Abstract
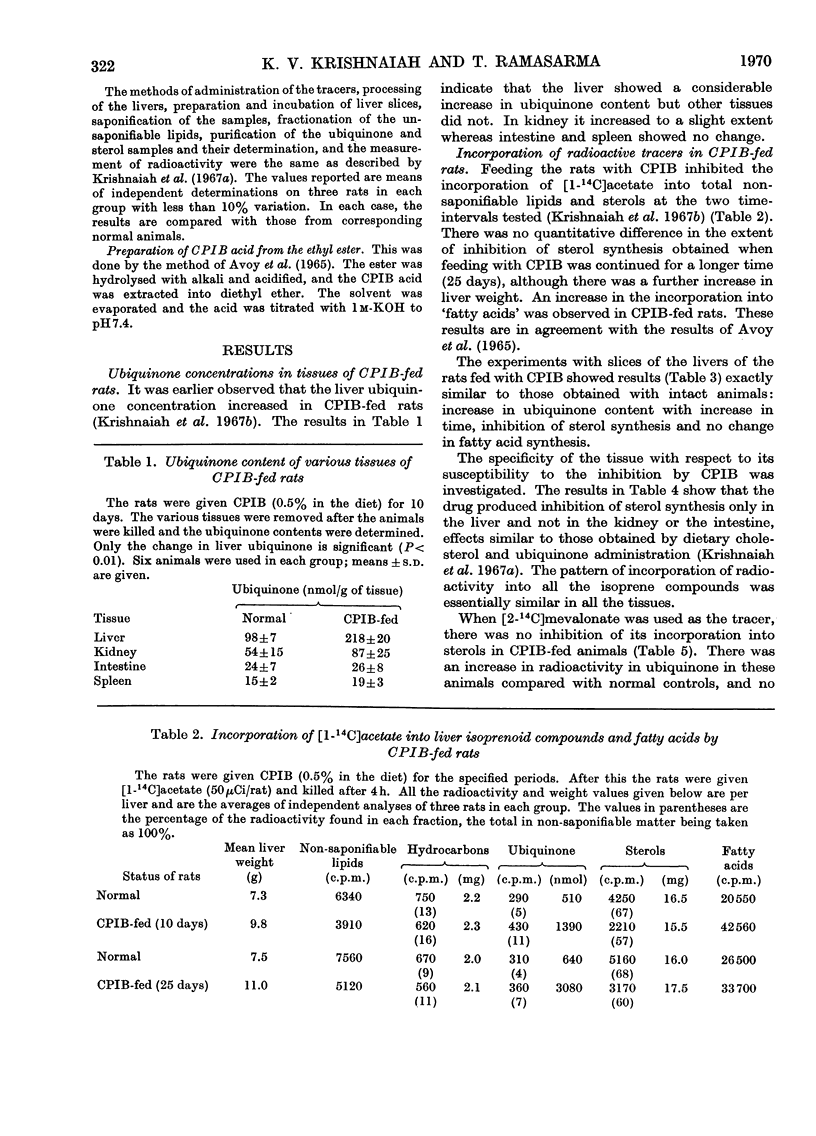
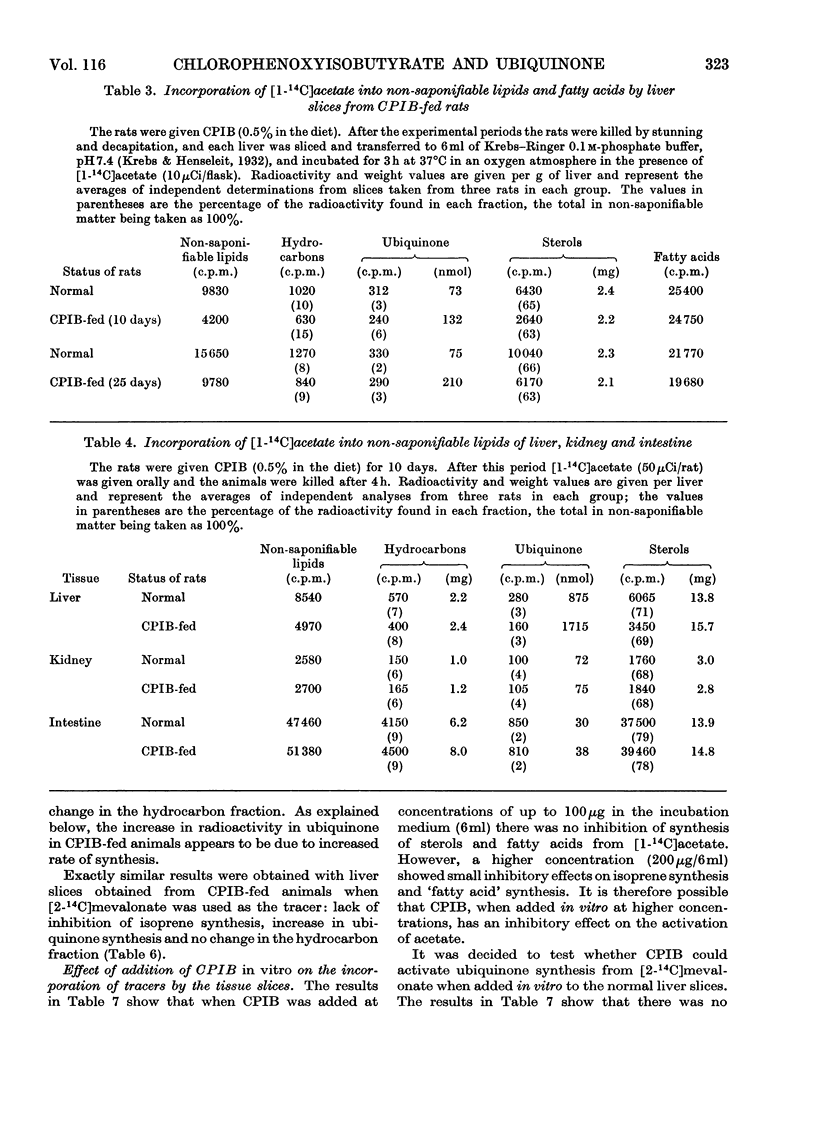
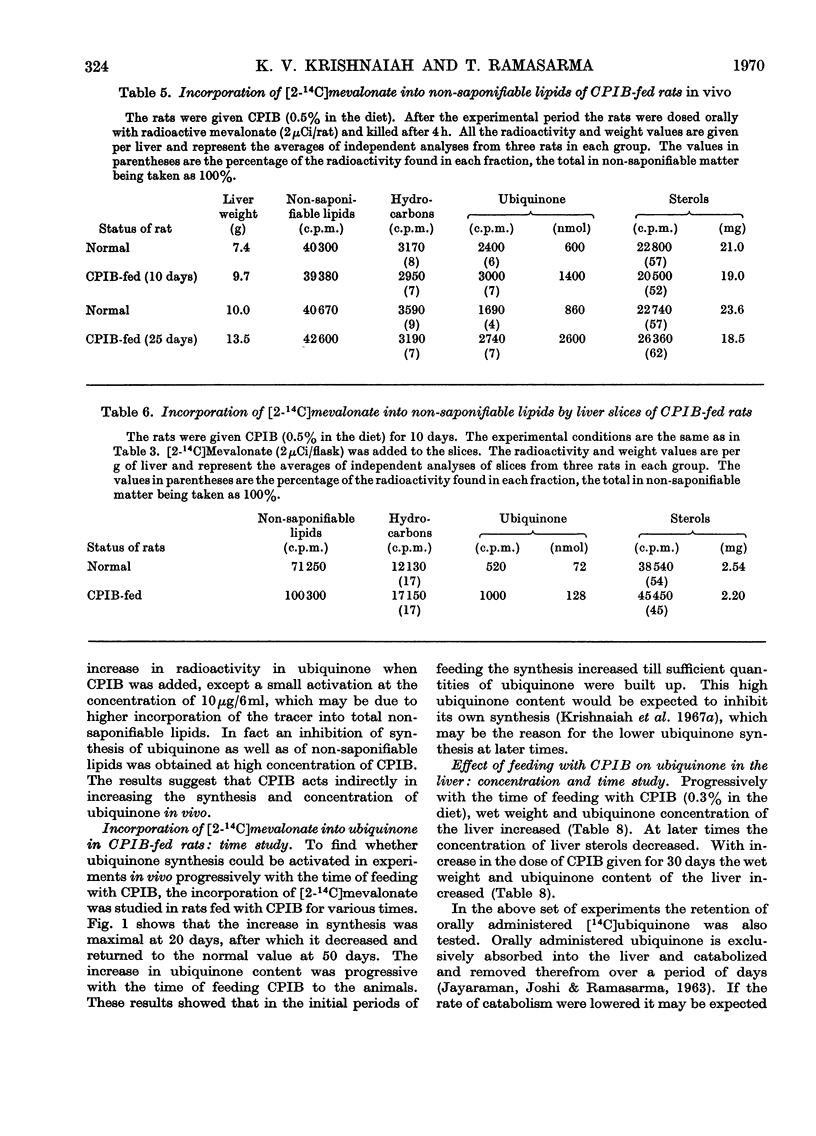
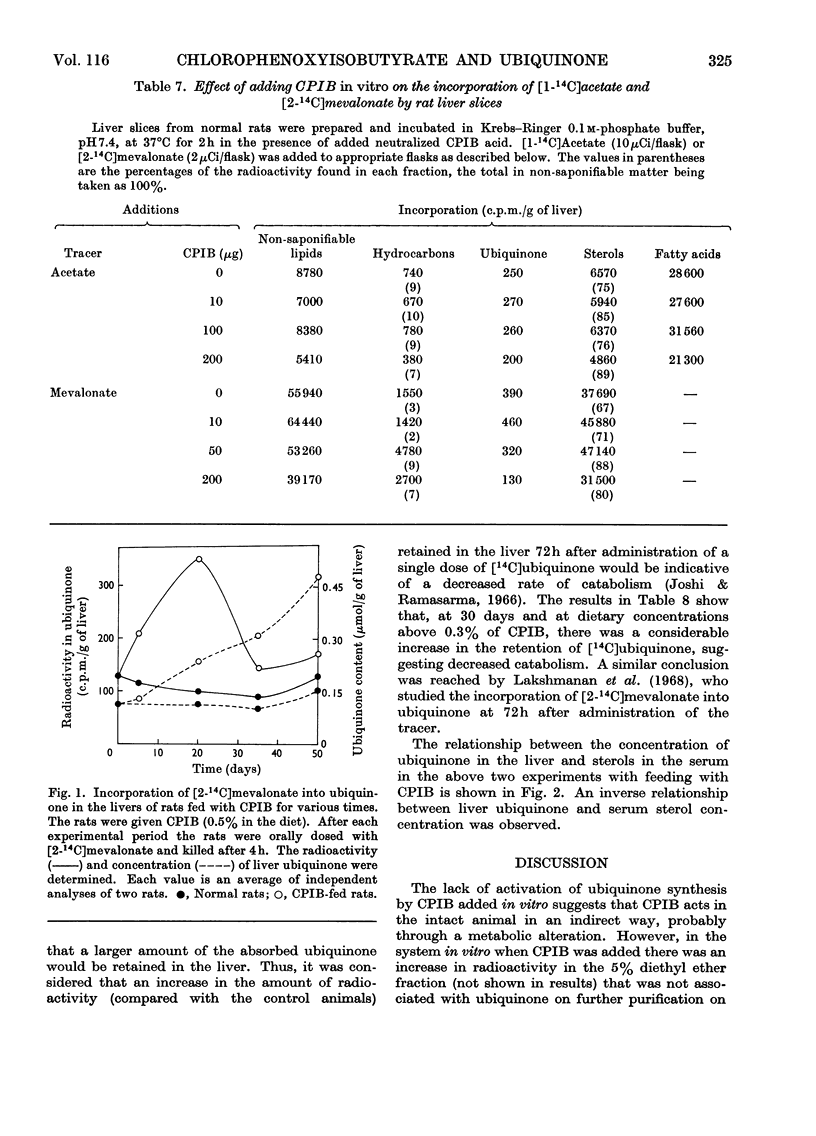
1. Feeding of α-p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate (CPIB) to rats increased ubiquinone concentration in the liver but not in other tissues. The increase was progressive with the time of feeding and related to the concentration of CPIB in the diet. 2. Incorporation of [1-14C]acetate, but not of [2-14C]mevalonate, into sterols in the liver in vivo or by liver slices in vitro was decreased on feeding the rats with CPIB. However, incorporation of mevalonate into ubiquinone increased. 3. CPIB, when added in low concentrations to liver slices, had no effect on isoprene synthesis from acetate; higher concentrations, however, were inhibitory. 4. No activation of ubiquinone synthesis from mevalonate was observed when CPIB was added to the liver slices synthesizing ubiquinone. 5. The increase in ubiquinone in CPIB-fed animals appears to be due to increased synthesis in the initial stages and to decreased catabolism in the later stages. 