Abstract
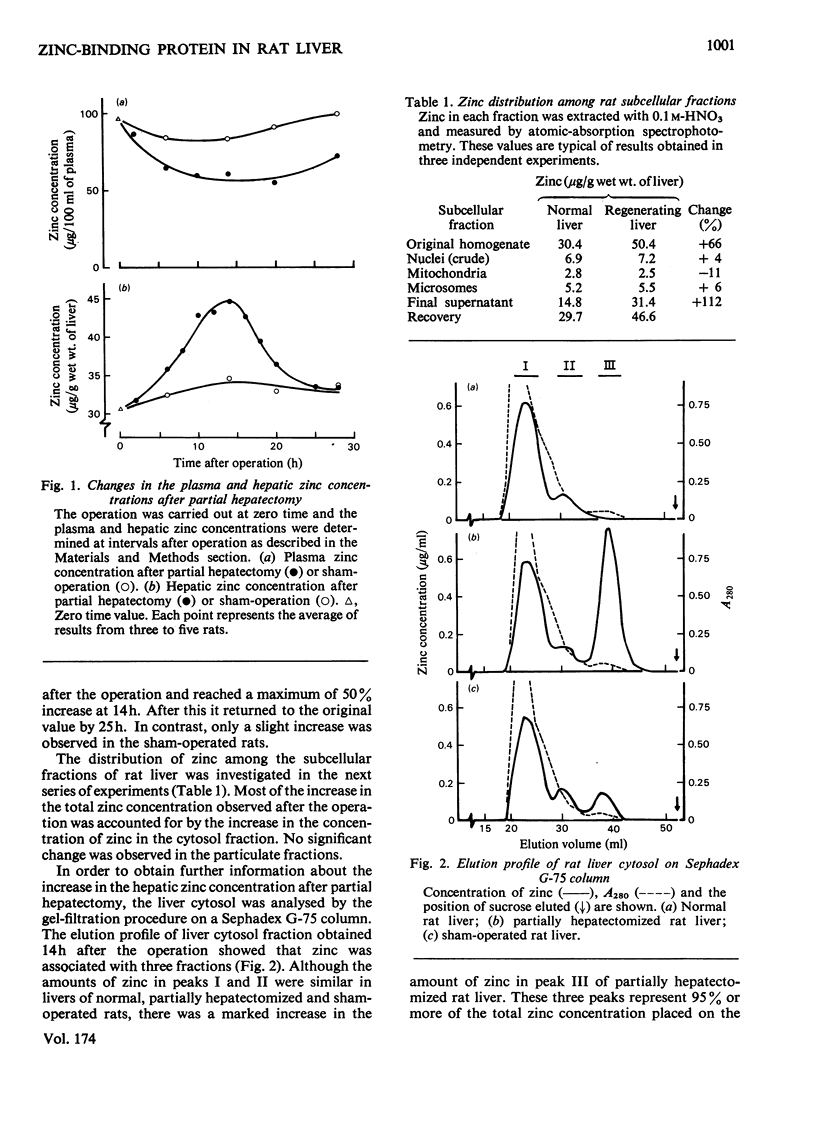
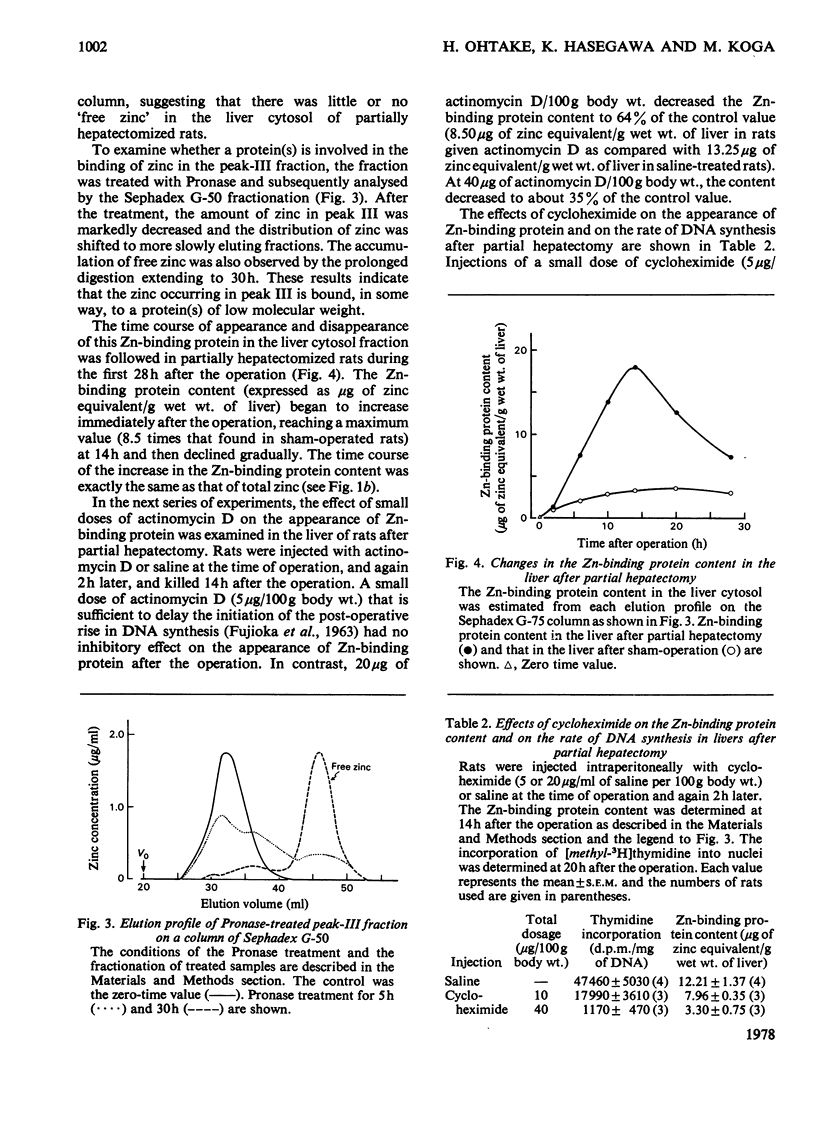
In the livers of rats after partial hepatectomy the zinc concentration began to increase soon after the operation, reached a maximum value at 14h, and decreased to the original value by 25h after the operation. In contrast, the plasma zinc concentration continued to decrease during the first 10h after the operation and remained depressed for at least 28h. The plasma and hepatic zinc concentrations were relatively unaffected by sham-operation. Synchronous with the increase in the hepatic zinc concentration after the partial hepatectomy, there was an appearance of zinc-binding protein (Zn-binding protein) in the liver cytosol. Studies with small doses of actinomycin D and cycloheximide suggest that both RNA and protein syntheses are necessary for the induction of Zn-binding protein after partial hepatectomy. A high content of the Zn-binding protein was found in neonatal rat liver. The Zn-binding protein, however, was undetectable 40 days after birth. The Zn-binding protein was also found in the adult rat liver when stimulated to proliferate after the administration of isoprenaline followed by glucagon. These findings indicate a close linkage between the appearance of Zn-binding protein in the liver cytosol and the regulation of DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPELMANS F., WATTIAUX R., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 5. The association of acid phosphatase with a special class of cytoplasmic granules in rat liver. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):438–445. doi: 10.1042/bj0590438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld D. S., Kawaguchi H., Livingston D. M., Vallee B. L. Zinc reverse transcriptases from mammalian RNA type C viruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):296–302. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. The relation between the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid and the synthesis of protein in the multiplication of bacteriophage T2. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):473–483. doi: 10.1042/bj0610473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner I., Davies N. T. The induction of metallothionein in rat liver by zinc injection and restriction of food intake. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):733–738. doi: 10.1042/bj1490733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R. H., Kägi J. H. Human hepatic metallothioneins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Vasey E. J., Whanger P. D. Accumulation and depletion of zinc in rat liver and kidney metallothionens. J Nutr. 1977 May;107(5):805–813. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.5.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters J. K. The role of zinc ions in the transformation of lymphocytes by phytohaemagglutinin. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):133–139. doi: 10.1042/bj1300133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJIOKA M., KOGA M., LIEBERMAN I. METABOLISM OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID AFTER PARTIAL HEPATECTOMY. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3401–3406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJIOKA M., LIEBERMAN I. A ZN++ REQUIREMENT FOR SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1164–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. L., Cousins R. J. Degradation of hepatic zinc-thionein after parenteral zinc administration. