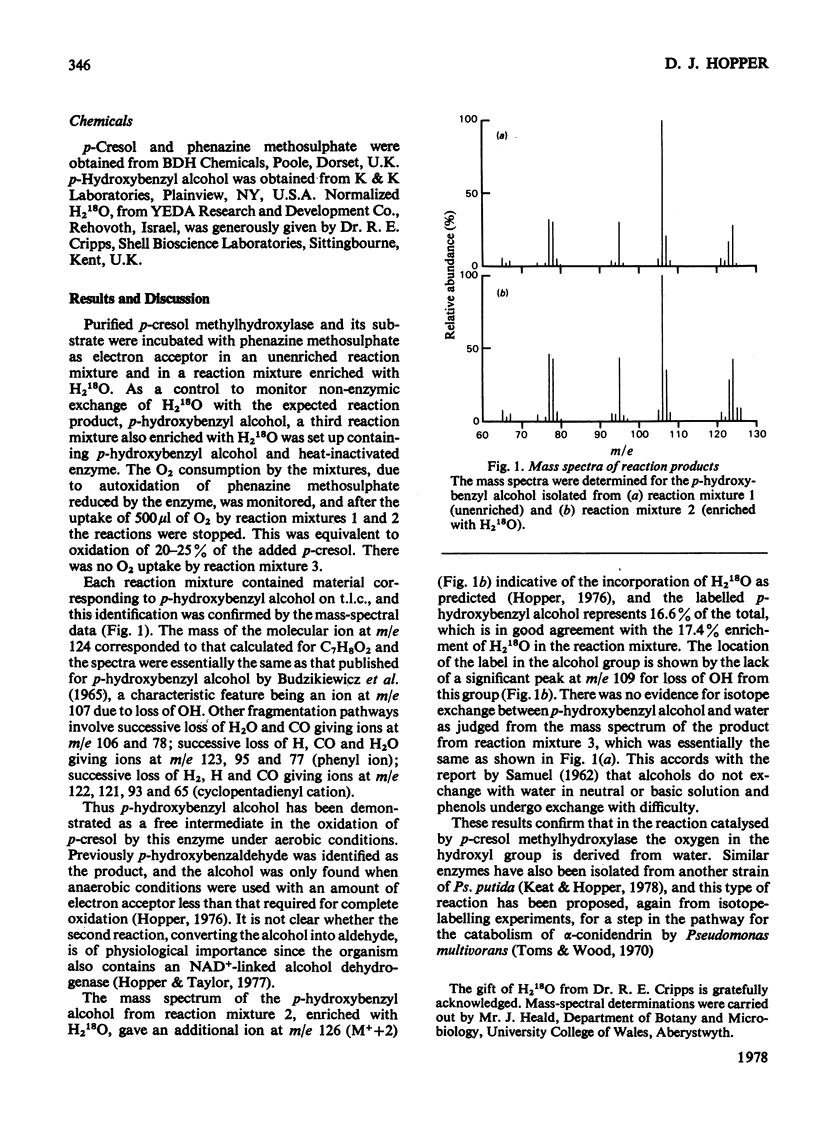
Abstract
In the hydroxylation of the methyl group of p-cresol by an enzyme from Pseudomonas putida the oxygen atom is derived from water. Although a second reaction by the same enzyme converts the product, p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol, into the aldehyde, the alcohol is an enzyme-free intermediate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhardt F. H., Pachowsky H., Staudinger H. A 4-methoxybenzoate O-demethylase from Pseudomonas putida. A new type of monooxygenase system. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):241–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Hopper D. J. The bacterial metabolism of 2,4-xylenol. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):491–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1100491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Taylor D. G. The purification and properties of p-cresol-(acceptor) oxidoreductase (hydroxylating), a flavocytochrome from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):155–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1670155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J. The hydroxylation of P-cresol and its conversion to P-hydroxybenzaldehyde in Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90544-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E. J., Coon M. J. Enzymatic omega-oxidation. IV. Purification and properties of the omega-hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3882–3889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toms A., Wood J. M. Early intermediates in the degradation of alpha-conidendrin by a Pseudomonas multivorans. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):733–740. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


