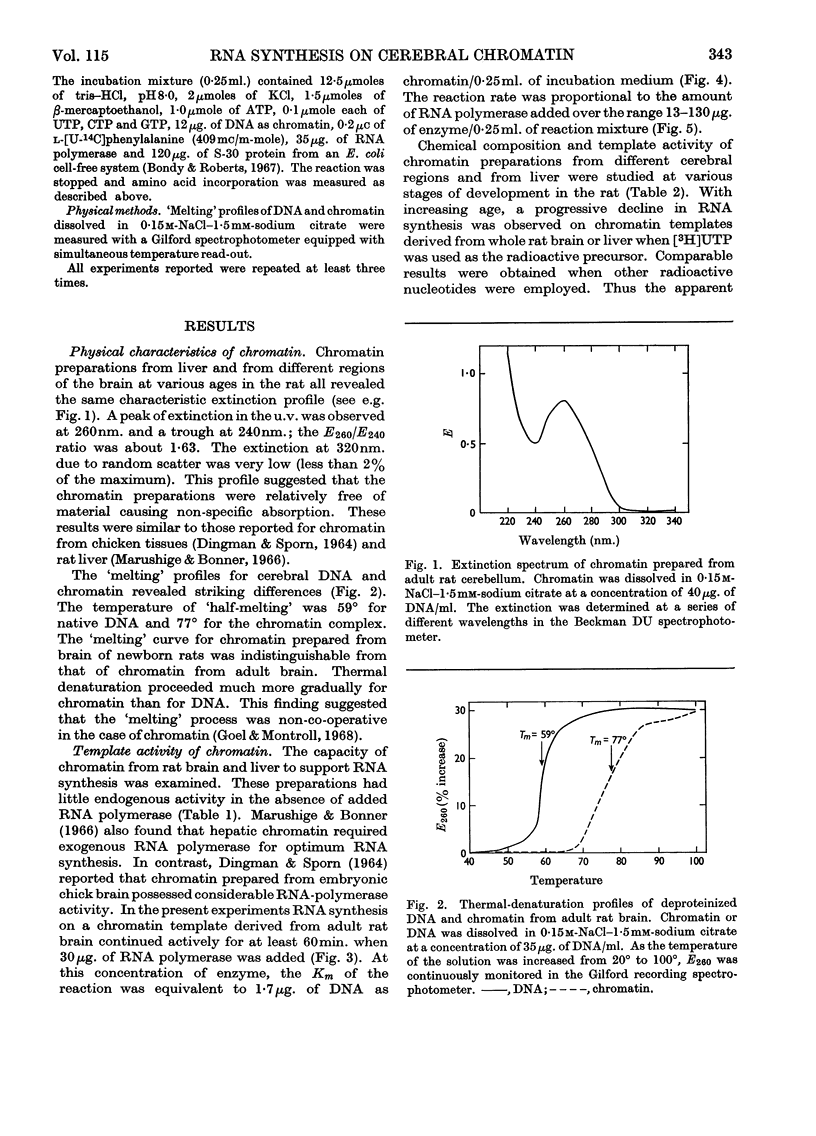
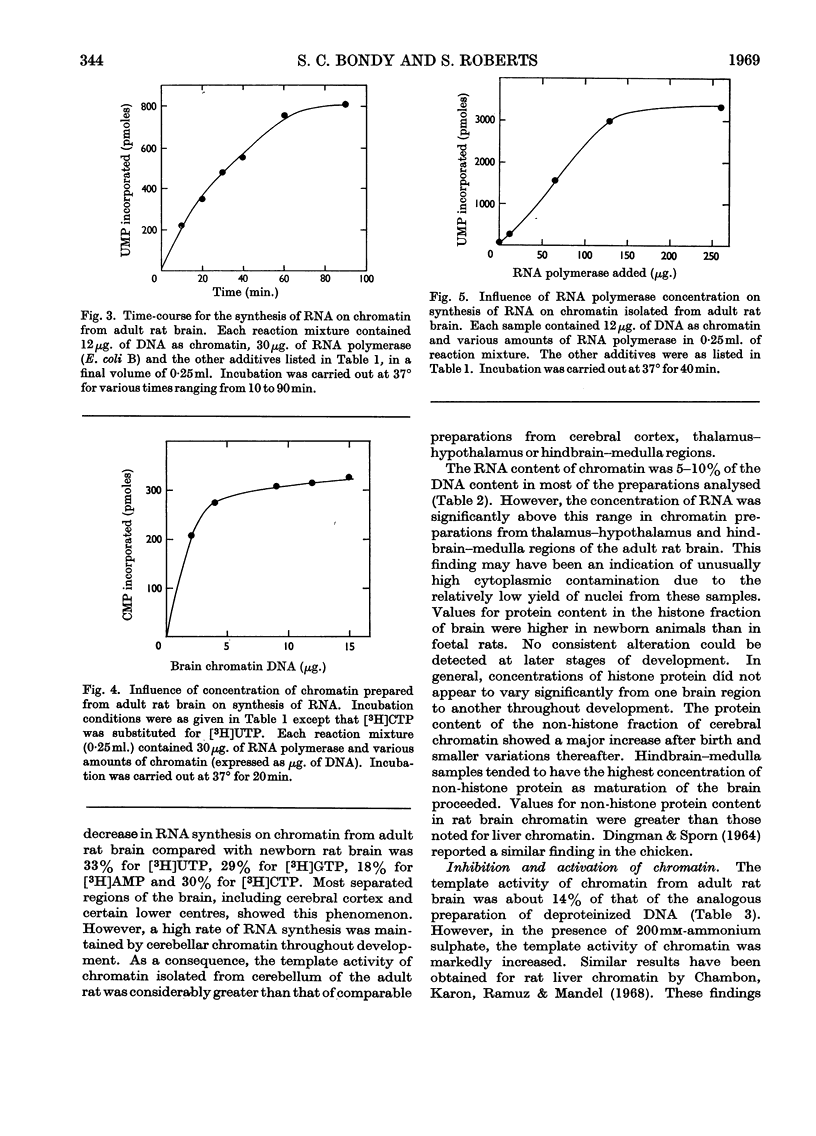
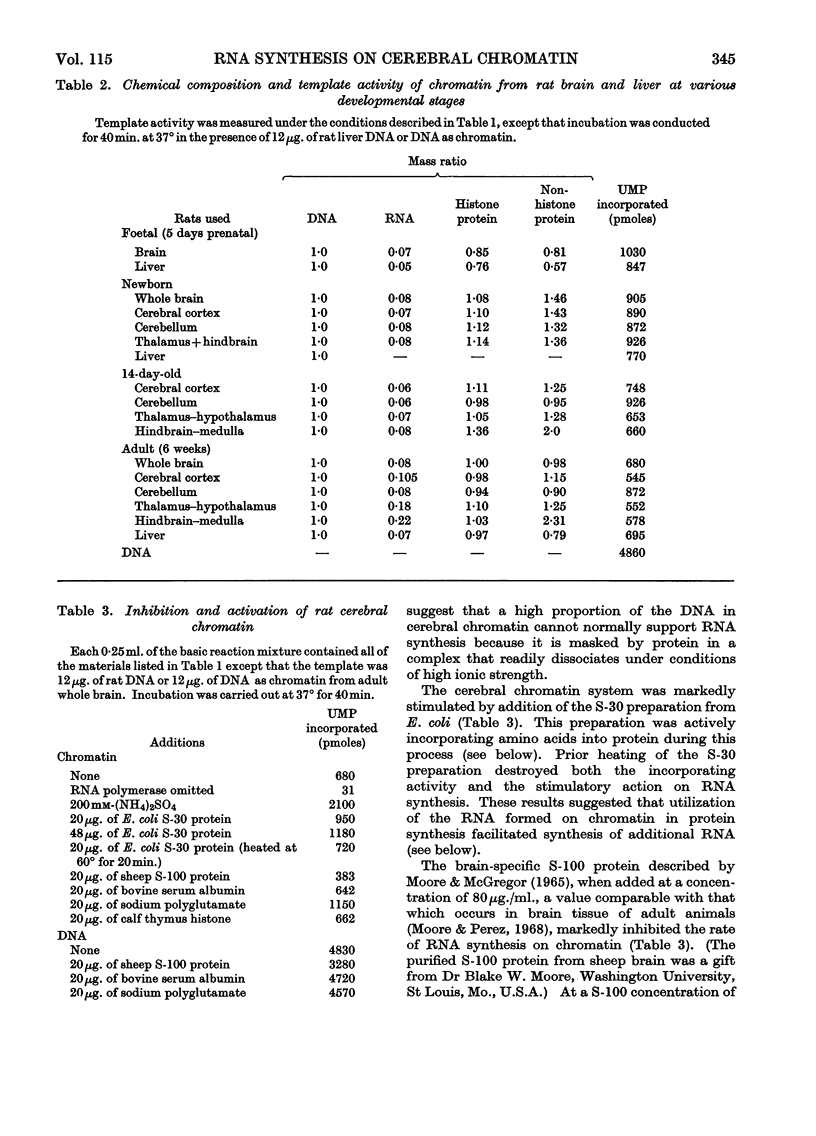
Abstract
1. Chromatin was prepared from purified nuclei isolated from liver and cerebral regions of the rat. 2. The capacity of these preparations to promote RNA synthesis in the presence of bacterial RNA polymerase was determined. 3. The rate of RNA synthesis on chromatin was normally 12–21% of the rate observed with native DNA, but was markedly stimulated on addition of 200mm-ammonium sulphate. 4. At physiological concentrations (80μg./ml.), the brain-specific S-100 protein inhibited RNA synthesis on DNA and chromatin. 5. Cerebral chromatin from foetal and newborn animals was more active in RNA synthesis than were the analogous preparations from liver. 6. Cerebellar chromatin maintained a high rate of RNA synthesis during brain maturation. In contrast, RNA synthesis on chromatin from other brain regions and liver declined with age of the rat. 7. RNA synthesized on chromatin stimulated amino acid incorporation in an Escherichia coli ribosomal system and hybridized with homologous DNA. 8. RNA synthesized on chromatin from adult cortex or hindbrain hybridized with DNA to a greater extent than that synthesized on cerebellar chromatin. 9. The proportion of RNA formed on cerebral-cortical chromatin that hybridized with DNA increased with age of the rat. 10. The results indicate that the total amount and the types of RNA synthesized on cerebral chromatin vary regionally and during development.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONNER J., HUANG R. C., GILDEN R. V. CHROMOSOMALLY DIRECTED PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:893–900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Kovács S., Teichgräber P., Cocks W. A., Eayrs J. T. Biochemical effects of thyroid deficiency on the developing brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Nov;15(11):1335–1349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Roberts S. Hybridizable ribonucleic acid of rat brain. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1090533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Roberts S. Messenger ribonucleic acid of cerebral nuclei. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1111–1118. doi: 10.1042/bj1051111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J., Dahmus M. E., Fambrough D., Huang R. C., Marushige K., Tuan D. Y. The Biology of Isolated Chromatin: Chromosomes, biologically active in the test tube, provide a powerful tool for the study of gene action. Science. 1968 Jan 5;159(3810):47–56. