Abstract
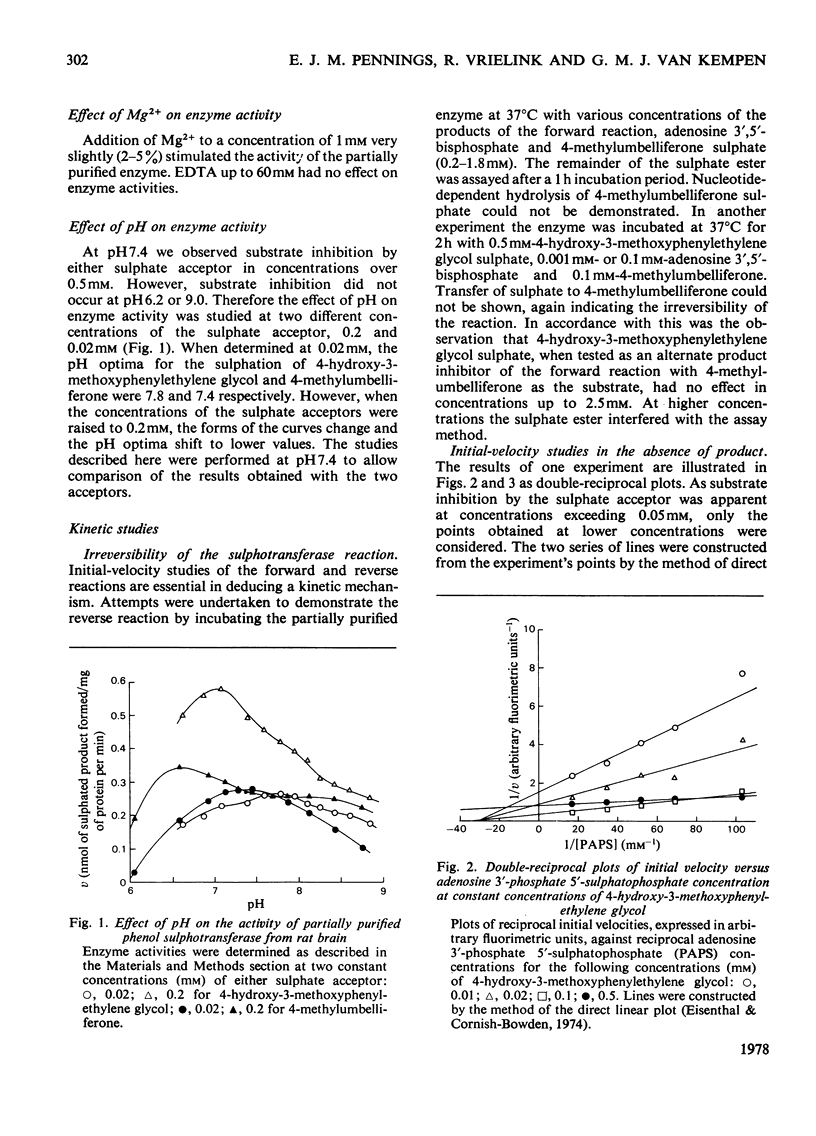
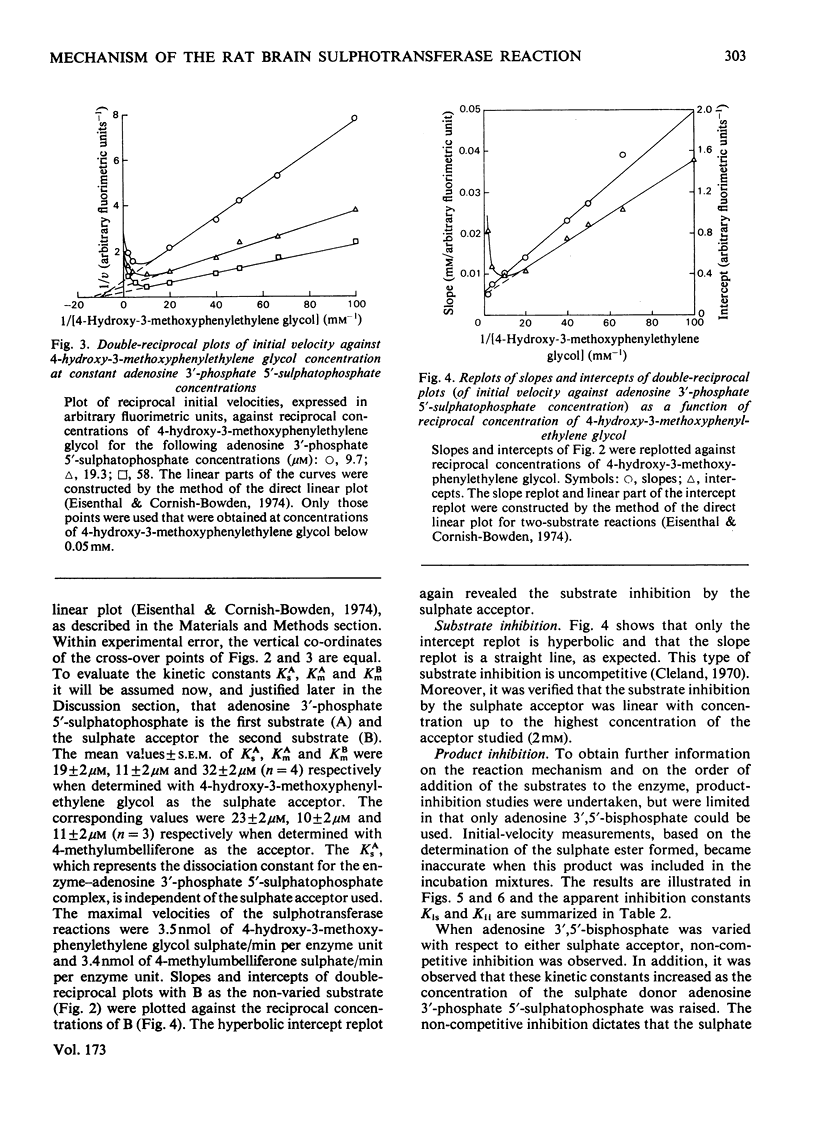
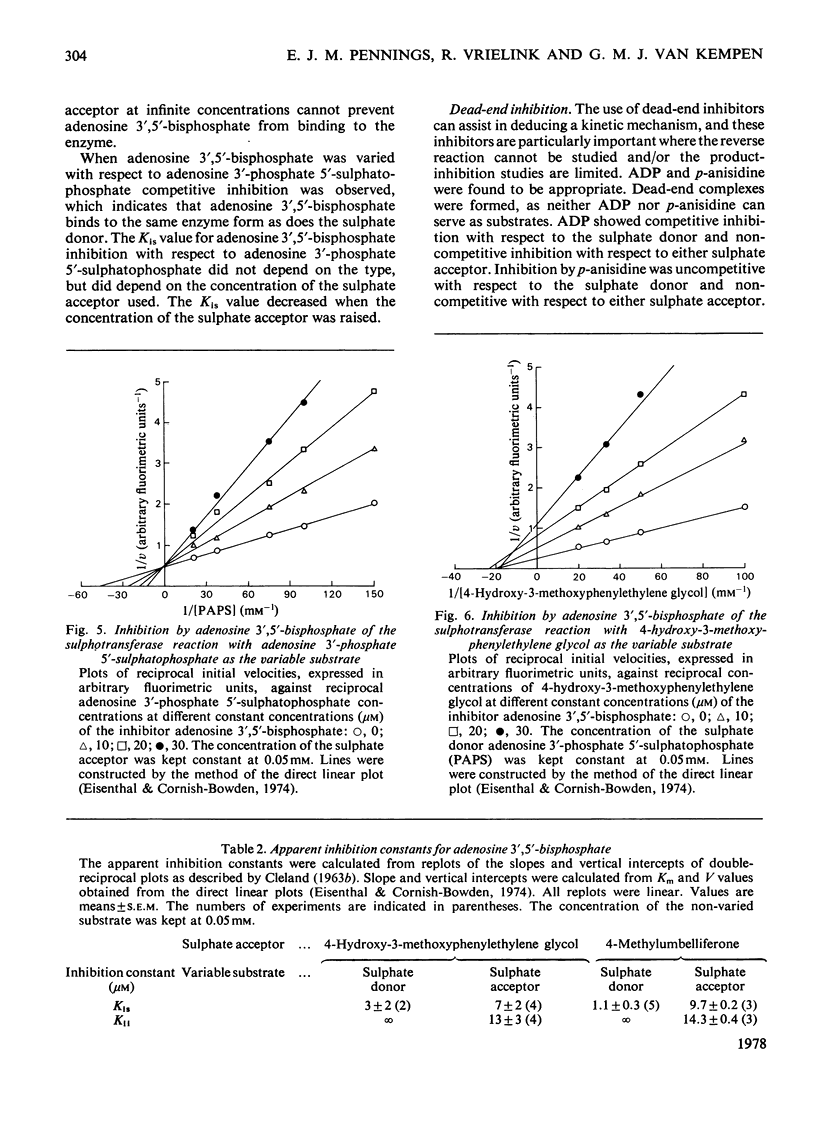
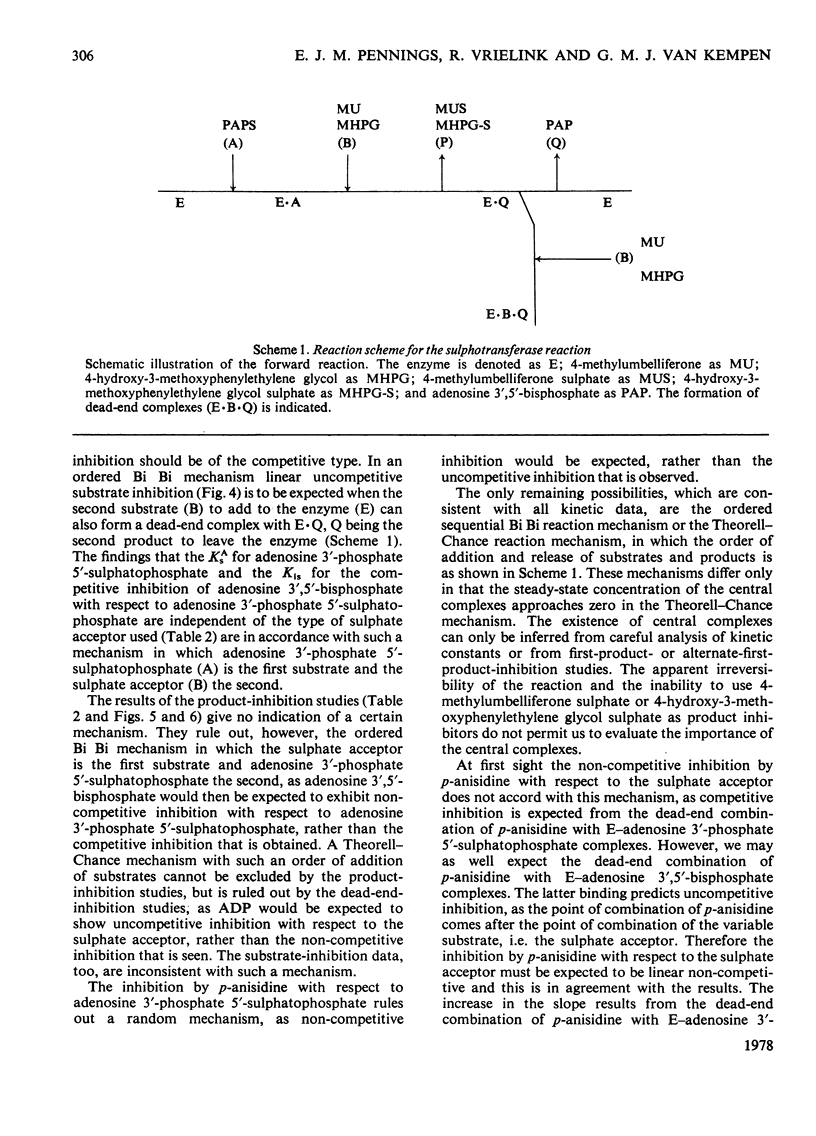
Some properties of rat brain phenol sulphotransferase were investigated in in vitro at pH7.4. The enzyme was purified 10-fold by chromatography on DEAE-Sephadex -50. It can be assayed with 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylethylene glycol or 4-methylumbelliferone as the sulphate acceptor. The partially purified enzyme is stable for at least 1 week when stored at 4 degrees C. It is, however, additionally activated (10--20%) and stabilized by 1 mM-dithiothreitol. The activity of the enzyme does not depend on the addition of exogenous Mg2+. The pH optima for the sulphation of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylethylene glycol and 4-methylumbelliferone are 7.8 and 7.4 respectively. Substrate inhibition by the sulphate acceptor is apparent at concentrations over 0.05mM. Initial-velocity studies in the absence and presence of product and dead-end inhibitors suggested that the mechanism of the rat brain sulphotransferase reaction is sequential ordered Bi Bi with a dead-end complex of enzyme with adenosine 3',5'-biphosphate and sulphate acceptor. The sulphate donor adenosine 3'-phosphate 5'-sulphatophosphate is the first substrate that adds to the enzyme, and the sulphate acceptor is the second substrate. The dissociation constant for the complex of enzyme with sulphate donor is 21 micron. The sulphated substrate is the first product and adenosine 3',5'-biphosphate is the second product that leaves the enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee R. K., Roy A. B. Kinetic studies of the phenol sulphotranferase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):573–586. