Abstract
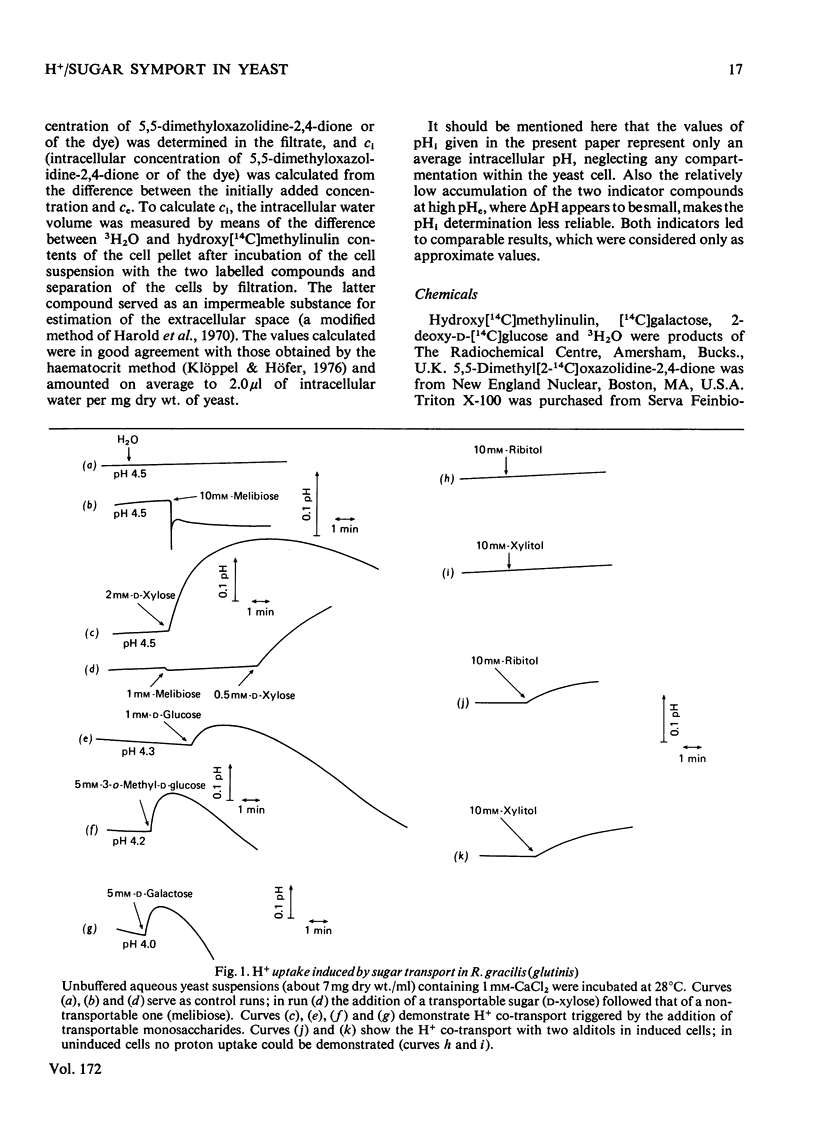
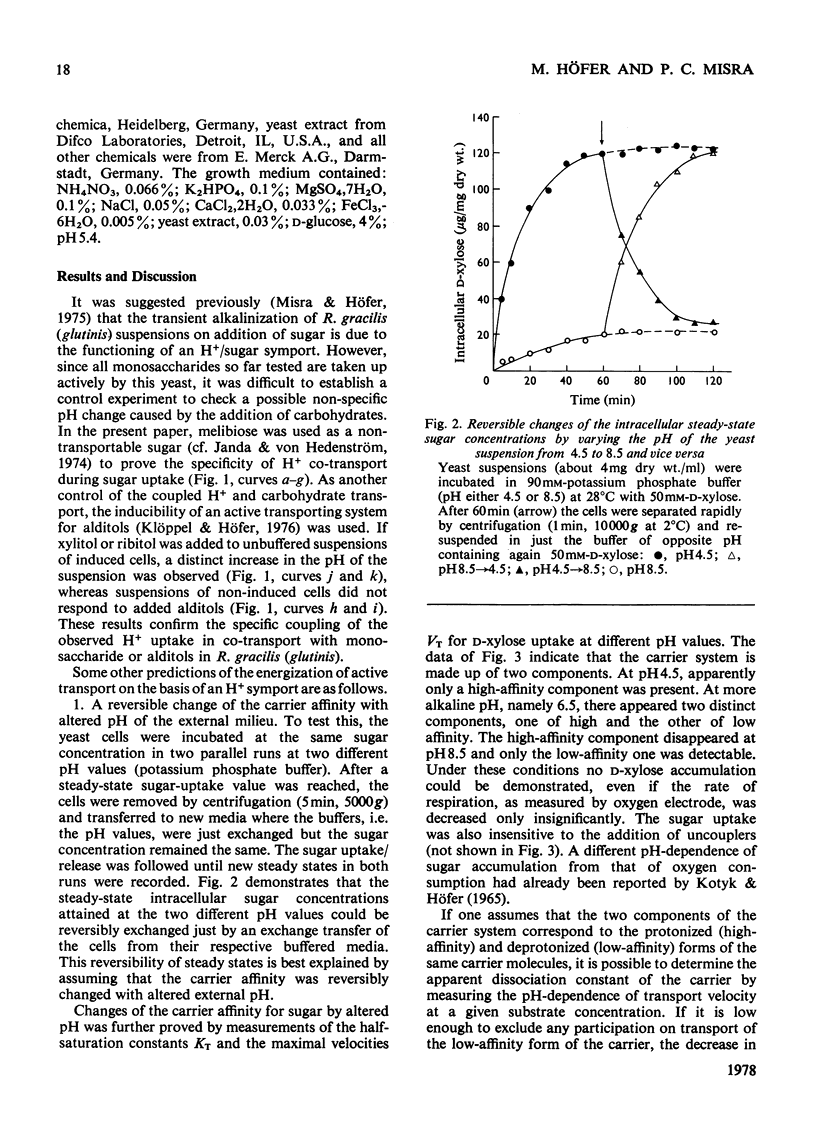
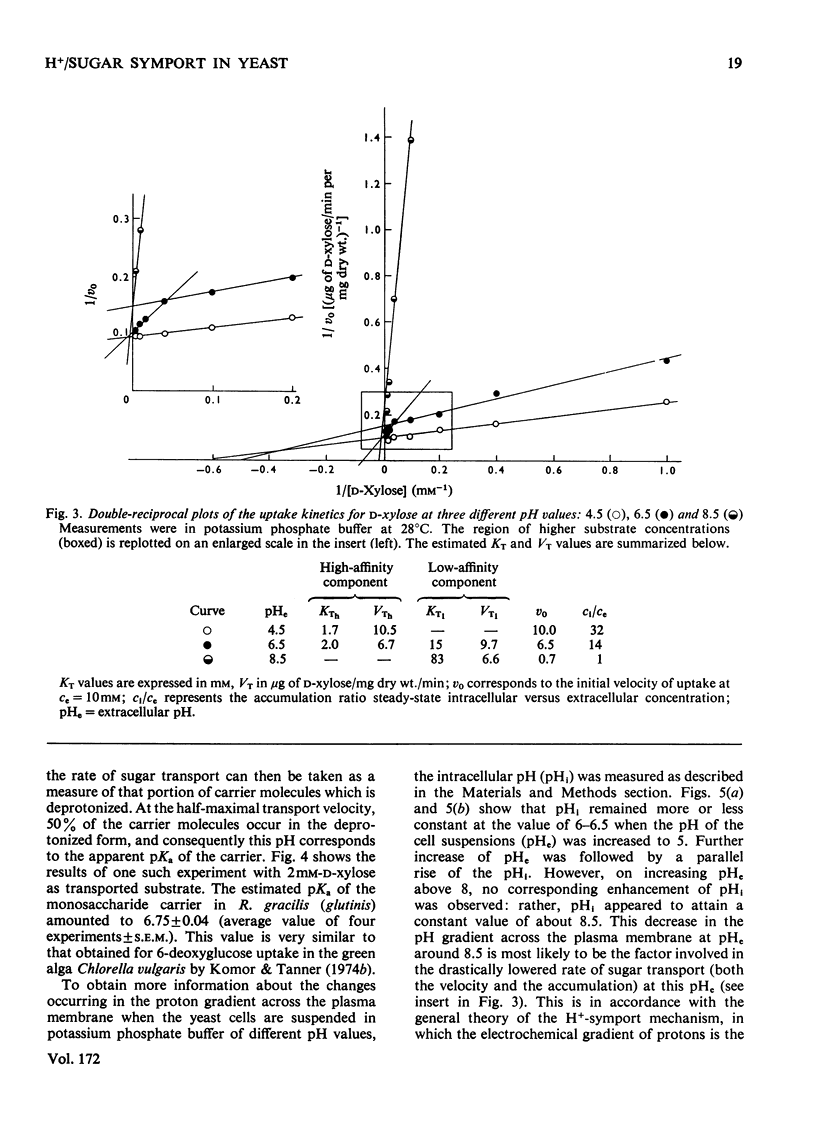
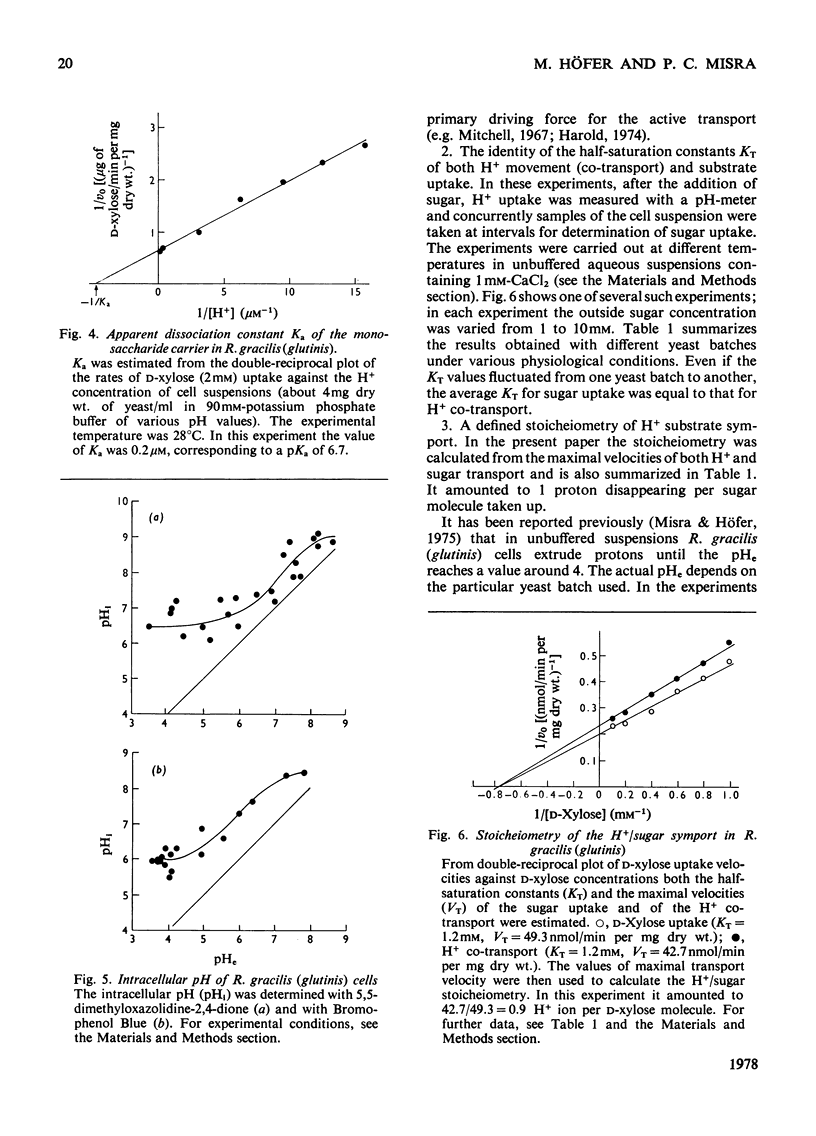
1. The uptake of monosaccharides and polyols in the obligatory aerobic yeast Rhodotorula gracilis (glutinis) was accompanied by proton uptake. 2. The half-saturation constant of transport, KT, depended on pH, changing from about 2mM at pH 4.5 to 80mM at pH8.5 for D-xylose; this change of the effective carrier affinity was reversible. 3. The apparent dissociation constant of the monosaccharide carrier was estimated at pKa 6.75. 4. At pH8.5, when the pH gradient across the cell membrane vanished, no sugar accumulation was demonstrable. 5. The half-saturation constants of sugar uptake and H+ co-transport were very similar to each other, the latter obviously being controlled by the former. 6. The H+/sugar stoicheiometry remained constant under various physiological conditions; it amounted to one H+ ion per sugar molecule taken up. 7. The data are interpreted as a strong piece of evidence in favour of the active monosaccharide transport in R. gracilis (glutinis) being an H+-symport energized by the electrochemical gradient of H+ across the plasma membrane of the yeast.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cockburn M., Earnshaw P., Eddy A. A. The stoicheiometry of the absorption of protons with phosphate and L-glutamate by yeasts of the genus Saccharomyces. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):705–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1460705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., Indge K. J., Backen K., Nowacki J. A. Interctions between potassium ions and glycine transport in the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):845–852. doi: 10.1042/bj1200845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., Nowacki J. A. Stoicheiometrical proton and potassium ion movements accompanying the absorption of amino acids by the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):701–711. doi: 10.1042/bj1220701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S. J., Rosenberg H. Succinate uptake and related proton movements in Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):647–654. doi: 10.1042/bj1520647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Chemiosmotic interpretation of active transport in bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Feb 18;227:297–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Pavlasová E., Baarda J. R. A transmembrane pH gradient in Streptococcus faecalis: origin, and dissipation by proton conductors and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K. B., Höfer M. Temperature dependence of the energy-linked monosaccharide transport across the cell membrane of Rhodotorula gracilis. J Membr Biol. 1975;21(3-4):261–271. doi: 10.1007/BF01941071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfer M., Betz A., Kotyk A. Metabolism of the obligatory aerobic yeast Rhodotorula gracilis. IV. Induction of an enzyme necessary for D-xylose catabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;252(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfer M., Kotyk A. Tight coupling of monosaccharide transport and metabolism in Rhodotorula gracilis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(3):197–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02871034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda S., von Hedenström M. Uptake of disaccharides by the aerobic yeast Rhodotorula glutinis. Hydrolysis of beta-fructosides and trehalose. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(3):273–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00455944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOTYK A. Intracellular pH of Baker's yeast. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1963 Jan;8:27–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02868762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöppel R., Höfer M. Transport und Umsatz von Polyalkoholen bei der Hefe Rhodotorula gracilis glutinis. II. Induzierbarer Transport und Abbau von Pentitolen. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Apr 1;107(3):335–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00425349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. The hexose-proton cotransport system of chlorella. pH-dependent change in Km values and translocation constants of the uptake system. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):568–581. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. The hexose-proton symport system of Chlorella vulgaris. Specificity, stoichiometry and energetics of sugar-induced proton uptake. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 2;44(1):219–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotyk A., Höfer M. Uphill transport of sugars in the yeast Rhodotorula gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 22;102(2):410–422. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra P. C., Höfer M. An energy-linked proton-extrusion across the cell membrane Rhodotorula gracilis. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaston A., Inkson C., Eddy A. A. The absorption of protons with specific amino acids and carbohydrates by yeast. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1031–1043. doi: 10.1042/bj1341031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayman C. L., Slayman C. W. Depolarization of the plasma membrane of Neurospora during active transport of glucose: evidence for a proton-dependent cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1935–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Stoicheiometry of lactose-H+ symport across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):587–592. doi: 10.1042/bj1320587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I., Mitchell P. Proton-coupled beta-galactoside translocation in non-metabolizing Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg. 1972 Aug;3(5):445–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01516082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



