Abstract
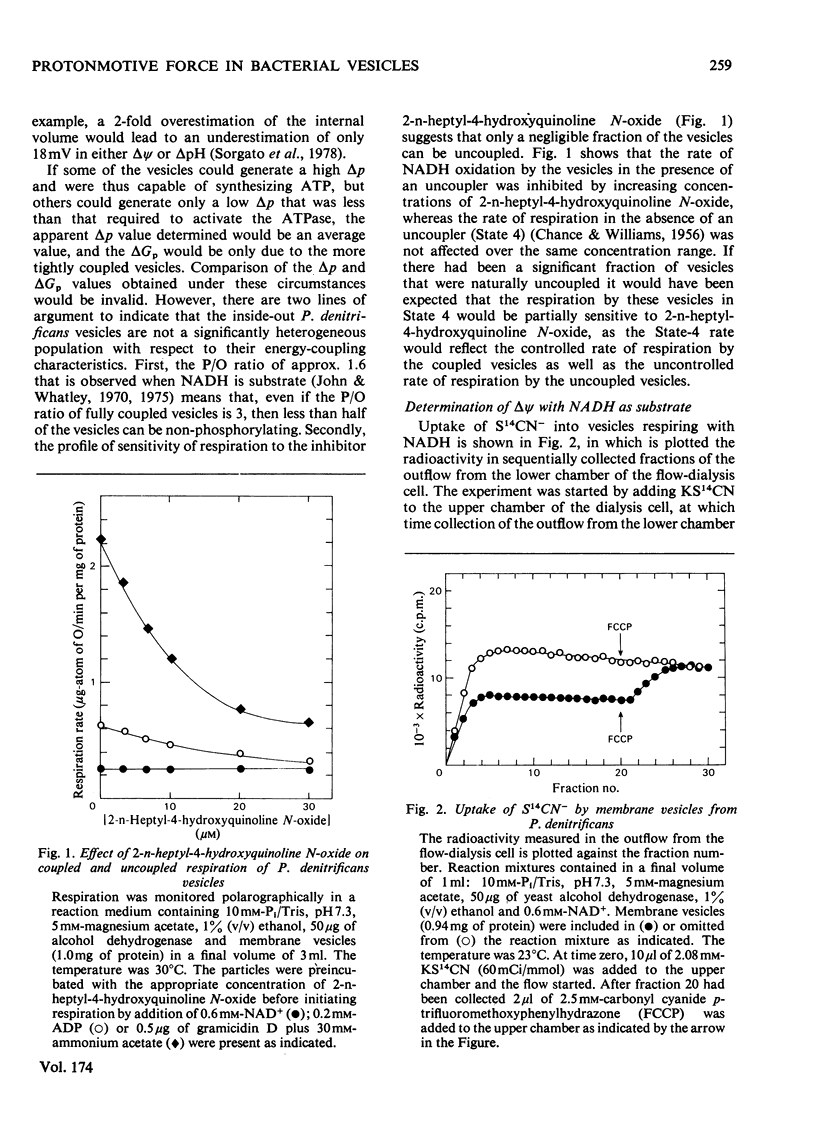
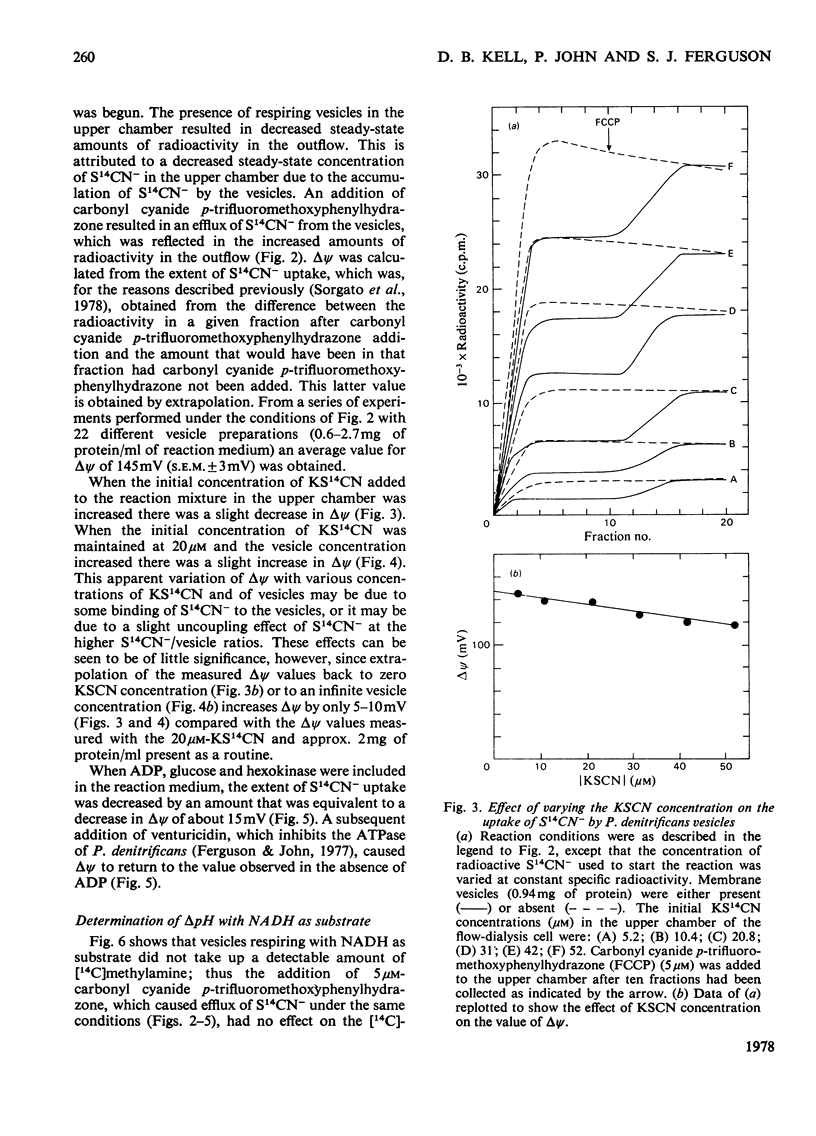
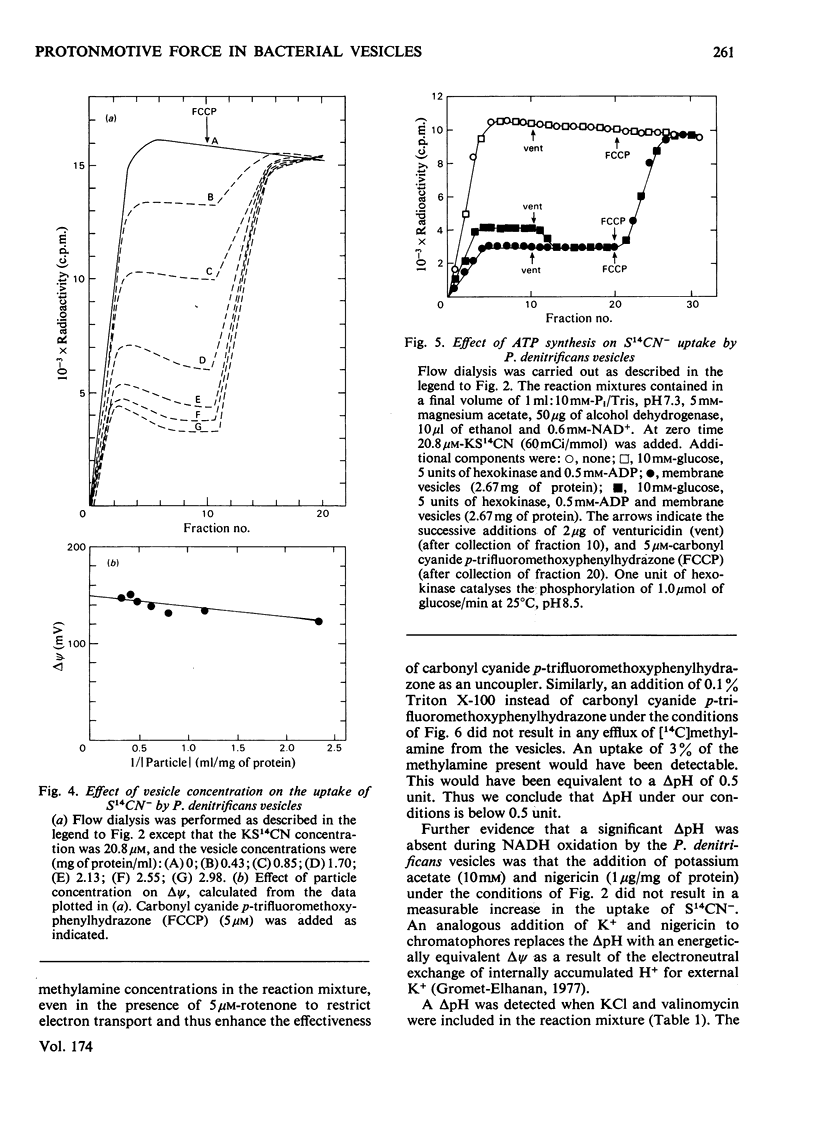
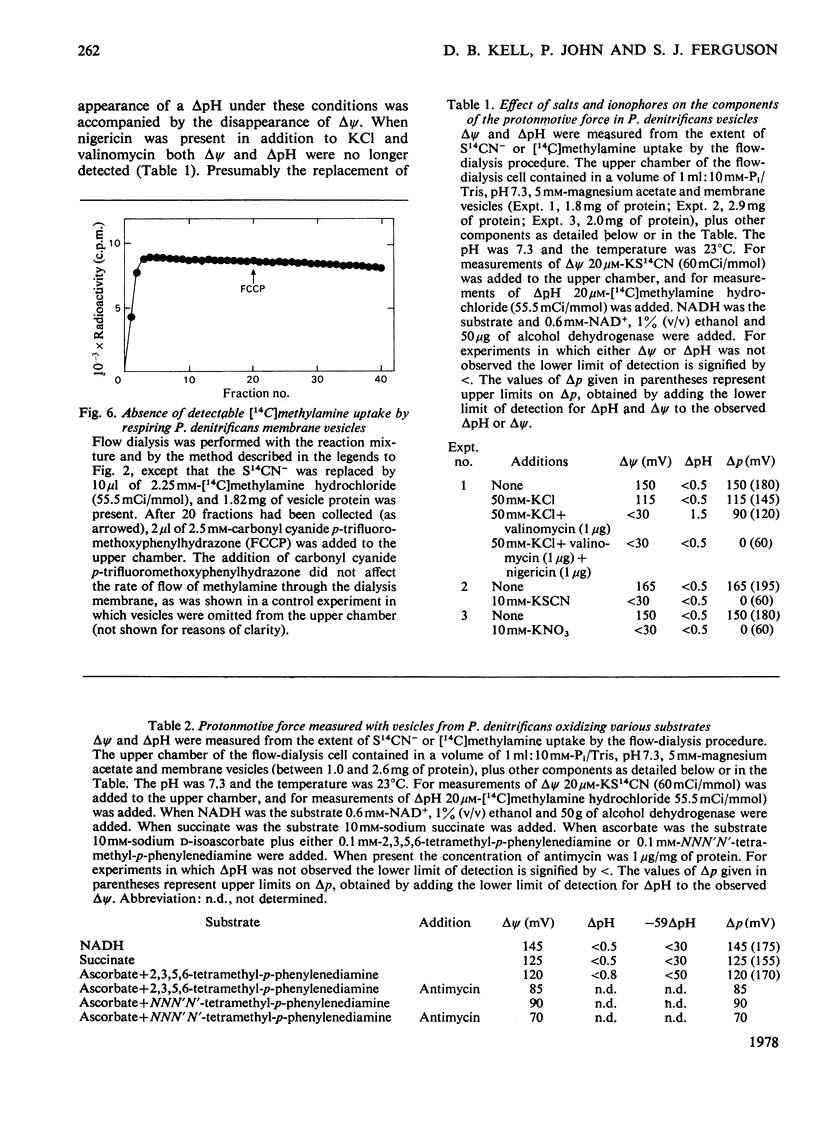
1. The magnitude of the protonmotive force in phosphorylating membrane vesicles from Paracoccus denitrificans was estimated. The membrane potential component was determined from the uptake of S14CN−, and the transmembrane pH gradient component from the uptake of [14C]methylamine. In each case a flow-dialysis technique was used to monitor uptake. 2. With NADH as substrate, the membrane potential was about 145mV and the pH gradient was below 0.5 pH unit. The membrane potential was decreased by approx. 