Abstract
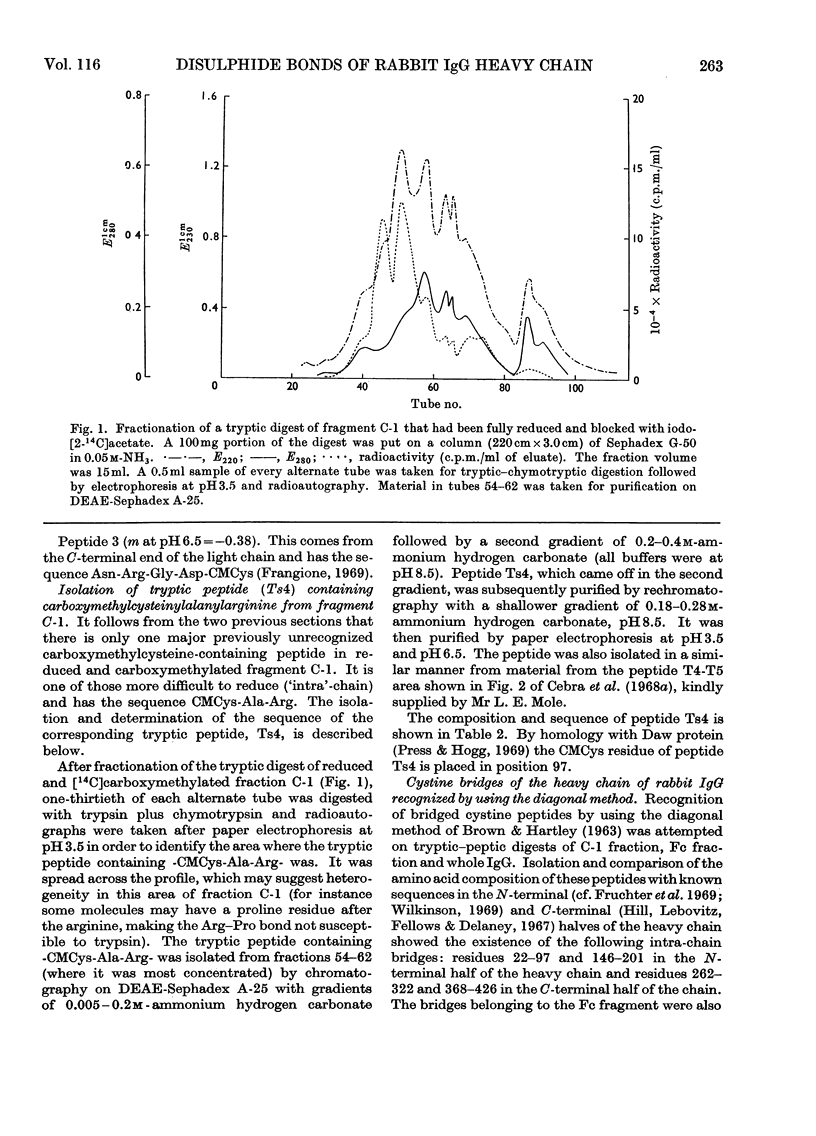
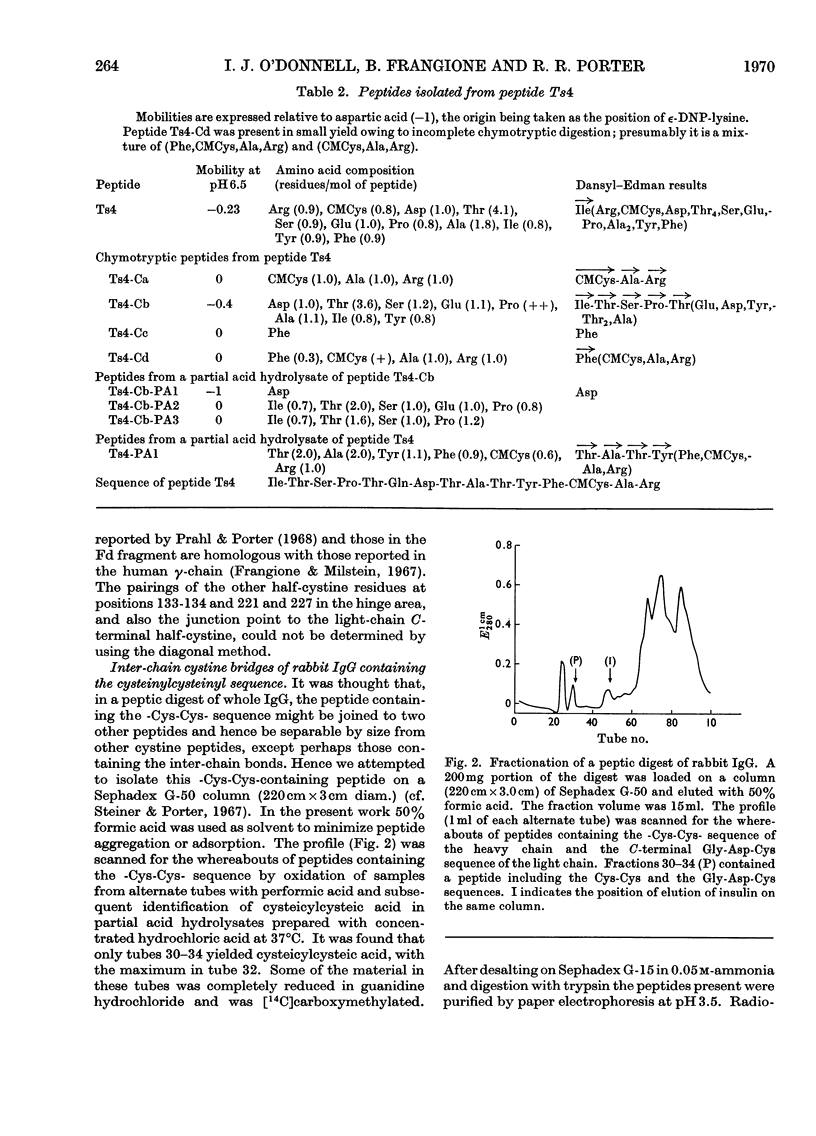
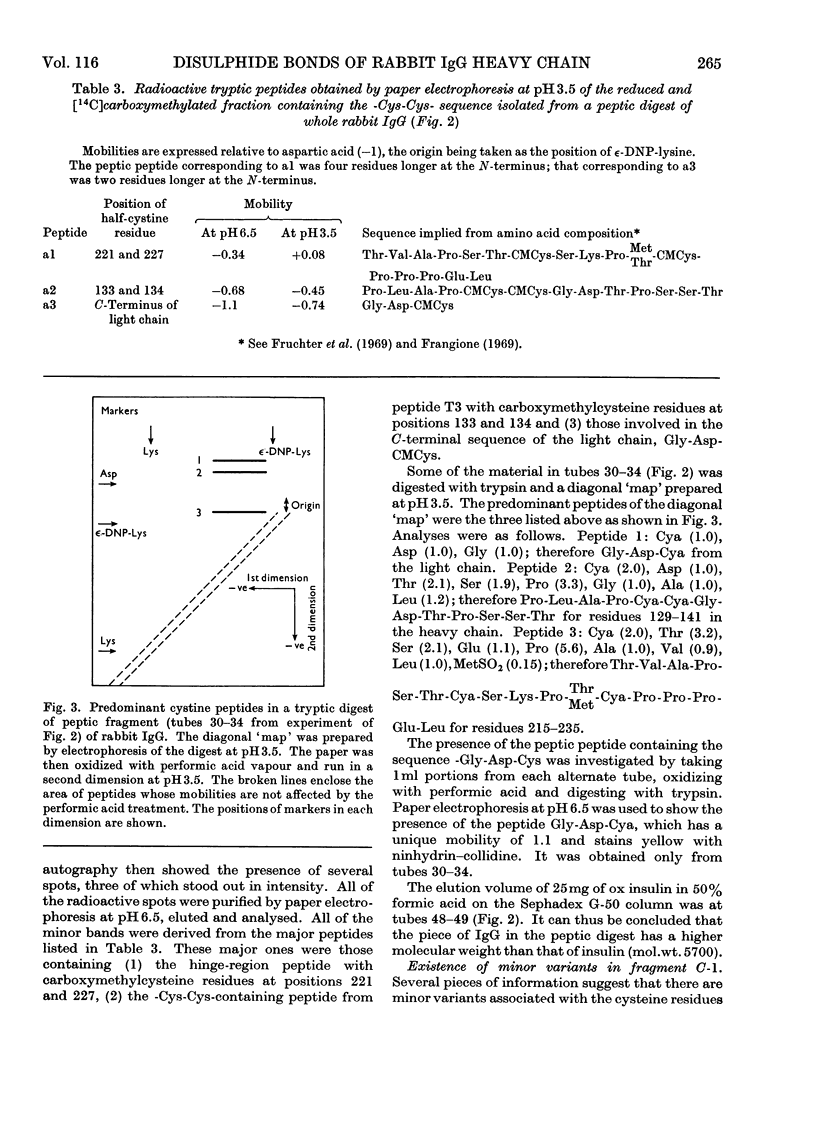
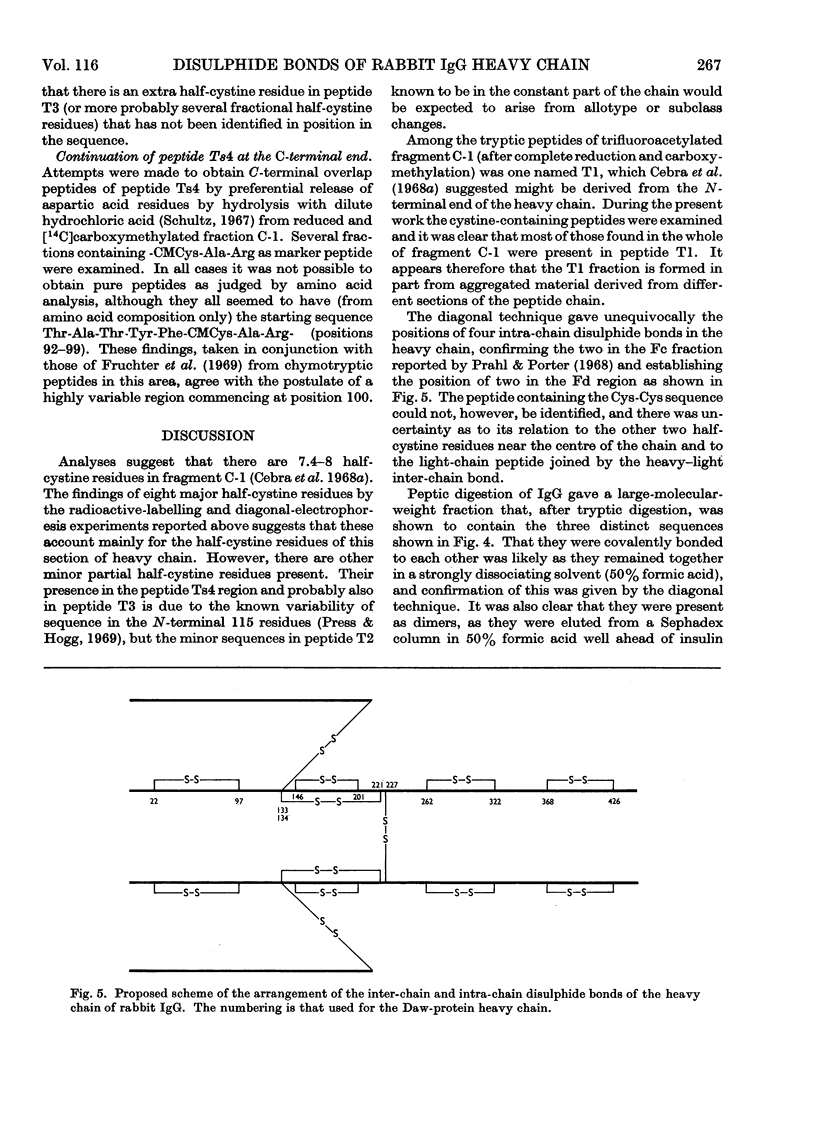
Six peptides containing eight half-cystine residues were isolated in good yield, after either oxidation or reduction and carboxymethylation of fragment C-1, which contains the N-terminal half of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. The sequences of five of these peptides had been reported previously (Cebra, Steiner & Porter, 1968b; Wilkinson, 1969) and that of the sixth was established. Other peptides containing half-cystine residues were isolated in much lower yield and are presumed to be derived from minor sequence variants. The cystine-containing peptides from enzymic digests of whole immunoglobulin G and Fc fraction were studied by several techniques and the results obtained enable us to put forward a scheme of the arrangement of the inter- and intra-chain disulphide bonds.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cebra J. J., Givol D., Porter R. R. Common peptides from the N-terminal half of heavy chain of immunoglobulin G from normal rabbit serum and a specific antibody. