Abstract
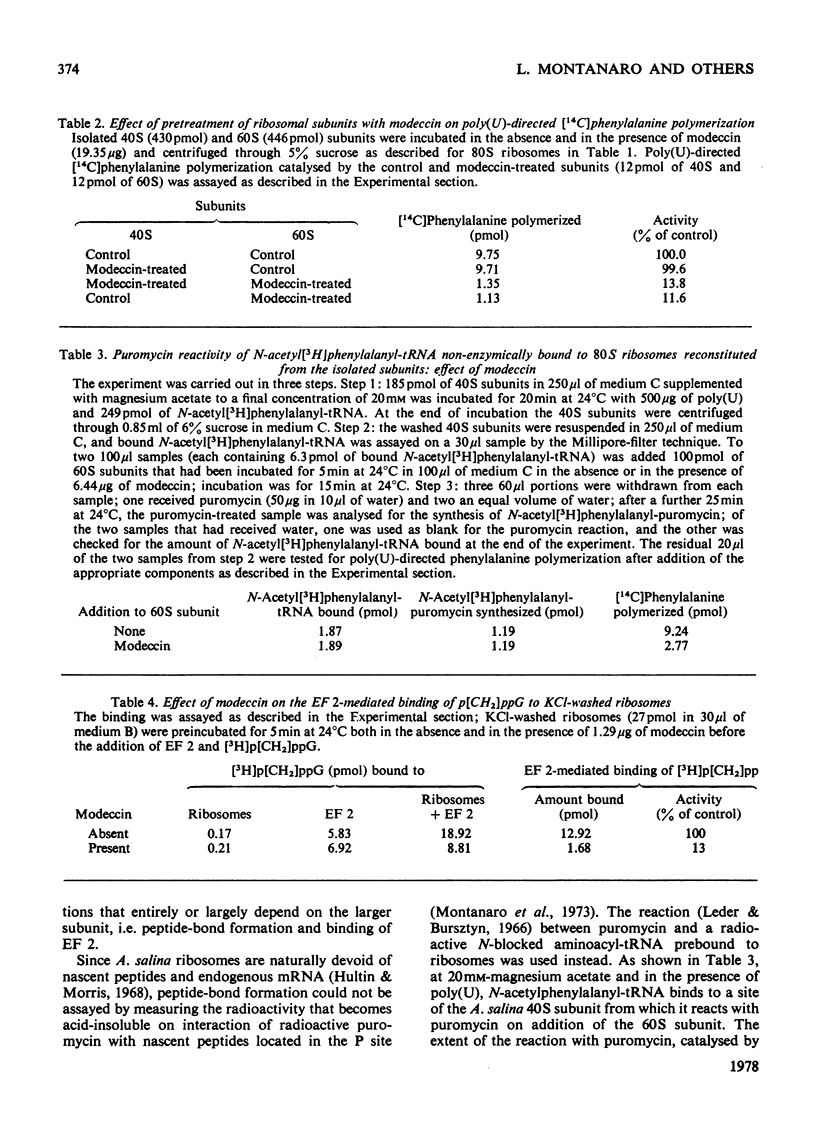
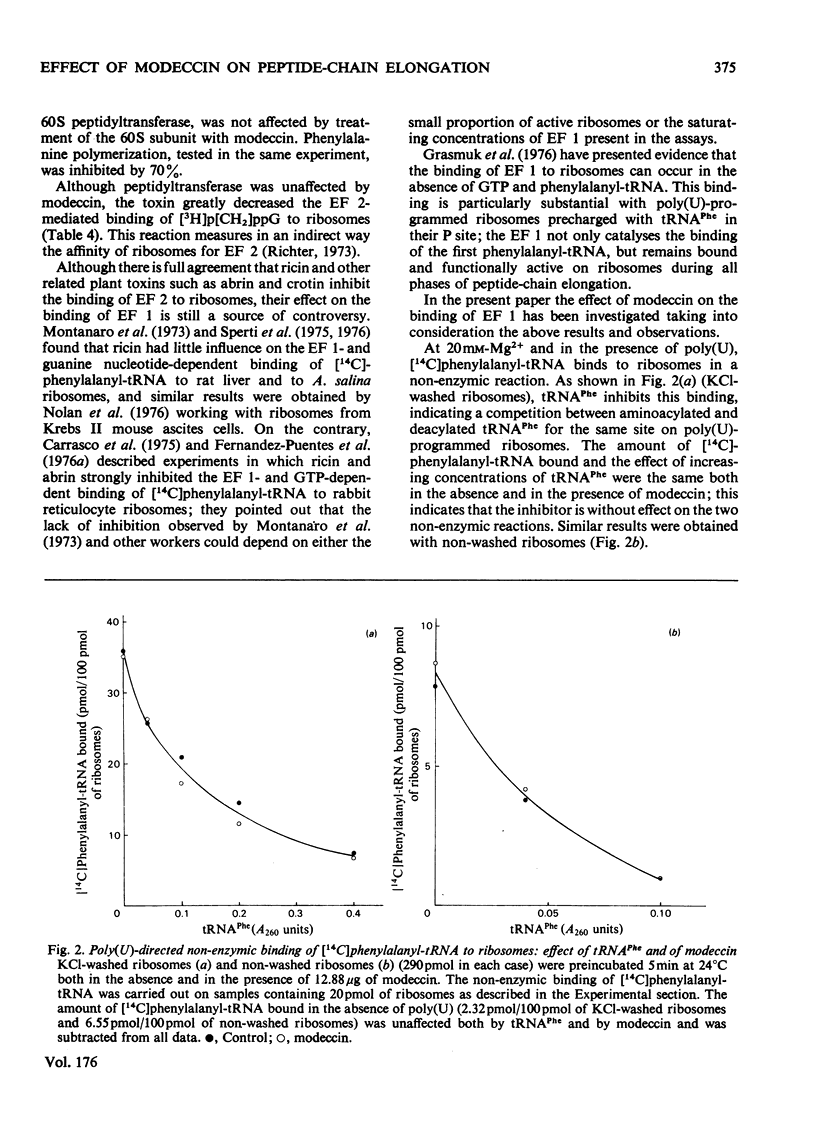
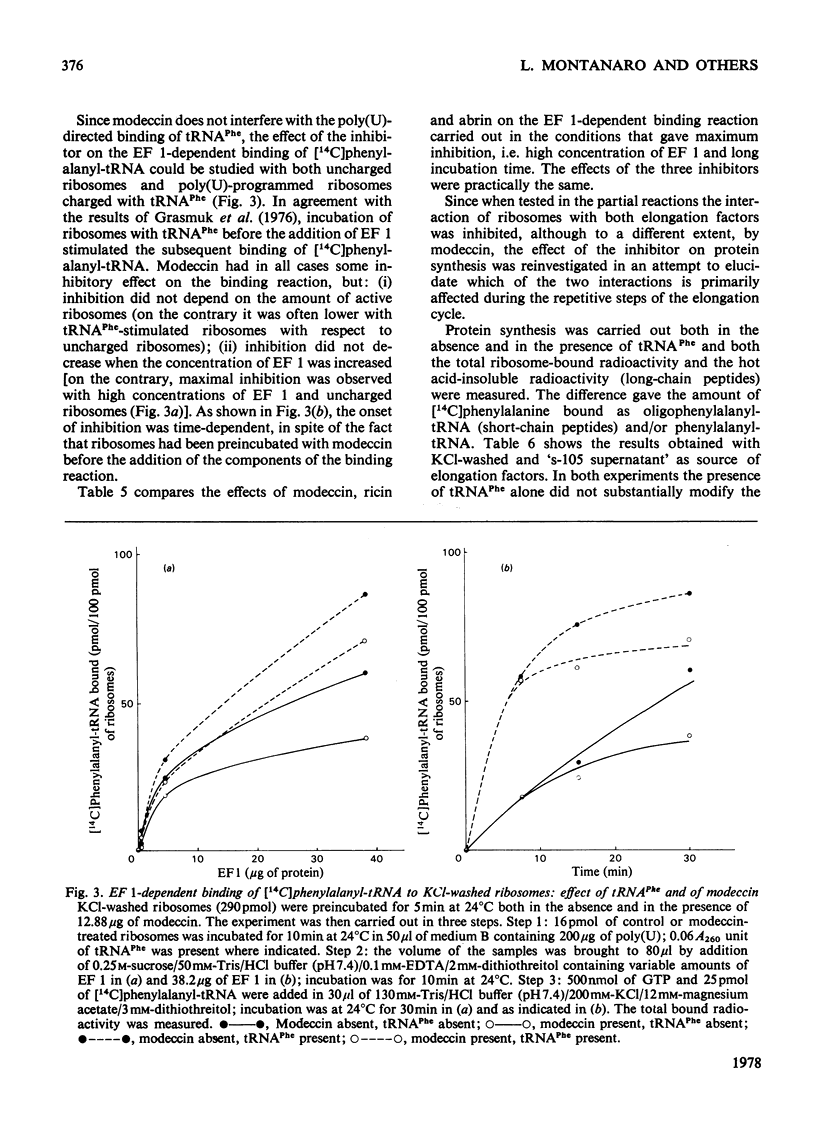
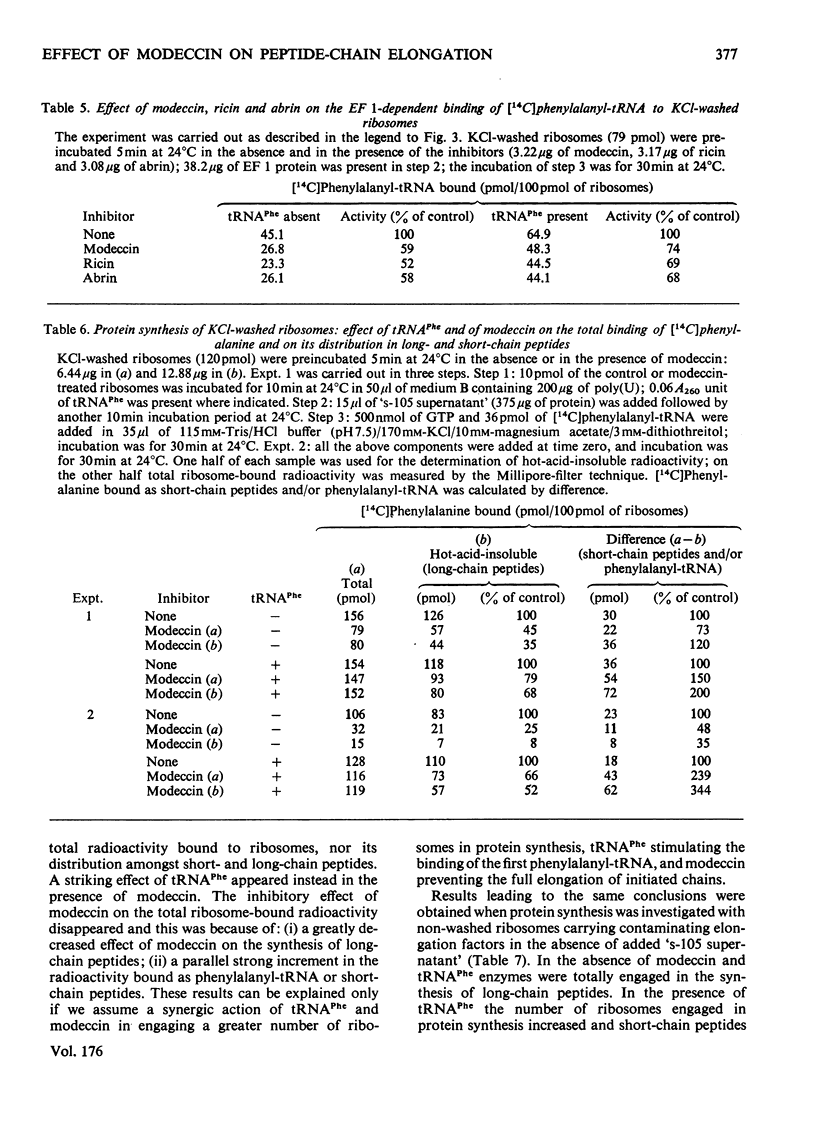
Modeccin inhibits polypeptide-chain elongation catalysed by Artemia salina (brine shrimp) ribosomes by inactivating the 60 S ribosomal subunit. Among the individual steps of elongation, peptide-bond formation, catalysed by 60 S peptidyltransferase, is unaffected by the toxin, whereas the binding of EF 2 (elongation factor 2) to ribosomes is strongly inhibited. Modeccin does not affect the poly(U)-dependent non-enzymic binding of either deacylated tRNAPhe or phenylalanyl-tRNA to ribosomes. The inhibitory effect of modeccin on the EF 1 (elongation factor 1)-dependent binding of phenylalanyl-tRNA is discussed, since it is decreased by tRNAPhe, which stimulates the binding reaction. The analysis of the distribution of ribosome-bound radioactivity during protein synthesis shows that modeccin consistently inhibits the radioactivity bound as long-chain peptides, but depending on the experimental conditions, can leave unchanged or even greatly stimulates the radioactivity bound as phenylalanyl-tRNA and/or short-chain peptides. It is concluded that, during the complete elongation cycle, modeccin does not affect the binding of the first aminoacyl-tRNA to ribosomes, but inhibits some step in the subsequent repetitive activity of either EF 1 or EF 2. The results obtained indicate that the mechanism of