Abstract
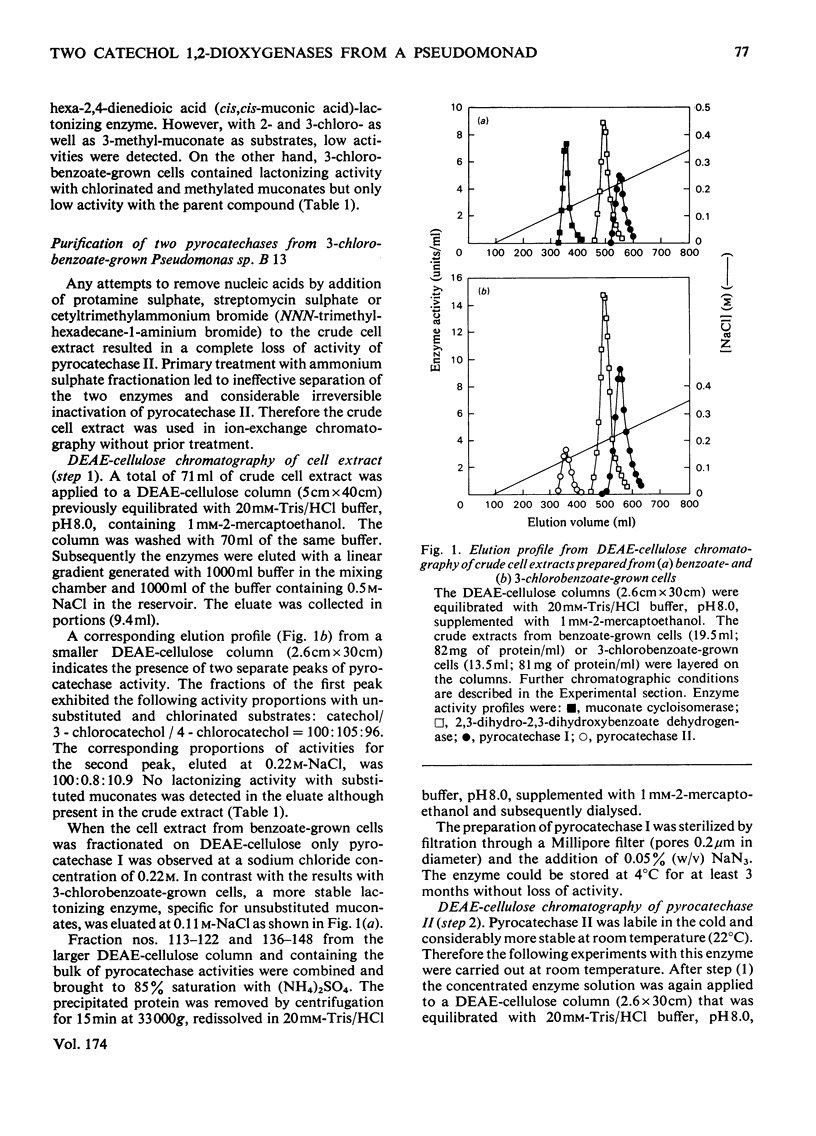
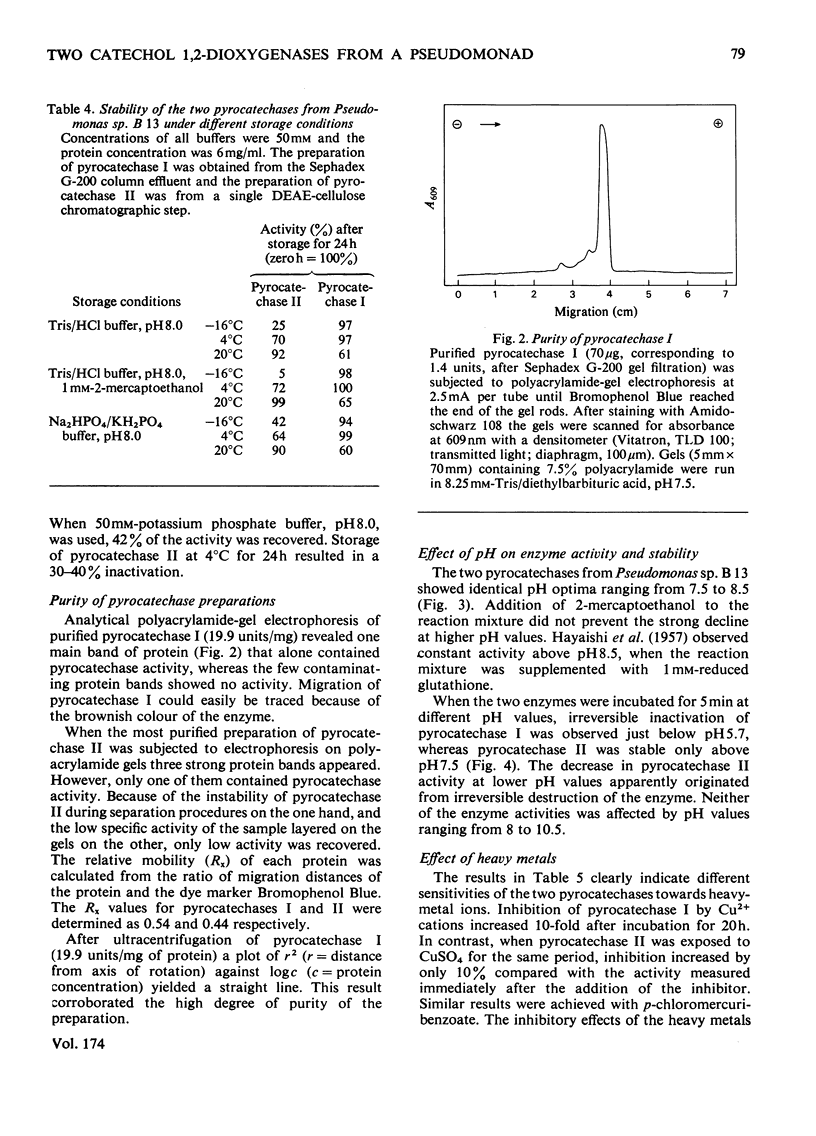
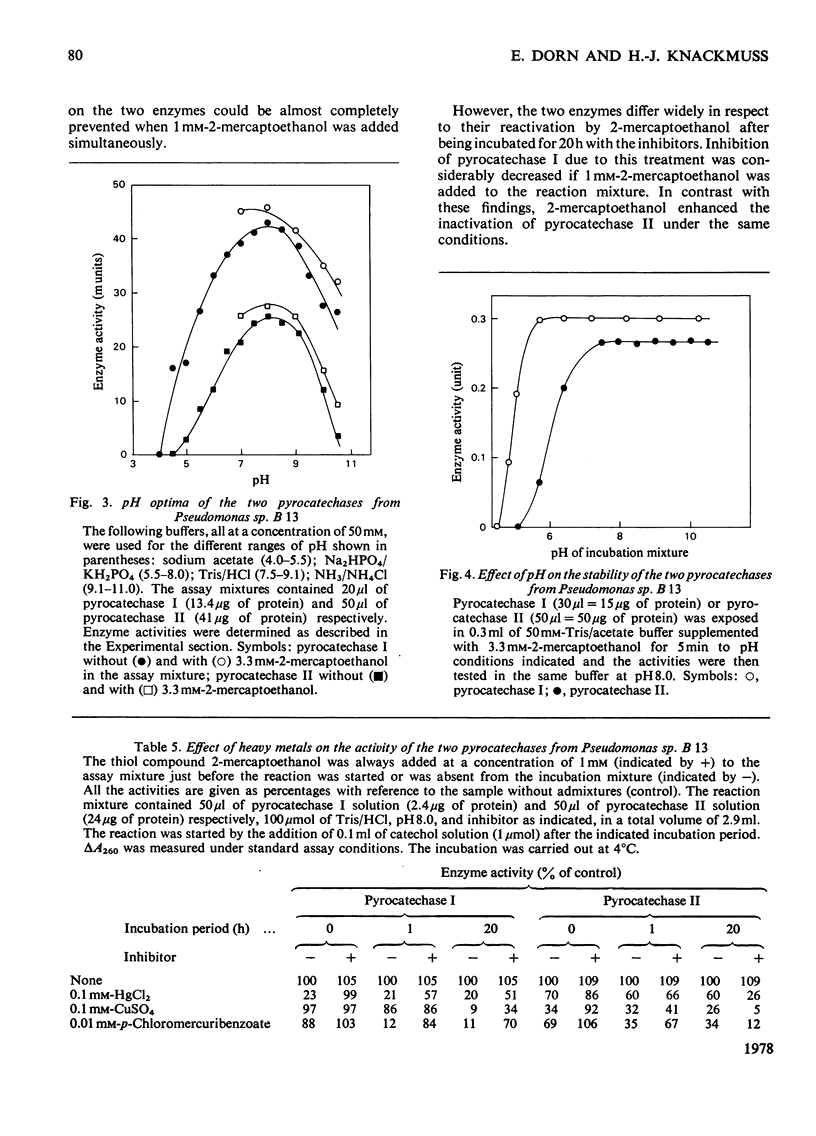
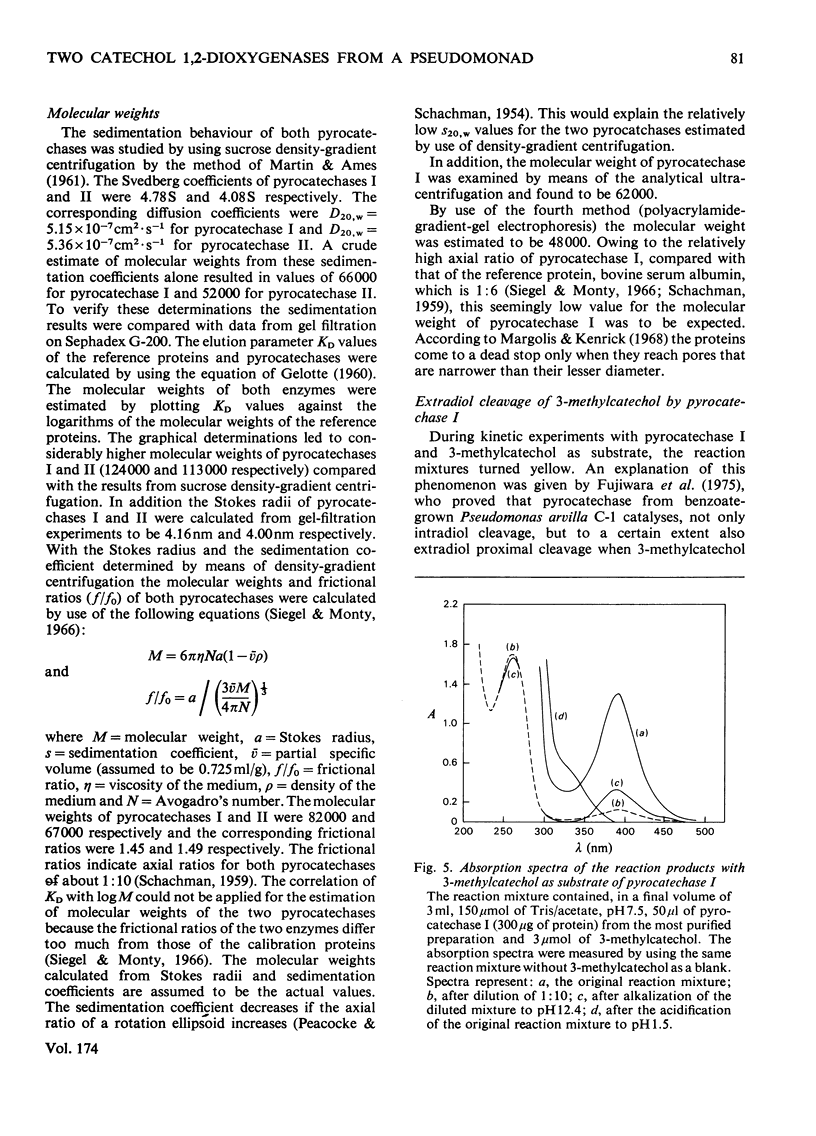
1. Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases, pyrocatechase I and pyrocatechase II, were found in 3-chlorobenzoate-grown cells of Pseudomonas sp. B 13. The latter enzyme showed high relative activities with 3- and 4-chlorocatechol compared with catechol. 2. In benzoate-grown cells, only pyrocatechase I was induced. It was purified 29-fold with a final specific activity of 20 mumol of catechol oxygenated/min per mg of protein and an overall yield of 22%. Because of the instability of pyrocatechase II on chromatography and dialysis, no increase of specific activity was obtained during the purification experiments. 3. Molecular weights of pyrocatechase I and pyrocatechase II were 82000 and 67000 respectively. 4. For both pyrocatechases the pH optimum was found to be at 8.0.5. Inhibitions of the two pyrocatechases by Cu2+ and Hg2+ ions and p-chloromercuribenzoate were different. The effect on pyrocatechase I after incubation for 20 h with the heavy metals was decreased by addition of 1 mM-2-mercaptoethanol to the reaction mixture. The inhibition of pyrocatechase II was even enhanced under these conditions. 6. Extradiol cleavage of 3-methylcatechol in addition to intradiol fission at a ratio of 1:14 was observed only with pyrocatechase I.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREWS P. Estimation of molecular weights of proteins by gel filtration. Nature. 1962 Oct 6;196:36–39. doi: 10.1038/196036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed M., Focht D. D. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by two species of Achromobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m73-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Hellwig M., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00696222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):85–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1740085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Fernley H. N., Davies J. I. Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1220543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Moss P., Fernley H. N. Bacterial metabolism of 4-chlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1220509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara M., Golovleva L. A., Saeki Y., Nozaki M., Hayaishi O. Extradiol cleavage of 3-substituted catechols by an intradiol dioxygenase, pyrocatechase, from a Pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4848–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt J. K., Evans W. C. Metabolism of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate by a soil pseudomonad. Preliminary evidence for the metabolic pathway. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):519–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1220519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt J. K., Evans W. C. Metabolism of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate by a soil pseudomonad. Ring-fission, lactonizing and delactonizing enzymes. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):533–542. doi: 10.1042/bj1220533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Schuld C. L., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. II. Metabolism of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):3795–3802. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAISHI O., KATAGIRI M., ROTHBERG S. Studies on oxygenases; pyrocatechase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):905–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. B., Blakley E. R. The metabolism of p-fluorobenzoic acid by a Pseudomonas sp. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Aug;17(8):1015–1023. doi: 10.1139/m71-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath R. S., Alexander M. Cometabolism of m-chlorobenzoate by an Arthrobacter. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):254–258. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.254-258.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath R. S. Cometabolism of the herbicide 2,3,6-trichlorobenzoate. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Mar-Apr;19(2):291–293. doi: 10.1021/jf60174a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ICHIHARA A., ADACHI K., HOSOKAWA K., TAKEDA Y. The enzymatic hydroxylation of aromatic carboxylic acids; substrate specificities of anthranilate and benzoate oxidases. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S. The enzymic conversion of 4-fluorophenylalanine to tyrosine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 19;51:619–621. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90632-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Fujisawa H., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T., Kanetsuna F., Taniuchi H., Nozaki M., Hayaishi O. Studies on pyrocatechase. I. Purification and spectral properties. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3270–3278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentz K. A simple polyacrylamide gradient gel preparation for estimating molecular weights. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J., Kenrick K. G. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in a continuous molecular sieve gradient. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):347–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason H. S., North J. C., Vanneste M. Microsomal mixed-function oxidations: the metabolism of xenobiotics. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1172–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne G. W., Goldman P., Holtzman J. L. The metabolism of 2-fluorobenzoic acid. II. Studies with 18-O2. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5374–5376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mires M. H., Alexander C. H. The prophylactic treatment tuberculosis. Del Med J. 1972 Jul;44(7):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAGAWA H., INOUE H., TAKEDA Y. CHARACTERISTICS OF CATECHOL OXYGENASE FROM BREVIBACTERIUM FUSCUM. J Biochem. 1963 Jul;54:65–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Parke D. Evolution of catabolic pathways. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(3):468–472. doi: 10.1042/bst0040468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):87–116. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.87-116.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Stanier R. Y. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3776–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. 3. Enzymes of the catechol pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3795–3799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACOCKE A. R., SCHACHMAN H. K. Studies on the sedimentation behaviour of thymus deoxypentose nucleic acid with reference to its homogeneity, size and shape. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Oct;15(2):198–210. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A. M. Metabolism of aromatic compounds in bacteria. Purification and properties of the catechol-forming enzyme, 3,5-cyclohexadiene-1,2-diol-1-carboxylic acid (NAD + ) oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):4960–4965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANIER R. Y., INGRAHAM J. L. Protocatechuic acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):799–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M., Toms A., Wood J. M. Influence of side-chain substituents on the position of cleavage of the benzene ring by Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1192–1197. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1192-1197.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpee K. W., Duxbury J. M., Alexander M. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetate metabolism by Arthrobacter sp.: accumulation of a chlorobutenolide. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):445–447. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.445-447.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J. M., Neujahr H. Y. Purification and properties of catechol 1,2-oxygenase from Trichosporon cutaneum. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(3):427–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


