Abstract
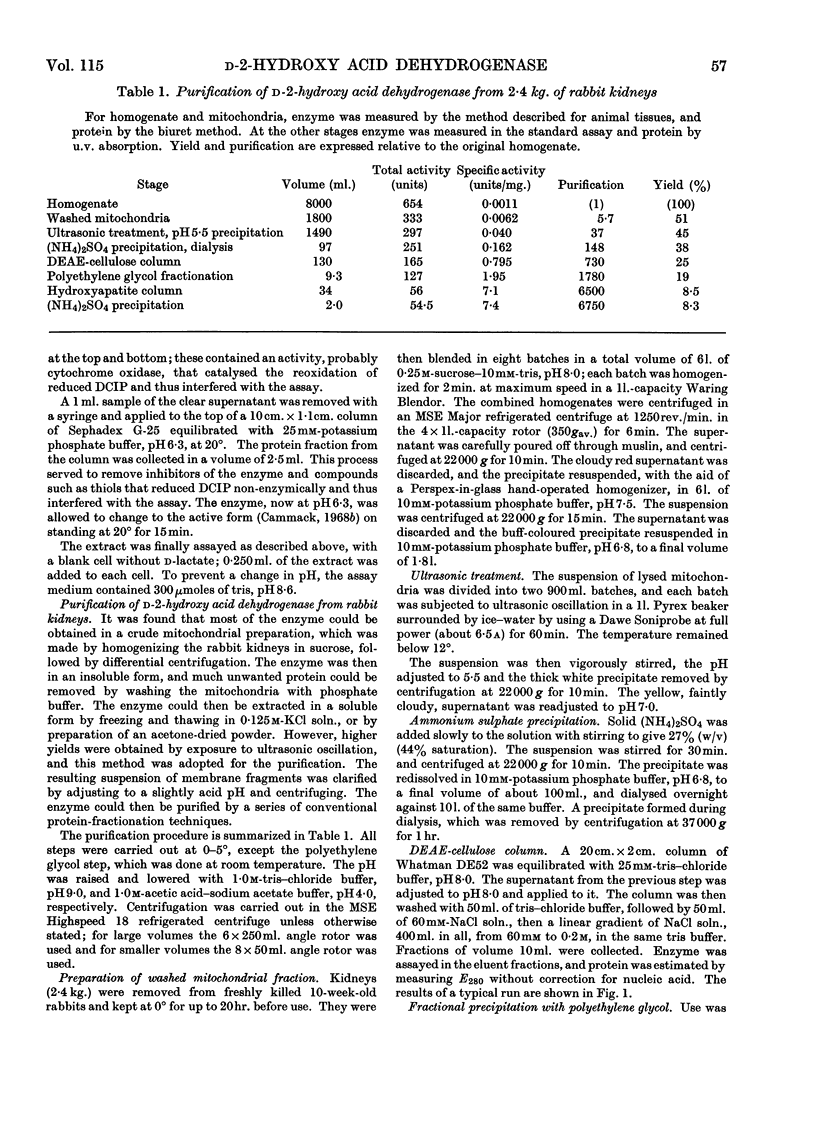
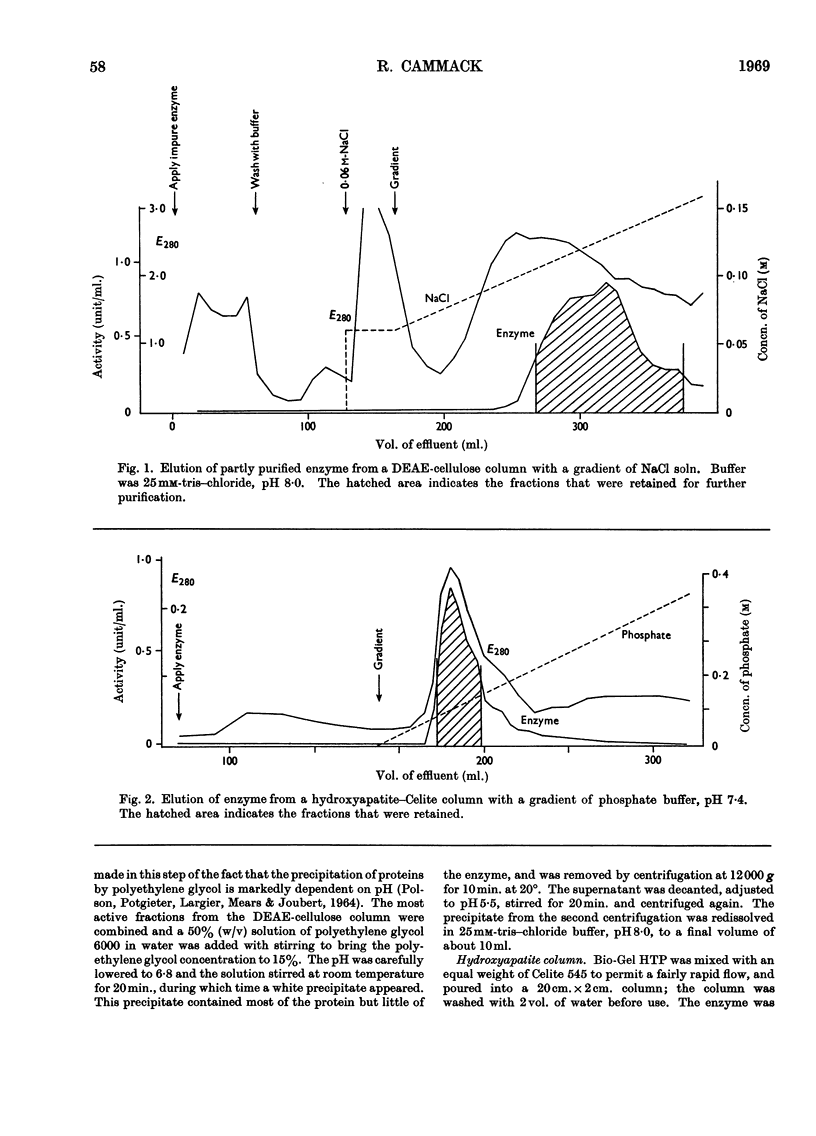
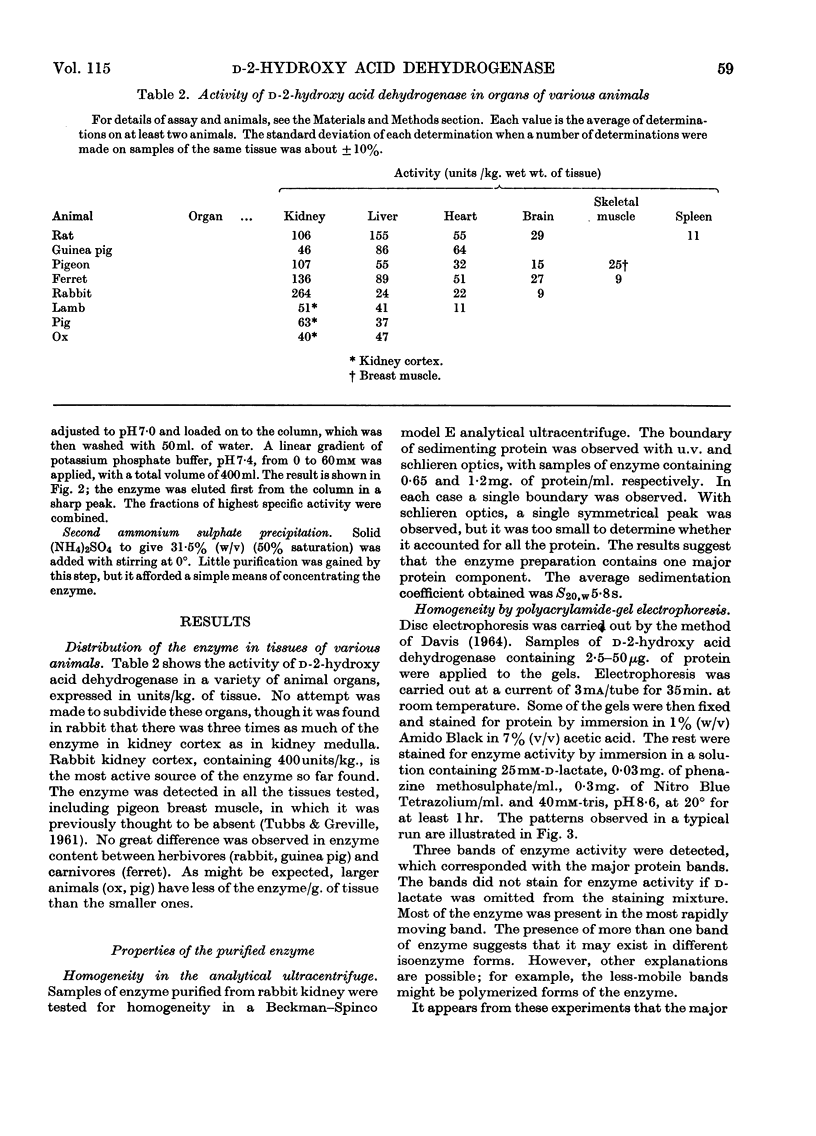
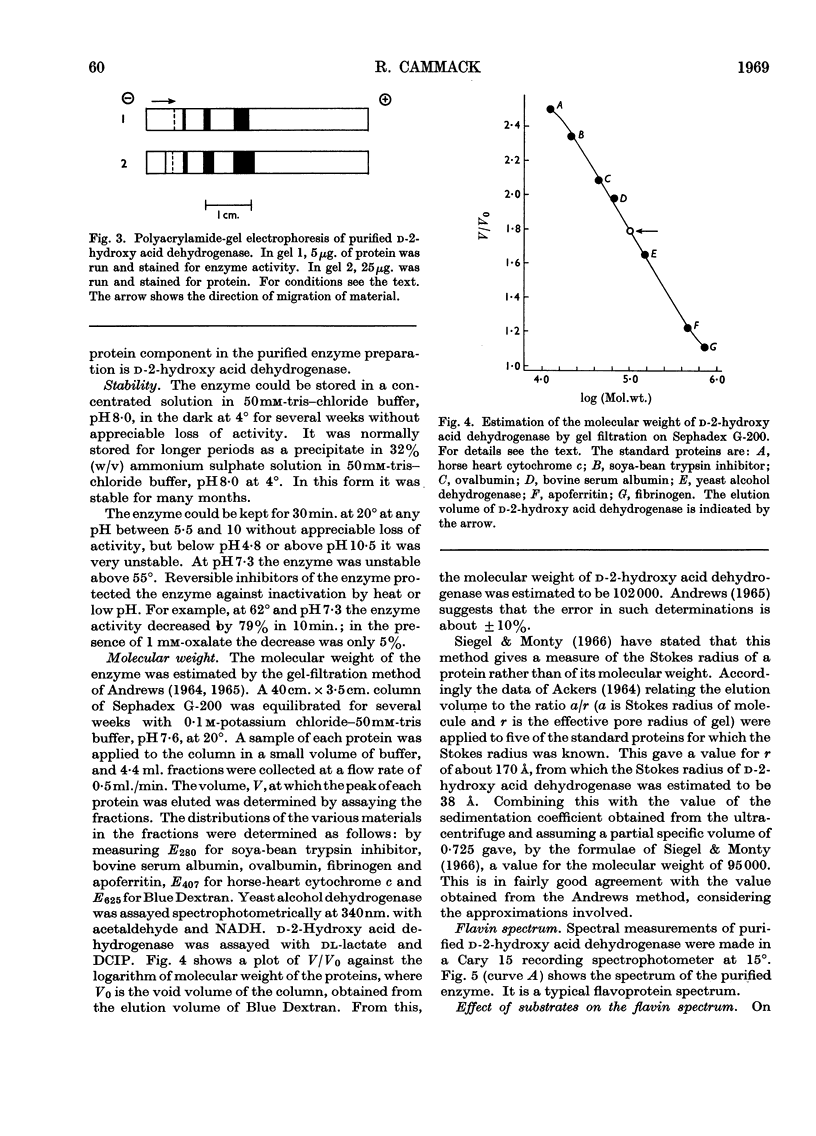
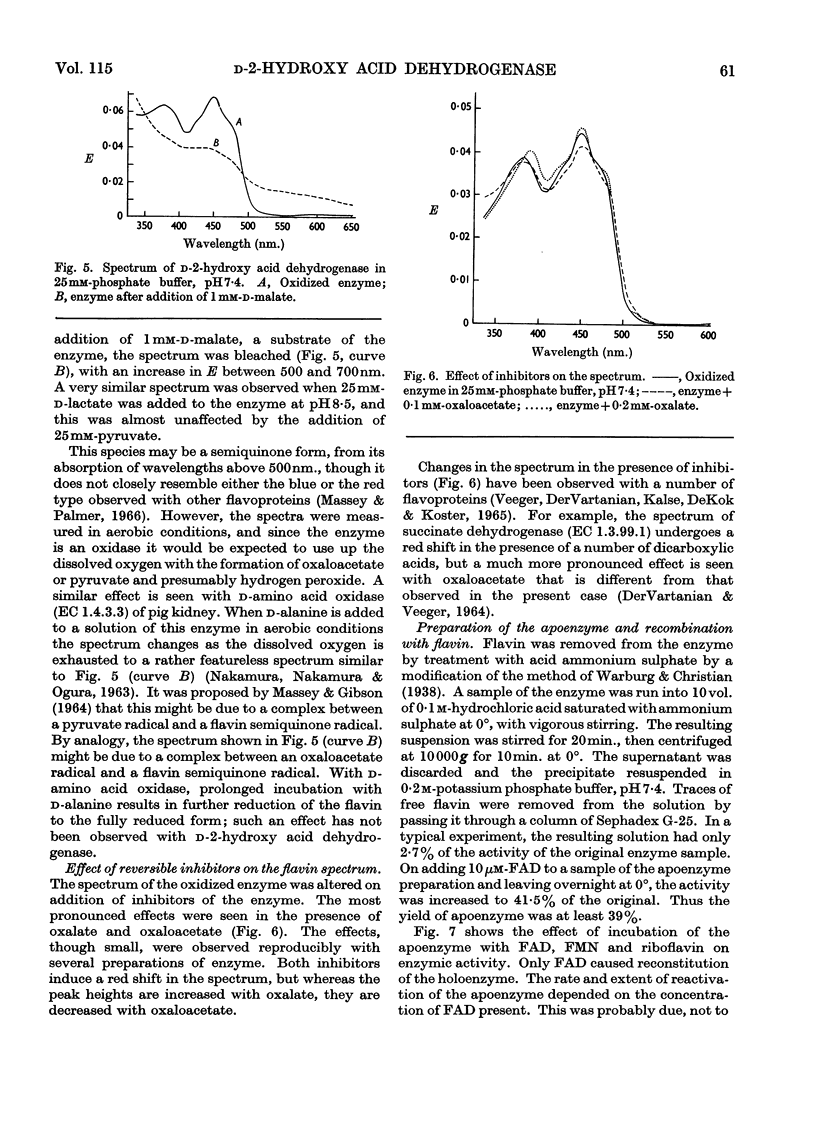
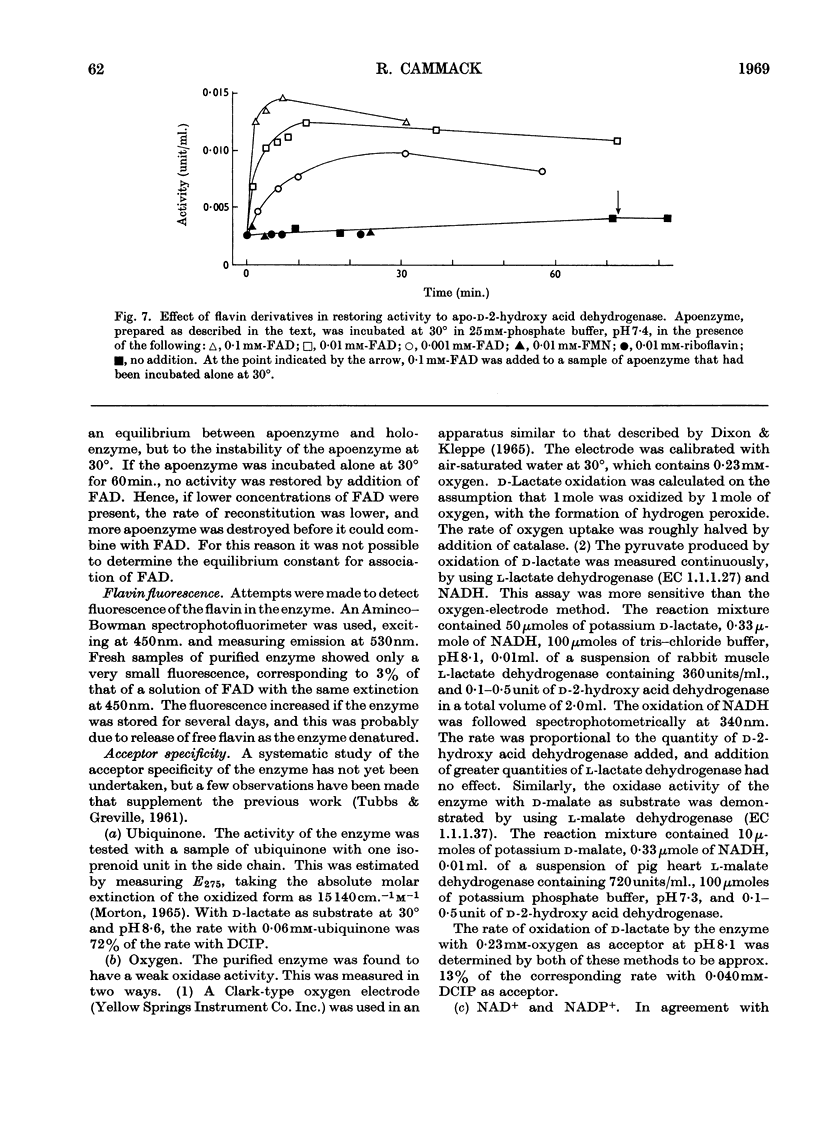
1. A new method is described for the measurement of d-2-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase in samples of animal tissues. 2. The distribution of the enzyme in a number of animals was determined. Of the animal tissues tested, the most active source of the enzyme was found to be rabbit kidney cortex. 3. The enzyme was purified from rabbit kidney to a stage at which it appears to be homogeneous in the analytical ultracentrifuge and on polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. 4. The molecular weight was estimated by gel filtration to be approx. 102000; combination of gelfiltration data and the sedimentation coefficient gave a value of 95000. 5. The purified enzyme has a spectrum typical of a flavoprotein. The change induced in the spectrum on addition of d-malate or d-lactate suggests the formation of a flavin semiquinone. 6. Flavin can be removed by treatment with acid ammonium sulphate, and activity can be restored to the inactive apoenzyme by addition of FAD, but not of FMN or riboflavin. 