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Scheel-Krüger J. Accumulation and disappearance of noradrenaline and its major metabolites synthesized from intraventricularly injected (3H)dopamine in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Sep;23(3):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb06061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. C., Horn L. Hepatic sulfation of estrogen metabolites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;231(1):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNIAK R., DAVIDSON E. A. SYNTHESIS OF ADENYLYL SULFATE AND ADENYLYL SULFATE 3'-PHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2986–2990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. II. Inhibition: nomenclature and theory. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston D., Ritchie I. M. Sulphate ester formation from catecholamine metabolites and pyrogallol in rat brain in vivo. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):635–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foldes A., Meek J. L. Occurrence and localization of brain phenolsulphotransferase. J Neurochem. 1974 Aug;23(2):303–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foldes A., Meek J. L. Rat brain phenolsulfotransferase: partial purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 19;327(2):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek J. K., Neff N. H. Biogenic amines and their metabolites as substrates for phenol sulphotransferase (EC 2.8.2.1) of brain and liver. J Neurochem. 1973 Jul;21(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki M., Yoshizawa I., Fishman J. Directive O methylation of estrogen catechol sulfates. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1669–1672. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennings E. J., Vrielink R., Van Kempen G. M. Anomalous effect of probenecid on rat brain phenolsulphotransferase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jul 15;25(14):1687–1690. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennings E. J., Vrielink R., Wolters W. L., Van Kempen G. M. Inhibition of rat brain phenol sulphotransferase in vitro by noradrenaline and dopamine metabolites. J Neurochem. 1976 Oct;27(4):915–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb05155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanberg S. M., Breese G. R., Schildkraut K. K., Gordon E. K., Kopin I. J. 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol sulfate in brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;17(9):2006–2008. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanberg S. M., Schildkraut J. J., Breese G. R., Kopin I. J. Metabolism of normetanephrine-H3 in rat brain--identification of conjugated 3-methoxy-4-hydrophenylglycol as the major metabolite. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Feb;17(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90330-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. A. Accumulation and metabolism of norepinephrine in rat hypothalamus after exhaustive stress. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):589–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden R. F., Eccleston D. Glycol sulphate ester formation from ( 14 C)noradrenaline in brain and the influence of a COMT inhibitor. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2461–2468. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang M. L., Lemieux J., Schiff J. A., Bojarski T. B. Preparation of adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS) from adenosine 3'-phosphate 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) prepared by an improved procedure. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):623–626. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanKempen G. M., Wolters W. L., Van Elk R. Distribution of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethyleneglycol sulphotransferase in brain fractions. J Neurochem. 1975 Apr;24(4):825–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. P. The biosynthesis of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol sulphate by liver and brain. J Neurochem. 1975 May;24(5):1059–1063. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb03677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kempen G. M., Jansen G. S. Quantitative determination of phenolsulfotransferase using 4-methylumbelliferone. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):438–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


