Abstract
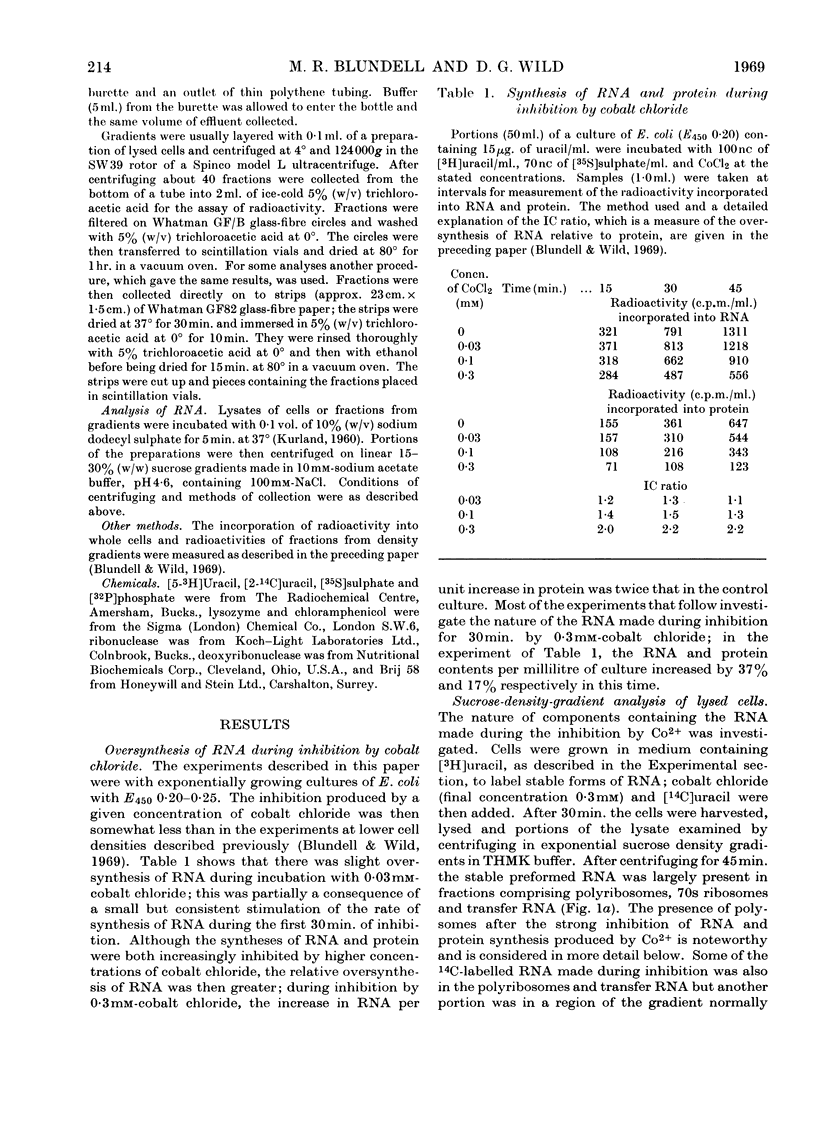
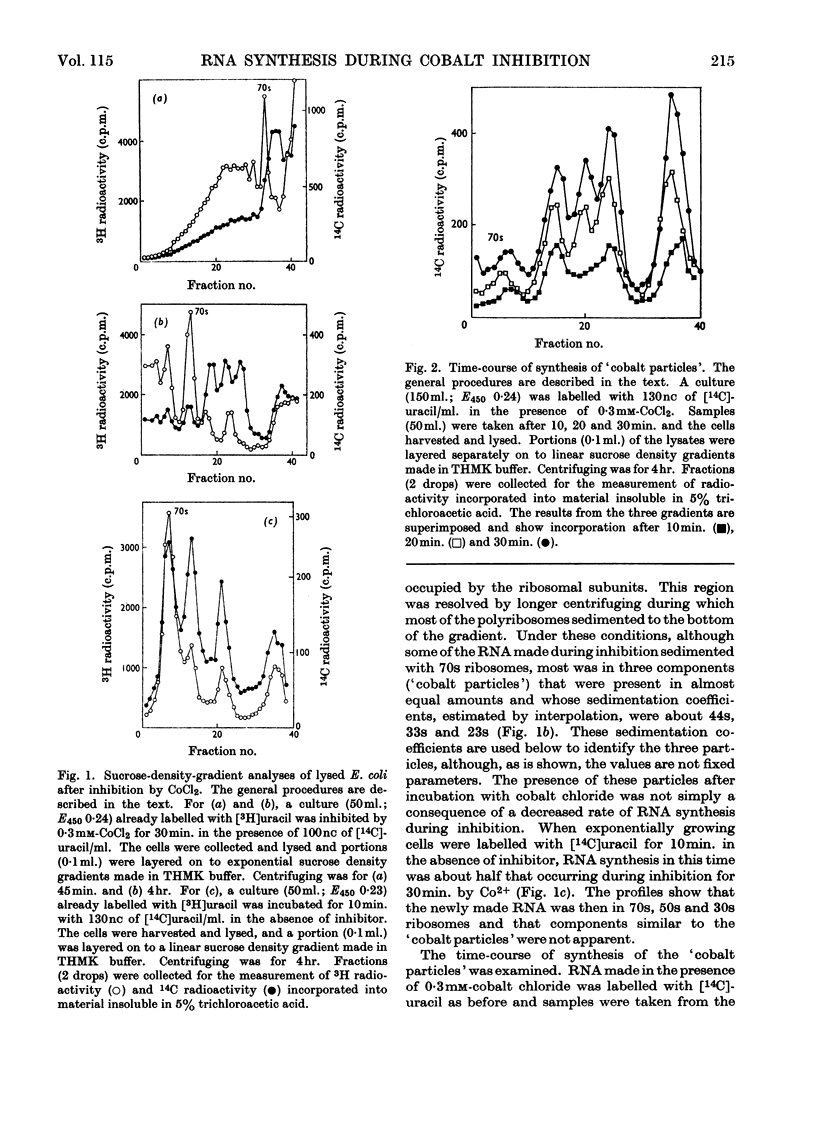
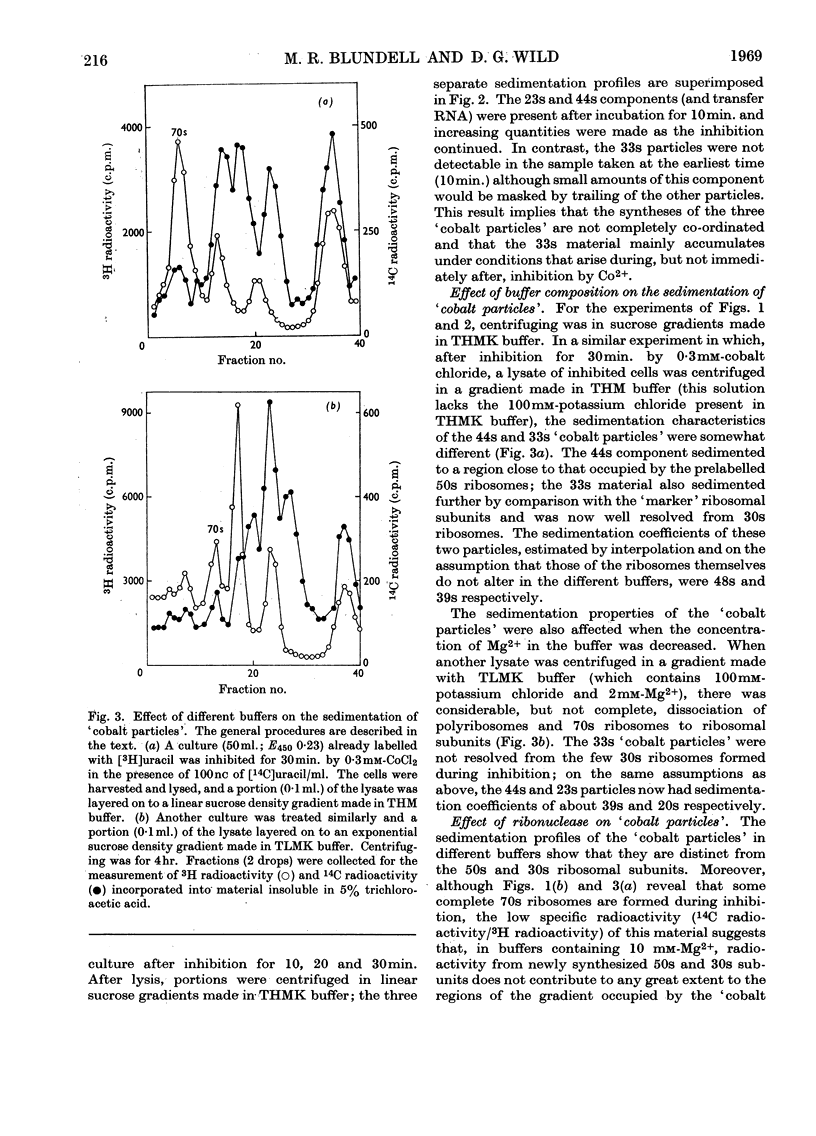
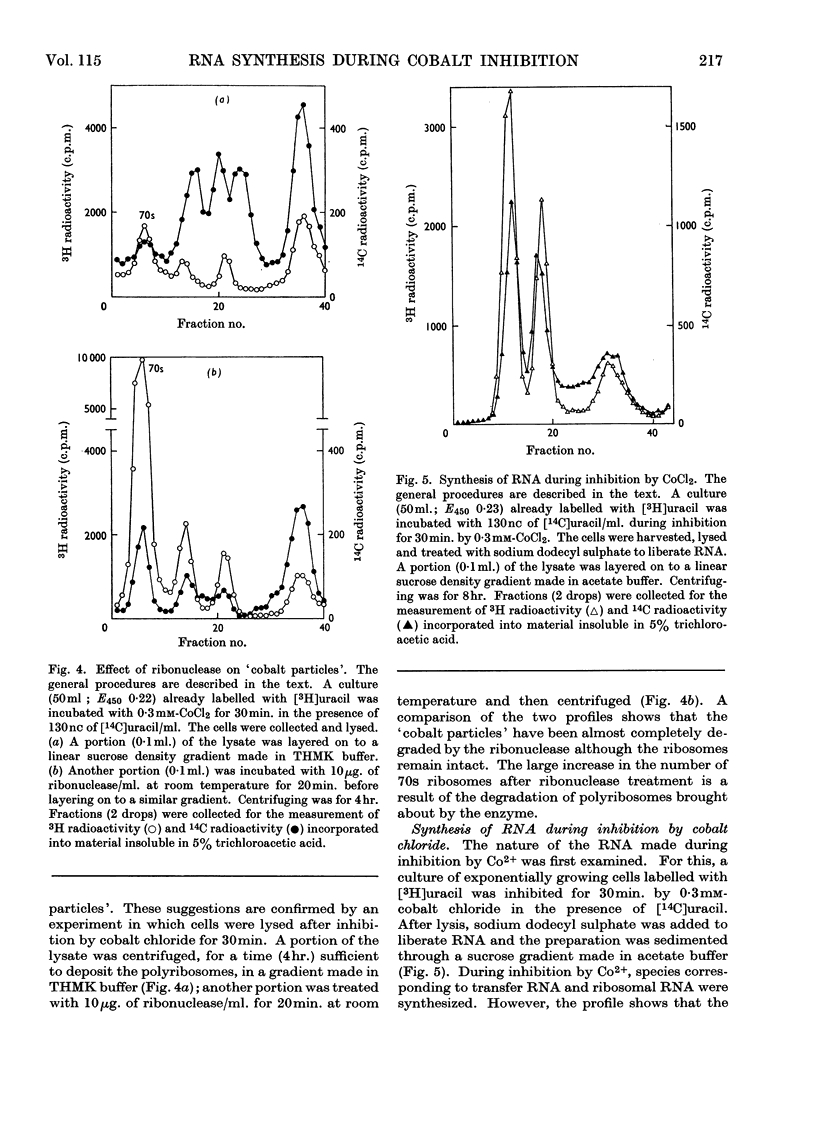
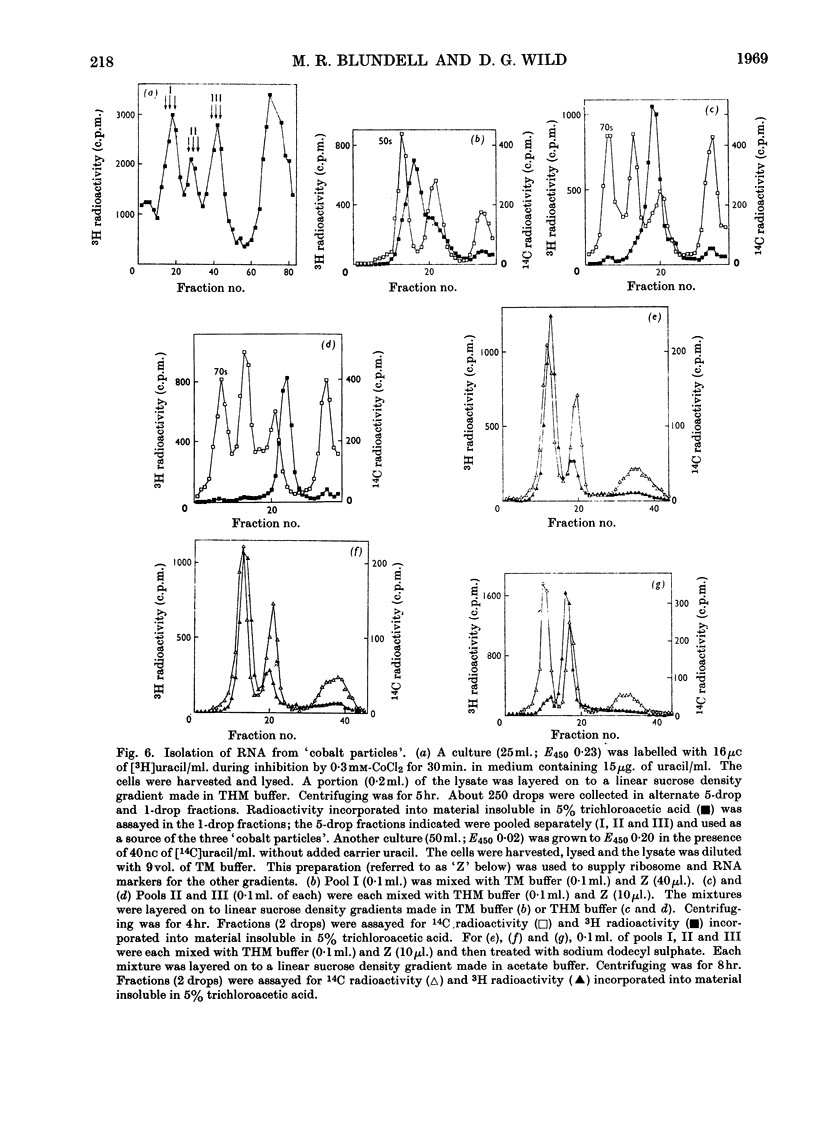
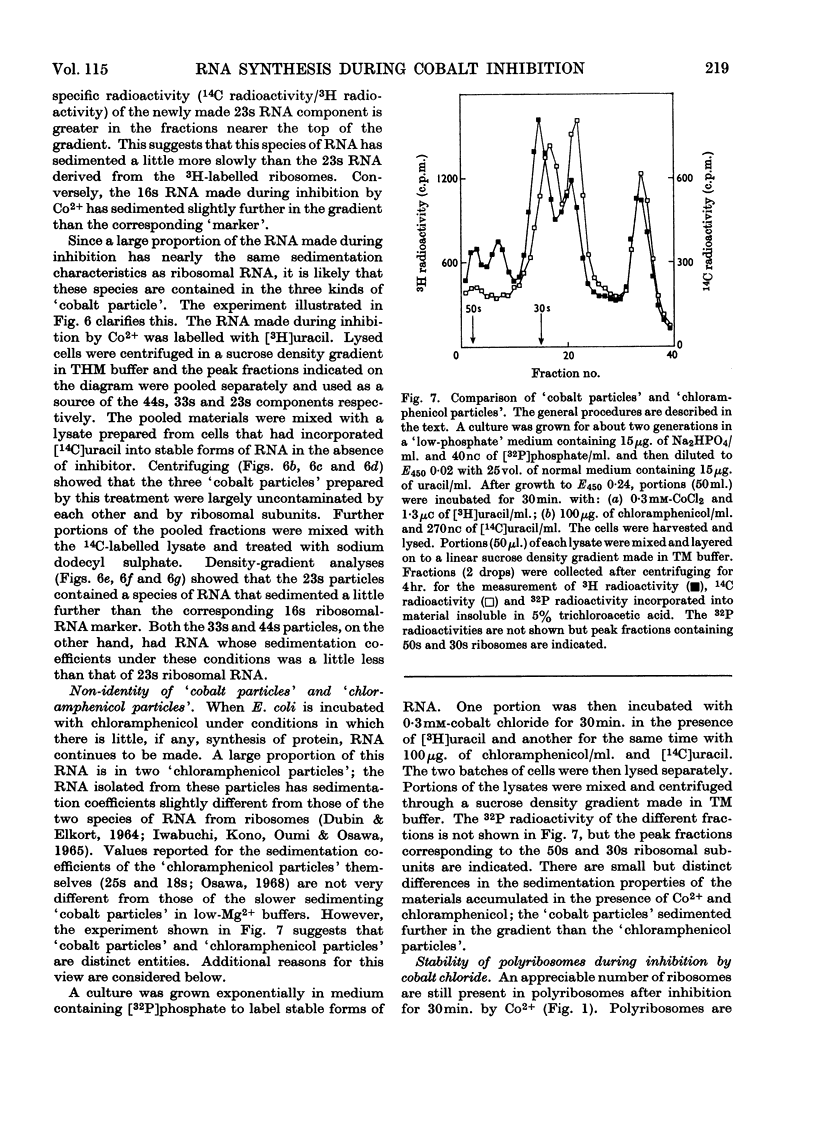
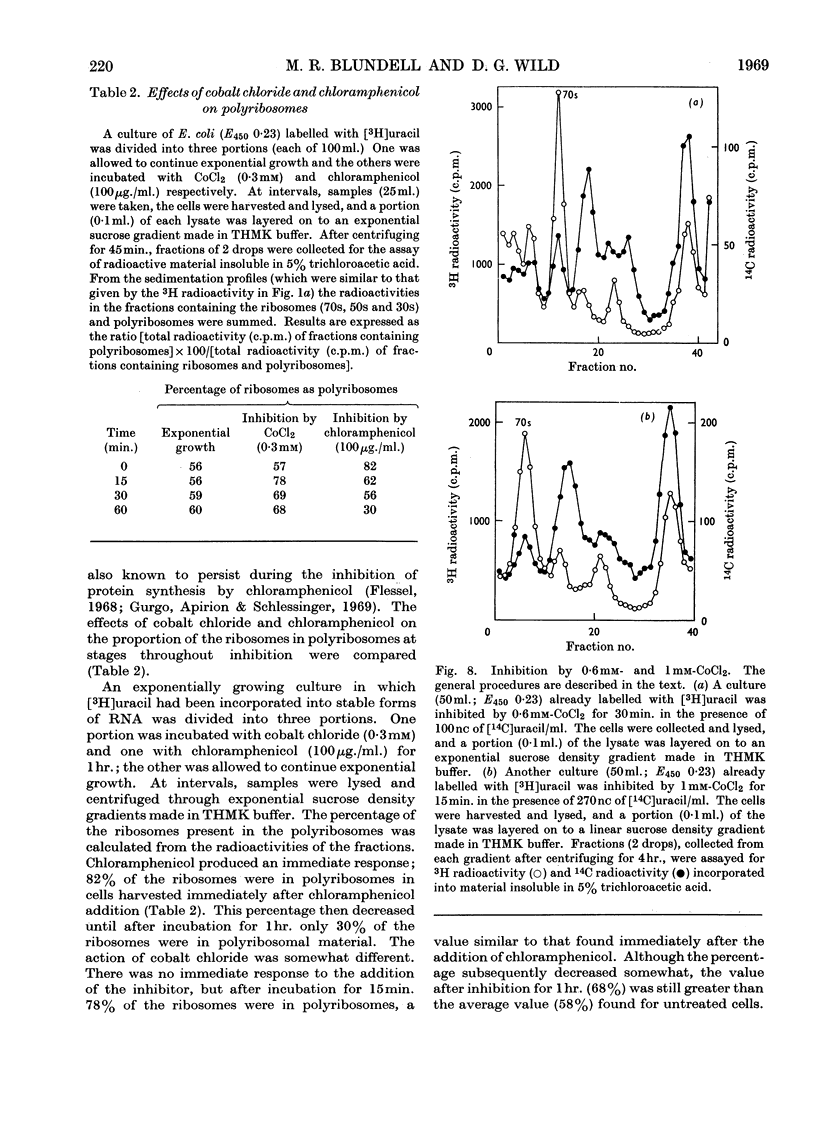
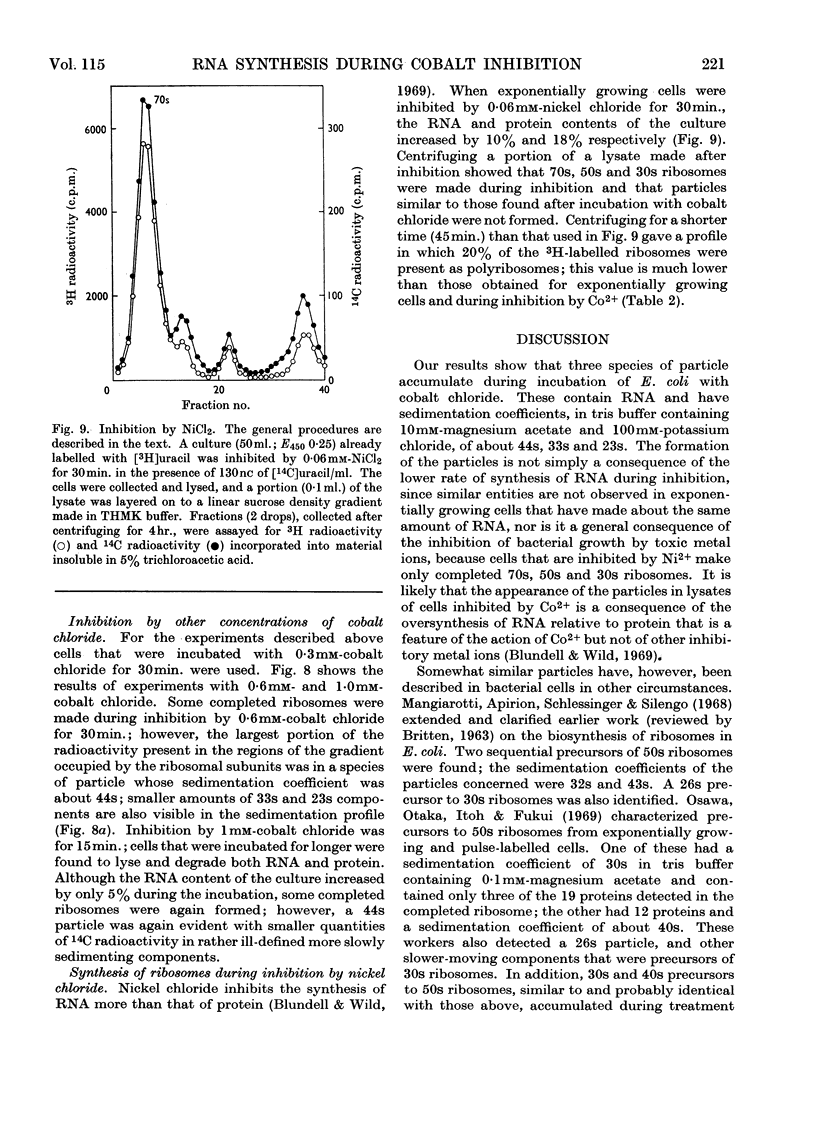
During inhibition of the growth of Escherichia coli by cobalt chloride protein synthesis was decreased more than the synthesis of RNA. Three species of particle accumulated during the incubation. These had sedimentation coefficients of about 44s, 33s and 23s in tris buffer containing 10 mm-magnesium acetate and 100 mm-potassium chloride, but their sedimentation properties were susceptible to changes in buffer