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3810.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J., Kung G., Bekhor I. A method for the hybridization of nucleic acid molecules at low temperature. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3650–3653. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. Determination of nucleic acids in animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P., Karon H., Ramuz M., Mandel P. The influence of ionic strength and a polyanion on transcription in vitro. II. Effects on the template efficiency of rat liver chromatin for a purified bacterial RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):520–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGMAN C. W., SPORN M. B. STUDIES ON CHROMATIN. I. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NUCLEAR COMPLEXES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID, RIBONUCLEIC ACID, AND PROTEIN FROM EMBRYONIC AND ADULT TISSUES OF THE CHICKEN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3483–3492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E., Bonner J. Increased template activity of liver chromatin, a result of hydrocortisone administration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Nov;54(5):1370–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.5.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd L., Okamura N., Busch H. Base composition of rapidly sedimenting nuclear ribonucleic acid of the regenerating liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel N. S., Montroll E. W. Denaturation and renaturation of DNA. II. Possible use of synthetic periodic copolymers to establish model and parameters. Biopolymers. 1968;6(5):731–765. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman C. J., Lapham L. W. DNA content of neurons in the cat hippocampus. Science. 1968 May 3;160(3827):537–537. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3827.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hydén H., McEwen B. A glial protein specific for the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):354–358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubinski H., Koch G. Regulation of the synthesis of various ribonucleic acids in animal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Feb 3;22(3):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. I., Sinex F. M. Age related differences in the association of brain DNA and nuclear protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):840–842. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapham L. W. Tetraploid DNA content of Purkinje neurons of human cerebellar cortex. Science. 