Abstract
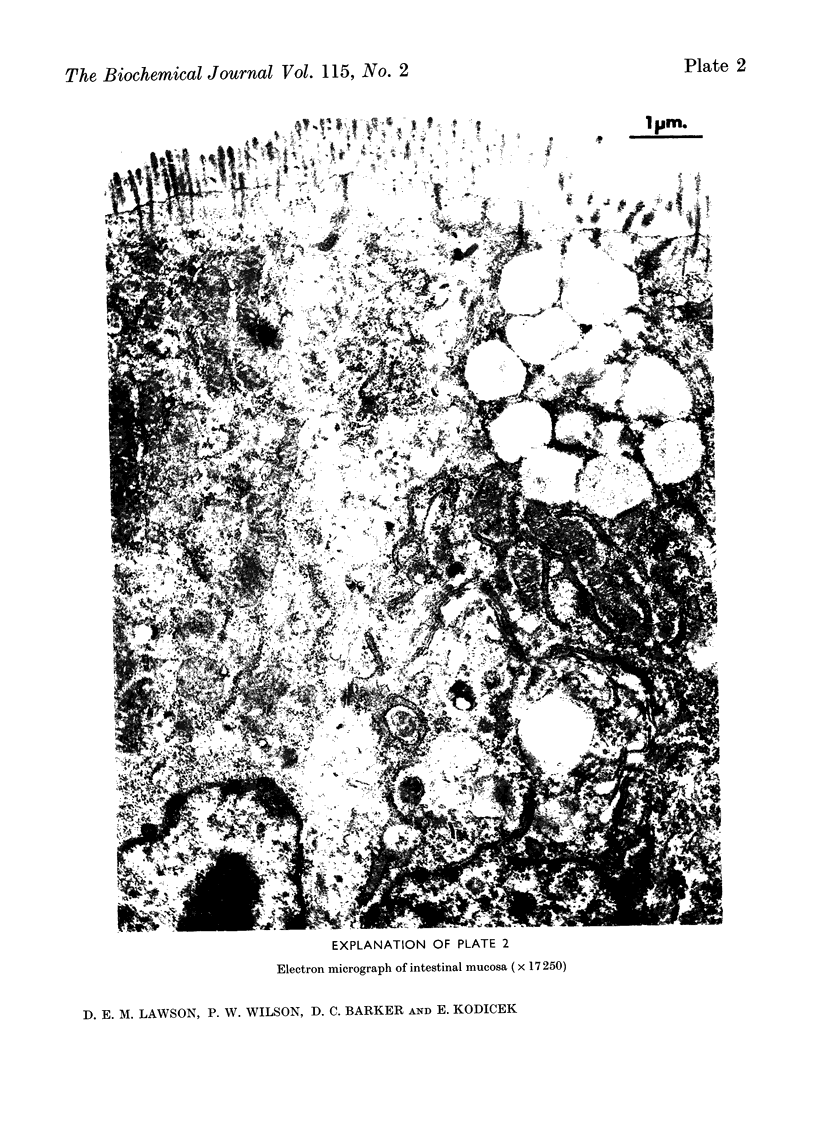
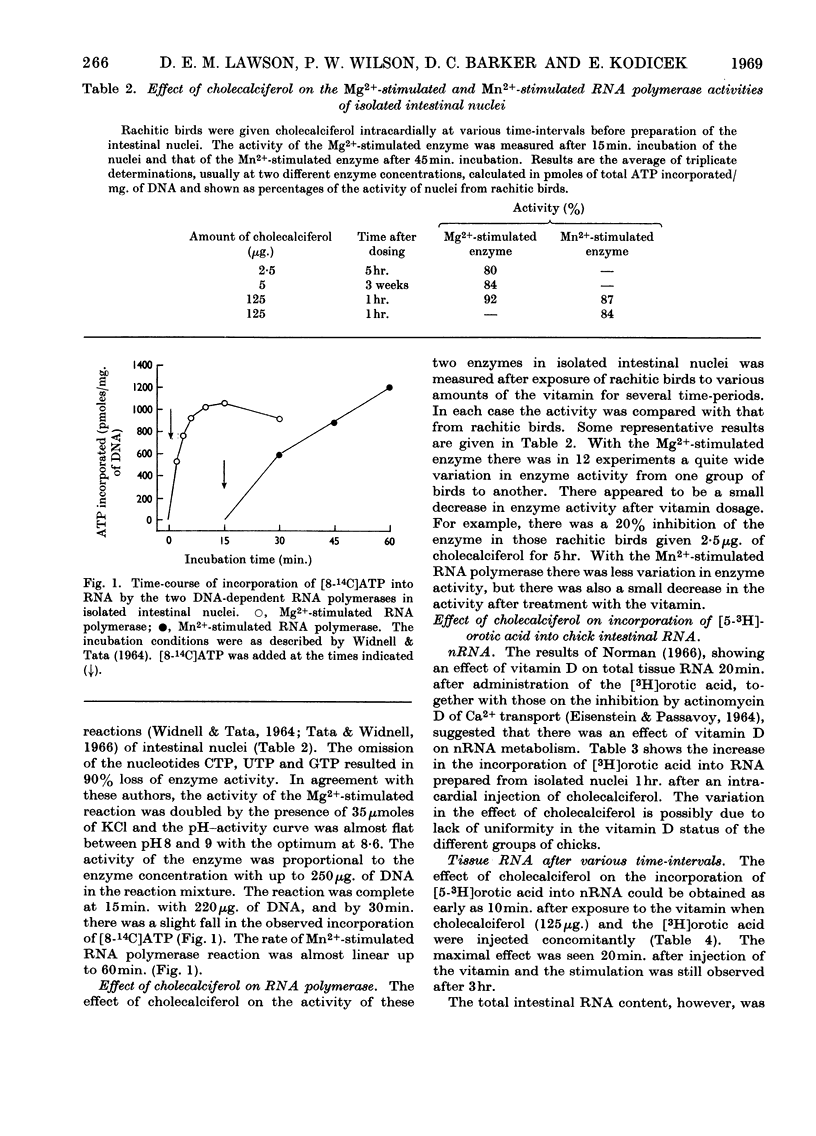
1. Chick intestinal nuclei were isolated, with practically no contamination from other organelles and whole cells, by centrifugation through 2·4m-sucrose. 2. The proportions of RNA, DNA and protein of the isolated nuclei were unaffected by the vitamin D status of the birds. The RNA/DNA ratio was 0·15. 3. The incorporation of [5-3H]orotic acid into the rapidly labelled intestinal nuclear RNA, after a 10min. pulse of the orotic acid, was increased in vitamin D-deficient chicks only 10min. after a 125μg. dose of cholecalciferol. 4. There was no stimulation of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity of the isolated nuclei from birds treated with cholecalciferol. 5. The results are discussed in relation to the changes occurring during the lag period, after administration of cholecalciferol and before Ca2+ transport is detected, and the function of the vitamin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSCH H., DAVIS J. R., ANDERSON D. C. Labeling of histones and other nuclear proteins with L-lysine-U-C14 in tissues of tumor-bearing rats. Cancer Res. 1958 Sep;18(8 Pt 1):916–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker K. L., Warren J. C. Template capacity of uterine chromatin: control by estradiol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARNIE J. A., PORTEOUS J. W. The invertase activity of rabbit small intestine. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:450–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0850450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. Determination of nucleic acids in animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., McLEAN P. Further studies on the properties and assay of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase of rat liver. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):400–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0550400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher G., West G. R., Brindley D. N. Studies on the fractionation of mucosal homogenates from the small intestine. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):629–642. doi: 10.1042/bj0970629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. E., Wilson P. W., Kodicek E. Metabolism of vitamin D. A new cholecalciferol metabolite, involving loss of hydrogen at C-1, in chick intestinal nuclei. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):269–277. doi: 10.1042/bj1150269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovtrup-Rein H., McEwen B. S. Isolation and fractionation of rat brain nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):405–415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGGIO R., SIEKEVITZ P., PALADE G. E. STUDIES ON ISOLATED NUCLEI. I. ISOLATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF A NUCLEAR FRACTION FROM GUINEA PIG LIVER. J Cell Biol. 1963 Aug;18:267–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. The digestive function of the epithelium of the small intestine. I. An intracellular locus of disaccharide and sugar phosphate ester hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:281–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90677-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A. W., DELUCA