Abstract
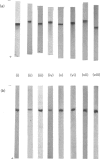
Malate dehydrogenase from a number of bacteria drawn from several genera and representing the mesophilic, moderately thermophilic and extremely thermophilic classes was isolated by procedures which involve only a small number of steps (in most cases only two), of which the key one is affinity chromatography on 5'-AMP--Sepharose and/or on NAD+--hexane--agarose. Electrophoretic analysis of the native enzymes in polyacrylamide gel and of the denaturated enzymes in sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gel revealed no significant protein impurity in the purified preparations. The yields ranged from about 40% to over 80%. The malate dehydrogenases from the extreme thermophiles and from some of the moderate thermophiles are appreciably less efficient catalytically than their mesophilic homologues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Epstein I., Grossowicz N. Prototrophic thermophilic bacillus: isolation, properties, and kinetics of growth. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):414–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.414-417.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert R. D., DeGuzman A., Fields M. L. Studies on variants of Bacillus stearothermophilus strain NCA 1518. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):693–698. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.693-698.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Jakoby W. B. Tartaric acid metabolism. IV. Crystalline L-malic dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2472–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey W. H., Barnaby C., Lin F. J., Kaplan N. O. Malate dehydrogenases. II. Purification and properties of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus stearothermophilus, and Escherichia coli malate dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1548–1559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey W. H., Kitto G. B., Everse J., Kaplan N. Malate dehydrogenases. I. A survey of molecular size measured by gel filtration. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):603–610. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaley R. F., Hixson J. Isolation of a nonpigmented, thermophilic bacterium similar to Thermophilic bacterium similar to Thermus aquaticus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):527–528. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.527-528.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram T. K., Cazzulo J. J., Kornberg H. L. Anaplerotic CO2 fixation in mesophilic and thermophilic bacilli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):355–357. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram T. K. Physiological role of pyruvate carboxylase in a thermophilic bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):549–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.549-557.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA A. PURIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MALATE DEHYDROGENASE OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1113–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You K. S., Kaplan N. O. Purification and properties of malate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas testosteroni. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):704–716. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.704-716.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]