Abstract
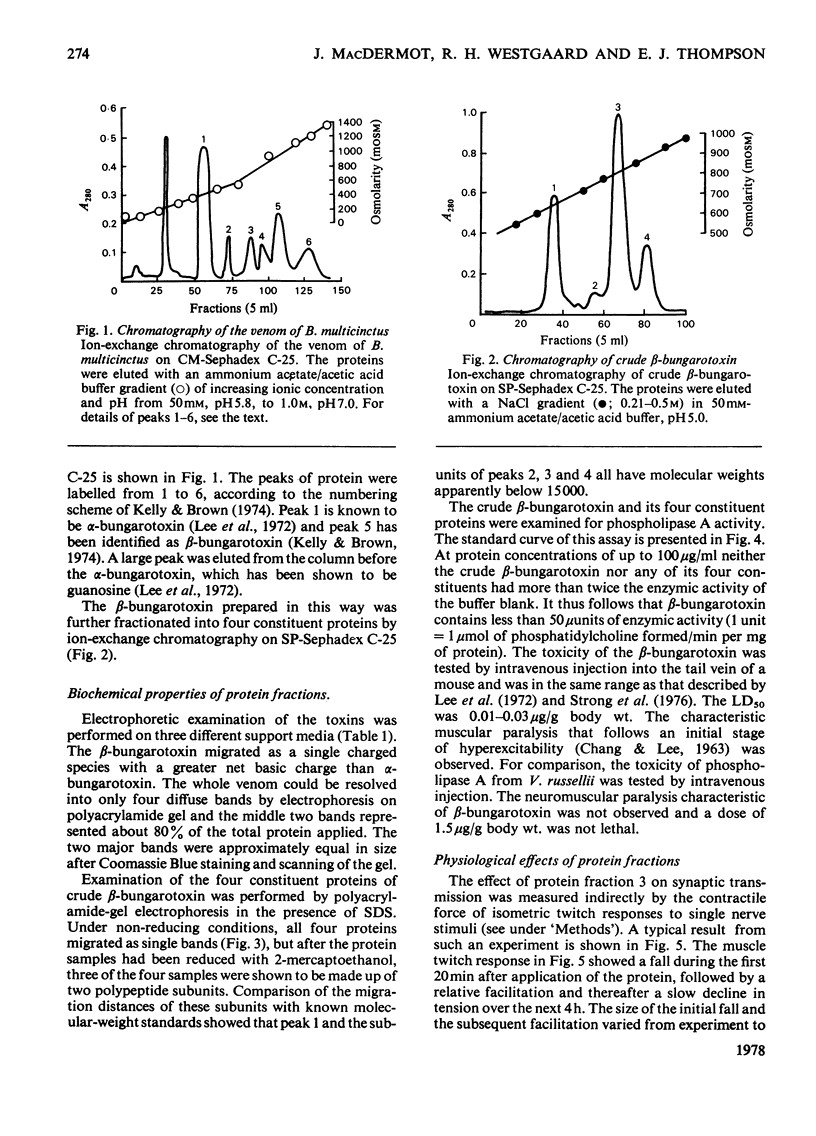
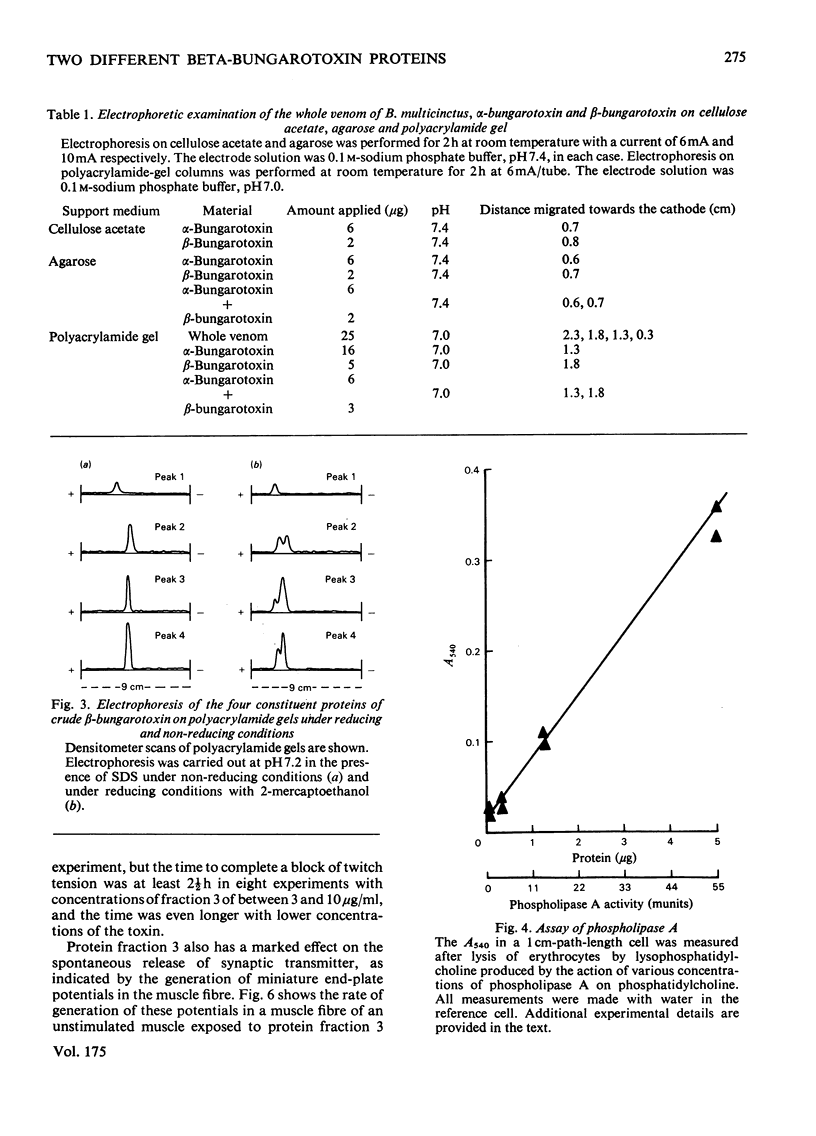
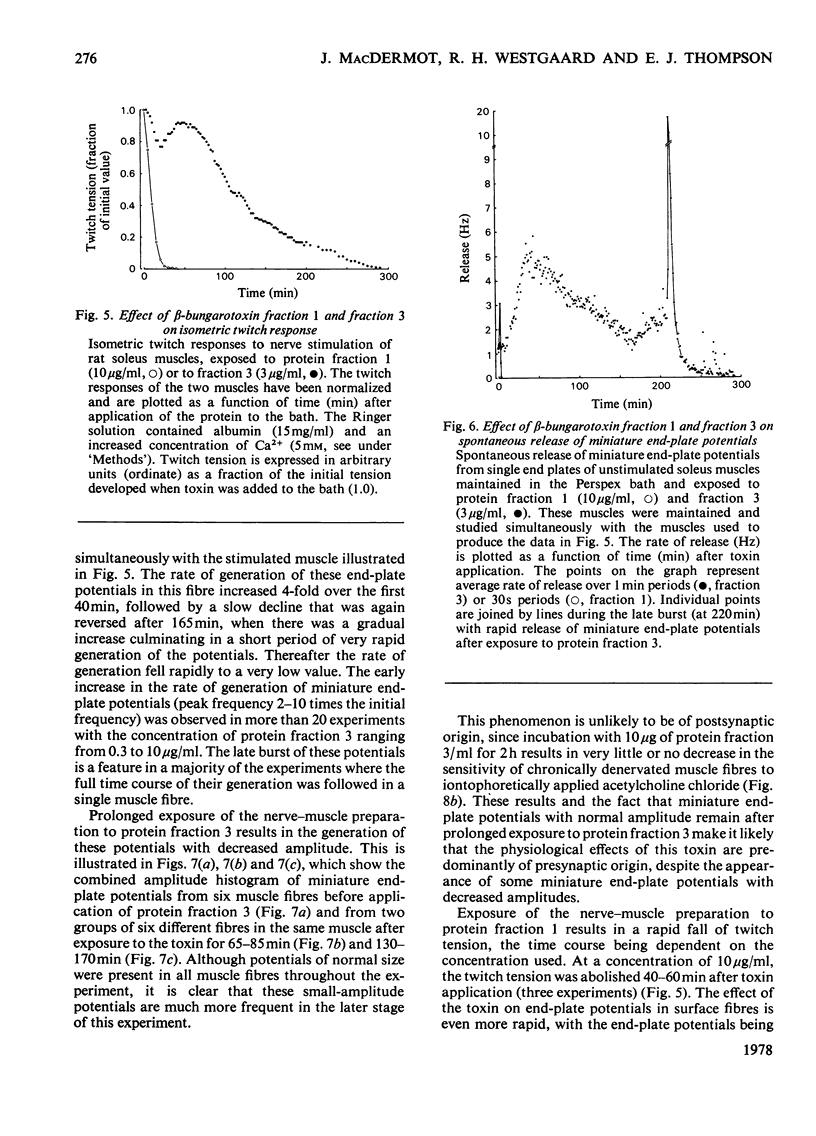
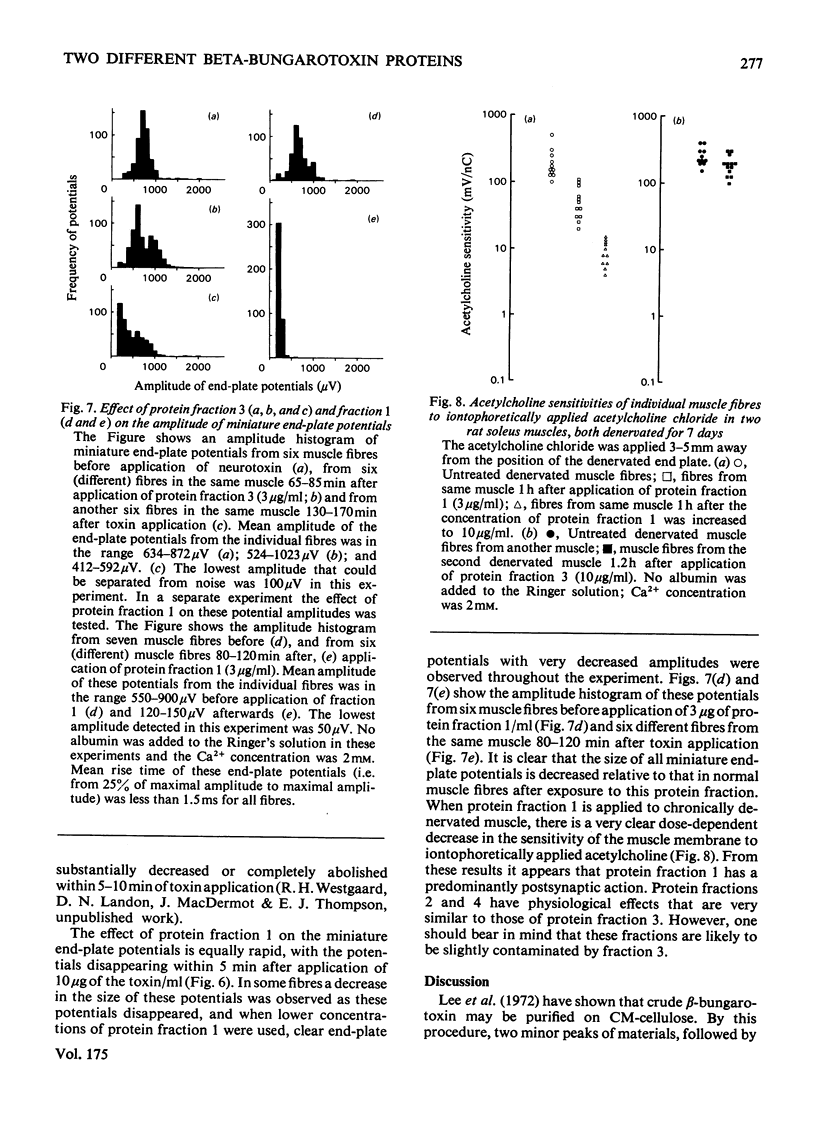
beta-Bungarotoxin, a specific presynaptic blocking agent, was prepared in two stages from the crude venom of Bungarus multicinctus by ion-exchange chromatography on the weakly acidic ion exchanger, CM-Sephadex, and on the strongly acidic ion exchanger, sulphopropyl-Sephadex. By these procedures it was purified to a single protein, which was shown by reduction to contain two polypeptide chains with mol.wts. of less than 15000. During purification of beta-bungarotoxin three other proteins were isolated. Two of these proteins have similar molecular weights, subunit structure and physiological properties to the major protein component. This latter is referred to as beta-bungarotoxin, since it has the same physiological properties as those described for unpurified beta-bungarotoxin by other workers. The first protein has very different physiological effects and biochemical properties from beta-bungarotoxin. This protein has a single class of polypeptide chains with an apparent molecular weight that is lower than the main beta-bungarotoxin protein, and appears to block synaptic transmission by a predominantly postsynaptic effect. It has been suggested [Oberg & Kelly (1976) J. Neurobiol. 7, 129-141] that the action of beta-bungarotoxin depends on its phospholipase A activity; however, in this preparation of the toxin less than 50 muunits of phospholipase A activity were detected (1 unit of activity is the amount of enzyme forming 1 mumol of L-alpha-phosphatidylcholine/min per mg of protein).