Abstract
Desmosine-enriched peptides were isolated from a thermolysin digest of bovine ligamentum nuchae elastin and a partial sequence was determined. A 'two-cross-link' model is proposed in which a second cross-link, perhaps lysinonorleucine, joins two peptide chains approx. 35 amino acid residues removed from the desmosine. Implied in this model is a certain asymmetry or directionality which places restrictions on the 'sense' of the peptide chains (either always parallel or anti-parallel) in order to align the cross-linking sites. Imposing such restrictions raises the possibility of specific alignment of elastin precursor molecules by microfibrillar proteins and/or aligning peptides on the precursor molecules themselves.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braunitzer G., Schrank B., Ruhfus A. Zum vollständigen und autoatischen Abbau von Peptiden nach der Quadrolmethode. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1589–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davril M., Han K. K. Isolation and characterization of a highly cross-linked peptide from elastin of porcine aorta. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 1;43(3):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
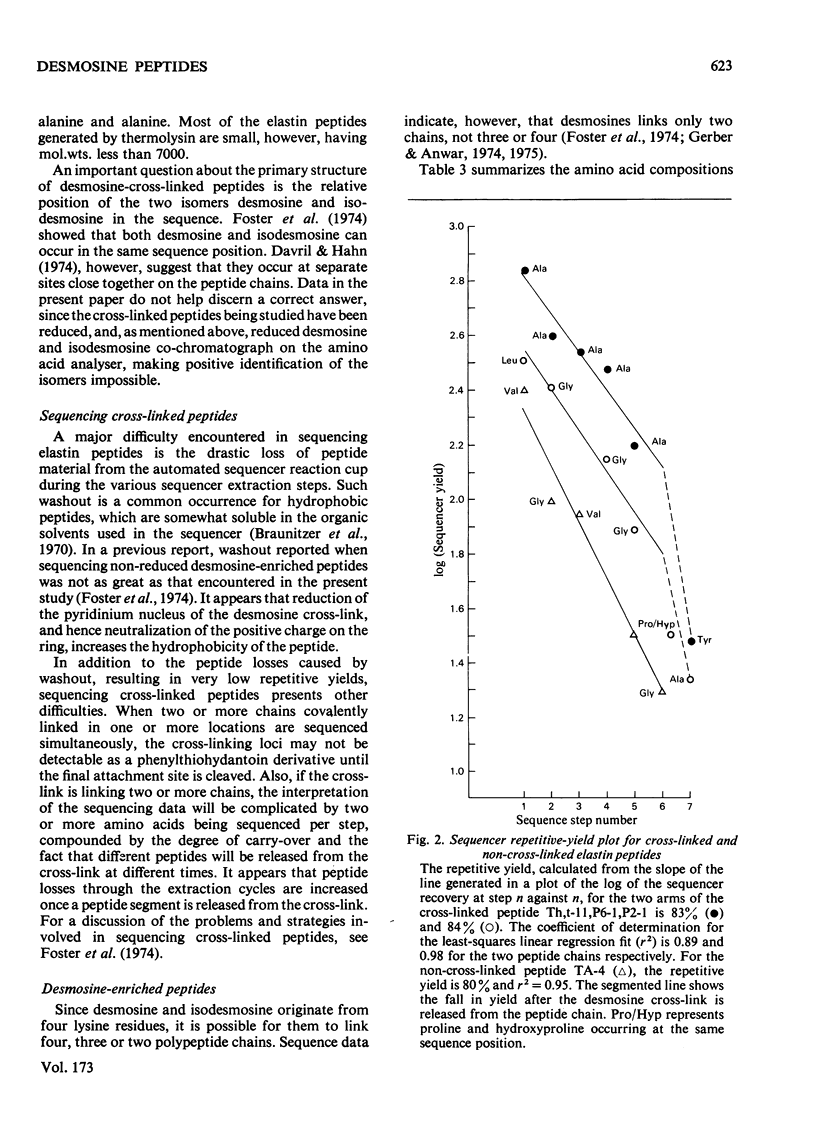
- Foster J. A., Bruenger E., Hu C. L., Albertson K., Franzblau C. A new, improved technique for automated sequencing of non-polar peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91402-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Bruenger E., Rubin L., Imberman M., Kagan H., Mecham R., Franzblau C. Circular dichroism studies of an elastin crosslinked peptide. Biopolymers. 1976 May;15(5):833–841. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
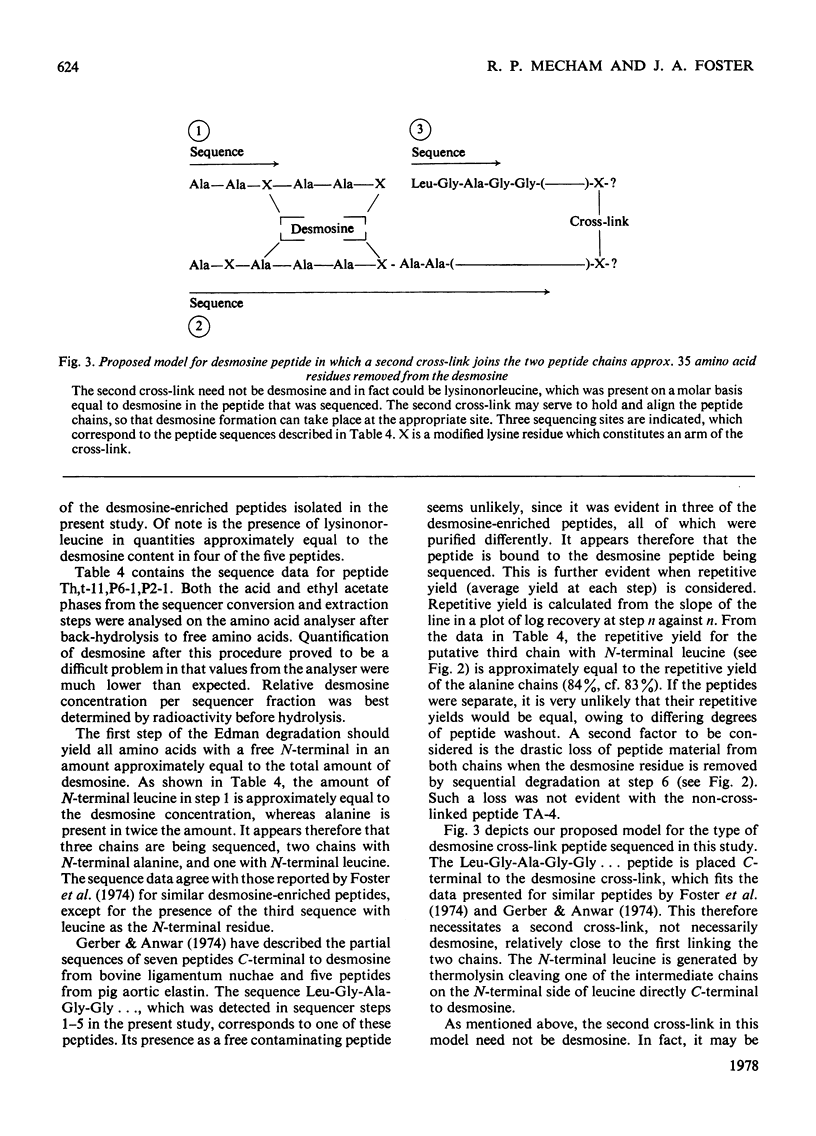
- Foster J. A., Rubin L., Kagan H. M., Franzblau C., Bruenger E., Sandberg L. B. Isolation and characterization of cross-linked peptides from elastin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6191–6196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G., John R., Thomas J. Biosynthetic pathway of desmosines in elastin. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):45–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1360045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Anwar R. A. Comparative studies of the cross-linked regions of elastin from bovine ligamentum nuchae and bovine, porcine and human aorta. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):685–695. doi: 10.1042/bj1490685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Anwar R. A. Structural studies on cross-linked regions of elastin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5200–5207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Epstein E. H., Jr, Sherr C. J. Precursors of collagen secreted by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Sandberg L. B., Foster J. A. Molecular model for elastin structure and function. Nature. 