Abstract
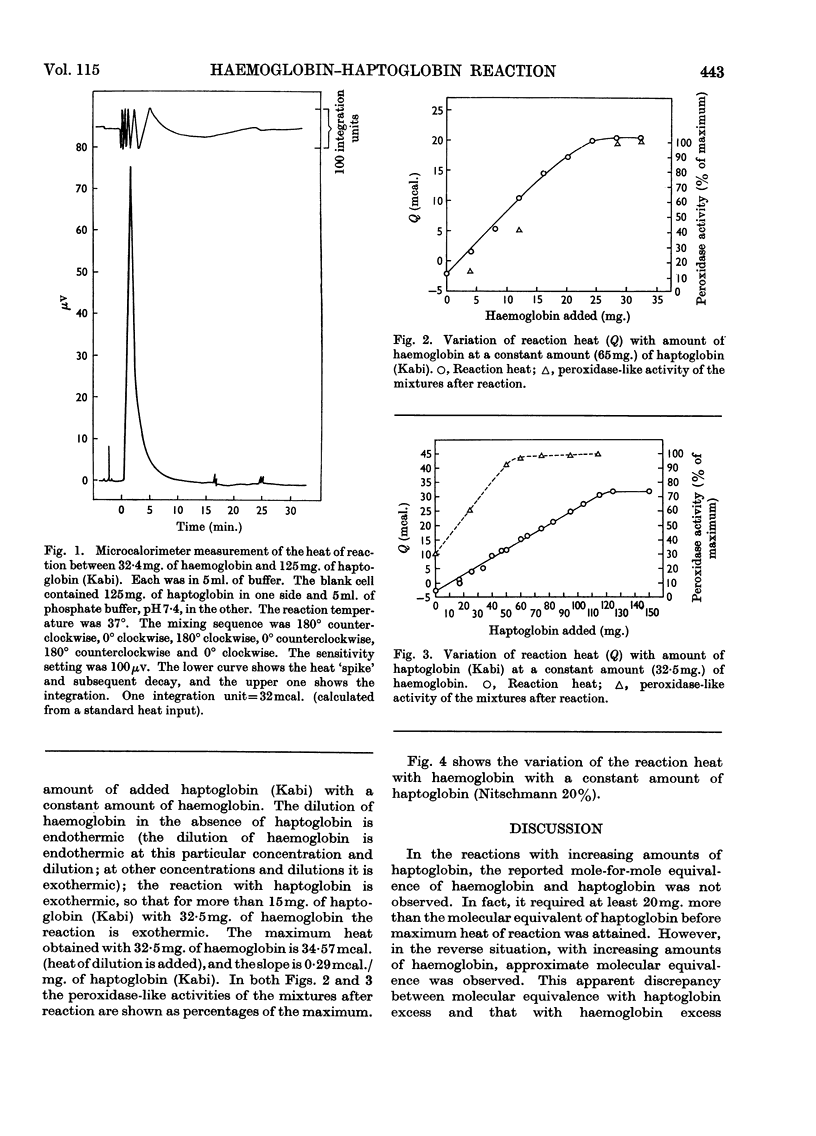
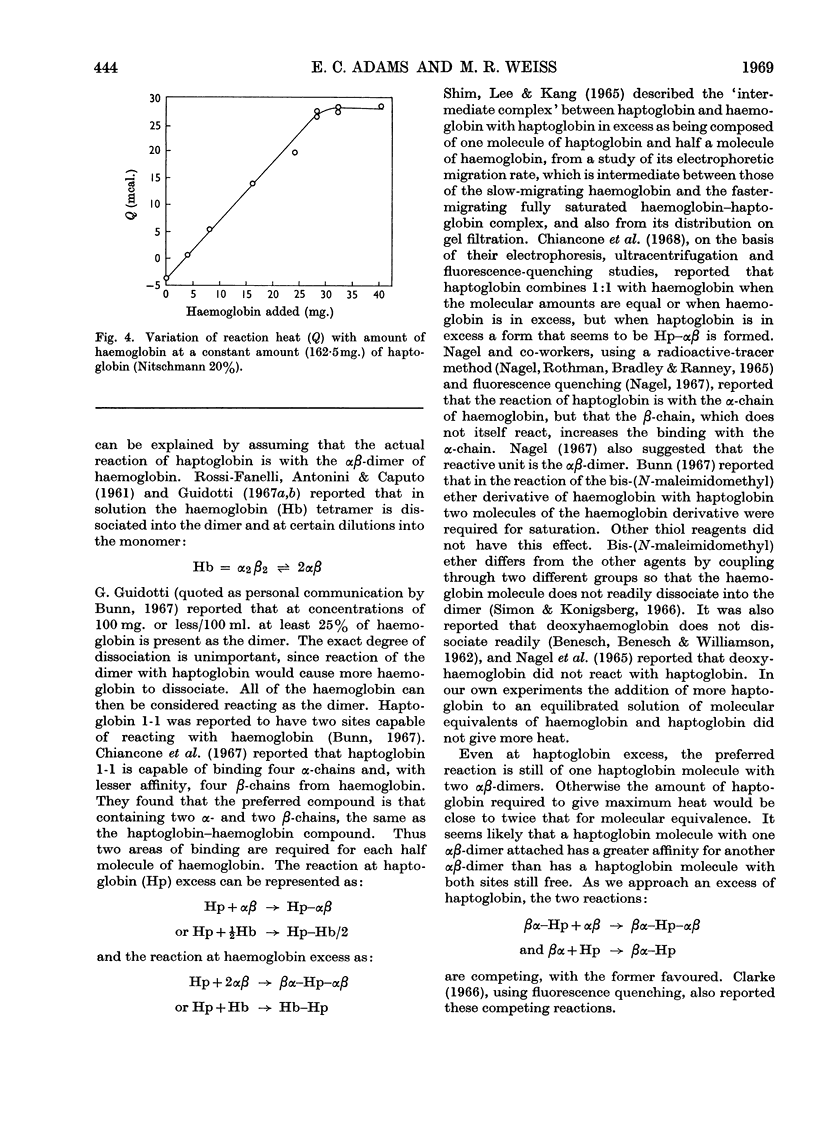
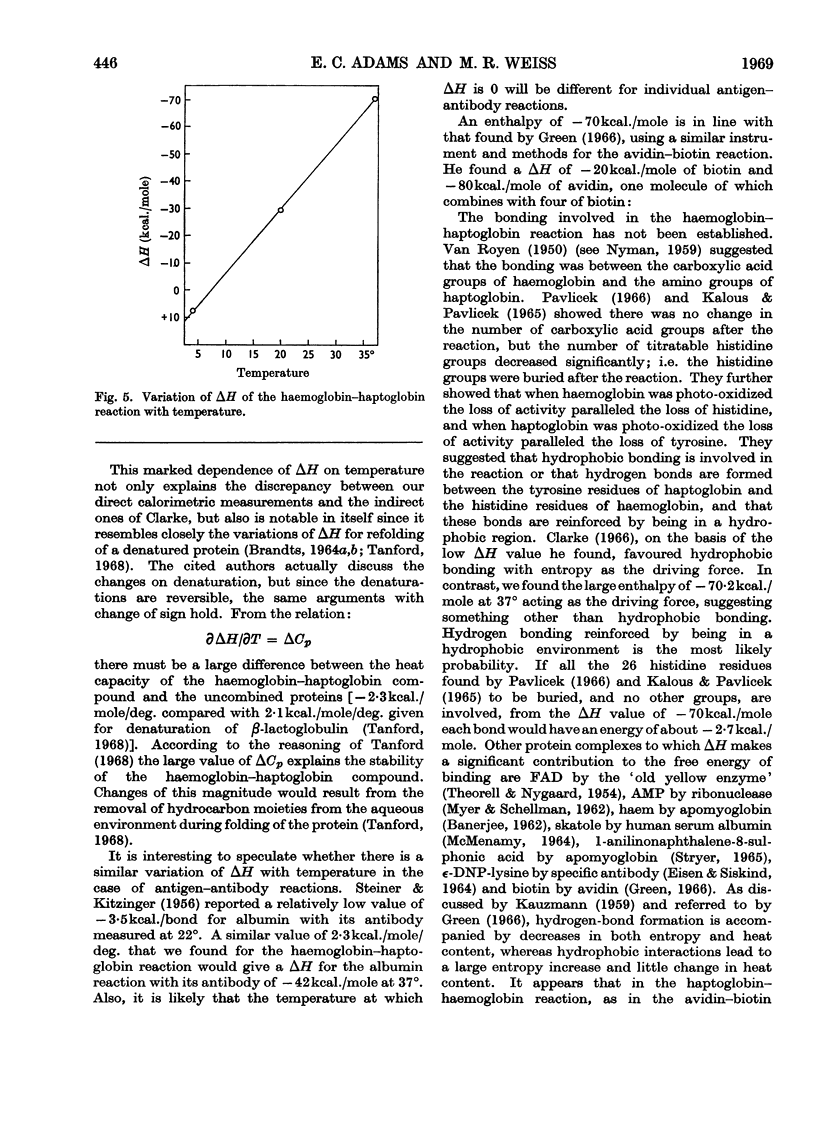
Haptoglobin binds haemoglobin so firmly that there is practically no dissociation. It would be expected that the heat of the reaction would be relatively large. The development of the microcalorimeter by Benzinger offered the opportunity to measure the heat of reaction. The experiments were carried out in the Beckman 190B Microcalorimeter in two ways: (1) a constant amount of haptoglobin (Kabi; 65mg.) with different amounts of haemoglobin, and (2) a constant amount of haemoglobin (32·5mg.) with different amounts of haptoglobin. The proteins, each in 5ml. of 0·15m-phosphate buffer, pH7·4, were placed in equal-volume calorimeter cells. The heat produced/mg. of haemoglobin was calculated from the slope of the curve for a constant amount of haptoglobin and from the maximum heat for a constant amount of haemoglobin. This heat is about 70kcal./mole at 37°. ΔH varies with temperature, being −70·2 at 37°, −29·7 at 20° and 7·2 at 4°. From the amount of haptoglobin required to attain maximum heat with 32·5mg. of haemoglobin and the amount of haemoglobin required to attain maximum heat with 65mg. of haptoglobin, it appears that at excess of haptoglobin there is competition between the reactions of 2moles of haptoglobin with 1mole of haemoglobin (or 2 αβ-chains) and 1mole of haptoglobin with 1mole of haemoglobin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANERJEE R. [Thermodynamic study of the heme-globin association. I. Dissociation equilibrium of metmyoglobin: thermodynamic data]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 22;64:368–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90746-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESCH R. E., BENESCH R., WILLIAMSON M. E. The influence of reversible oxygen binding on the interaction between hemoglobin submits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F. Effect of sulfhydryl reagents on the binding of human hemoglobin to haptoglobin. