Abstract
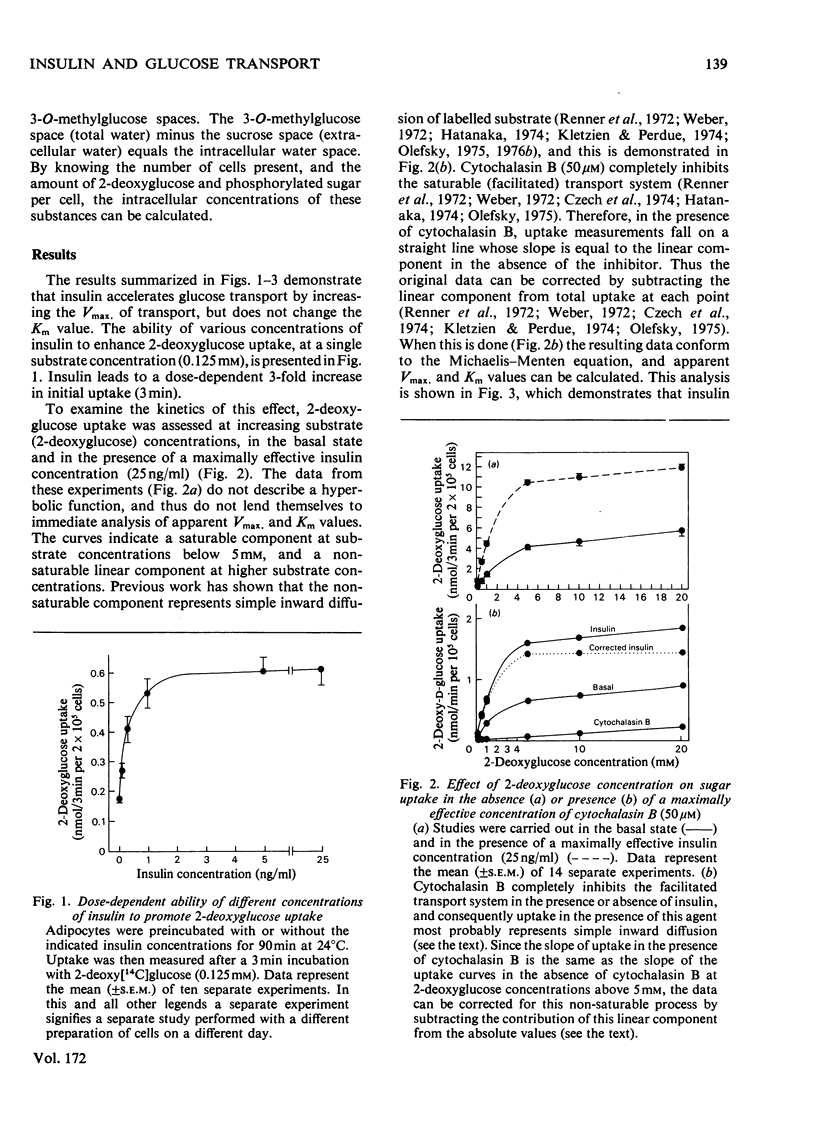
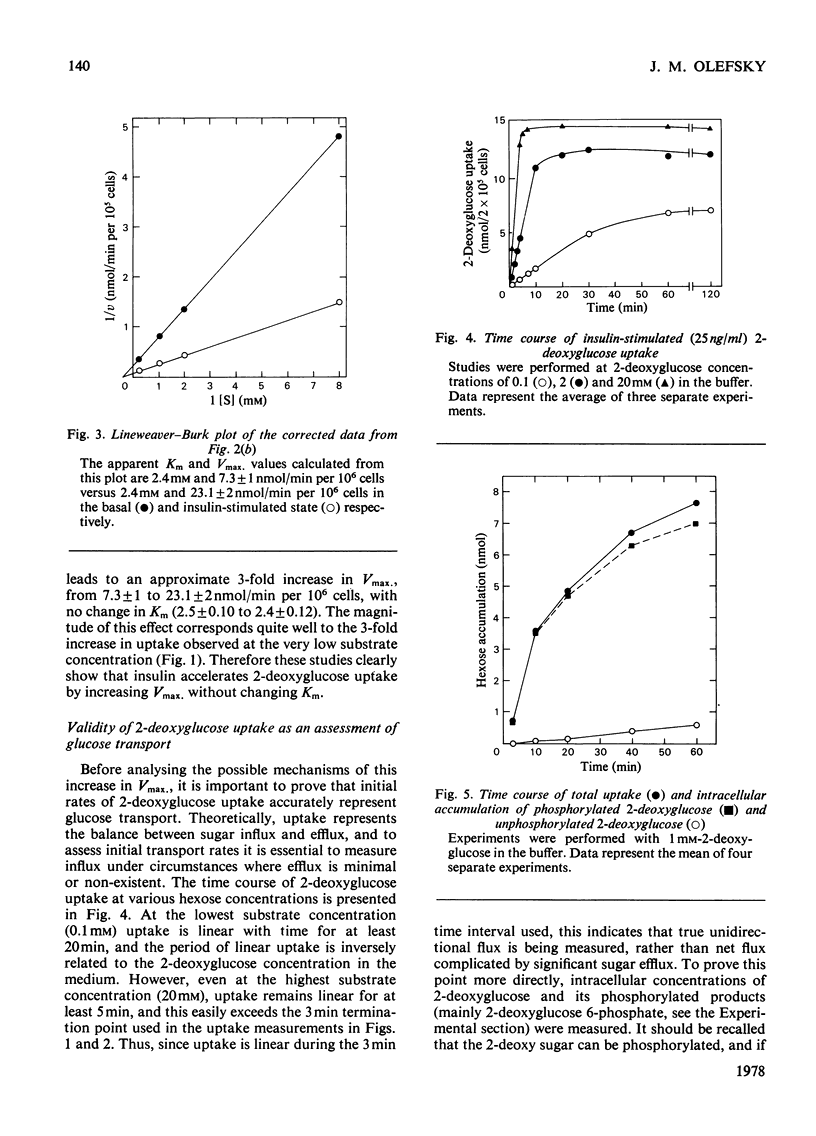
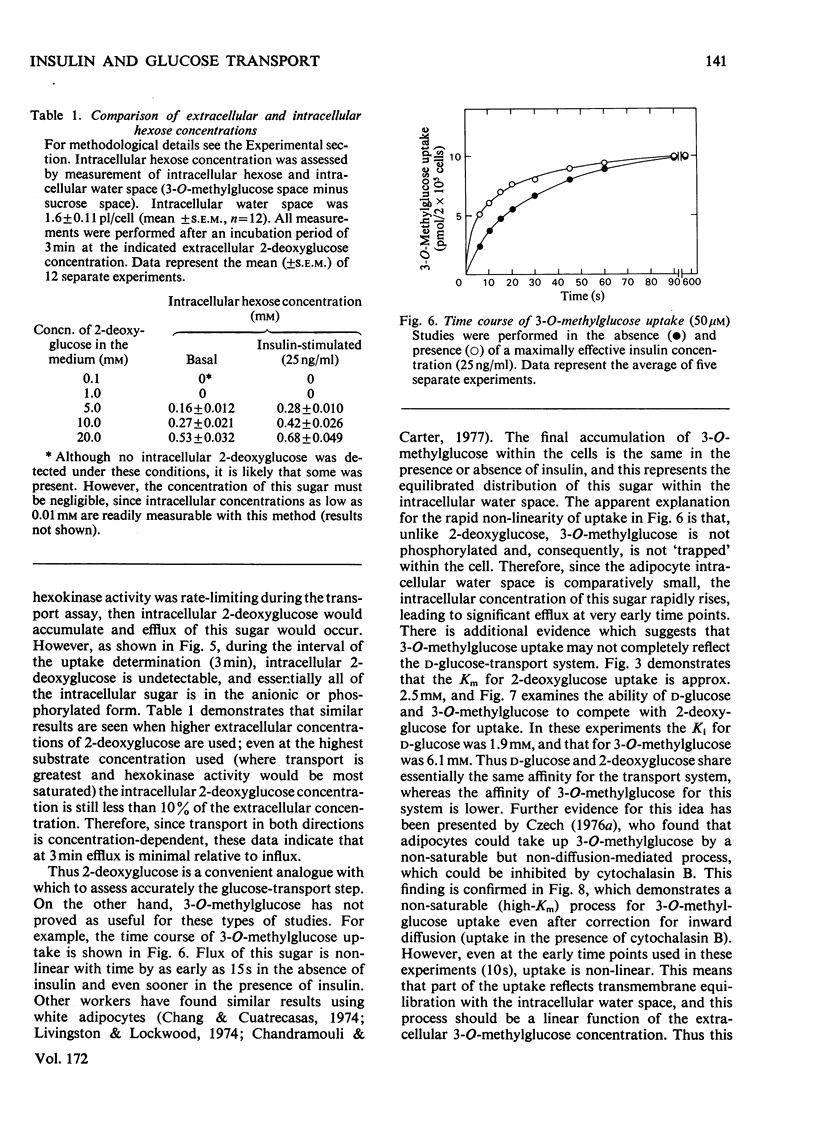
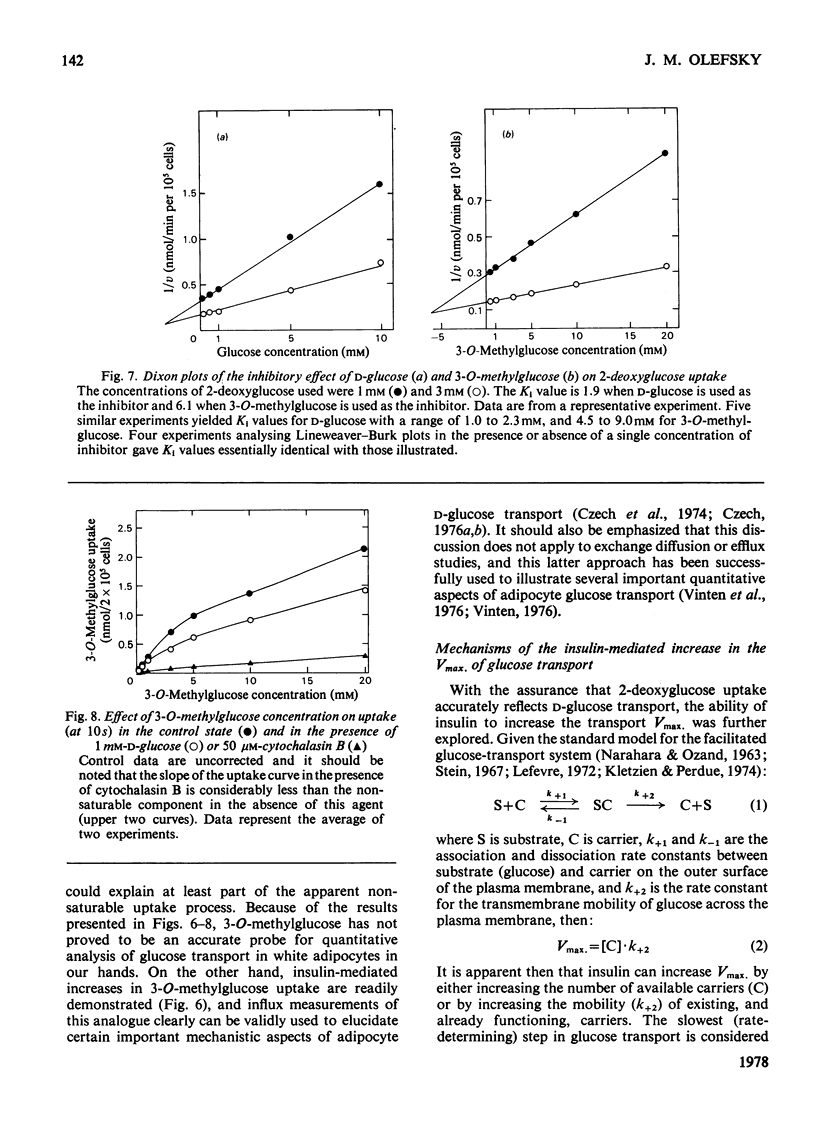
Isolated rat adipocytes were used to assess the mechanisms of the ability of insulin to accelerate glucose transport. Glucose transport was determined by measuring the initial rates of 2-deoxyglucose uptake, and at 24 degrees C insulin increased the Vmax. of transport from 7.3 +/- 1 to 23.1 +/- 2 nmol/min per 10(6) cells, but the Km value remained unchanged (2.5, cf. 2.4 mM). When the Vmax. of basal and insulin-stimulated transport was measured as a function of temperature (15-37 degrees C), parallel Arrhenius plots were obtained yielding equal activation energies of approx. 59kJ/mol. Since both processes have equal activation energies the data indicate that insulin increases Vmax. by increasing the number of available carriers rather than enhancing intrinsic activity of already functioning carriers. Since the ability of insulin to activate glucose transport did not decrease with temperature (whereas plasma-membrane fluidity declines), it is suggested that lateral diffusion of insulin receptors within the plasma-membrane bilayer is not a rat-determining step in insulin action.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandramouli V., Carter J. R., Jr Metabolic effects of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 28;496(2):278–291. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Adenosine triphosphate-dependent inhibition of insulin-stimulated glucose transport in fat cells. Possible role of membrane phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3170–3180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Cellular basis of insulin insensitivity in large rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1523–1532. doi: 10.1172/JCI108422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lynn W. S. Hexose transport in isolated brown fat cells. A model system for investigating insulin action on membrane transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5421–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Regulation of the D-glucose transport system in isolated fat cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Mar 26;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01792833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Yorke R. E., Randle P. J. Measurement of concentrations of metabolites in adipose tissue and effects of insulin, alloxan-diabetes and adrenaline. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):407–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1000407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Osterlind K., Vinten J., Gammeltoft S. A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M. Transport of sugars in tumor cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;355(1):77–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(74)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. The mobile receptor hypothesis and "cooperativity" of hormone binding. Application to insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):482–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Perdue J. F. Sugar transport in chick embryo fibroblasts. I. A functional change in the plasma membrane associated with the rate of cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3366–3374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARDS J. R., LANDAU B. R. METABOLISM OF FRUCTOSE BY ADIPOSE TISSUE, AND THE EFFECT OF INSULIN. Endocrinology. 1964 Jan;74:142–144. doi: 10.1210/endo-74-1-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Jr, Guinovart J. J., Larner J. Activation of rat adipocyte glycogen synthase by insulins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):444–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHARA H. T., OZAND P. Studies of tissue permeability. IX. The effect of insulin on the penetration of 3-methylglucose-H3 in frog muscle. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:40–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effect of dexamethasone on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1499–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI108231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effects of fasting on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation in isolated rat adipocytes: relationships between insulin receptors and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1450–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI108601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Insulin's effect on glucose oxidation independent of glucose transport. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90255-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Effects of age and obesity on insulin binding to isolated adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1486–1498. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The effects of spontaneous obesity on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):842–851. doi: 10.1172/JCI108360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. D., Plagemann P. G., Bernlohr R. W. Permeation of glucose by simple and facilitated diffusion by Novikoff rat hepatoma cells in suspension culture and its relationship to glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5765–5776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi K. K., Petricciani J. C. Concentrative accumulation (active transport) of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in primate fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinten J., Gliemann J., Osterlind K. Exchange of 3-O-methylglucose in isolated fat cells. Concentration dependence and effect of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICK A. N., DRURY D. R., NAKADA H. I., WOLFE J. B. Localization of the primary metabolic block produced by 2-deoxyglucose. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):963–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J. Hexose transport in normal and in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):2978–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