15mV during ATP synthesis, and was abolished on addition of carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone. In the presence of KCl plus valinomycin the membrane potential was replaced by a pH gradient of 1.5 units. 3. Succinate oxidation generated a membrane potential of approx. 125mV and the pH gradient was below 0.5 pH unit. Oxidation of ascorbate (in the presence of antimycin) with either 2,3,5,6-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine or NNN′N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine as electron mediator usually generated a membrane potential of approx. 90mV. On occasion, ascorbate oxidation did not generate a membrane potential, suggesting that the presence of a third energy-coupling site in P. denitrificans vesicles is variable. 4. With NADH or succinate as substrate, the phosphorylation potential (ΔGp=ΔG0′+RTln[ATP]/ [ADP][Pi]) was approx. 53.6kJ/mol (12.8kcal/mol). Comparison of this value with the protonmotive force indicates that more than 3 protons need to be translocated via the adenosine triphosphatase of P. denitrificans for each molecule of ATP synthesized by a chemiosmotic mechanism. In the presence of 10mm-KNO3 the protonmotive force was not detectable (<60mV) but ΔGp was not altered. This result may indicate either that there is no relationship between the protonmotive force and ΔGp, or that for an unidentified reason the equilibration of SCN− or methylamine with the membrane potential and the pH gradient is prevented by NO3− in this system.