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj1600583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinandus J. A., Morris H. P., Weber G. Behavior of opposing pathways of thymidine utilization in differentiating, regenerating, and neoplastic liver. Cancer Res. 1971 May;31(5):550–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa K., Koga M. Induction of liver cell proliferation in intact rats by amines and glucagon. Life Sci. 1977 Dec 15;21(12):1723–1728. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3460–3465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALLEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containign protein from equine renal cortex. II. Physico-chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., ABRAMS R., HUNT N., OVE P. LEVELS OF ENZYME ACTIVITY AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN MAMMALIAN CELLS CULTURED FROM THE ANIMAL. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3955–3962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., OVE P. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and its inhibition in mammalian cells cultured from the animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1634–1642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg G. F., Nordberg M., Piscator M., Vesterberg O. Separation of two forms of rabbit metallothionein by isoelectric focusing. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):491–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1260491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Mammalian zinc homeostasis: requirement for RNA and metallothionein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jun 16;64(4):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in animal cells by ethylene diamine tetraacetate, and its reversal by zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstead H. H., Rinaldi R. A. Impairment of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by dietary zinc deficiency in the rat. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Feb;73(1):81–83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton M. C., Wu C. W., Goldthwait D. A. The presence and possible role of zinc in RNA polymerase obtained from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2497–2501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J., Brown R. F., Husakova A., Gilbertson J. R., Zemel R., Lieberman I. Induction of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the liver of the intact animal. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1757–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. P., Mildvan A. S., Loeb L. A. Zinc in DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLEE B. L. Biochemistry, physiology and pathology of zinc. Physiol Rev. 1959 Jul;39(3):443–490. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L. Zinc biochemistry in normal and neoplastic growth processes. Experientia. 1977 May 15;33(5):600–601. doi: 10.1007/BF01946521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volm M., Schumacher J., Wayss K., Wesch H. Changes in the concentrations of elements in liver after partial hepatectomy. Experientia. 1974 Nov 15;30(11):1255–1257. doi: 10.1007/BF01945170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weser U., Rupp H., Donay F., Linnemann F., Voelter W., Voetsch W., Jung G. Characterization of Cd, Zn-thionein (metallothionein) isolated from rat and chicken liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):127–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Rajagopalan K. V. Purification and some properties of Cd-binding protein from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


