Abstract
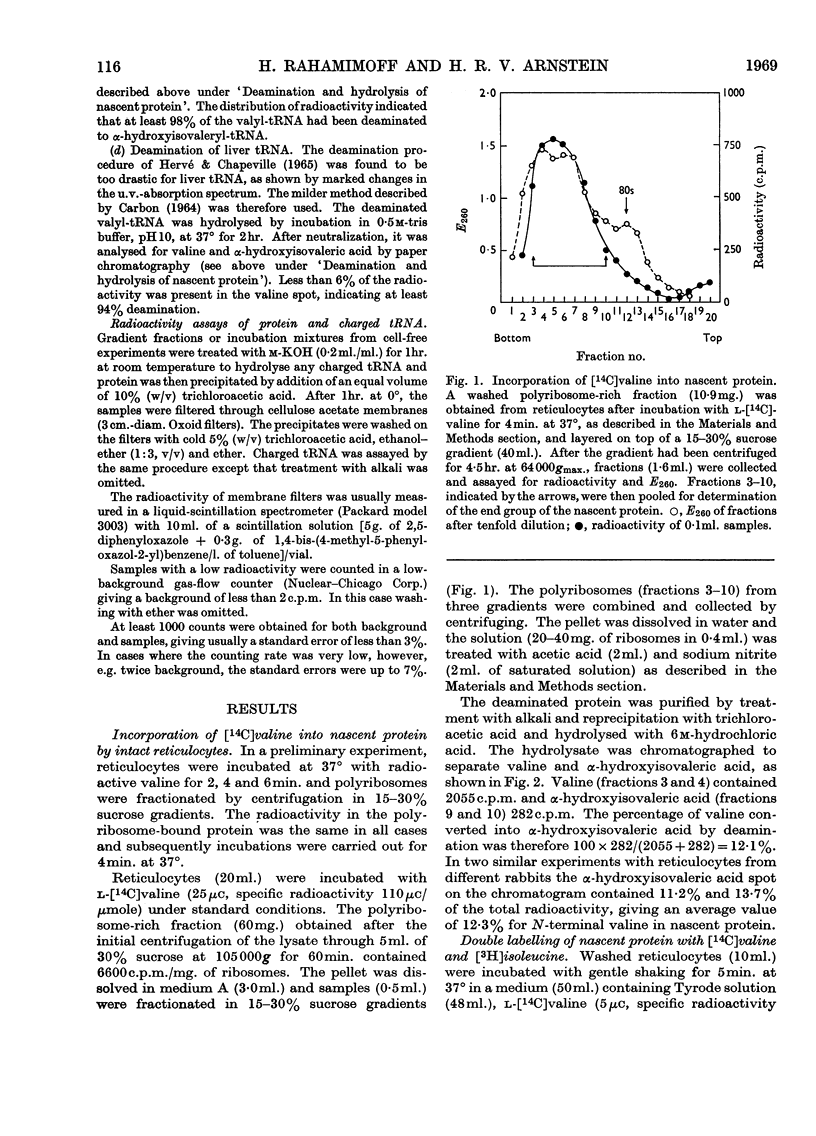
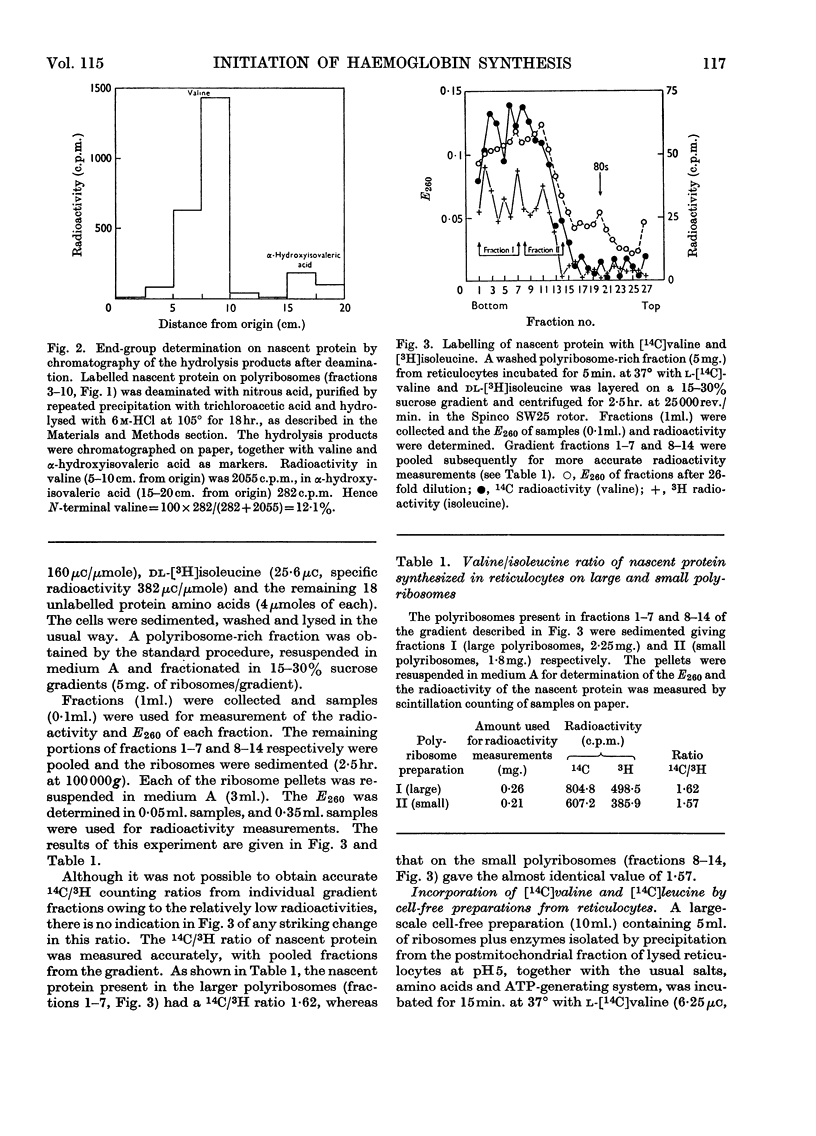
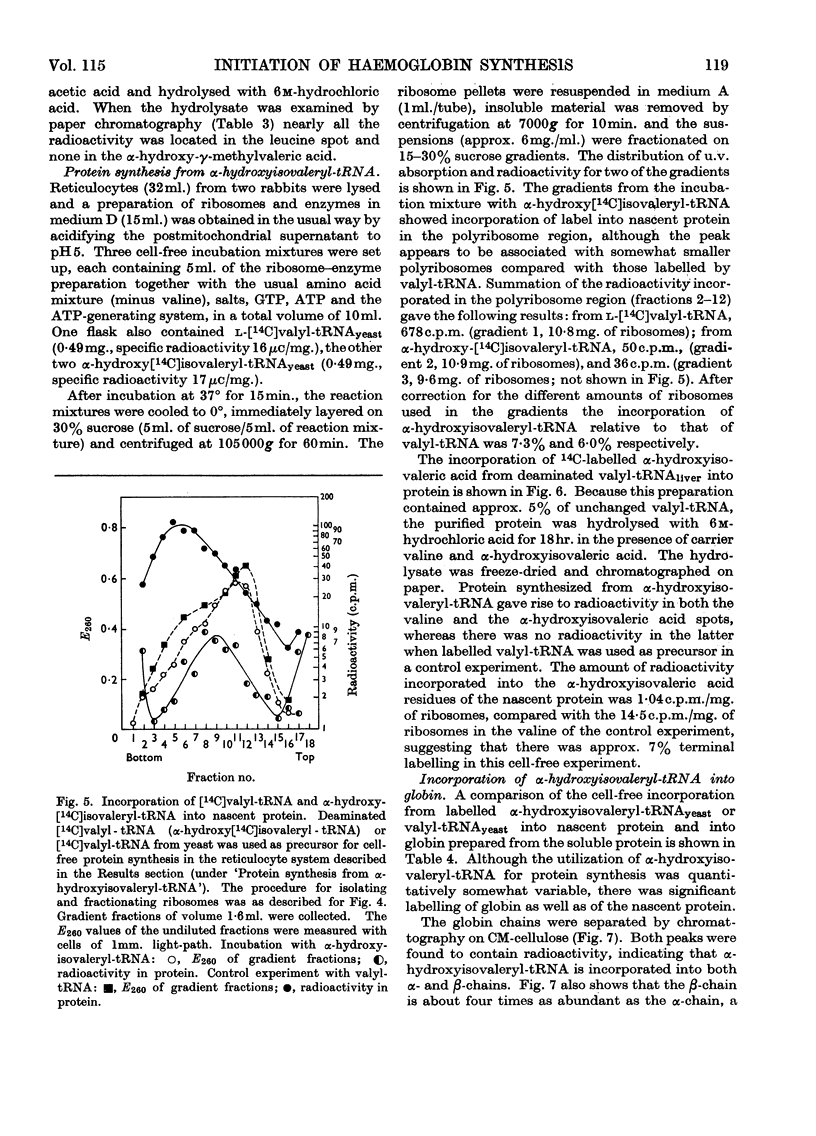
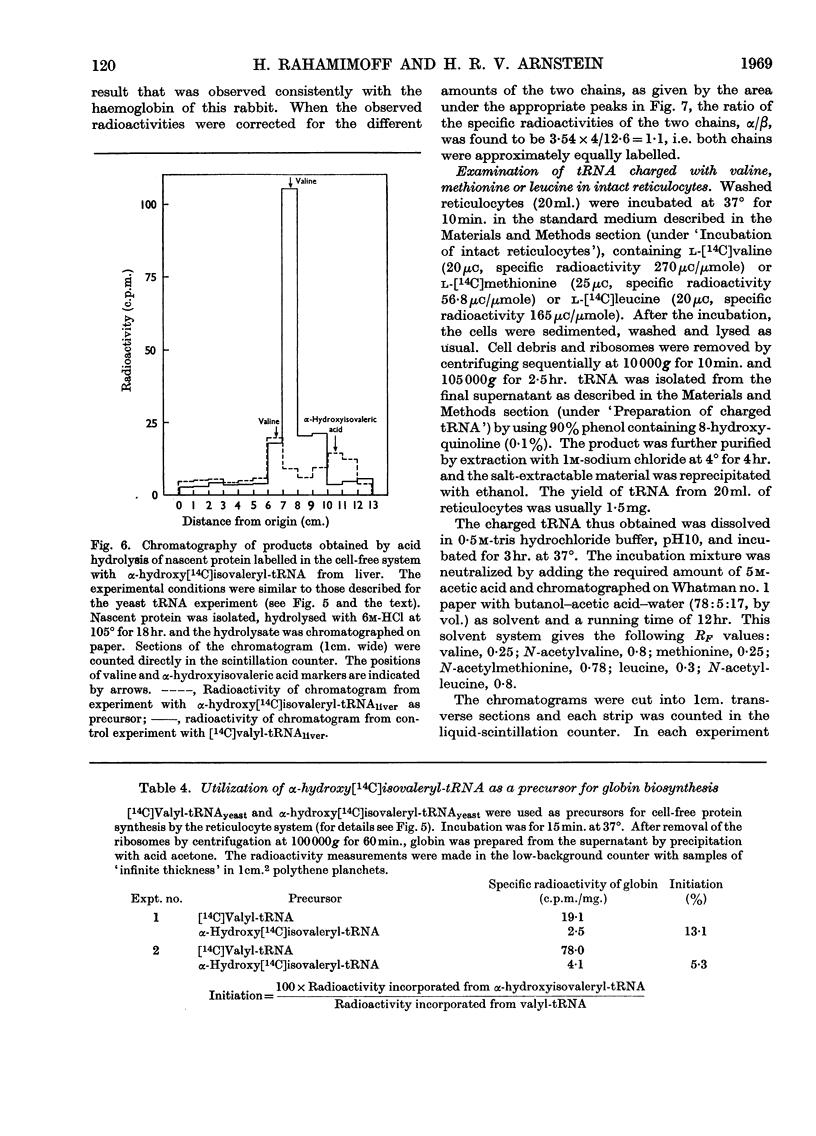
1. The incorporation of labelled valine by rabbit reticulocytes into the N-terminal position of nascent haemoglobin was investigated by deaminating the nascent peptides with nitrous acid and isolating labelled α-hydroxyisovaleric acid and valine after acid hydrolysis. 2. The amount of radioactivity in α-hydroxyisovaleric acid relative to that in valine indicated the presence of 12·3% N-terminal valine having a free amino group. This high value suggests that most if not all nascent peptides contain valine in the N-terminal position. 3. Cell-free preparations containing reticulocyte ribosomes and pH5 enzymes incorporated α-hydroxy-[14C]isovaleryl-tRNA (where tRNA refers to transfer RNA), which was obtained by deamination of [14C]valyl-tRNA from yeast or liver with nitrous acid, into both soluble and nascent protein. 4. When the soluble protein was chromatographed on CM-cellulose, radioactivity was found to be associated with both the α-and β-globin chains. 5. The kinetics of hydrolysis of [14C]valine, was also investigated. Most of the material was hydrolysed rapidly at pH10, but a minor component that was relatively stable appeared to be present to the extent of about 10% of the total valyl-tRNA. Valine was, however, the only hydrolysis product detected by paper chromatography. 6. It is concluded that chain initiation in haemoglobin synthesis involves valine as the N-terminal amino acid and that the amino group of nascent protein is probably not substituted.
