Abstract
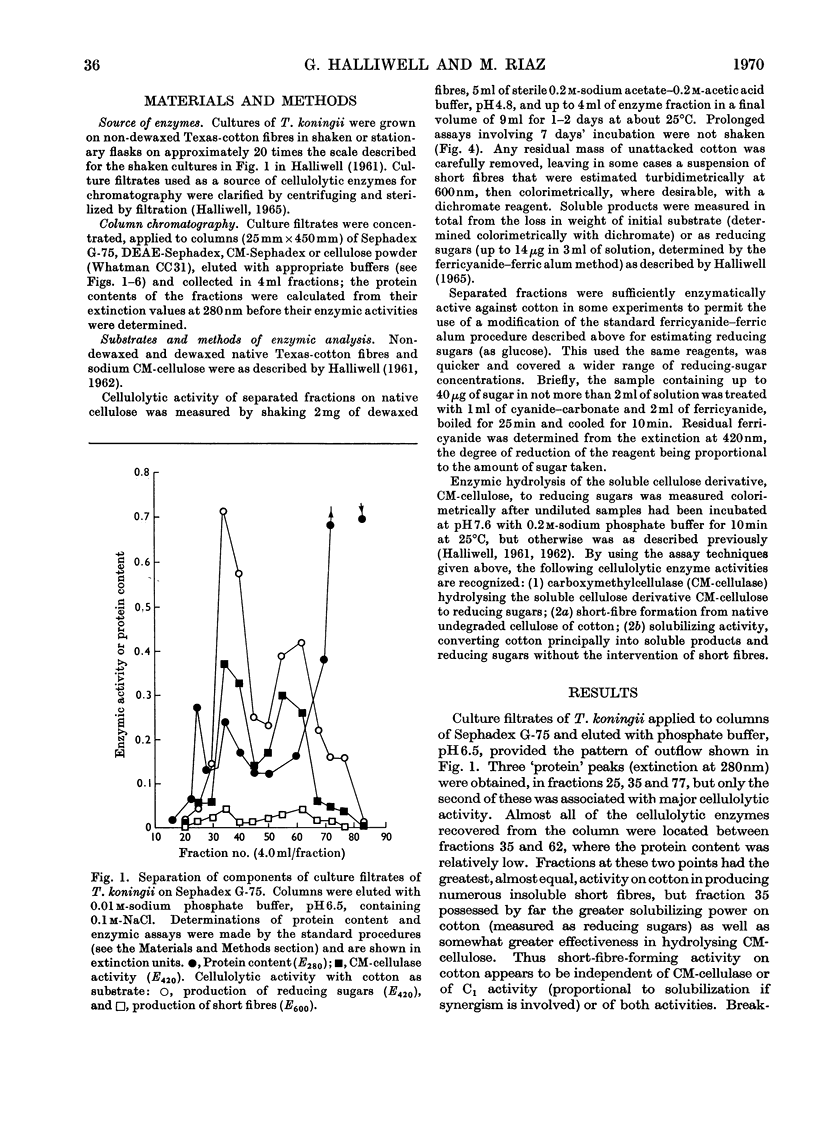
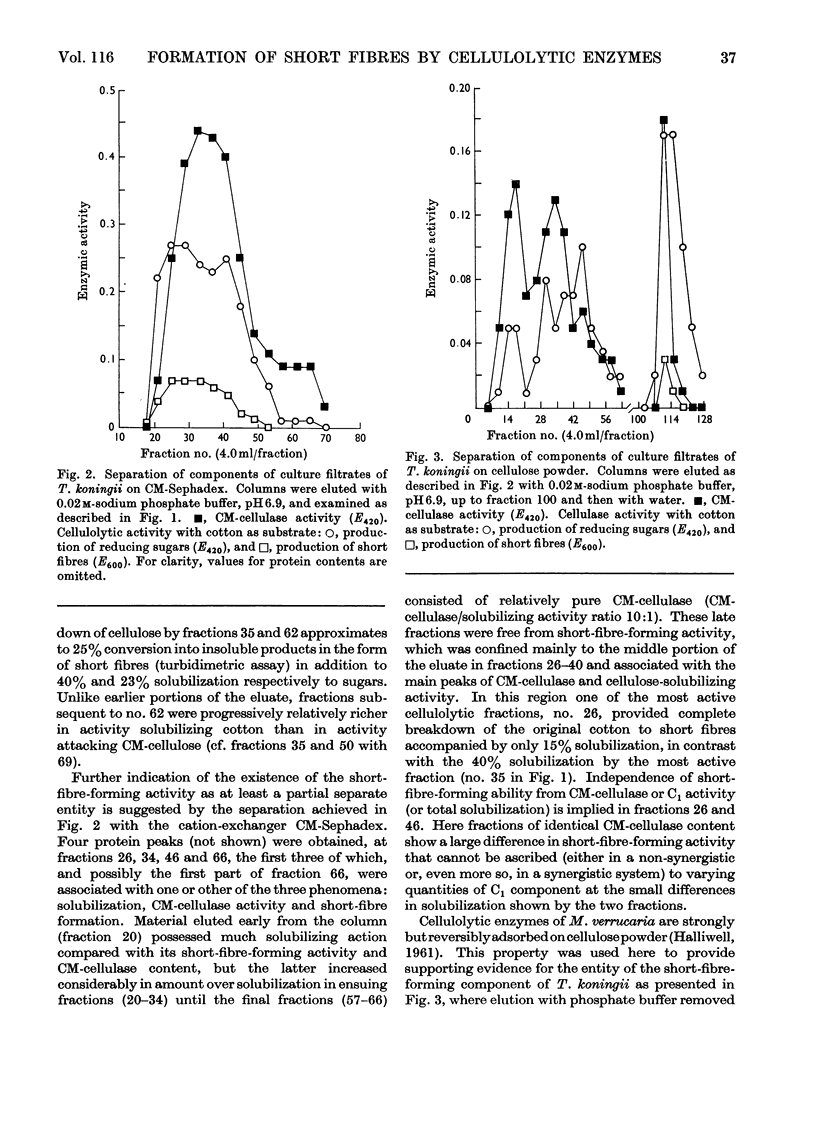
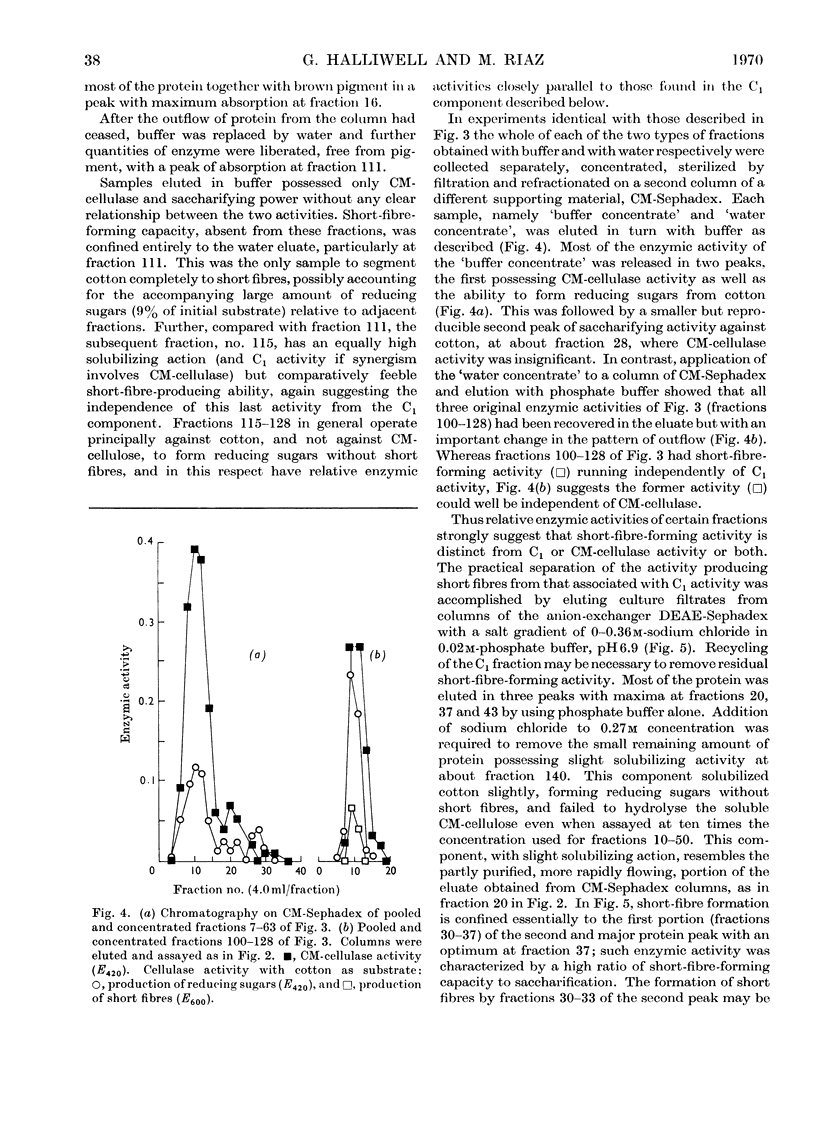
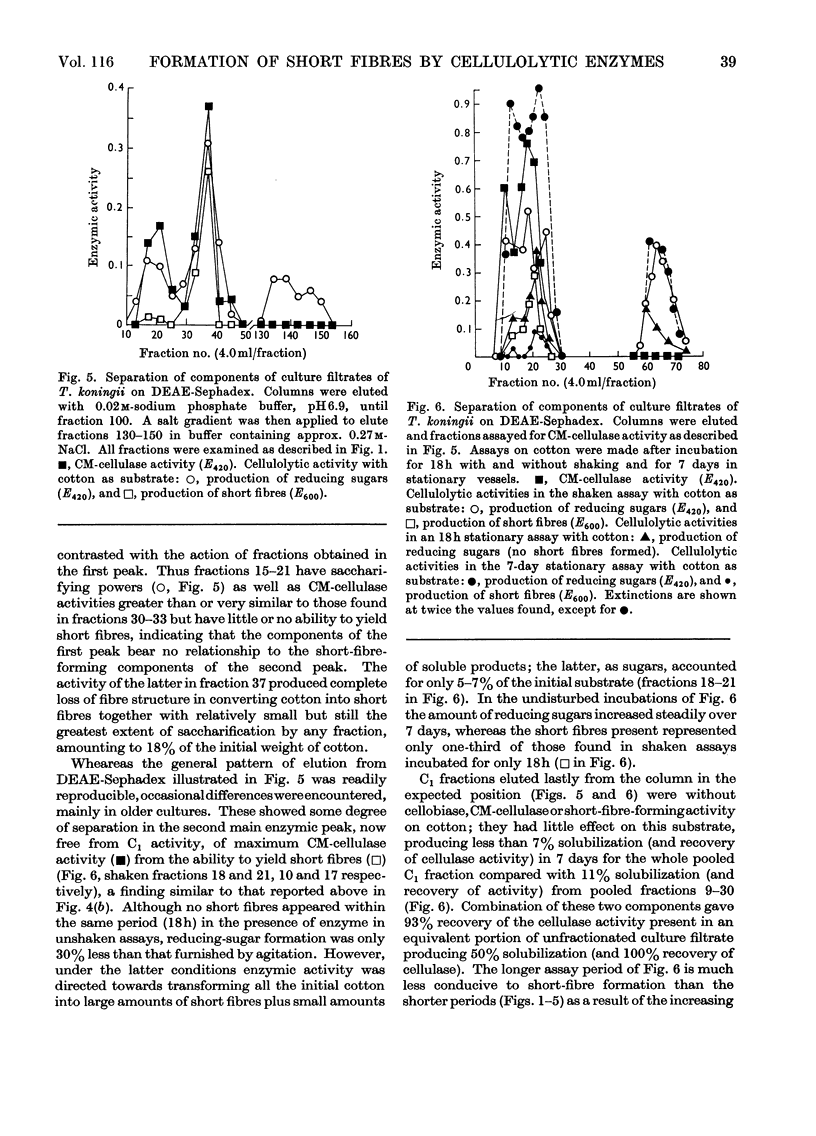
Cellulolytic enzyme components of culture filtrates of Trichoderma koningii were fractionated on ionic and non-ionic forms of Sephadex and on cellulose powder (Whatman) and examined for their ability to hydrolyse soluble carboxymethyl-cellulose, and to saccharify, solubilize and form short fibres from native undegraded cellulose of the type found in cotton. DEAE-Sephadex provided two CM-cellulase components and a C1 component; the C1 component acted weakly and solely on cotton, forming soluble products but not short fibres. The ability to form short fibres was confined almost wholly to one of the CM-cellulase components which completely degraded cotton, minimally to soluble products and extensively to short fibres. The latter action was unaffected by the presence of the other two components. The two CM-cellulase components solubilized cellulose synergistically whereas the short-fibre-forming component and C1 component were inhibitory.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HALLIWELL G. HYDROLYSIS OF FIBROUS COTTON AND REPRECIPITATED CELLULOSE BY CELLULOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM SOIL MICRO-ORGANISMS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:270–281. doi: 10.1042/bj0950270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. The action of cellulolytic enzymes from Myrothecium verrucaria. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:185–192. doi: 10.1042/bj0790185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. The breakdown of cellulose and its derivatives by enzymes from Myrothecium verrucaria. Biochem J. 1962 Oct;85:67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj0850067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G. Solubilization of native and derived forms of cellulose by cell-free microbial enzymes. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):315–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1000315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., SIU R. G. H., LEVINSON H. S. The biological degradation of soluble cellulose derivatives and its relationship to the mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):485–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.485-497.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby K., Maitland C. C. The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Separation of the components involved in the solubilization of cotton. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):716–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1040716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby K., Maitland C. C., Thompson K. V. The degradation of cotton cellulose by the extracellular cellulase of Myrothecium verrucaria. 2. The existence of an ;exhaustible' cellulase. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88(2):288–296. doi: 10.1042/bj0880288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. M. Cellulolytic enzyme system of Trichoderma koningii. Separation of components attacking native cotton. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1090217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