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):606–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E., Alfsen A., Ioppolo C., Vecchini P., Agrò A. F., Wyman J., Antonini E. Studies on the reaction of haptoglobin with haemoglobin and haemoglobin chains. I. Stoichiometry and affinity. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Thermodynamics of the binding of biotin and some analogues by avidin. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):774–780. doi: 10.1042/bj1010774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Studies on the chemistry of hemoglobin. II. The effect of salts on the dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3685–3693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Studies on the chemistry of hemoglobin. IV. The mechanism of reaction with ligands. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3704–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSHNER A. G., TANFORD C. THE DISSOCIATION OF HEMOGLOBIN BY INORGANIC SALTS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:291–296. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZINGER C., STEINER R. F. A calorimetric determination of the heat of an antigen-antibody reaction. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):271–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalous V., Pavlícek Z. The interaction between haptoglobin and haemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 15;111(1):337–338. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90504-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCMENAMY R. H. THE BINDING OF INDOLE ANALOGUES TO DEFATTED HUMAN SERUM ALBUMIN AT DIFFERENT CHLORIDE CONCENTRATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2835–2841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYER Y. P., SCHELLMAN J. A. The interaction of ribonuclease with purine and pyrimidine phosphates. I. Binding of adenosine 5'-monophosphate to ribonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:361–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90791-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattenheimer H., Adams E. C., Jr The peroxidase-like activity of the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1968 Mar;6(2):69–78. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1968.6.2.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN J. A., BETTER F. C., HOBAN J. A simple method for the determination of serum haptoglobins. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Mar;13:163–164. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI-FANELLI A., ANTONINI E., CAPUTO A. Studies on the relations between molecular and functional properties of hemoglobin. I. The effect of salts on the molecular weight of human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O., WALKER N. F. Notation for serum-protein groups and the genes controlling their inheritance. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):694–695. doi: 10.1038/178694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim B. S., Lee T. H., Kang Y. S. Immunological and biochemical investigations of human serum haptoglobin: composition of haptoglobin-haemoglobin intermediate, haemoglobin-binding sites and presence of additional alleles for beta-chain. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1264–1267. doi: 10.1038/2071264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. R., Konigsberg W. H. Chemical modification of hemoglobins: a study of conformation restraint by internal bridging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):749–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. The interaction of a naphthalene dye with apomyoglobin and apohemoglobin. A fluorescent probe of non-polar binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):482–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


