Abstract
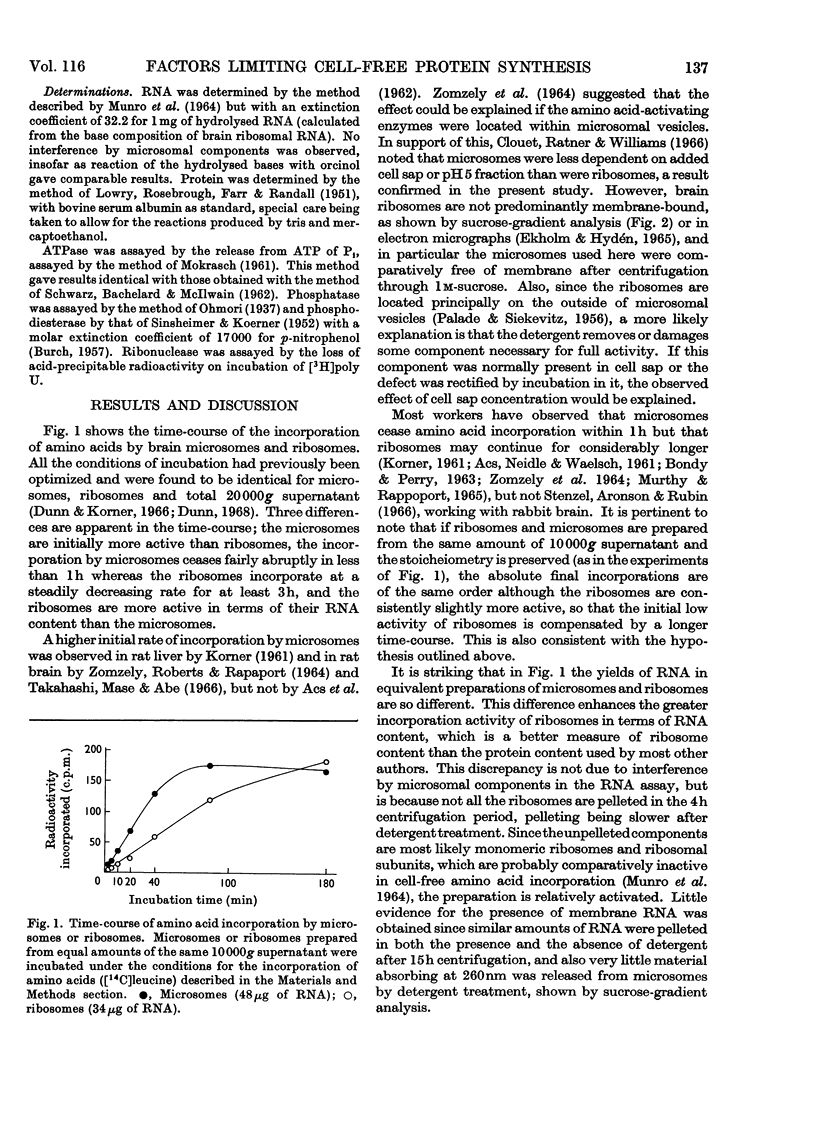
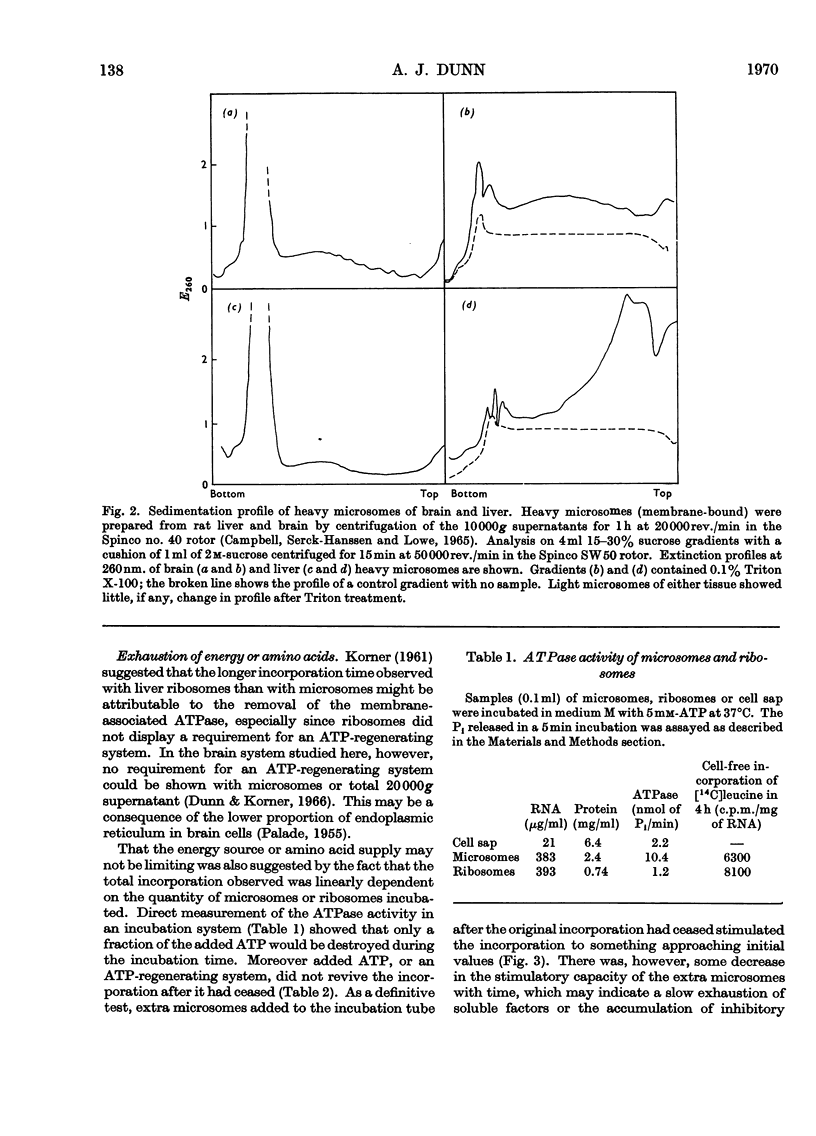
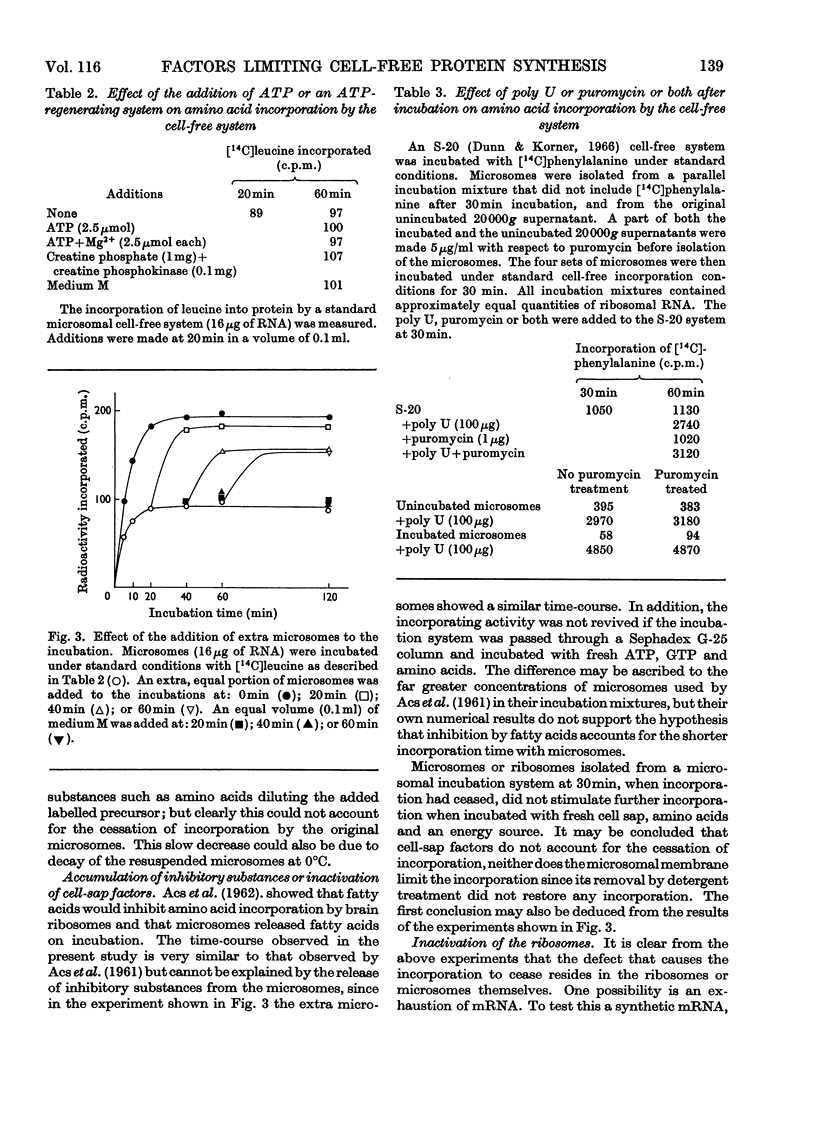
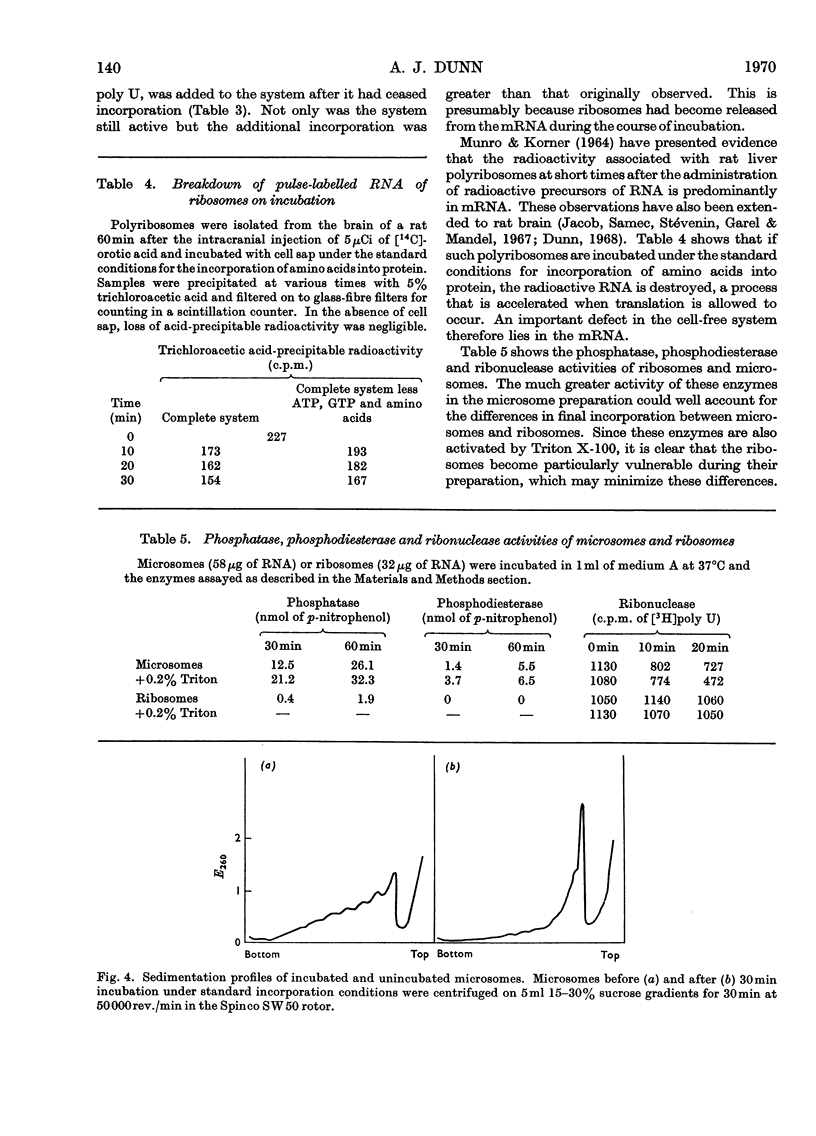
The limiting factors of a cell-free system from rat brain for incorporating amino acids into protein were studied. The initial more rapid incorporation by microsomes, as opposed to that by ribosomes, is suggested to be due to damage of the ribosomes by detergent. The defect is rectifiable by incubation of the ribosomes in cell sap, so that ribosomes eventually incorporate more amino acid than do microsomes. This may be because ribonuclease, which is associated with the microsomes but removed by detergent treatment, inactivates the microsomal system. The factor that causes incorporation by microsomes to cease abruptly within 1h is not the lack of any precursor or of adenosine triphosphate, of the inactivation of cell-sap factors or the accumulation of inhibitory substances, but is a deficiency of usable messenger ribonucleic acid. Chain initiation in the system is negligible. Ribosomes also become jammed at the end of messenger ribonucleic acid molecules, unable to terminate protein chains. This eventually leads to jammed polyribosomes, which can be partially relieved by very low concentrations of puromycin. A study of the release of polypeptides synthesized in response to the addition of synthetic messengers did not provide any conclusive information on chain-termination sequences, but did indicate some phenomena that were artifacts. It is concluded that ribonuclease action is sufficient to account for all the deficiencies of the cell-free system, but a lack of chain initiation may be a contributory factor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACS G., NEIDLE A., SCHNEIDERMAN N. The effect of fatty acids on amino acid incorporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:373–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90582-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ACS G., NEIDLE A., WAELSCH H. Brain ribosomes and amino acid incorporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 24;50:403–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLEN D. W., ZAMECNIK P. C. The effect of puromycin on rabbit reticulocyte ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:865–874. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90899-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONDY S. C., PERRY S. V. INCORPORATION OF LABELLED AMINO ACIDS IN THE SOLUBLE PROTEIN FRACTION OF RABBIT BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1963 Aug;10:603–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb05058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Goodman H. M., Menninger J. R., Smith J. D. Polypeptide chain termination using synthetic polynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Polypeptide chain termination: an active process. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N., Serck-Hanssen G., Lowe E. Studies on the protein-synthesizing activity of the ribosomes of rat liver. The activity of free polysomes. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):422–431. doi: 10.1042/bj0970422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouet D. H., Ratner M., Williams N. [14C]leucine incorporation into brain ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 20;123(1):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus J. C., Schapira G. Action du fluorure de sodium sur la synthèse acellulaire d'hémoglobine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):601–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekholm R., Hydén H. Polysomes from microdissected fresh neurons. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Oct;13(3):269–280. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER R. S., WAHBA A. J., BASILIO C., MILLER R. S., LENGYEL P., SPEYER J. F. Synthetic polynucleotides and the amino acid code. VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2087–2094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT W. Polypeptide synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. The polypeptide chain and S-RNA. J Mol Biol. 1963 May;6:389–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTIN T., ABRAHAM K. A. AMINO ACID INCORPORATION AND PROTEIN SOLUBILIZATION BY RAT-LIVER RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN PARTICLES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 22;87:232–246. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTIN T. Solubilization of labelled protein from pre-labelled rat-liver ribonucleoprotein particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:916–929. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter A. R., Korner A. The response of rat liver polysomes to added homopolynucleotides: the removal of inactive ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;179(1):115–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Samec J., Stevenin J., Garel J. P., Mandel P. Polysomes and polysomal RNA of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1967 Feb;14(2):169–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb05889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNER A. Studies on incorporation of amino acids into protein in isolated rat-liver ribosomes. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:168–178. doi: 10.1042/bj0810168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khairallah E. A., Pitot H. C. 3',5'-Cyclic AMP and the release of polysome-bound proteins in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 17;29(3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Adams D. H. Microsomal components in relation to amino acid incorporation by preparations from the developing rat brain. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):229–238. doi: 10.1042/bj1040229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNRO A. J., KORNER A. MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID OF RAT LIVER CYTOPLASM. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1194–1197. doi: 10.1038/2011194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURTHY M. R., RAPPOPORT D. A. BIOCHEMISTRY OF THE DEVELOPING RAT BRAIN. VI. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF RIBOSOMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin L. I., Rich A. Partial resistance of nascent polypeptide chains to proteolytic digestion due to ribosomal shielding. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):329–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro A. J., Jackson R. J., Korner A. Studies on the nature of polysomes. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):289–299. doi: 10.1042/bj0920289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M., Mosteller R. D., Hardesty B. NaF inhibition of the initial binding of aminoacyl-sRNA to reticulocyte ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):701–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ A., BACHELARD H. S., McIL WAIN H. The sodium-stimulated adenosine-triphosphatase activity and other properties of cerebral microsomal fractions and subfractions. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:626–637. doi: 10.1042/bj0840626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINSHEIMER R. L., KOERNER J. F. A purification of venom phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRETTON A. O., BRENNER S. MOLECULAR CONSEQUENCES OF THE AMBER MUTATION AND ITS SUPPRESSION. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:456–465. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel K. H., Aronson R. F., Rubin A. L. In vitro synthesis of brain protein. II. Properties of the complete system. Biochemistry. 1966 Mar;5(3):930–936. doi: 10.1021/bi00867a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Mase K., Abe S. The protein biosynthesis in a ribosomal system of the brain. J Biochem. 1966 Oct;60(4):363–371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takanami M., Yan Y. The release of polypeptide chains from ribosomes in cell-free amino acid-incorporating systems by specific combinations of bases in synthetic polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Nov;54(5):1450–1458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.5.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZOMZELY C. E., ROBERTS S., RAPAPORT D. REGULATION OF CEREBRAL METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS-3. CHARACTERISTICS OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN OF MICROSOMAL AND RIBOSOMAL PREPARATIONS OF RAT CEREBRAL CORTEX. J Neurochem. 1964 Aug;11:567–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb11454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