action of modeccin is very similar to that of ricin and related plant toxins such as abrin and crotin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bermek E. Formation of a complex involving ADP-ribosylated human translocation factor, guanosine nucleotide and ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Fernandez-Puentes C., Vazquez D. Effects of ricin on the ribosomal sites involved in the interaction of the elongation factors. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):499–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Puentes C., Benson S., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Protective effect of elongation factor 2 on the inactivation of ribosomes by the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 1;64(2):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Puentes C., Carrasco L., Vázquez D. Site of action of ricin on the ribosome. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4364–4369. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Bonetti E., Stirpe F. Modeccin, the toxin of Adenia digitata. Purification, toxicity and inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):491–496. doi: 10.1042/bj1740491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasmuk H., Nolan R. D., Drews J. A new concept of the function of elongation factor 1 in peptid chain elongation. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec;71(1):271–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin T., Morris J. E. The ribosomes of encysted embryos of Artemia salina during cryptobiosis and resumption of development. Dev Biol. 1968 Feb;17(2):143–164. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Bursztyn H. Initiation of protein synthesis II. A convenient assay for the ribosome-dependent synthesis of N-formyl-C14-methionylpuromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Ribosomes as the target of the toxin. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1360677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J., Etzler M. E. Characterization of two plant lectins from Ricinus communis and their quantitative interaction with a murine lymphoma. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):196–204. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J. The interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin with normal and tumor cell surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan R. D., Grasmuk H., Drews J. The binding of tritiated elongation-factors 1 and 2 to ribosomes from Krebs II mouse ascites-tumore cells. The influence of various antibiotics and toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refsnes K., Haylett T., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Modeccin--a plant toxin inhibiting protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1176–1183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. Competition between the elongation factors 1 and 2, and phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid for the ribosomal binding sites in a polypeptide-synthesizing system from brain. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2853–2857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., Meier D., Ochoa S. Effect of development on the translation of messenger RNA in Artemia salina embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Testoni G. Relationship between elongation factor I- and elongation factor II- dependent guanosine triphosphatase activities of ribosomes. Inhibition of both activities by ricin. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):447–451. doi: 10.1042/bj1480447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Testoni G., Stirpe F. Inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro by crotins and ricin. Effect on the steps of peptide chain elongation. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):7–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1560007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Bonetti E. Inhibition of protein synthesis by modeccin, the toxin of Modecca digitata. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 20;85(1):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. H., Hartman F. C., Pfuderer P., Yang W. K. Purification and characterization of two major toxic proteins from seeds of Abrus precatorius. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3061–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