Full text
PDF

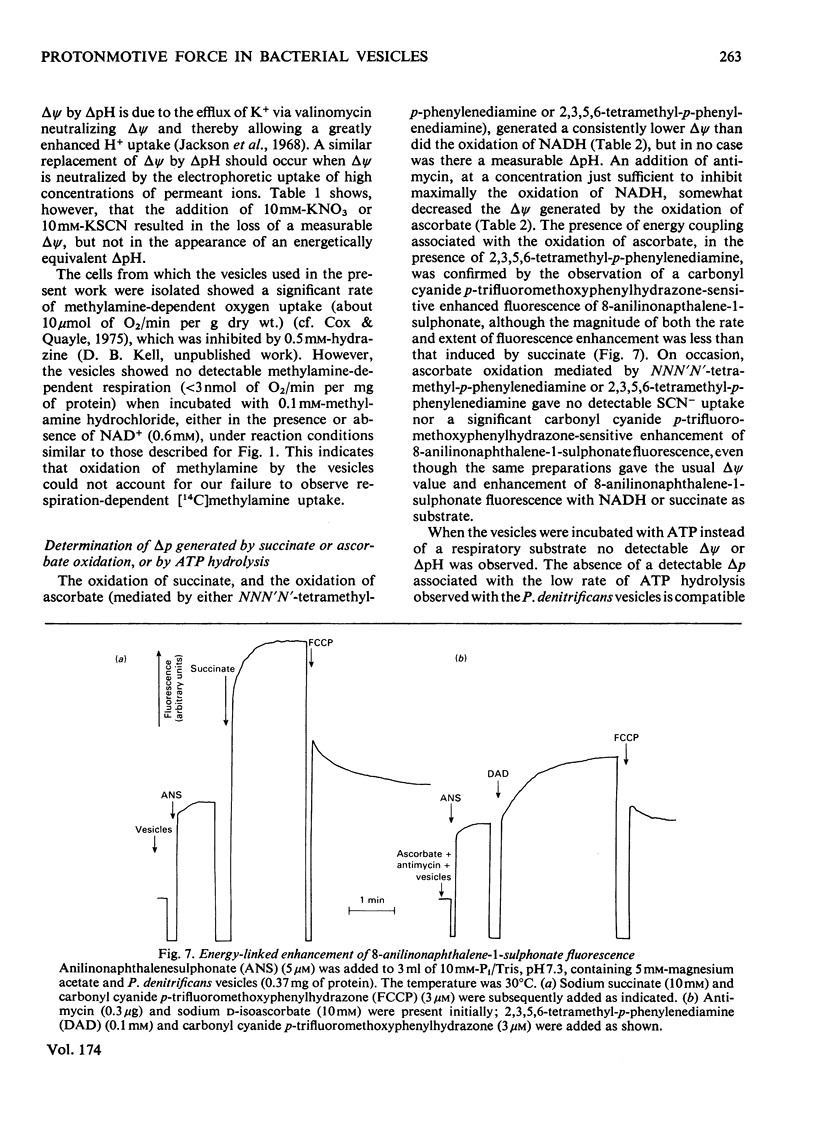
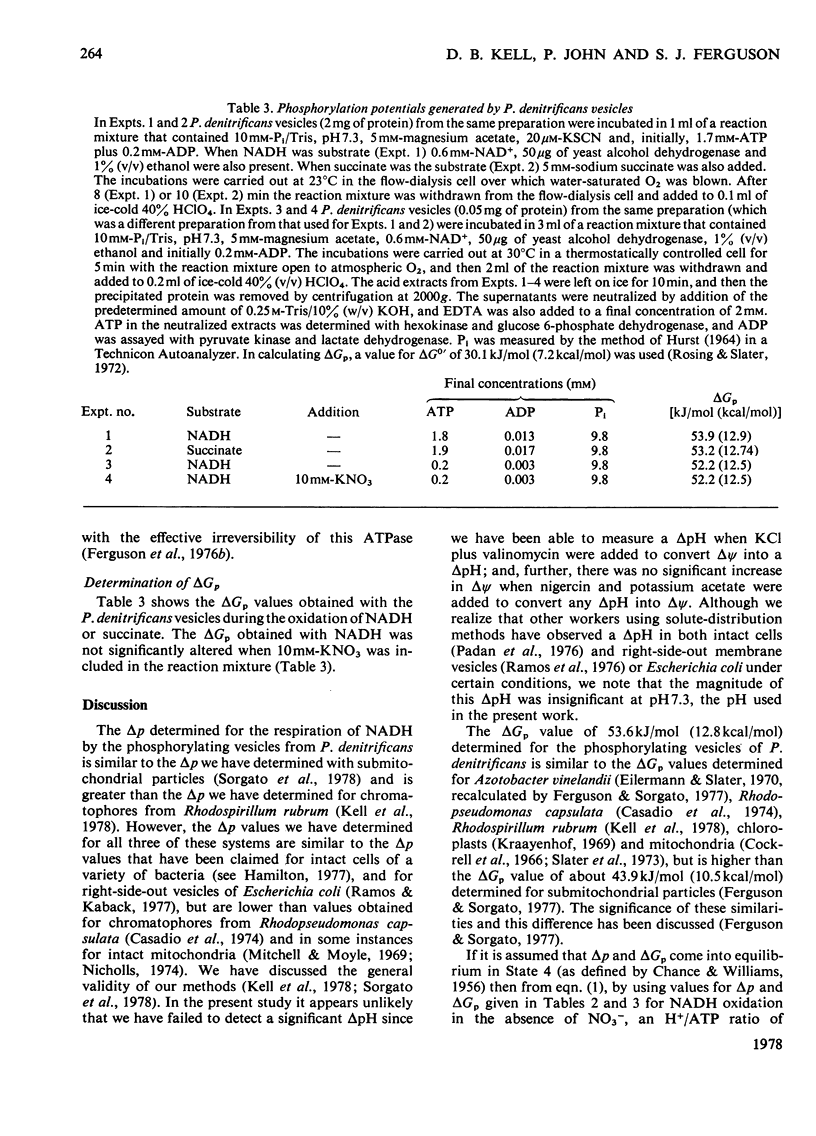


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccarini Melandri A., Casadio R., Melandri B. A. Thermodynamics and kinetics of photophosphorylation in bacterial chromatophores and their relation with the transmembrane electrochemical potential difference of protons. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):389–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D. The stoicheiometric relationships between electron transport, proton translocation and adenosine triphosphate synthesis and hydrolysis in mitochondria. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1615–1620. doi: 10.1042/bst0051615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnell J. N., John P., Whatley F. R. The reversibility of active sulphate transport in membrane vesicles of Paracoccus denitrificans. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):527–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1500527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:65–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadio R., Baccarini Melandri A., Zannoni D., Melandri B. A. Electrochemical proton gradient and phosphate potential in bacterial chromatophores. FEBS Lett. 1974 Dec 15;49(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80512-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockrell R. S., Harris E. J., Pressman B. C. Energetics of potassium transport in mitochondria induced by valinomycin. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2326–2335. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. B., Quayle J. R. The autotrophic growth of Micrococcus denitrificans on Methanol. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):569–571. doi: 10.1042/bj1500569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilermann L. J., Slater E. C. The phosphate potential generated by membrane fragments of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):226–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. J., John P., Lloyd W. J., Radda G. K., Whatley F. R. The ATPase as an irreversible component in electron transport linked ATP synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):272–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. J., John P. The inhibitor-sensitivity of the plasma-membrane adenosine triphosphatase of Paracoccus denitrificans: comparison with the mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1525–1527. doi: 10.1042/bst0051525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. J., Lloyd W. J., Radda G. K. On the nature of the energised state of submitochondrial particles; investigations with N-aryl naphthalene sulphonate probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 16;423(2):174–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. J., Sorgato M. C. The phosphorylation potential generated by respiring bovine heart submitochondrial particles. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):299–303. doi: 10.1042/bj1680299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURST R. O. THE DETERMINATION OF NUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHORUS WITH A STANNOUS CHLORIDE-HYDRAZINE SULPHATE REAGENT. Can J Biochem. 