1973 Dec 21;246(5434):461–466. doi: 10.1038/246461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lent R. W., Smith B., Salcedo L. L., Faris B., Franzblau C. Studies on the reduction of elastin. II. Evidence for the presence of alpha-aminoadipic acid delta-semialdehyde and its aldol condensation product. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2837–2845. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F., ADAIR G. S. The chemistry of connective tissues. 2. Soluble proteins derived from partial hydrolysis of elastin. Biochem J. 1955 Sep;61(1):11–21. doi: 10.1042/bj0610011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., ELSDEN D. F., THOMAS J. Constitution of the cross-linkages in elastin. Nature. 1963 Mar 30;197:1297–1298. doi: 10.1038/1971297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz M. A., Pereyra B., Gallop P. M., Seifter S. Isomers of desmosine and isodesmosine and related reduced compounds in elastin. J Mechanochem Cell Motil. 1974 Mar;2(4):231–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piez K. A. Cross-linking of collagen and elastin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:547–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.002555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg L. B., Gray W. R., Bruenger E. Structural studies of alanine- and lysine-rich regions of porcine aortic tropoelastin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 28;285(2):453–458. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg L. B., Weissman N., Gray W. R. Structural features of tropoelastin related to the sites of cross-links in aortic elastin. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 5;10(1):52–56. doi: 10.1021/bi00777a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J., ELSDEN D. F., PARTRIDGE S. M. PARTIAL STRUCTURE OF TWO MAJOR DEGRADATION PRODUCTS FROM THE CROSS-LINKAGES IN ELASTIN. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:651–652. doi: 10.1038/200651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres A. R., Alvarez V. L., Sanberg L. B., Gray W. R. The isolation and amino acid sequence of some thrombin produced porcine tropoelastin peptides. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;79:267–276. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-9093-0_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wender D. B., Treiber L. R., Bensusan H. B., Walton A. G. Synthesis and characterization of poly(LysAla3). Biopolymers. 1974;13(10):1929–1941. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


