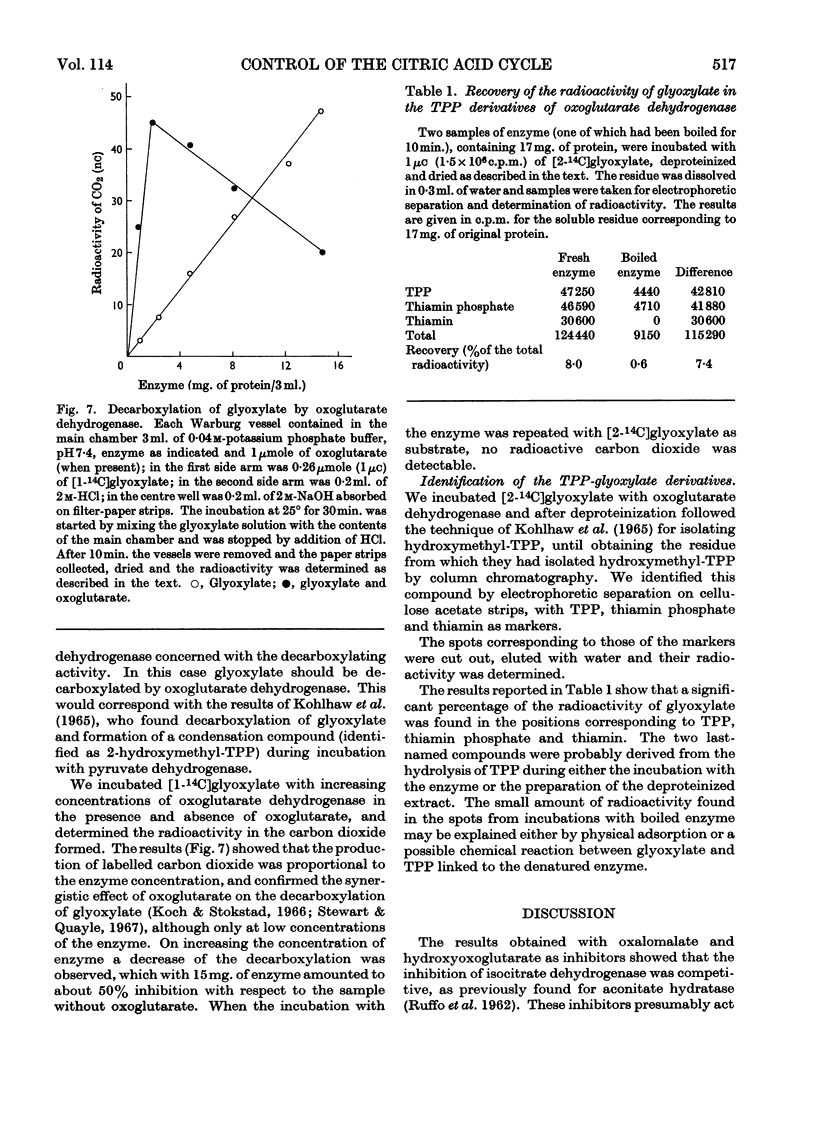
1. The effects of glyoxylate on partially purified preparations of aconitate hydratase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and oxoglutarate dehydrogenase were compared with those of oxalomalate and hydroxyoxoglutarate (obtained by condensation of glyoxylate with oxaloacetate and pyruvate respectively). 2. Glyoxylate (1mm) did not affect aconitate hydratase and isocitrate dehydrogenase, whereas oxalomalate (1mm) inhibited the enzyme activities completely. 3. Glyoxylate (0·025mm) inhibited oxoglutarate dehydrogenase irreversibly, whereas the same concentrations of oxalomalate and hydroxyoxoglutarate were ineffective. This inhibitory effect was prevented if oxoglutarate, pyruvate or oxaloacetate was mixed with the enzyme before the glyoxylate. 4. Incubation of oxoglutarate dehydrogenase with radioactive glyoxylate produced radioactive carbon dioxide; radioactivity was also recovered in the portion of the enzyme identified with thiamin pyrophosphate. 5. The behaviour of glyoxylate in producing multiple inhibitions of the citric acid cycle, either by direct interaction with oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, or by means of its condensation compounds which inhibit aconitate hydratase and isocitrate dehydrogenase, is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi A., Olezza S., Ruffo A. Inhibition of oxoglutarate dehydrogenase by glyoxylate and its condensation compounds. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):50P–51P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIFT H., OUELLET L., LITTLEFIELD J. W., SANADI D. R. Alpha-Ketoglutaric dehydrogenase. IV. Coupled phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):565–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHLHAW G., DEUS B., HOLZER H. ENZYMATIC PREPARATION, STRUCTURE, AND PROPERTIES OF THIAMINE PYROPHOSPHATE-ACTIVATED FORMALDEHYDE. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2135–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J., Stokstad E. L. Partial purification of a 2-oxo-glutarate:glyoxylate carboligase from rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUFFO A., TESTA E., ADINOLFIA, PELIZZA G. Control of the etric acid cycle by glyoxylate. I. A new inhibitor of aconitase formed by the condensation of glyoxylate with oxaloacetate. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:588–593. doi: 10.1042/bj0850588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffo A., Testa E., Adinolfi A., Pelizza G., Moratti R. Control of the citric acid cycle by glyoxylate. Mechanism of the inhibition by oxalomalate and gamma-hydroxy-alpha-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):19–23. doi: 10.1042/bj1030019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANADI D. R., LITTLEFIELD J. W., BOCK R. M. Studies on alpha-ketoglutaric oxidase. II. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(2):851–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. R., Quayle J. R. The synergistic decarboxylation of glyoxylate and 2-oxoglutarate by an enzyme system from pig-liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):885–897. doi: 10.1042/bj1020885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