1968 Jan 19;159(3812):310–312. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3812.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewus M. W. Analysis of chromatin in male and female mealy bugs. Nature. 1968 May 4;218(5140):474–476. doi: 10.1038/218474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY B. J., HOYER B. H. IDENTITY OF DNA AND DIVERSITY OF MESSENGER RNA MOLECULES IN NORMAL MOUSE TISSUES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:915–922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE B. W., MCGREGOR D. CHROMATOGRAPHIC AND ELECTROPHORETIC FRACTIONATION OF SOLUBLE PROTEINS OF BRAIN AND LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1647–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Bonner J. Template properties of liver chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):160–174. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie H. R., Zimm B. H. Molecular weight of the DNA in the chromosomes of E. coli and B. subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1636–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDLE A., WAELSCH H. HISTONES: SPECIES AND TISSUE SPECIFICITY. Science. 1964 Sep 4;145(3636):1059–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3636.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J., Gilmour R. S. Organ-specific restriction of transcription in mammalian chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90255-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J., Gilmour R. S. Restriction of deoxyribonucleic acid template activity in chromatin is organ-specific. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):992–993. doi: 10.1038/210992a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyhtilä M. J., Sherman F. G. Age-associated studies on thermal stability and template effectiveness of DNA and nucleoproteins from beef thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 10;31(3):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTEN R. J., AGRANOFF B. W. Studies on the estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid in rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:251–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg B. P., Zubay G. Nucleohistone as a primer for RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):415–420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler M. M., Willee C. A. Template activities in normal, regenerating, and developing rat liver chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2055–2062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