composition. The particles contained RNA but were more readily degraded by ribonuclease than were the ribosomes. RNA isolated from the particles differed slightly in sedimentation properties from the major species of ribosomal RNA. The particles are likely to be closely related to ribosome precursors that have been detected in other circumstances. Changes in the polyribosome fraction during inhibition by cobalt chloride, nickel chloride and chloramphenicol provided further evidence that inhibition by Co2+ involves specific effects on the protein-synthesizing machinery.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITTEN R. The pattern of flow and sequential stages in bacterial nucleic acid synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 10;108:273–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell M. R., Wild D. G. Inhibition of bacterial growth by metal salts. A survey of effects on the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):207–212. doi: 10.1042/bj1150207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Roberts R. B. High-Resolution Density Gradient Sedimentation Analysis. Science. 1960 Jan 1;131(3392):32–33. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3392.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TURNOCK G., WILD D. G. THE ACCUMULATION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID BY A MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:555–566. doi: 10.1042/bj0880555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., WHITE A. E., WILD D. G., SYKES J. Synthesis of protein and ribosomes by bacteria. Nature. 1962 Apr 7;194:25–27. doi: 10.1038/194025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T., ELKORT A. T. SOME ABNORMAL PROPERTIES OF CHLORAMPHENICOL RNA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:508–518. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurgo C., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Effects of chloramphenicol and fusidic acid on polyribosome metabolism in escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1969 Apr;3(1):34–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. A., Wild D. G. The synthesis of ribonucleic acid during inhibition of Escherichia coli by chlortetracycline. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):277–283. doi: 10.1042/bj0970277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi M., Kono M., Oumi T., Osawa S. The RNA components in ribonucleoprotein particles occurring during the course of ribosome formation in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 11;108(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONO M., OTAKA E., OSAWA S. CHANGES IN SEDIMENTATION PROPERTIES OF RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACIDS DURING THE COURSE OF RIBOSOME FORMATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:612–618. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski L. J., Brownstein B. L. Characterization of a 43 s ribonucleoprotein component of a mutant of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr;41(2):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Apirion D., Schlessinger D., Silengo L. Biosynthetic precursors of 30S and 50S ribosomal particles in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):456–472. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli. I. Extraction of polyribosomes and ribosomal subunits from fragile, growing Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):123–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Otaka E., Itoh T., Fukui T. Biosynthesis of 50 s ribosomal subunit in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 28;40(3):321–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S. Ribosome formation and structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:109–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI H., HAYASHI Y. THE FORMATION OF "RIBOSOMAL RNA" IN ESCHERICHIA COLI DURING RECOVERY FROM MAGNESIUM STARVATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 12;87:610–620. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. F. Origin of chloramphenicol particle protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnock G., Wild D. G. The effect of 5-methyltryptophan on the synthesis of protein and RNA by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 21;114(3):578–592. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Osawa S. Origin of the protein component of chlormaphenicaol particles in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