1964 Feb;42:287–292. doi: 10.1139/o64-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A., Jones C. W. Bacterial respiration. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):47–99. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.47-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Crofts A. R., von Stedingk L. V. Ion transport induced by light and antibiotics IN CHROMATOPHORES FROM Rhodospirillum rubrum. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Oct 17;6(1):41–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P. Aerobic and anaerobic bacterial respiration monitored by electrodes. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):231–238. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P., Hamilton W. A. Release of respiratory control in particles from Micrococcus denitrificans by ion-translocating antibiotics. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 10;23(3):528–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P., Whatley F. R. Oxidative phosphorylation coupled to oxygen uptake and nitrate reduction in Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 1;216(2):342–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P., Whatley F. R. Paracoccus denitrificans and the evolutionary origin of the mitochondrion. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):495–498. doi: 10.1038/254495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P., Whatley F. R. The bioenergetics of Paracoccus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 5;463(2):129–153. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(77)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Barnes E. M., Jr Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. II. The mechanism of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5523–5531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B., Ferguson S. J., John P. Measurement by a flow dialysis technique of the steady-state proton-motive force in chromatophores from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Comparison with phosphorylation potential. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 11;502(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N. Active transport of solutes in bacterial membrane vesicles. Adv Microb Physiol. 1977;15:175–251. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraayenhof R. 'State 3--state 4 transition' and phosphate potential in 'Class I' spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May;180(1):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90214-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford H. G. Energy transduction in the mitochondrionlike bacterium Paracoccus denitrificans during carbon- or sulphate-limited aerobic growth in continuous culture. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jan;56(1):13–22. doi: 10.1139/o78-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiser M., Gromet-Elhanan Z. Comparison of the electrochemical proton gradient and phosphate potential maintained by Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores in the steady state. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 15;178(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord P. W., Brooks A. G., Edwards J. M. Variation between observers in the estimation of airway resistance and thoracic gas volume. Thorax. 1977 Feb;32(1):67–70. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty R. E., Portis A. R., Jr A simple, quantitative approach to the coupling of photophosphorylation to electron flow in terms of proton fluxes. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5110–5114. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer E. M., van Verseveld H. W., van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Energy conservation during aerobic growth in Paracoccus denitrificans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):25–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00446650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Estimation of membrane potential and pH difference across the cristae membrane of rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):471–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The effective proton conductance of the inner membrane of mitochondria from brown adipose tissue. Dependency on proton electrochemical potential gradient. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):349–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The influence of respiration and ATP hydrolysis on the proton-electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane of rat-liver mitochondria as determined by ion distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):848–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Slater E. C. The value of G degrees for the hydrolysis of ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 25;267(2):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Gutman M. Control of the rate of reverse electron transport in submitochondrial particles by the free energy. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3220–3227. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of transmembrane electrochemical proton gradients. J Bioenerg. 1975 May;7(2):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01558427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. C., Rosing J., Mol A. The phosphorylation potential generated by respiring mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 5;292(3):534–553. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorgato M. C., Ferguson S. J., Kell D. B., John P. The protonmotive force in bovine heart submitochondrial particles. Magnitude, sites of generation and comparison with the phosphorylation potential. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):237–256. doi: 10.1042/bj1740237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Verseveld H. W., Stouthamer A. H. Oxidative phosphorylation in Micrococcus denitrificans: calculation of the P/O ratio in growing cells. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Apr 1;107(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00425334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