Full text
PDF



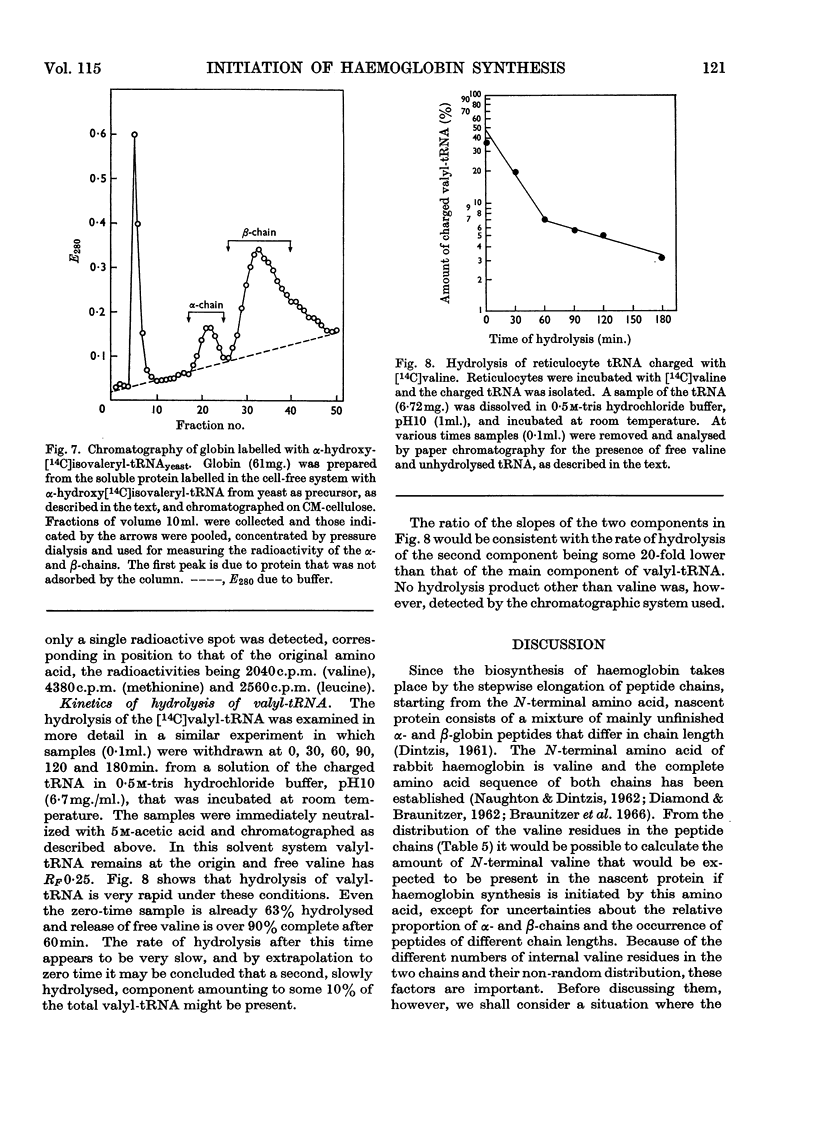
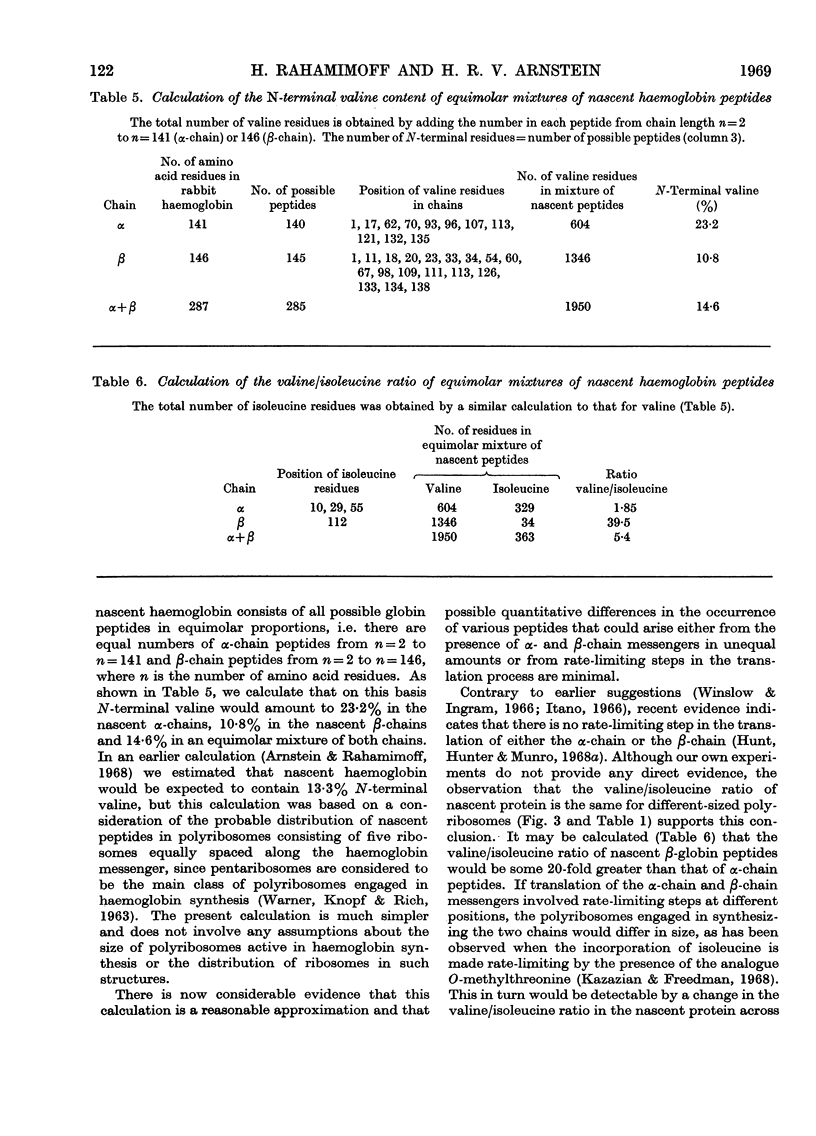


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Gould H., Potter H. A comparison of methods for the isolation and fractionation of reticulocyte ribosomes. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):500–506. doi: 10.1042/bj0960500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Hunt J. A. The function of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid from rabbit reticulocytes in haemoglobin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):648–661. doi: 10.1042/bj0920648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnstein H. R., Rahamimoff H. Haemoglobin initiation in protein synthesis by animal cells and the universality of the genetic code. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):942–944. doi: 10.1038/219942a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunitzer G., Best J. S., Flamm U., Schrank B. Zur Phylogenie des Hämoglobins: Untersuchungen am Hämoglobin des Kaninchens (Caniculus) Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1966;347(4):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. F., Marcker K. A. N-formyl-methionyl-sigma-ribonucleic acid and chain initiation in protein biosynthesis. Polypeptide synthesis directed by a bacteriophage ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system. Nature. 1966 Jul 23;211(5047):378–380. doi: 10.1038/211378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Staehelin M. The preparation of rat-liver soluble ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 19;119(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Chapeville F. The behaviour of acetylphenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid in polyphenylalanine synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt R. T., Hunter A. R., Munro A. J. Control of haemoglobin synthesis: a difference in the size of the polysomes making alpha and beta chains. Nature. 1968 Nov 2;220(5166):481–483. doi: 10.1038/220481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Freedman M. L. The characterization of separated alpha and beta-chain polyribosomes in rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6446–6450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMFROM H. Factors determining the specificity of hemoglobin synthesized in a cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:241–252. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laycock D. G., Hunt J. A. Synthesis of rabbit globin by a bacterial cell free system. Nature. 1969 Mar 22;221(5186):1118–1122. doi: 10.1038/2211118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Caskey C. T., Nirenberg M. Fine structure of RNA codewords recognized by bacterial, amphibian, and mammalian transfer RNA. Science. 1967 Feb 17;155(3764):820–826. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3764.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAUGHTON M. A., DINTZIS H. M. Sequential biosynthesis of the peptide chains of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Oct 15;48:1822–1830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.10.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Eikenberry E. F., Malkin L. I. Experiments on hemoglobin polypeptide chain initiation and on the shielding actionof the ribosome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:303–310. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Ingram V. M. Peptide chain synthesis of human hemoglobins A and A2. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1144–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