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Alemá S., Miledi R. Isolation and characterization of presynaptically acting neurotoxins from the venom of Bungarus snakes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe T., Limbrick A. R., Miledi R. Acute muscle denervation induced by beta-bungarotoxin. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Nov 12;194(1117):545–553. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Wieckowski J., Chiu T. H. Cholinergic receptor molecules and cholinesterase molecules at mouse skeletal muscle junctions. Nature. 1971 Nov 26;234(5326):207–209. doi: 10.1038/234207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated rat diaphragm muscle. I. Purification and interaction with [125I]-alpha-bungarotoxin. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2092–2099. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG C. C., LEE C. Y. ISOLATION OF NEUROTOXINS FROM THE VENOM OF BUNGARUS MULTICINCTUS AND THEIR MODES OF NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING ACTION. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Jul 1;144:241–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Chen T. F., Lee C. Y. Studies of the presynaptic effect of -bungarotoxin on neuromuscular transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):339–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Lee C. Y. Use of a snake venom toxin to characterize the cholinergic receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1241–1247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdall M. J., Fohlman J. P., Eaker D. Inhibition of high-affinity choline transport in peripheral cholinergic endings by presynaptic snake venom neurotoxins. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):700–702. doi: 10.1038/269700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden W. F., Harvey A. L., Marshall I. G. Pharmacological studies on the bungarotoxins: separation of the fractions and their neuromuscular activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 May;26(2):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Gel chromatography of proteins in denaturing solvents. Comparison between sodium dodecyl sulfate and guanidine hydrochloride as denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5166–5168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. D. Effects of beta-bungarotoxin on mitochondrial respiration are caused by associated phospholipase A activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Brown F. R., 3rd Biochemical and physiological properties of a purified snake venom neurotoxin which acts presynaptically. J Neurobiol. 1974;5(2):135–150. doi: 10.1002/neu.480050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Oberg S. G., Strong P. N., Wagner G. M. beta-Bungarotoxin, a phospholipase that stimulates transmitter release. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:117–125. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang C. C. Modes of actions of purified toxins from elapid venoms on neuromuscular transmission. Mem Inst Butantan. 1966;33(2):555–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang S. L., Kau S. T., Luh S. H. Chromatographic separation of the venom of Bungarus multicinctus and characterization of its components. J Chromatogr. 1972 Oct 5;72(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(72)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. Further studies on the control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):603–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R. H., Howard B. D. Failure of a phospholipase A inhibitor to inhibit beta-bungarotoxin phospholipase A. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 28;120(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg S. G., Kelly R. B. The mechanism of beta-bungarotoxin action. I. Modification of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Neurobiol. 1976 Mar;7(2):129–141. doi: 10.1002/neu.480070206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen I., Grantham P. A., Cooper J. R. Mechanism of action of beta-bungarotoxin on synaptosomal preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2664–2668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong P. N., Goerke J., Oberg S. G., Kelly R. B. beta-Bungarotoxin, a pre-synaptic toxin with enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):178–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernicke J. F., Oberjat T., Howard B. D. Beta-neurotoxin reduces neurotransmitter storage in brain synapses. J Neurochem. 1974 May;22(5):781–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernicke J. F., Vanker A. D., Howard B. D. The mechanism of action of beta-bungarotoxin. J Neurochem. 1975 Oct;25(4):483–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