H. F. THE SUBCELLULAR LOCATION OF H3 VITAMIN D3 IN KIDNEY AND INTESTINE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul;107:69–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville E., Holdsworth E. S. A "second messenger" for Vitamin D. FEBS Lett. 1969 Mar;2(5):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville E., Holdsworth E. S. Phosphorus metabolism during transport of calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W. Vitamin D mediated synthesis of rapidly labeled RNA from intestinal mucosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 3;23(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTEOUS J. W., CLARK B. THE ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SUBCELLULAR COMPONENTS OF THE EPITHELIAL CELLS OF RABBIT SMALL INTESTINE. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:159–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0960159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER R. M. The effect of anions on the optical properties of rat liver nuclei isolated in glycerol solutions. Exp Cell Res. 1955 Feb;8(1):24–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(55)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEFFNER A. L. The reduction in vitro in viscosity of mucoprotein solutions by a new mucolytic agent, N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:298–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPORN M. B., WANKO T., DINGMAN W. The isolation of cell nuclei from rat brain. J Cell Biol. 1962 Oct;15:109–120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohs S. J., DeLuca H. F. Subcellular location of vitamin D and its metabolites in intestinal mucosa after a 10-IU dose. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3338–3349. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohs S. J., Zull J. E., DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D stimulation of [3H]orotic acid incorporation into ribonucleic acid of rat intestinal mucosa. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1304–1310. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON V. W., DELUCA H. F. VITAMIN D AND PHOSPHOLIPID METABOLISM. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:984–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Hormonal regulation of growth and protein synthesis. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):331–337. doi: 10.1038/219331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Widnell C. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during the early action of thyroid hormones. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):604–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0980604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Corradino R. A., Taylor A. N. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3978–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. W., Lawson D. E., Kodicek E. The intracellular distribution of [1-3H]cholecalciferol in the intestine of vitamin D-deficient and -supplemented rats. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):165–171. doi: 10.1042/bj1030165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]