7. Studies of acceptor specificity showed that the enzyme has a relatively weak d-2-hydroxy acid oxidase activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten J. S. Enzymic estimation of D-malate and other D-2-hydroxy acids. Anal Biochem. 1968 Aug;24(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMONA T. THE LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES OF YEAST. IV. D-ALPHA-HYDROXY ACID DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1457–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R. Flavoprotein properties of D-2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase purified from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):45P–46P. doi: 10.1042/bj1090045pb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWKINS P. D., DICKENS F. THE OXIDATION OF D- AND L-GLYCERATE BY RAT LIVER. Biochem J. 1965 Feb;94:353–367. doi: 10.1042/bj0940353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERVARTANIAN D. V., VEEGER C. STUDIES ON SUCCINATE DEHYDROGENASE. I. SPECTRAL PROPERTIES OF THE PURIFIED ENZYME AND FORMATION OF ENZYME-COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR COMPLEXES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 22;92:233–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop R. H., Hammond P. B. D-lactic acidosis of ruminants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 31;119(3):1109–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb47466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT W. H. Amino-acetone; its isolation and role in metabolism. Nature. 1959 Apr 11;183(4667):1051–1052. doi: 10.1038/1831051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englard S., Britten J. S., Listowsky I. Stereochemical course of the maleate hydratase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2255–2259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATSUBO M., CURDEL A. [Relative determination of the molecular weight of unurified enzymes by the molecular sieve method]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 10;256:5224–5227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUN E., DECHARY J. M., PITOT H. C. The oxidation of glycolic acid by a liver enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1954 Sep;210(1):269–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline E. S., Mahler H. R. The lactic dehydrogenases of E. coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 31;119(3):905–919. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb47451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Lindstedt G., Lindstedt S. Metabolism of 2-amino-5-hydroxyadipic acid in the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90463-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSEY V., GIBSON Q. H. ROLE OF SEMIQUINONES IN FLAVOPROTEIN CATALYSIS. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:18–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Palmer G. On the existence of spectrally distinct classes of flavoprotein semiquinones. A new method for the quantitative production of flavoprotein semiquinones. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3181–3189. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monder C. Alpha-keto aldehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme that catalyzes the enzymic oxidation of methylglyoxal to pyruvate. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4603–4609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA T., NAKAMURA S., OGURA Y. SEMIQUINONE AND ENZYME KINETICS OF D-AMINO ACID OXIDASE. J Biochem. 1963 Dec;54:512–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLSON A., POTGIETER G. M., LARGIER J. F., MEARS G. E., JOUBERT F. J. THE FRACTIONATION OF PROTEIN MIXTURES BY LINEAR POLYMERS OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 16;82:463–475. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAVAGE N. Preparation and properties of highly purified diaphorase. Biochem J. 1957 Sep;67(1):146–155. doi: 10.1042/bj0670146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUBBS P. K., GREVILLE G. D. Dehydrogenation of D-lactate by a soluble enzyme from kidney mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:290–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUBBS P. K., GREVILLE G. D. The oxidation of D-alpha-hydroxy acids in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:104–114. doi: 10.1042/bj0810104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs P. K. The metabolism of D-alpha-hydroxy acids in animal tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 31;119(3):920–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb47452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN EYS J., JUDGE M. A., JUDD J., HILL W., BOZIAN R. C., ABRAHAMS S. A reinvestigation of methylglyoxal accumulation in thiamine deficiency. J Nutr. 1962 Apr;76:375–384. doi: 10.1093/jn/76.4.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


