Abstract
Cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo californica have been probed with the atomic force microscope in aqueous buffers to map and measure their elastic properties. Elastic properties were mapped with a new atomic force microscope technique known as force mapping. Force mapping of vesicles showed that the centers of the vesicles are harder or stiffer than the peripheral areas in the three buffers that were investigated. These were an isoosmotic buffer, a hypoosmotic buffer, and an isoosmotic buffer with 5 mM CaCl2 added. The hardness of the vesicular centers was quantified by calculation of the elastic modulus. Elastic moduli were in the range of 2-13 × 105 Pa. Vesicular centers were hardest in calcium-containing buffer and softest in isoosmotic buffer. Hypotheses are presented for the composition and function of the hard centers.
Full text
PDF

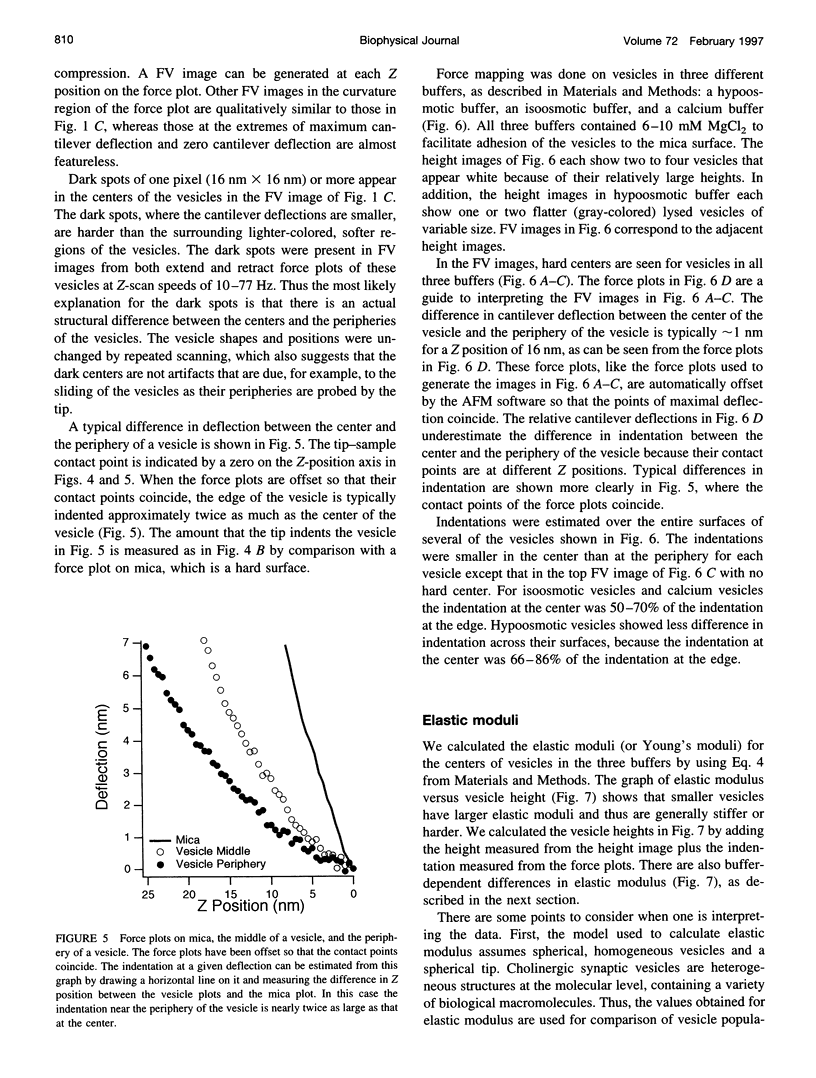
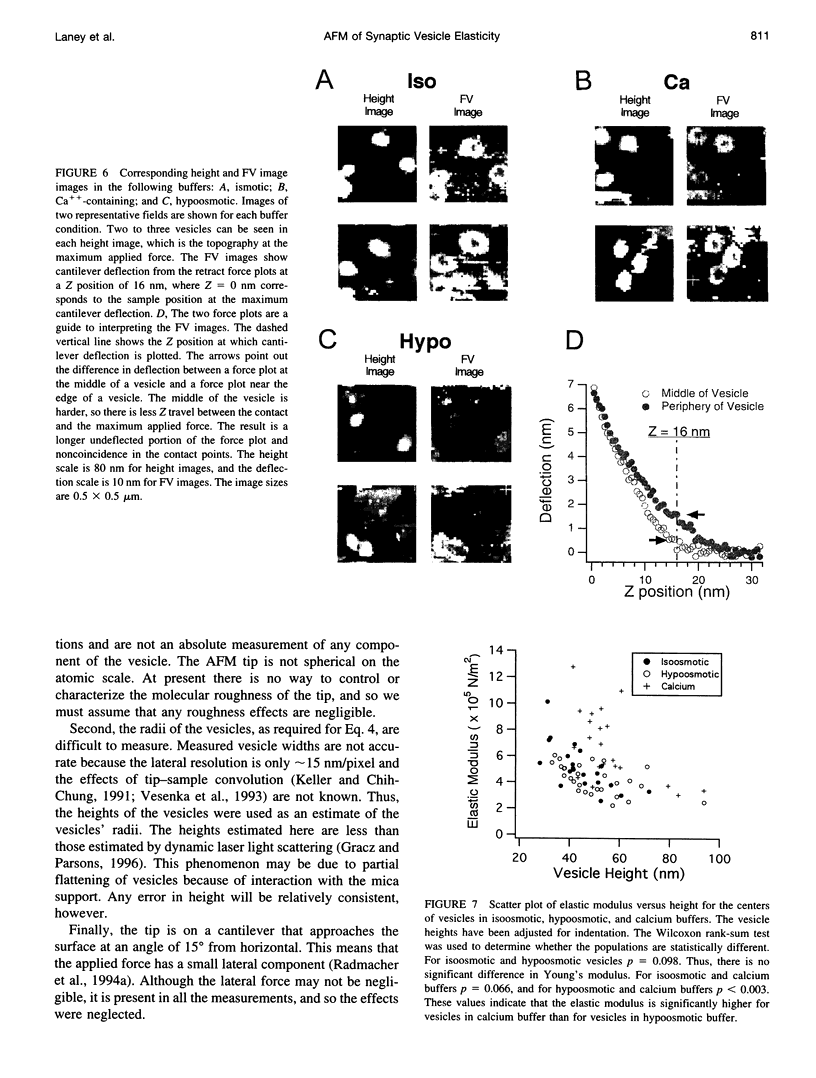


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyne A. F., Bohan T. P., Williams T. H. Effects of calcium-containing fixation solutions on cholinergic synaptic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):780–795. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C., Rivetti C. Visualizing protein-nucleic acid interactions on a large scale with the scanning force microscope. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1996;25:395–429. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.25.060196.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Synaptic vesicle biogenesis, docking, and fusion: a molecular description. Physiol Rev. 1996 Jan;76(1):1–29. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1996.76.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracz L. M., Parsons S. M. Purification of active synaptic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo californica and comparison to reserve vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Feb 8;1292(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(95)00222-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Hoh J. H. Biomolecular imaging with the atomic force microscope. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:115–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Laney D. E., Bezanilla M., Sinsheimer R. L., Hansma P. K. Applications for atomic force microscopy of DNA. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80343-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Haydon P. G., Sakaguchi D. S. Actin filament dynamics in living glial cells imaged by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1944–1946. doi: 10.1126/science.1411511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. K., Wong K. S., Kim J. J. Binding of calcium to glycosaminoglycans: an equilibrium dialysis study. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90437-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Walker J. H., Stadler H., Whittaker V. P. Further evidence that glycosaminoglycan specific to cholinergic synaptic vesicles recycles during electrical stimulation of the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;224(3):685–688. doi: 10.1007/BF00213763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Walker J. H., Stadler H., Whittaker V. P. Immunohistochemical localization of a synaptic-vesicle antigen in a cholinergic neuron under conditions of stimulation and rest. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;223(1):117–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00221503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. Searching for drugs that combat Alzheimer's. Science. 1996 Jul 5;273(5271):50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miklossy J., Kasas S., Janzer R. C., Ardizzoni F., Van der Loos H. Further ultrastructural evidence that spirochaetes may play a role in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport. 1994 Jun 2;5(10):1201–1204. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199406020-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Fujime S. Regulation by Ca2+ of membrane elasticity of bovine chromaffin granules. