Abstract
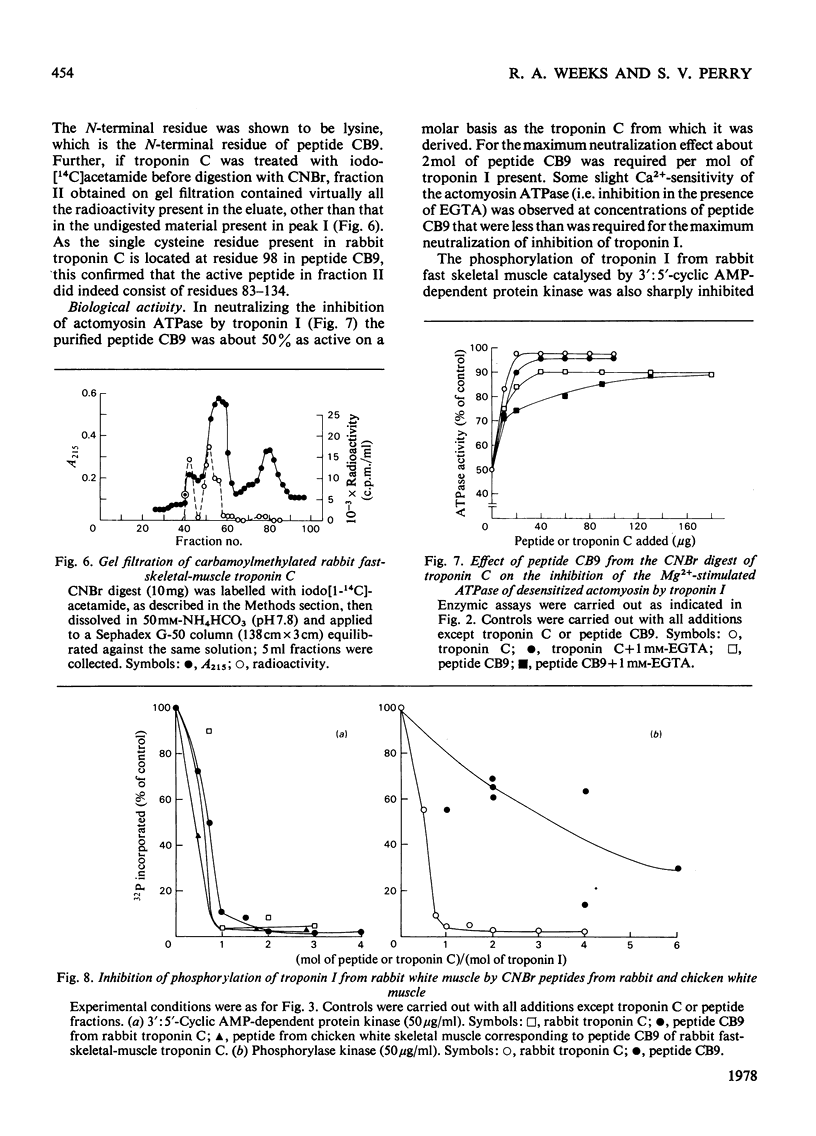
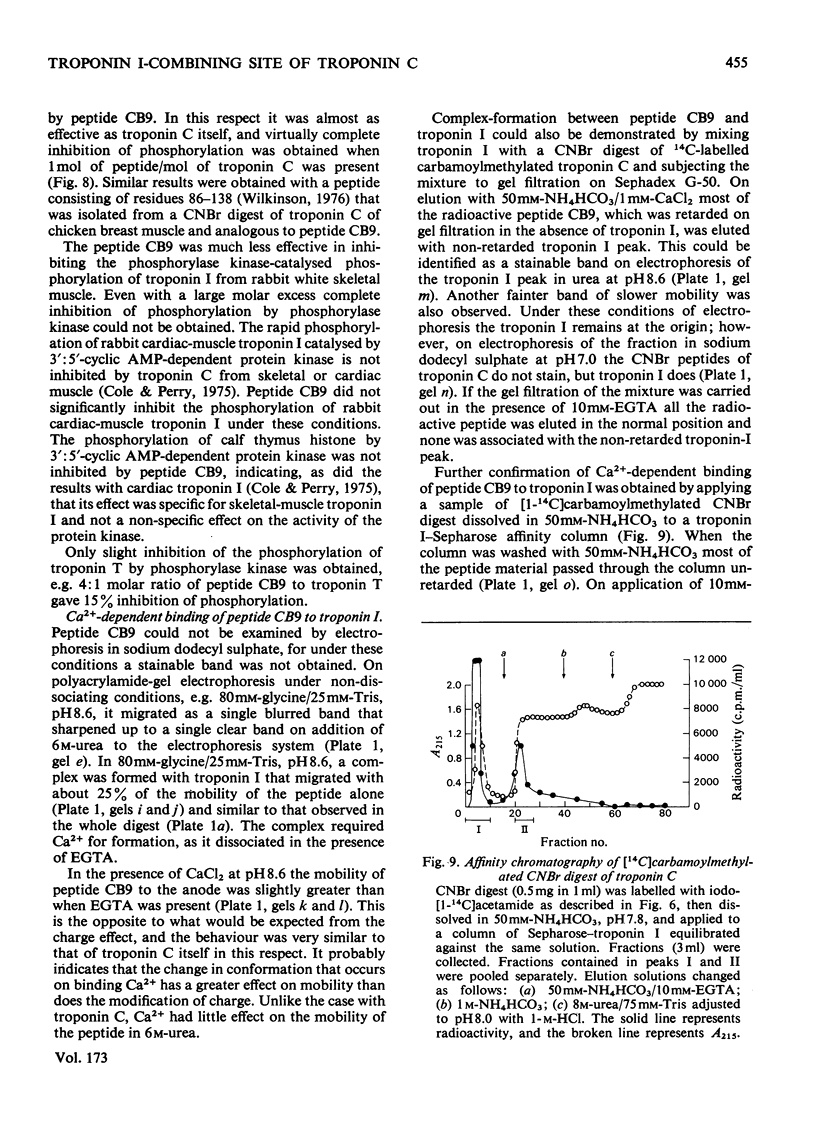
1. The CNBr digest of troponin C from rabbit fast skeletal muscle was shown to possess many of the functional properties of the whole troponin C molecule. 2. A peptide corresponding to residues 83-134 was isolated, which forms a Ca(2+-dependent complex with troponin I and neutralizes the inhibition by troponin I of the Mg(2+-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of desensitized actomyosin. 3. The peptide inhibits the phosphorylation of fast-skeletal-muscle, but not cardiac-muscle, troponin I, by 3' :5'-cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. In this property it was as effective as whole skeletal-muscle troponin C when compared on a molar basis. 4. Biological activity was also present in other fractions obtained from the CNBr digest. 5. By gel filtration and affinity chromatography of the whole CNBr digest of troponin C, two peptides, one of which was identified as representing residues 83-134, were shown to form Ca(2+-dependent complexes with troponin I. 6. The significance of these findings for the mechanism of interaction of troponin C and troponin I is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amphlett G. W., Vanaman T. C., Perry S. V. Effect of the troponin C-like protein from bovine brain (brain modulator protein) on the Mg2+-stimulated ATPase of skeletal muscle actinomyosin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80836-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation of troponin I from cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1490525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Potter J. D., Horn M. J., Wilshire G., Jackman N. The amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin C: gene replication and homology with calcium-binding proteins from carp and hake muscle. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins P., Perry S. V. The subunits and biological activity of polymorphic forms of tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):765–777. doi: 10.1042/bj1330765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Wakabayashi T., Ebashi F. Troponin and its components. J Biochem. 1971 Feb;69(2):441–445. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. M., Cather R., Winget G. D. Advantages of the use of Cerenkov vounting for determination of P 32 in photophosphorylation research. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):540–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Wilkinson J. M. The amino acid sequence of rabbit slow-muscle troponin I. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):183–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1670183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J. Interactions of desensitized actomyosin with tropomyosin, troponin A, troponin B, and polyanions. J Gen Physiol. 1970 May;55(5):585–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H. Fractionation of troponin into two distinct proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90610-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Perry S. V. The interaction of the calcium-binding protein (troponin C) with bivalent cations and the inhibitory protein (troponin I). Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):145–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1370145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1610465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Amphlett G. W., Perry S. V. The primary structure of troponin T and the interaction with tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):85–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1510085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Barry C. D. The predicted structure of the calcium-binding component of troponin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 9;405(1):40–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation sites of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80739-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4628–4633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Seidel J. C., Leavis P., Lehrer S. S., Gergely J. Effect of Ca2+ binding on troponin C. Changes in spin label mobility, extrinsic fluorescence, and sulfhydryl reactivity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7551–7556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEERS E., Jr, CRAVEN G. R., ANFINSEN C. B., BETHUNE J. L. EVIDENCE FOR NONIDENTICAL CHAINS IN THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2478–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Perry S. V. The relaxing protein system of striated muscle. Resolution of the troponin complex into inhibitory and calcium ion-sensitizing factors and their relationship to tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):993–1004. doi: 10.1042/bj1150993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The relationship between biological activity and primary structure of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):375–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1530375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eerd J. P., Kawasaki Y. Effect of calcium(II) on the interaction between the subunits of troponin and tropomyosin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4972–4980. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. A region of the troponic C molecule involved in interaction with troponin I [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1391–1392. doi: 10.1042/bst0051391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V., Cole H. A., Trayer I. P. The regulatory proteins of the myofibril. Separation and biological activity of the components of inhibitory-factor preparations. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):215–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1270215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The amino acid sequence of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80769-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The preparation and properties of the components of troponin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]