Abstract
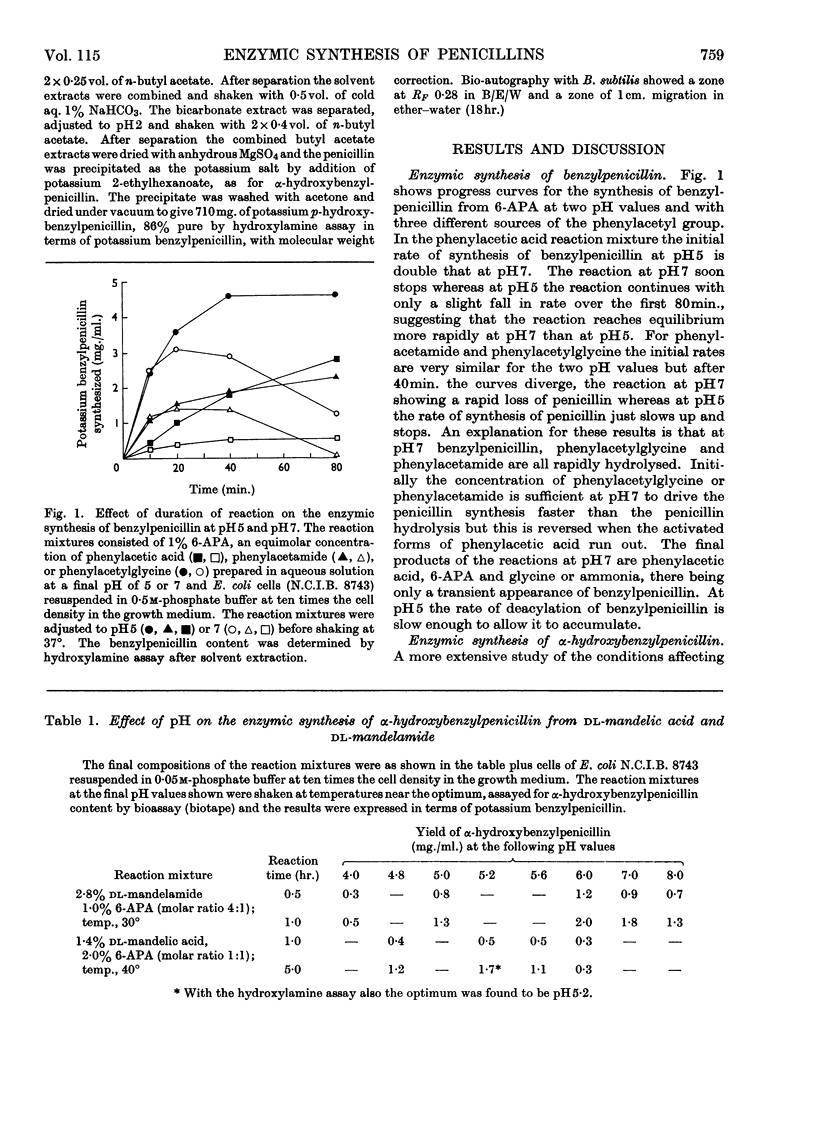
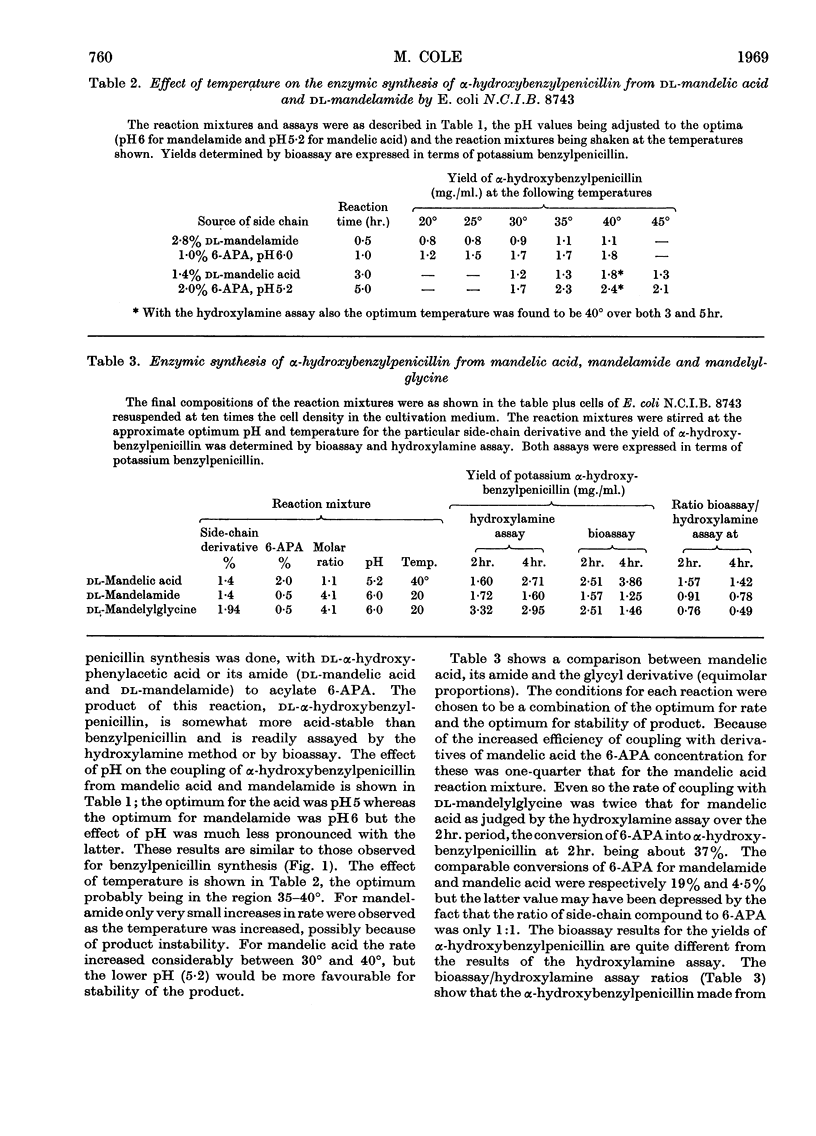
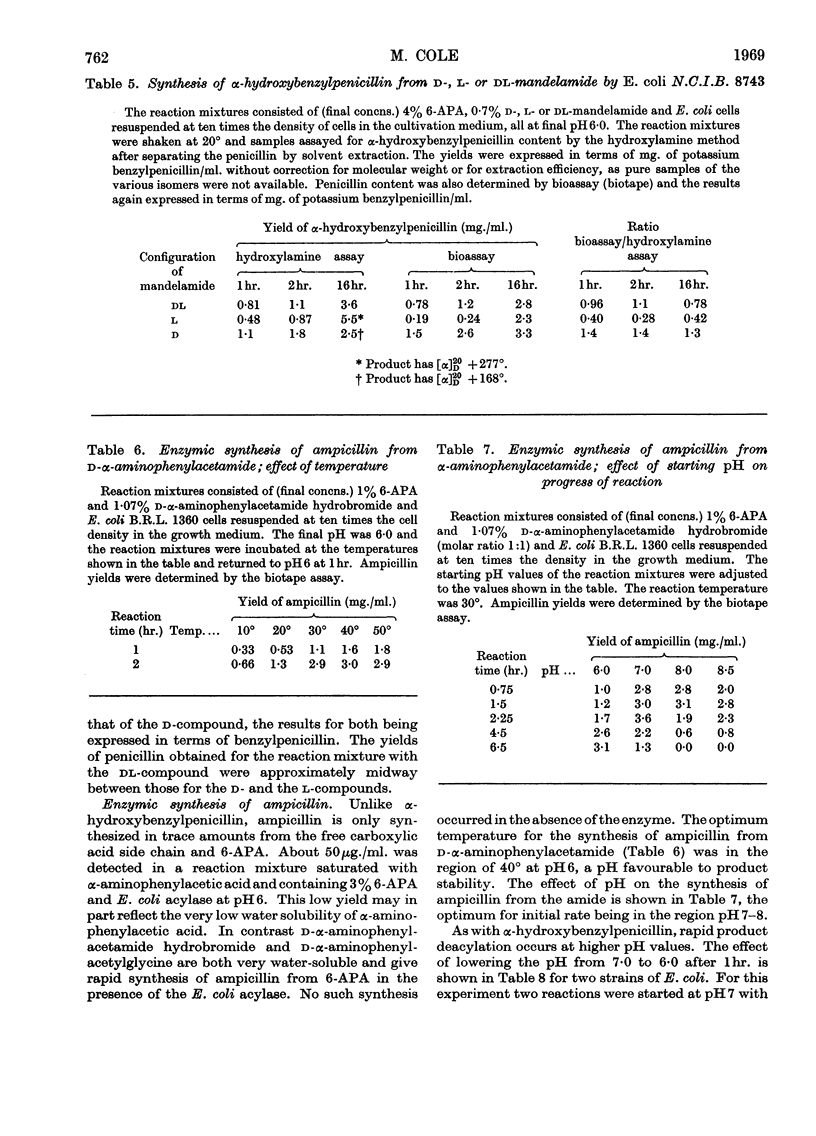
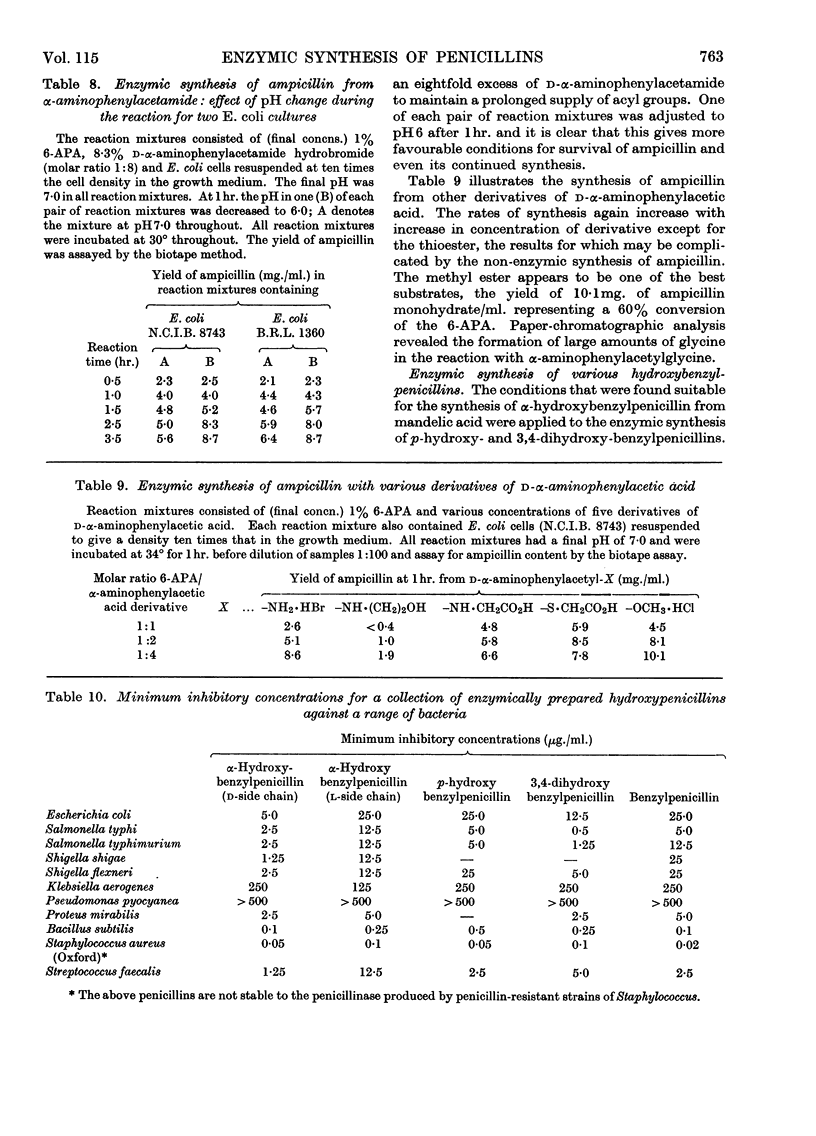
1. The effect of pH, temperature, reactant concentration and reaction time has been investigated for the synthesis of benzylpenicillin, dl-α-hydroxybenzylpenicillin and d-α-aminobenzylpenicillin from 6-aminopenicillanic acid by the penicillin acylase of Escherichia coli. 2. Synthesis of penicillins from carboxylic acids proceeds most rapidly at pH5; with amides the optimum pH is higher (6–7) but the reverse reaction rapidly sets in. This can be counteracted by lowering the pH or adding more amide. Optimum temperatures are 35–40°. 3. Most rapid synthesis of penicillin was obtained with the N-acylglycine and methyl ester derivatives of carboxylic acids. Increasing the amide/6-APA ratio above 1:1 raised the rate of synthesis of penicillins. 