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuhira V., Hasegawa H., Notoya M. Microwave fixation and localization of calcium in synaptic vesicles. J Neurosci Methods. 1994 Dec;55(2):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(94)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noremberg K., Parsons S. M. Regulation of the vesamicol receptor in cholinergic synaptic vesicles by acetylcholine and an endogenous factor. J Neurochem. 1989 Mar;52(3):913–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parducz A., Dunant Y. Transient increase of calcium in synaptic vesicles after stimulation. Neuroscience. 1993 Jan;52(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90178-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parducz A., Loctin F., Babel-Guérin E., Dunant Y. Exo-endocytotic activity during recovery from a brief tetanic stimulation: a role in calcium extrusion? Neuroscience. 1994 Sep;62(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpura V., Doyle R. T., Basarsky T. A., Henderson E., Haydon P. G. Dynamic imaging of purified individual synaptic vesicles. Neuroimage. 1995 Mar;2(1):3–7. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1995.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmacher M., Cleveland J. P., Fritz M., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Mapping interaction forces with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2159–2165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)81011-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmacher M., Fritz M., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Direct observation of enzyme activity with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1994 Sep 9;265(5178):1577–1579. doi: 10.1126/science.8079171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmacher M., Fritz M., Hansma P. K. Imaging soft samples with the atomic force microscope: gelatin in water and propanol. Biophys J. 1995 Jul;69(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79897-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmacher M., Fritz M., Kacher C. M., Cleveland J. P., Hansma P. K. Measuring the viscoelastic properties of human platelets with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1996 Jan;70(1):556–567. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79602-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A., Parsons S. M. Calmodulin stimulation of 45Ca2+ transport and protein phosphorylation in cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5783–5787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schabert F. A., Henn C., Engel A. Native Escherichia coli OmpF porin surfaces probed by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1995 Apr 7;268(5207):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.7701347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scranton T. W., Iwata M., Carlson S. S. The SV2 protein of synaptic vesicles is a keratan sulfate proteoglycan. J Neurochem. 1993 Jul;61(1):29–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shroff S. G., Saner D. R., Lal R. Dynamic micromechanical properties of cultured rat atrial myocytes measured by atomic force microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jul;269(1 Pt 1):C286–C292. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.1.C286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao N. J., Lindsay S. M., Lees S. Measuring the microelastic properties of biological material. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):1165–1169. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81692-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenka J., Manne S., Giberson R., Marsh T., Henderson E. Colloidal gold particles as an incompressible atomic force microscope imaging standard for assessing the compressibility of biomolecules. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):992–997. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81171-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Obrocki J., Zimmermann C. W. Identification of a proteoglycan antigen characteristic of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]