Abstract
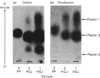
1. Of the three major human pepsins, pepsin 1 has greater proteolytic activity towards ovalbumin than has pepsin 3. Pepsin 5 has low activity towards this substrate. 2. Proteolytic pH-activity curves show only on pH maximum, about pH 1.4 for pepsin 1, pH 1.4--1.5 for pepsin 3 and pH 1.2--1.4 for pepsin 5. The curve for pepsin 3 has a shoulder between pH 2.4 and 3.4. 3. The rate of digestion of ovalbumin by pepsin 1 is approximately three times slower than are those of bovine haemoglobin or human globin. 4. The results suggest that there may be a physiological advantage in having more than one pepsin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castellino F. J., Barker R. Examination of the dissociation of multichain proteins in guanidine hydrochloride by membrane osmometry. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2207–2217. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J., Taylor W. H. The pepsins from human gastric mucosal extracts. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(4):587–594. doi: 10.1042/bj1180587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J., Taylor W. H. The pepsins of normal human gastric juice. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(4):663–668. doi: 10.1042/bj1130663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley W. B., Boyer S. H., Naughton M. A. Electrophoretic and functional heterogeneity of pepsinogen in several species. Nature. 1966 Mar 5;209(5027):996–1002. doi: 10.1038/209996a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO T., CGUROFF G., UDENFRIEND S. ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOR OF PLASMA ALBUMIN TYROSINE DERIVED FROM ADMINISTERED PHENYLALANINE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3385–3388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts N. B., Taylor W. H. The preparation and purification of individual human pepsins by using diethylaminoethyl-cellulose. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):607–615. doi: 10.1042/bj1690607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR W. H. Gastric proteolysis in disease. 2. The proteolytic activity of gastric juice and gastric mucosal extracts from patients with chronic gastric and duodenal ulcer. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jul;12:338–343. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Mills J., Chiang L., de Chiang L. Gastric pepsin, mucus and clinical secretory studies. I. Gastric pepsin and pepsin inhibitors. Comparative studies on the structure and specificity of human gastricsin, pepsin and zymogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jan 26;140(2):688–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. H. Pepsins of patients with peptic ulcer. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):76–77. doi: 10.1038/227076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]