Abstract
In certain lines of hepatoma tissue-culture cells, the extracellular glutamine concentration regulates the specific activity of glutamine synthetase. By quantifying the radioactivity in immunoprecipitated glutamine synthetase on polyacrylamide gels, we found that the rate of degradation, but not of synthesis, of glutamine synthetase is a sensitive function of extracellular glutamine. The activiy that degrades this enzyme appears to be labile.
Full text
PDF
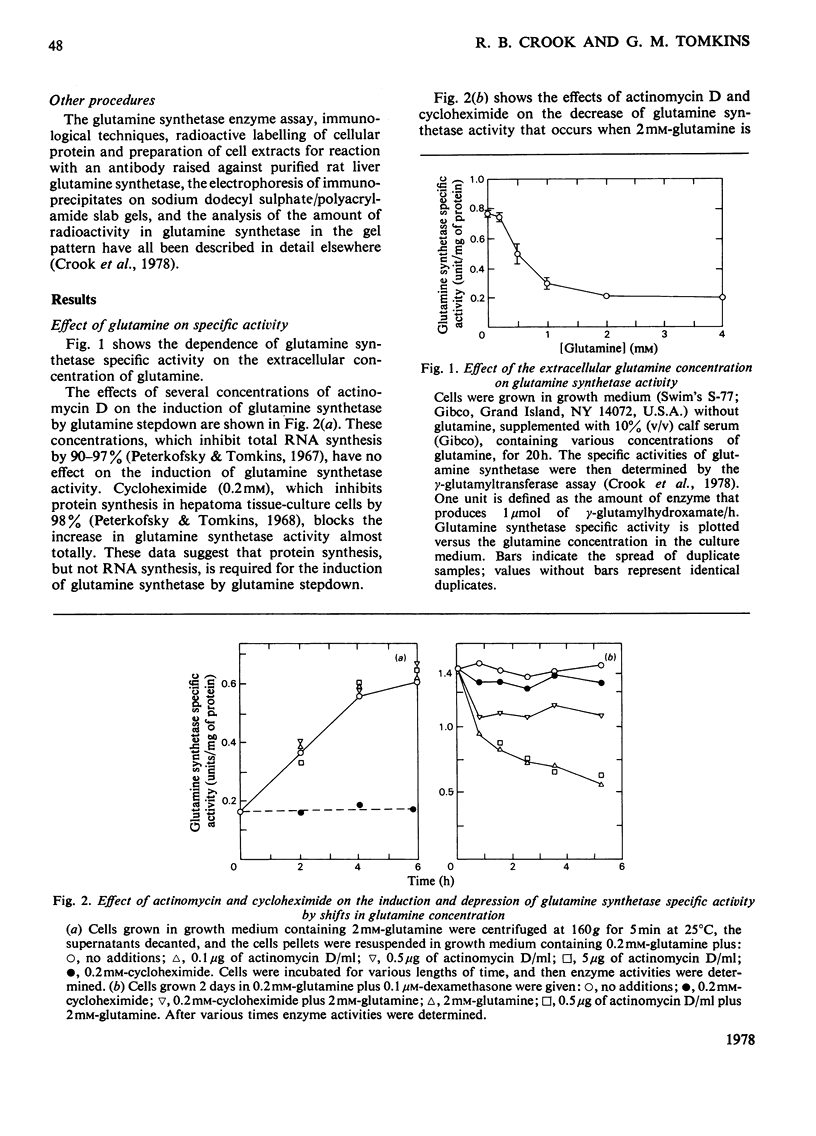
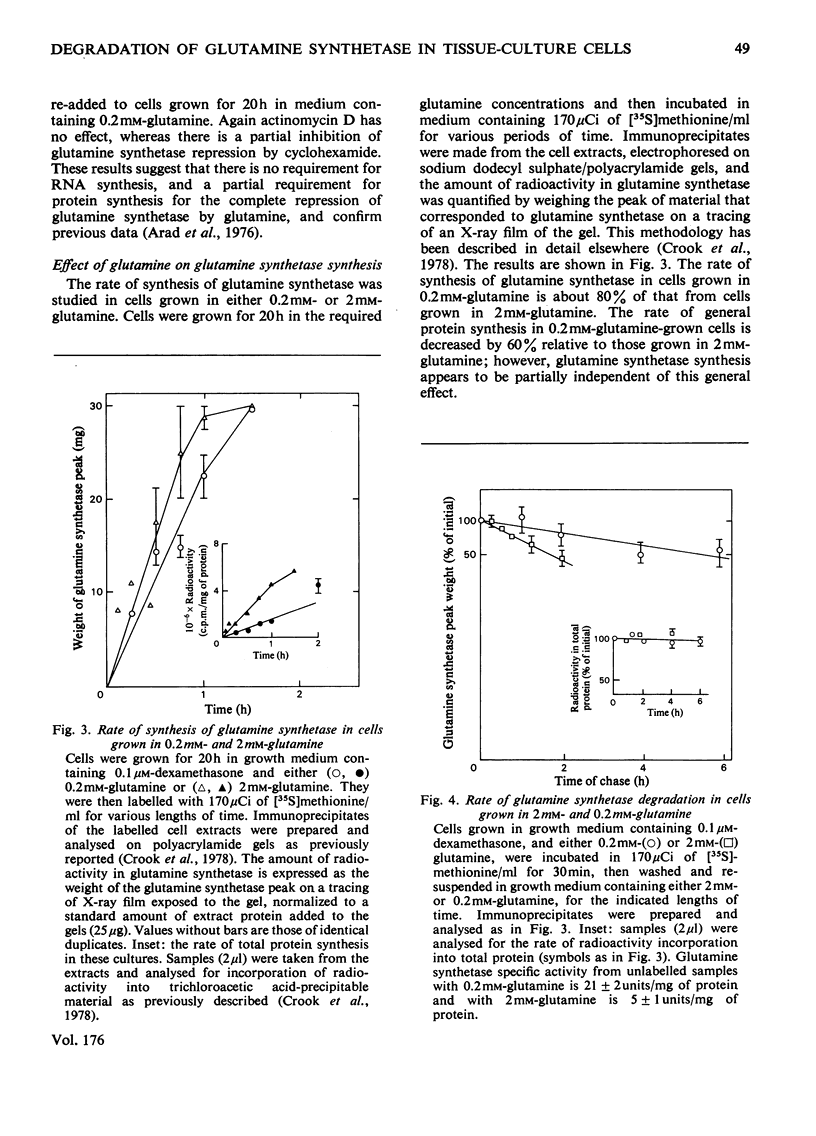
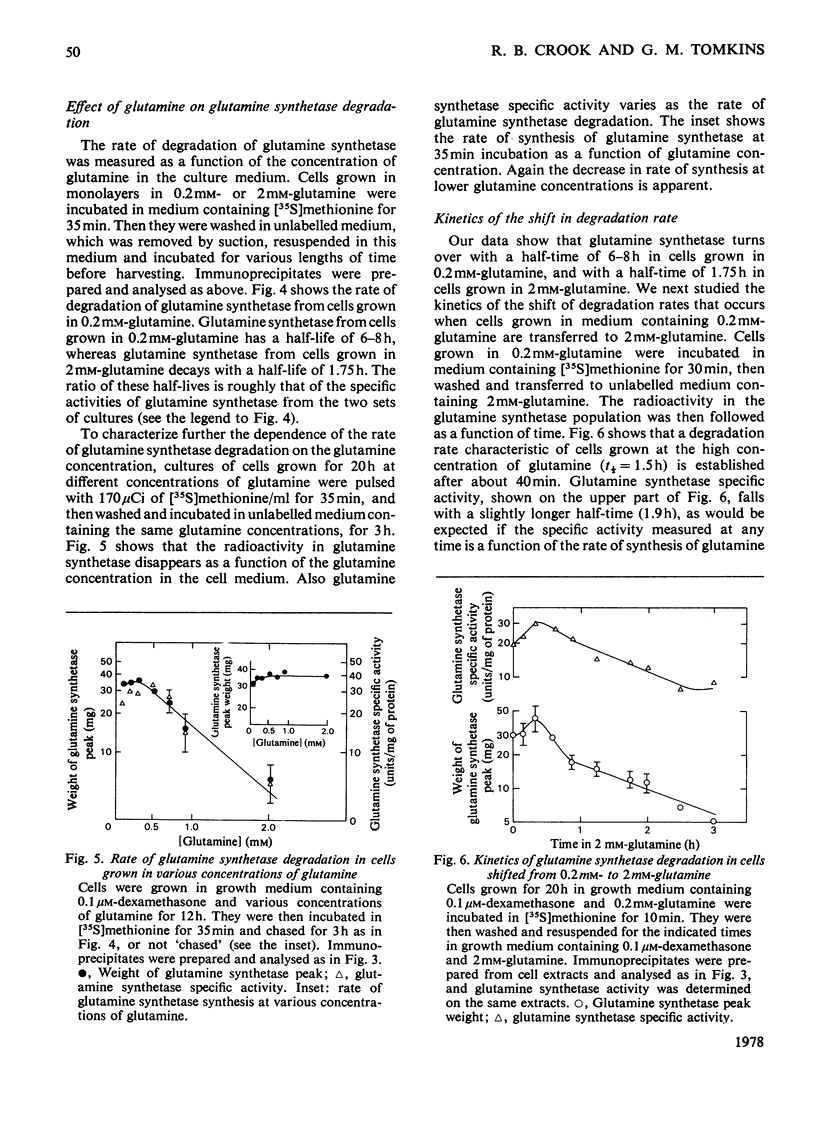
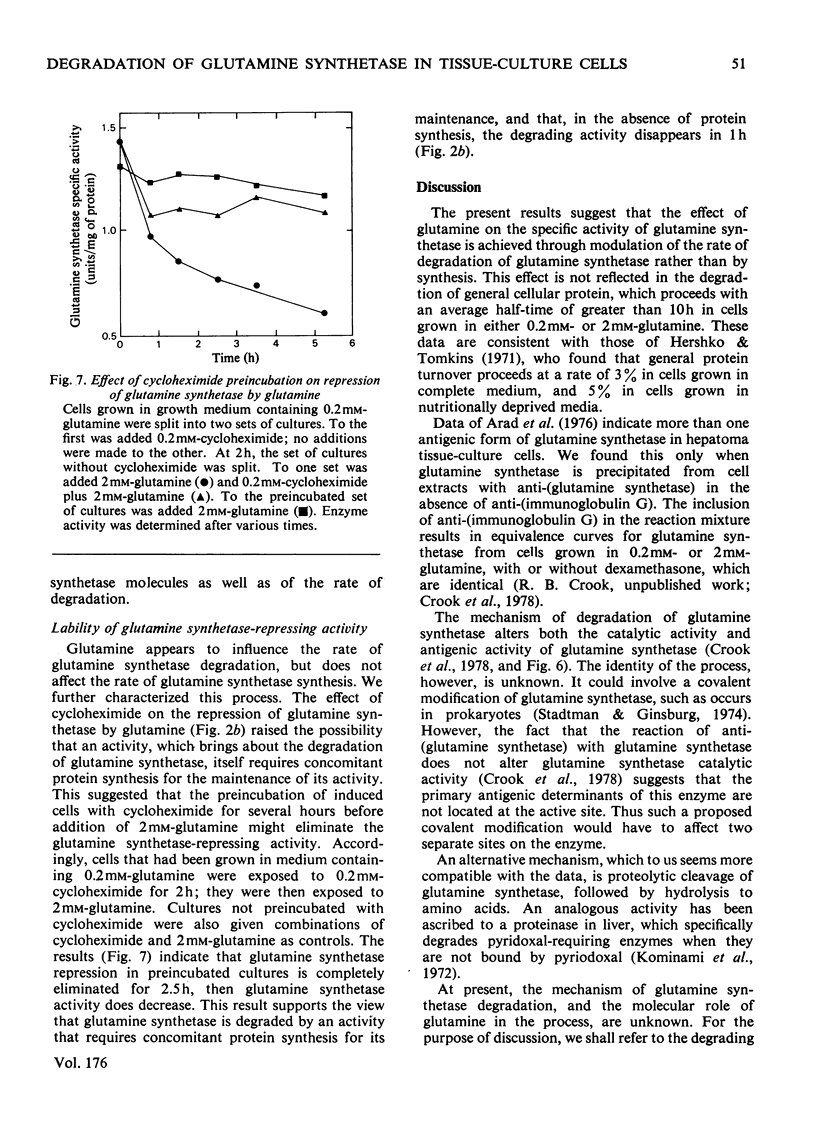

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arad G., Freikopf A., Kulka R. G. Glutamine-stimulated modification and degradation of glutamine synthetase in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMARS R. The inhibition by glutamine of glutamyl transferase formation in cultures of human cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):435–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Tomkins G. M. Studies on the degradation of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cells in culture. Influence of the composition of the medium and