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):69–77. doi: 10.1042/bj1070069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Steiner L. A., Porter R. R. The partial sequence of two large peptides from the N-terminal half of heavy chains from normal rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):79–88. doi: 10.1042/bj1070079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consden R., Gordon A. H. A study of the peptides of cystine in partial hydrolysates of wool. Biochem J. 1950 Jan;46(1):8–20. doi: 10.1042/bj0460008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B. Correlation of the c-terminal sequence of rabbit light chains with allotypes. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(5):341–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C. Disulphide bridges of immunoglobin G-1 heavy chains. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):939–941. doi: 10.1038/216939b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C., Pink J. R. Structural studies of immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):145–148. doi: 10.1038/221145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C. Variations in the S-S bridges of immunoglobins G: interchain disulfide bridges of gamma G3 myeloma proteins. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):893–906. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Jackson S. A., Mole L. E., Porter R. R. Sequence studies of the Fd section of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):249–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1160249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER J. L., NISONOFF A. DISSOCIATION OF RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULIN INTO HALF-MOLECULES AFTER REDUCTION OF ONE LABILE DISULFIDE BOND. Biochemistry. 1964 Jun;3:863–869. doi: 10.1021/bi00894a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W., Porter R. R. Allotype-related sequence variation of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(6):753–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1070753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press E. M., Piggot P. J., Porter R. R. The N- and c-terminal amino acid sequences of the heavy chain from a pathological human immunoglobulin IgG. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):356–366. doi: 10.1042/bj0990356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L. A., Porter R. R. The interchain disulfide bonds of a human pathological immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3957–3970. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. Variation in the N-terminal sequence of heavy chains of immunoglobulin G from rabbits of different allotype. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):173–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1120173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


