Abstract
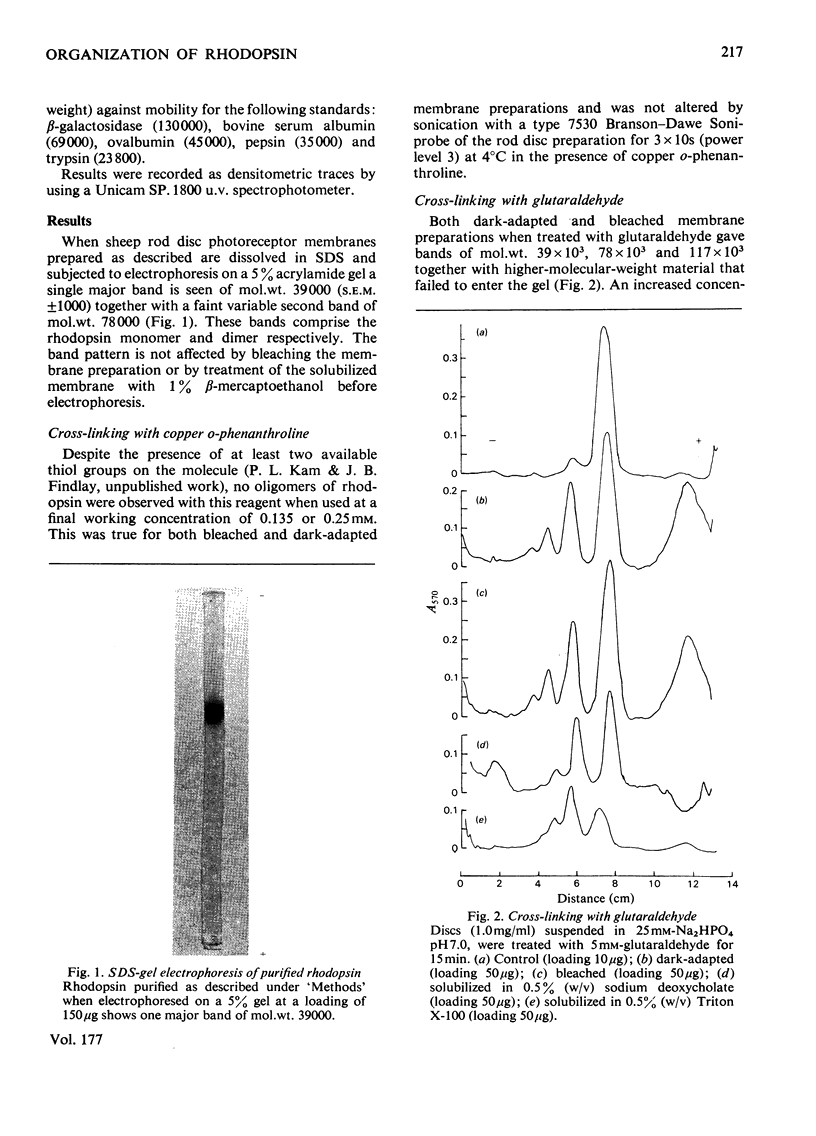
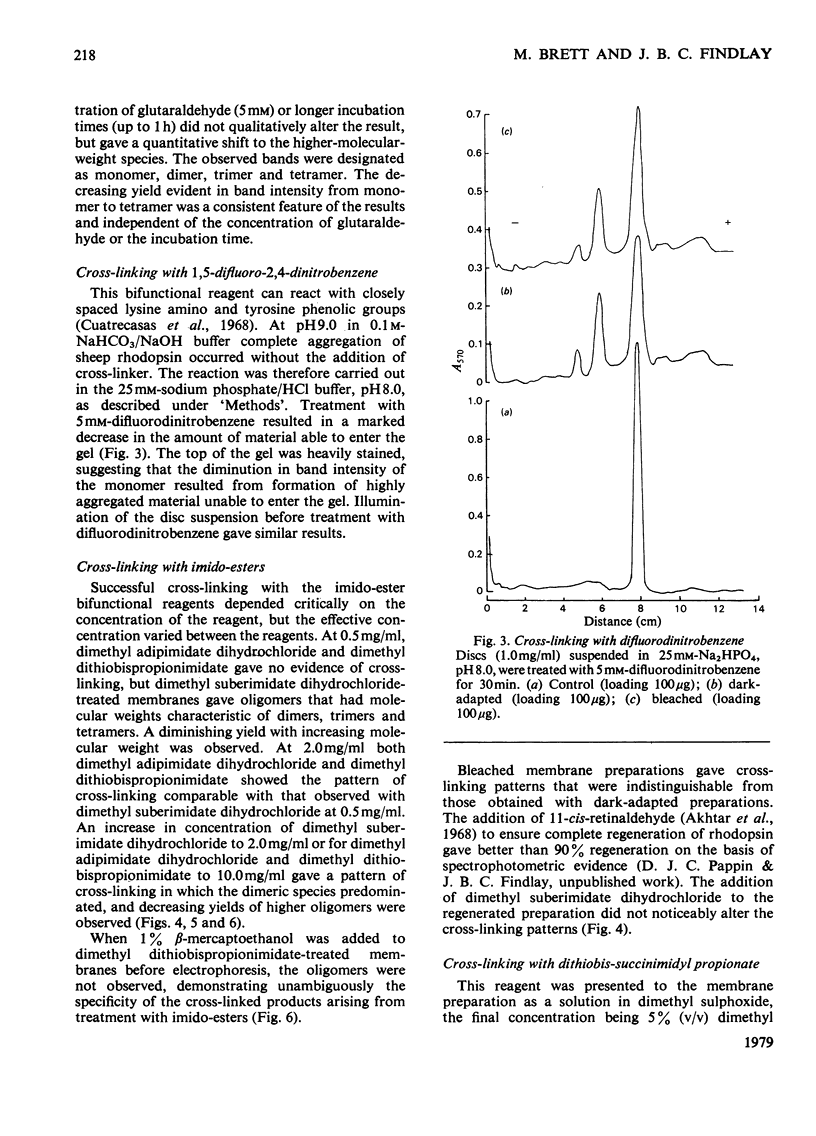
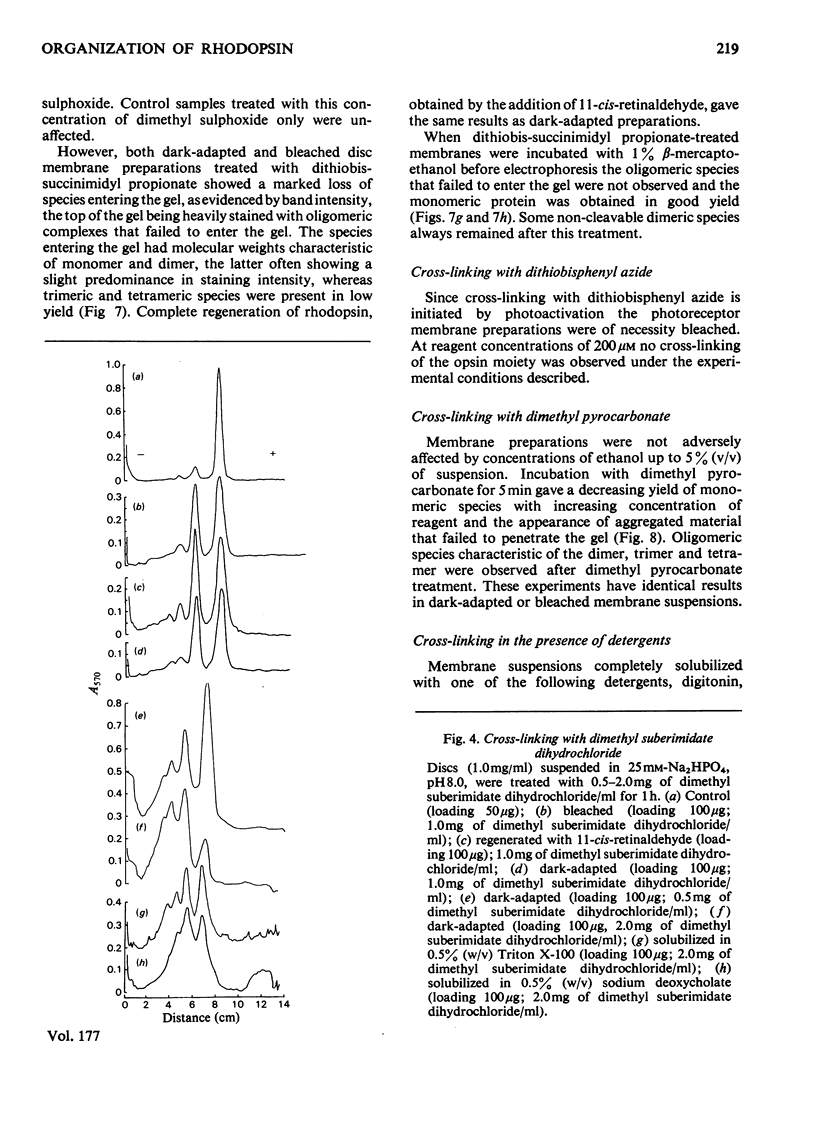
The organization of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane of sheep rod outer segments was investigated by using a variety of bifunctional reagents. Of the nine reagents used, seven gave oligomeric opsin species, whereas two, copper phenanthroline and dithiobisphenyl azide, failed to cross-link the protein. In general, the cross-linked species obtained showed diminishing yields from dimer to tetramer, together with some higher-molecular-weight aggregates. It is proposed that the patterns of cross-linking arise as a result of collision complexes and best describe a monomeric organization for native rhodopsin. No significant differences between the patterns obtained with dark-adapted bleached or regenerated protein states were observed. This interpretation is discussed in relation to the postulated mechanism of action of rhodopsin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M., Blosse P. T., Dewhurst P. B. Studies on vision. The nature of the retinal-opsin linkage. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):693–702. doi: 10.1042/bj1100693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K. Net electric charge on photopigment molecules and frog retinal receptor disk membrane structure. Biophys J. 1972 Feb;12(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86080-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K. The location of photopigment molecules in the cross-section of frog retinal receptor disk membranes. Biophys J. 1972 Feb;12(2):191–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86079-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Worthington C. R. Planar liquid-like arrangement of photopigment molecules in frog retinal receptor disk membranes. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):417–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. S., Hubbell W. L. Temperature- and light-dependent structural changes in rhodopsin-lipid membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):39–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio236039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Fuchs S., Anfinsen C. B. Cross-linking of aminotyrosyl residues in the active site of staphylococcal nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemen F. J. Vertebrate rod outer segment membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 28;300(3):255–288. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrey T. G. The use of Ammonyx LO in the purification of rhodopsin and rod outer segments. Vision Res. 1971 Sep;11(9):1007–1009. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B. The receptor proteins for concanavalin A and Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin in the membrane of the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4398–4403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD R. The molecular weight of rhodopsin and the nature of the rhodopsin-digitonin complex. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Jan 20;37(3):381–399. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD R. The thermal stability of rhodopsin and opsin. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Nov 20;42(2):259–280. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Müllner H., Sund H. Investigation of the symmetry of oligomeric enzymes with bifunctional reagents. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):79–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Williams T. P. Thermal stability of rhodopsin extracted with Triton X-100 surfactant. Vision Res. 1970 Jan;10(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(70)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeson T. S. Freeze-etch studies of rabbit eye. II. Outer segments of retinal photoreceptors. J Anat. 1971 Jan;108(Pt 1):147–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Darszon A., Trissl H. W. Transmembrane channel formation in rhodopsin-containing bilayer membranes. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):221–225. doi: 10.1038/267221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Korenbrot J. I. Incorporation of rhodopsin proteolipid into bilayer membranes. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):219–221. doi: 10.1038/246219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne H. B., Sardet C., Helenius A. Bovine rhodopsin: characterization of the complex formed with Triton X-100. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Richards F. M. Chemical cross-linking: reagents and problems in studies of membrane structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:523–551. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M. M., Cone R. A. Lateral diffusion of phodopsin in Necturus rods. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M., Cone R. A. Lateral diffusion of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):438–441. doi: 10.1038/247438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saari J. C. The accessibility of bovine rhodopsin in photoreceptor membranes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):480–491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichi H. Biochemistry of visual pigments. II. Phospholipid requirement and opsin conformation for regeneration of bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6178–6182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. G., Jr, Stubbs G. W., Litman B. J. The isolation and purification of osmotically intact discs from retinal rod outer segments. Exp Eye Res. 1975 Mar;20(3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(75)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodderly D. M., Jr Reversible and irreversible bleaching of rhodopsin in detergent solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1356–1362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinemann A., Wu C., Stryer L. Conformational aspects of rhodopsin and retinal disc membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(4):348–353. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs G. W., Smith H. G., Jr, Litman B. J. Alkyl glucosides as effective solubilizing agents for bovine rhodopsin. A comparison with several commonly used detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauble H., Sackmann E. Lipid motion and phodopsin rotation. Nature. 1973 Sep 28;245(5422):210–211. doi: 10.1038/245210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R. X-ray analysis of retinal photoreceptor structure. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Grip W. J., van de Laar G. L., Daemen F. J., Bonting S. L. Biochemical aspects of the visual process. 23. Sulfhydryl groups and rhodopsin photolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 22;325(2):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]