4. Preferential synthesis of d-α-hydroxybenzylpenicillin takes place in a reaction mixture containing dl-mandelic acid. 5. From d- and l-mandelamide, d- and l-α-hydroxybenzylpenicillins were prepared, the former being more bioactive than the latter. p-Hydroxy- and 3,4-dihydroxybenzylpenicillins were also prepared, the latter being more active against some Gram-negative bacteria than benzylpenicillin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole M. Deacylation of acylamino compounds other than penicillins by the cell-bound penicillin acylase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):741–745. doi: 10.1042/bj1150741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. Hydrolysis of penicillins and related compounds by the cell-bound penicillin acylase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):733–739. doi: 10.1042/bj1150733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. Penicillins and other acylamino compounds synthesized by the cell-bound penicillin acylase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):747–756. doi: 10.1042/bj1150747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROLINSON G. N., BATCHELOR F. R., BUTTERWORTH D., CAMERON-WOOD J., COLE M., EUSTACE G. C., HART M. V., RICHARDS M., CHAIN E. B. Formation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid from penicillin by enzymatic hydrolysis. Nature. 1960 Jul 16;187:236–237. doi: 10.1038/187236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND R. THE NATURE OF THE INSENSITIVITY OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA TOWARDS PENICILLINS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jan;34:85–98. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


