Abstract
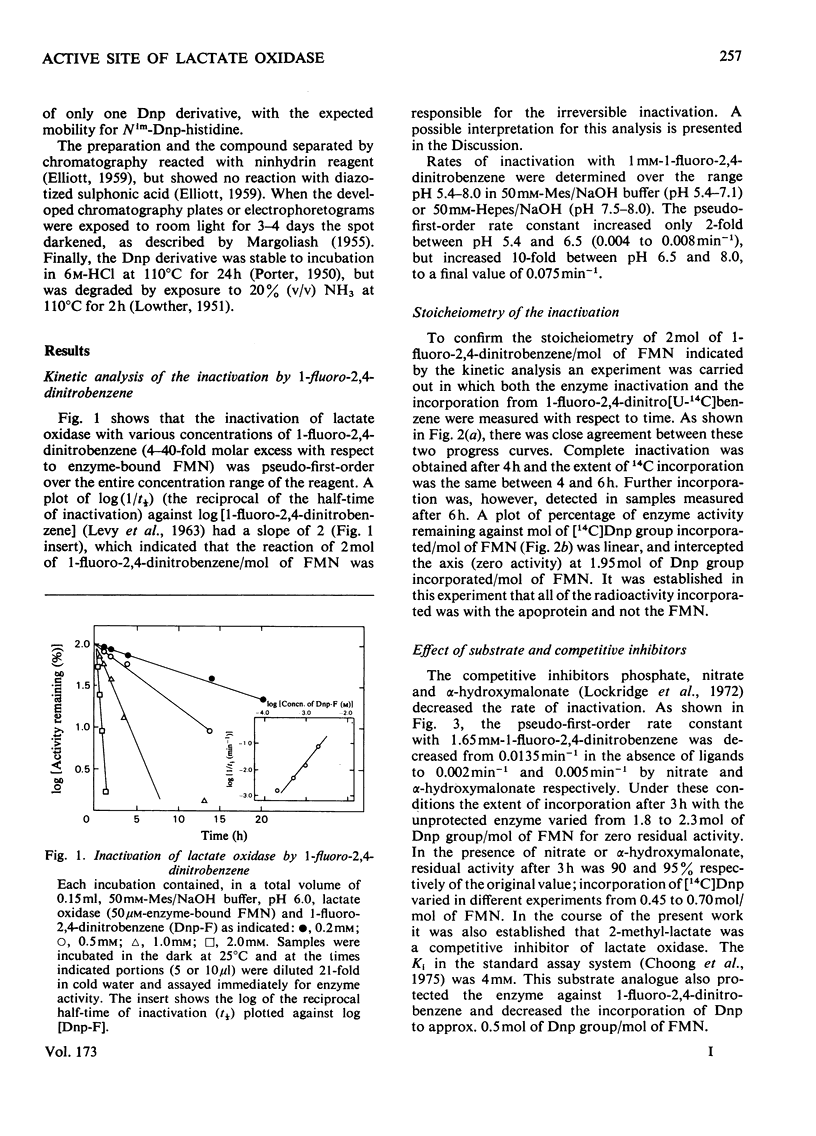
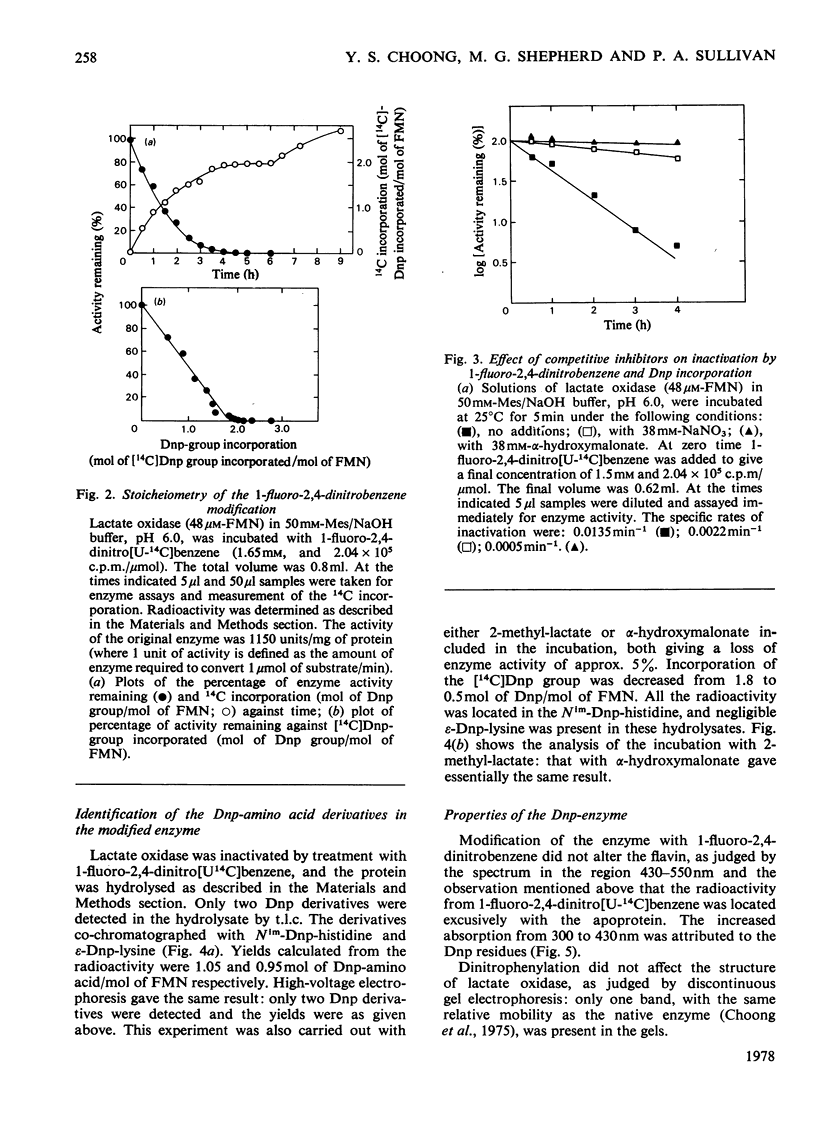
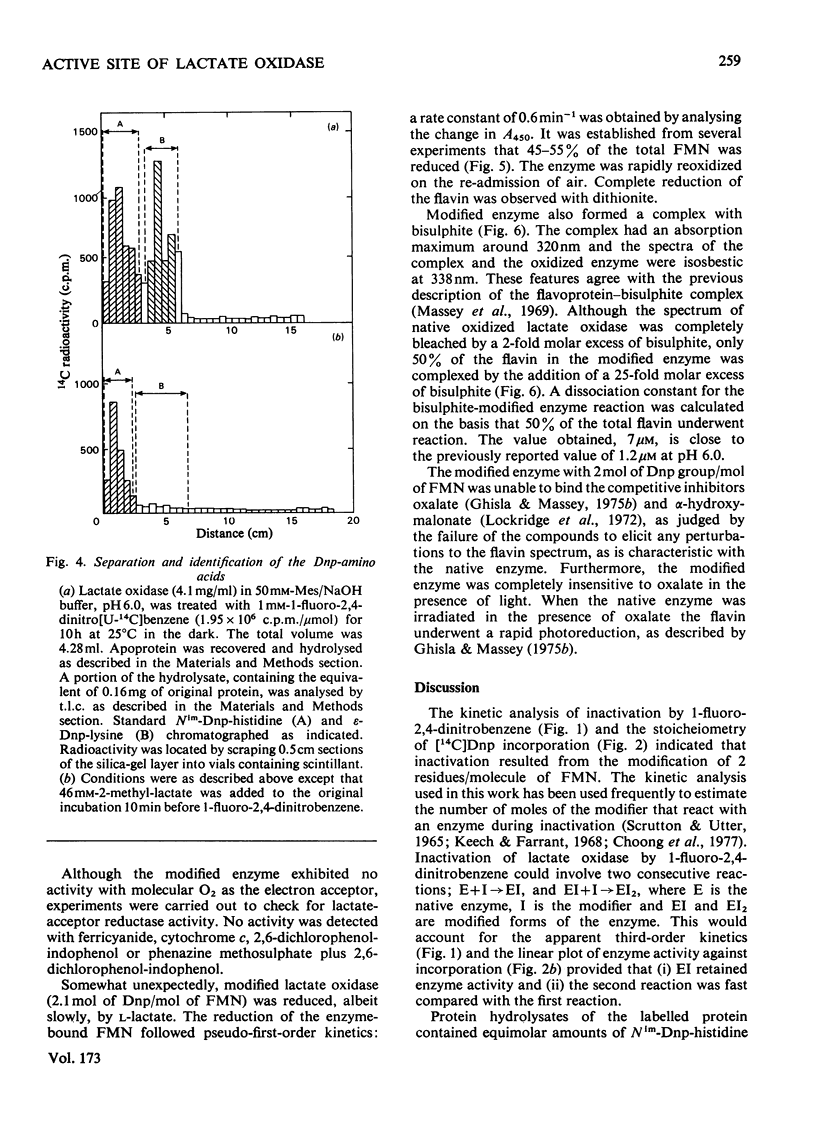
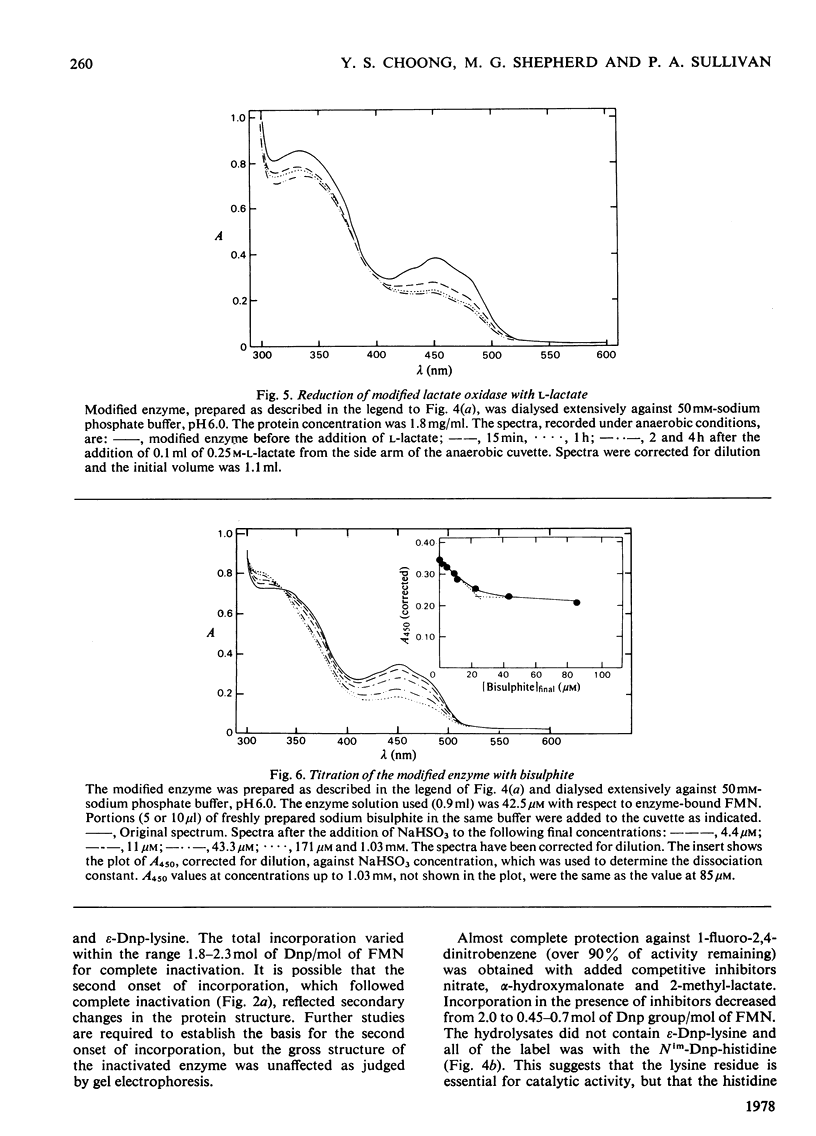
1. Dinitrophenylation of 2 +/- 0.2mol of residues/mol of enzyme-bound FMN resulted in the complete inactivation of the flavoenzyme L-lactate oxidase. 2. Hydrolysates of the inactivated enzyme contained 1mol each of Nim-Dnp-histidine (abbreviation: Dnp-,2,4-dinitrophenyl-; Nim indicates that either of the N atoms in the imidazole ring is substituted) and epsilon-Dnp-lysine/mol of FMN. 3. Competitive inhibitors decreased the extent of inactivation to a 10% loss of activity, and dinitrophenylation was decreased from 2 to approx. 0.5mol/mol of FMN. Only Nim-Dnp-histidine was detected in the hydrolysates. 4. Although the dinitrophenylated enzyme did not possess enzyme activitiy, L-lactate reduced approx. 50% of the enzyme-bound flavin slowly (0.6min-1), and approx. 50% of the flavin in the modified enzyme-bound flavin slowly (0.6min-1), and approx. 50% of the flavin in the modified enzyme formed a complex with bisulphite. 6. The modified enzyme (2mol of Dnp/mol of FMN) was unable to bind substrate analogues and competitive inhibitors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averill B. A., Schonbrunn A., Abeles R. H. Studies on the mechanism of Mycobacterium smegmatis L-lactate oxidase. 5-Deazaflavin mononucleotide as a coenzyme analogue. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1603–1605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choong Y. S., Shepherd M. G., Sullivan P. A. Preparation of the lactate oxidase apoenzyme and studies on the binding of flavin mononucleotide to the apoenzyme. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;145(1):37–45. doi: 10.1042/bj1450037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Massey V. Mechanism of inactivation of the flavoenzyme lactate oxidase by oxalate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):577–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerman L., Coffey D. S. Studies on crystalline D-amino acid oxidase. V. Characterization of borohydride-reduced enzyme-subtrate intermediate. Synthesis of epsilon-N-(1-carboxyethyl)-L-lysine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):582–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Jorns M. S. Use of 5-deazaFAD to study hydrogen transfer in the D-amino acid oxidase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8728–8734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keech D. B., Farrant R. K. The reactive lysine residue at the allosteric site of sheep kidney pyruvate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 5;151(2):493–503. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. M., LEBER P. D., RYAN E. M. INACTIVATION OF MYOSIN BY 2,4-DINITROPHENOL AND PROTECTION BY ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE AND OTHER PHOSPHATE COMPOUNDS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3654–3659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWTHER A. G. Identification of N-2: 4-dinitrophenylamino-acids. Nature. 1951 May 12;167(4254):767–768. doi: 10.1038/167767b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockridge O., Massey V., Sullivan P. A. Mechanism of action of the flavoenzyme lactate oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8097–8106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E. Position and reactivity of the histidine residues in cytochrome c. Nature. 1955 Feb 12;175(4450):293–295. doi: 10.1038/175293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Ganther H. On the interpretation of the absorption spectra of flavoproteins with special reference to D-amino acid oxidase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1161–1173. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Massey V. Flavin-sulfite complexes and their structures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4007–4016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Massey V., Heizmann C., Hemmerich P., Lhoste J. M., Gould D. C. The reduction of flavins by borohydride: 3,4-dihydroflavin. Struction, absorption and luminescence. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(3):392–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. J., Voet J. G., Bright H. J. Nitromethane. A novel substrate for D-amino acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1951–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The reactivity of the iminazole ring in proteins. Biochem J. 1950 Mar;46(3):304–307. doi: 10.1042/bj0460304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Rosen S. M. Chemical modification of the allosteric and catalytic sites of fructose 1,6-diphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1156–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonbrunn A., Abeles R. H., Walsh C. T., Ghisla S., Ogata H., Massey V. The structure of the covalent flavin adduct formed between lactate oxidase and the suicide substrate 2-hydroxy-3-butynoate. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1798–1807. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonbrunn A., Abeles R. H., Walsh C. T., Ghisla S., Ogata H., Massey V. The structure of the covalent flavin adduct formed between lactate oxidase and the suicide substrate 2-hydroxy-3-butynoate. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1798–1807. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Utter M. F. Pyruvate carboxylase. V. Interaction of the enzyme with adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3714–3723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soon C. Y., Shepherd M. G., Sullivan P. A. Modification of lactate oxidase with diethyl pyrocarbonate. Evidence for an active-site histidine residue. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):385–393. doi: 10.1042/bj1650385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan P. A., Soon C. Y., Schreurs W. J., Cutfield J. F., Shepherd M. G. The structure of L-lactate oxidase from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):375–383. doi: 10.1042/bj1650375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Schonbrunn A., Abeles R. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of D-amino acid oxidase. Evidence for removal of substrate -hydrogen as a proton. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6855–6866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Lockridge O., Massey V., Abeles R. Studies on the mechanism of action of the flavoenzyme lactate oxidase. Oxidation and elimination with beta-chlorolactate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7049–7054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