6. An inverse relationship was found between the concentration of ubiquinone in the liver and the serum sterol concentration in CPIB-fed rats.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVOY D. R., SWYRYD E. A., GOULD R. G. EFFECTS OF ALPHA-P-CHLOROPHENOXYISOBUTYRYL ETHYL ESTER (CPIB) WITH AND WITHOUT ANDROSTERONE ON CHOLESTEROL BIOSYNTHESIS IN RAT LIVER. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:369–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAYARAMAN J., JOSHI V. C., RAMASARMA T. SOME ASPECTS OF THE METABOLISM OF COENZYME Q IN THE RAT. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:369–373. doi: 10.1042/bj0880369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSHI V. C., JAYARAMAN J., RAMASARMA T. Tissue concentrations of conenzyme Q, ubichromenol and tocopherol in relation to protein status in the rat. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:25–31. doi: 10.1042/bj0880025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi V. C., Ramasarma T. Biosynthesis of ubiquinone and ubichromenol in vitamin A-deficient rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaiah K. V., Inamdar A. R., Ramasarma T. Regulation of steroidogenesis by ubiquinone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 May 25;27(4):474–478. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaiah K. V., Joshi V. C., Ramasarma T. Effect of dietary cholesterol and ubiquinone on isoprene synthesis in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Jul;121(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan M. R., Phillips W. E., Brien R. L. Effect of p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate (CPIB) fed to rats on hepatic biosynthesis and catabolism of ubiquinone. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):353–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORP J. M., WARING W. S. Modification of metabolism and distribution of lipids by ethyl chlorophenoxyisobutyrate. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:948–949. doi: 10.1038/194948a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


