Abstract
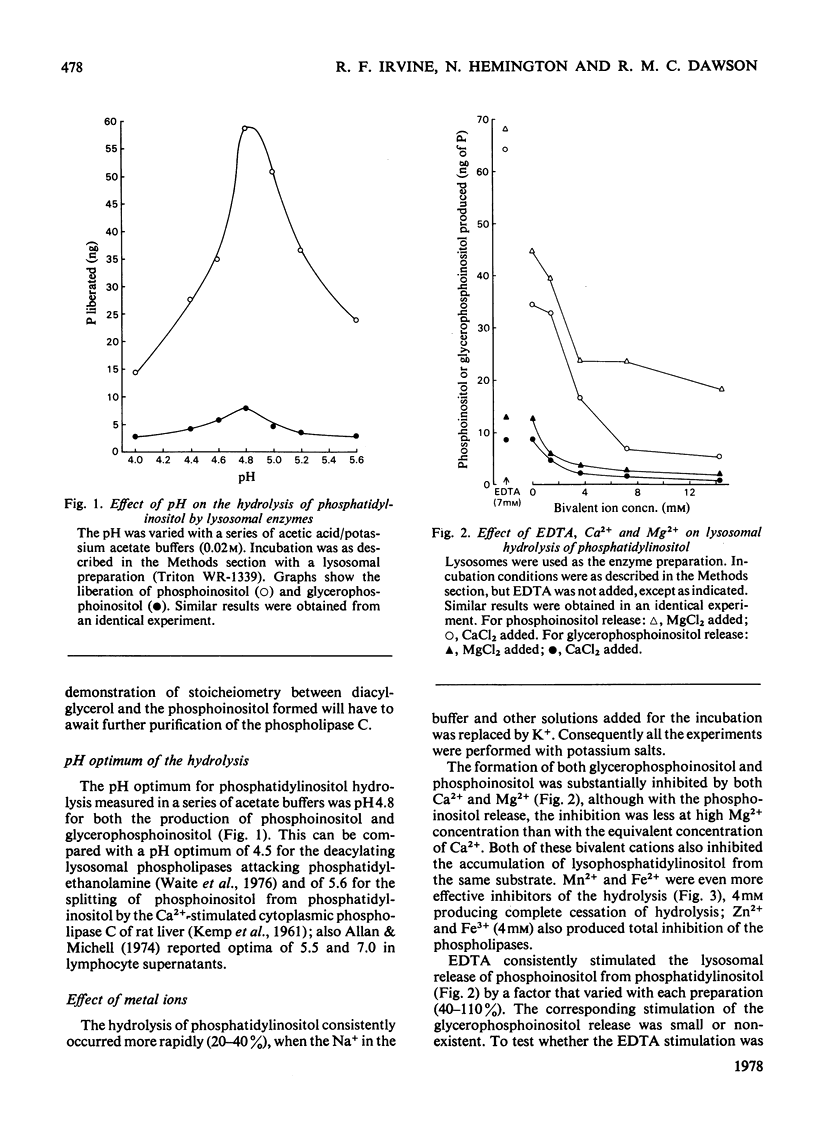
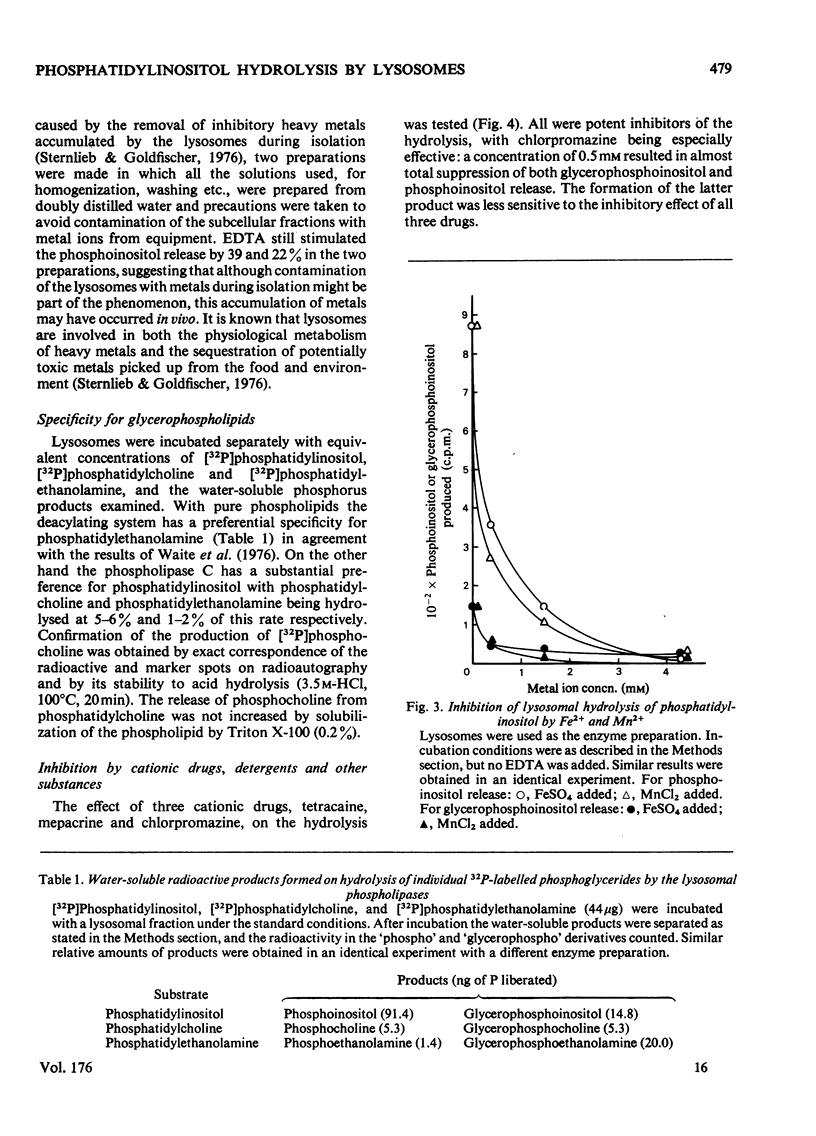
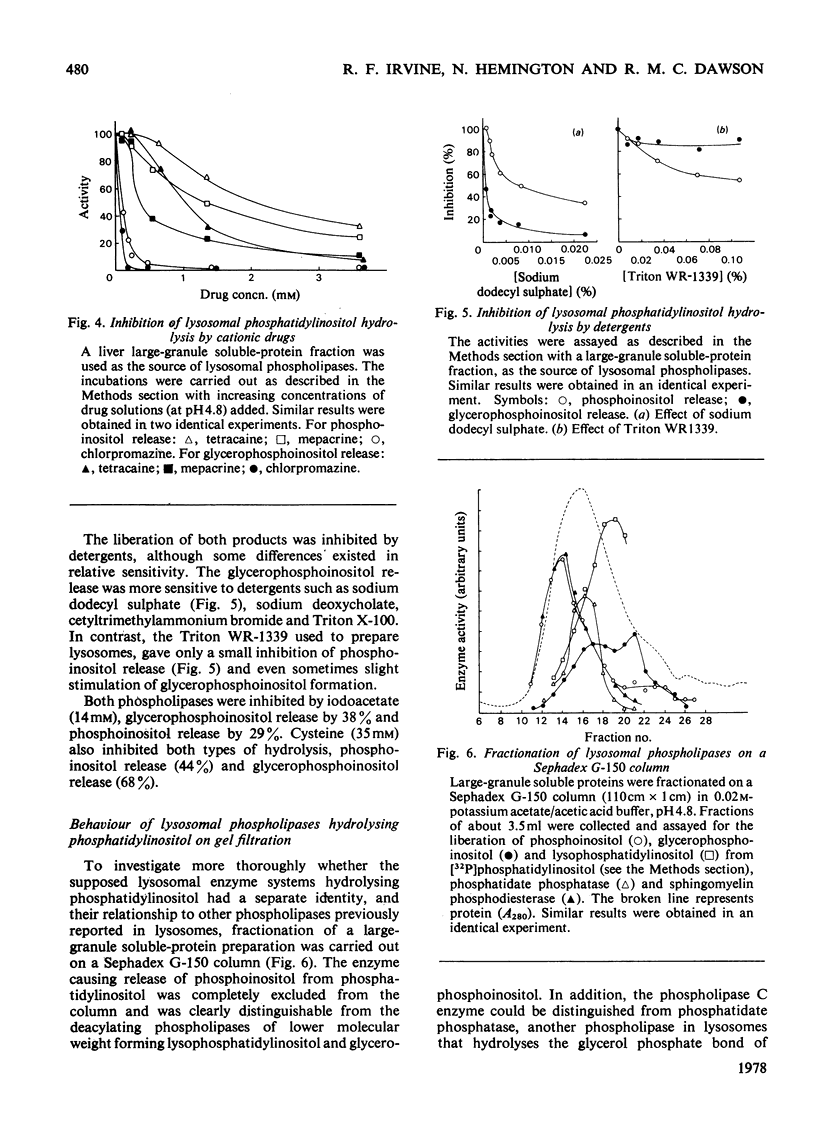
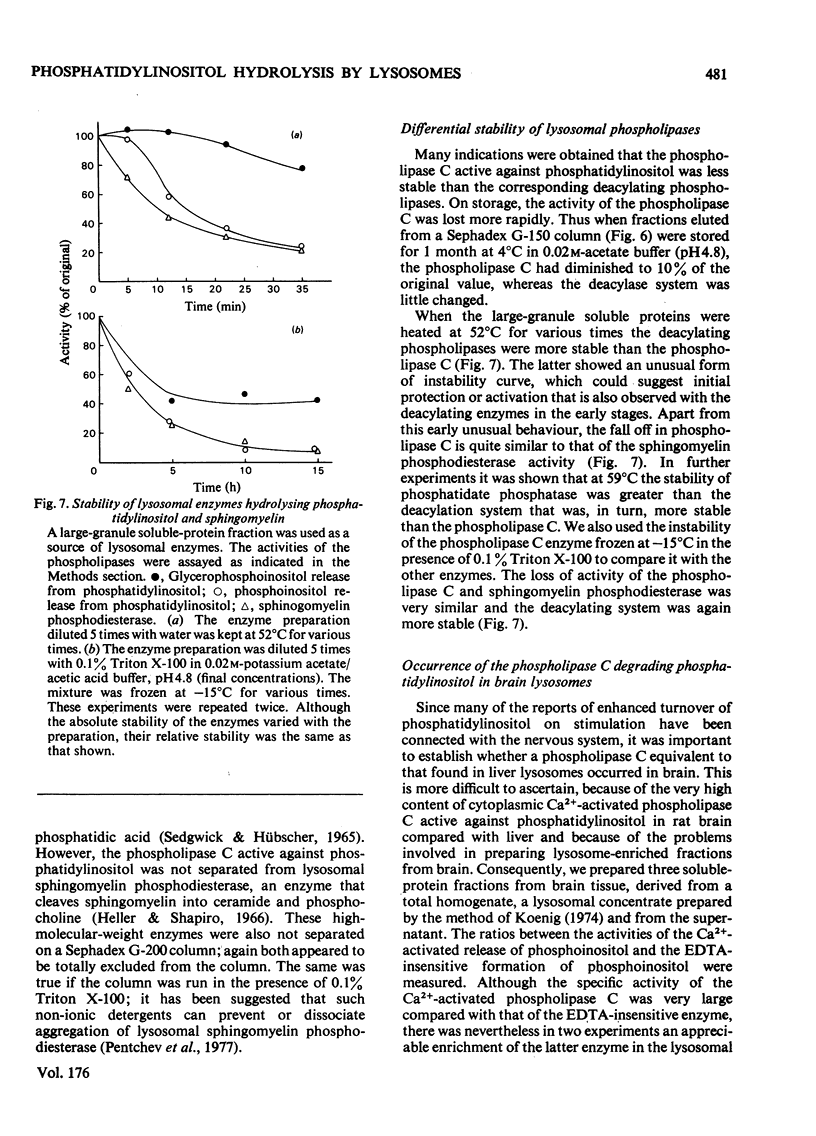
1. Lysosomes from rat liver contain two enzymic systems for hydrolysing phosphatidyl-inositol: a deacylation via lysophosphatidylinositol producing glycerophosphoinositol and non-esterified fatty acid, and a phospholipase C-like cleavage into inositol 1-phosphate and diaclygycerol. 2. The separate enzyme systems involved can be distinguished by gel filtration, differential temperature-stability and the inhibitory action of detergents. 3. The enzyme systems both have pH optima at 4.8 and their attack on a pure phosphatidylinositol substrate is inhibited by many bivalent metals including Ca2+ and Mg2+, and cationic drugs. 4. Whereas the deacylation system will attack other glycerophospholipids, the phospholipase C shows a marked specificity towards phosphatidylinositol, although it will also slowly attach phosphatidylcholine with the liberation of phosphocholine. 5. Gel filtration and temperature-stability distinguish the phospholipase C from lysosomal phosphatidic acid phosphatase, but not from sphingomyelinase. 6. Evidence is presented that an EDTA-insensitive phospholipase C degrading phosphatidylinositol is present in rat brain.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol cleavage in lymphocytes. Requirement for calcium ions at a low concentration and effects of other cations. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):599–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1420599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton R. S., Hawthorne J. N. The phosphoinositide inositolphosphohydrolase of guinea-pig intestinal mucosa. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):68–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightwell R., Tappel A. L. Subcellular distributions and properties of rat liver phosphodiesterases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the enzymic hydrolysis of monophosphoinositide by phospholipase preparations from P. notatum and ox pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 May;33(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Clarke N. D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate 2-phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1270113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Freinkel N., Jungalwala F. B., Clarke N. The enzymic formation of myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate from phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):605–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1220605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N. A phosphodiesterase in rat kidney cortex that hydrolyses glycerylphosphorylinositol. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):241–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1620241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Irvine R. F. Possible role of lysosomal phospholidpases in inducing tissue prostaglandin synthesis. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson R., Waite M., LaVia M. Identification of phospholipase A 1 and A 2 in the soluble fraction of rat liver lysosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1942–1946. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBSCHER G., HAWTHORNE J. N. The isolation of inositol monophosphate from liver. Biochem J. 1957 Nov;67(3):523–527. doi: 10.1042/bj0670523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The displacement of calcium ions from phospholipid monolayers by pharmacologically active and other organic bases. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):909–916. doi: 10.1042/bj1090909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Shapiro B. Enzymic hydrolysis of sphingomyelin by rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):763–769. doi: 10.1042/bj0980763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. Phosphatidylinositol-degrading enzymes in liver lysosomes. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1640277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. The role of lysosomes in phosphatidylinositol degradation [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(5):1297–1299. doi: 10.1042/bst0051297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEENAN R. W., HOKIN L. E. The identification of lysophosphatidylinositol and its enzymic conversion to phosphatidylinositol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:428–430. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP P., HUBSCHER G., HAWTHORNE J. N. Phosphoinositides. 3. Enzymic hydrolysis of inositol-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0790193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya M., Kaplan A. Effects of acidic phospholipids, nucleotides, and heparin on the activity of lipase from rat liver lysosomes. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. A., Diringer H. Isolation of cyclic inositol-1,2-phosphate from mammalian cells and a probable function of phosphatidylinositol turnover. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 20;58(2):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig H. The isolation of lysosomes from brain. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:457–477. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B. Cellular transport of lysosomal enzymes: an alternative hypothesis. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):281–282. doi: 10.1042/bj1640281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B. The endoplasmic reticulum: a cytochemist's view (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2781–2787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O., Gal A. E., Hibbert S. R. The isolation and characterization of sphingomyelinase from human placental tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 24;488(2):312–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Mills S. C., Freinkel N. The mechanism of thyrotrophin action in relation to lipid metabolism in thyroid tissue. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):325–332. doi: 10.1042/bj1090325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B., Hübscher G. Metabolism of phospholipids. IX. Phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 7;106(1):63–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. W., Lester R. L. Inositol phosphorylceramide, a novel substance and the chief member of a major group of yeast sphingolipids containing a single inositol phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3395–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouet A. Isolation of modified liver lysosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:323–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