adenosine triphosphate dependence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK D. L., MOSCONA A. A. SYNTHESIS OF EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED GLUTAMINE SYNTHETASE (GLUTAMOTRANSFERASE ACTIVITY) IN EMBRYONIC CHICK RETINA IN VITRO. Dev Biol. 1963 Dec;8:341–357. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami E., Kobayashi K., Kominami S., Katunuma N. Properties of a specific protease for pyridoxal enzymes and its biological role. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6848–6855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka R. G., Cohen H. Regulation of glutamine synthetase activity of hepatoma tissue culture cells by glutamine and dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6738–6743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka R. G., Tokins G. M., Crook R. B. Clonal differences in glutamine synthetase activity of hepatoma cells. Effects of glutamine and dexamethasone. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jul;54(1):175–179. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Portnoff L. S., Tiemeier D. C. Immunochemical evidence for glutamine-mediated degradation of glutamine synthetase in cultured Chinese hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL J., FOTTRELL P. F. Mechanism of D-glutamyltransferase repression in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:334–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91836-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Tomkins G. M. Effect of inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis on steroid-mediated induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Tomkins G. M. Evidence for the steroid-induced accumulation of tyrosine-aminotransferase messenger RNA in the absence of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):222–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C. E., Smith G. R., Cortese R., Ames B. N. [Mutant tRNA His ineffective in repression and lacking two pseudouridine modifications]. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):72–74. doi: 10.1038/newbio238072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeier D. C., Milman G. Regulation of glutamine synthetase in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Induction and repression by glutamine. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5722–5727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


