Abstract
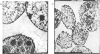
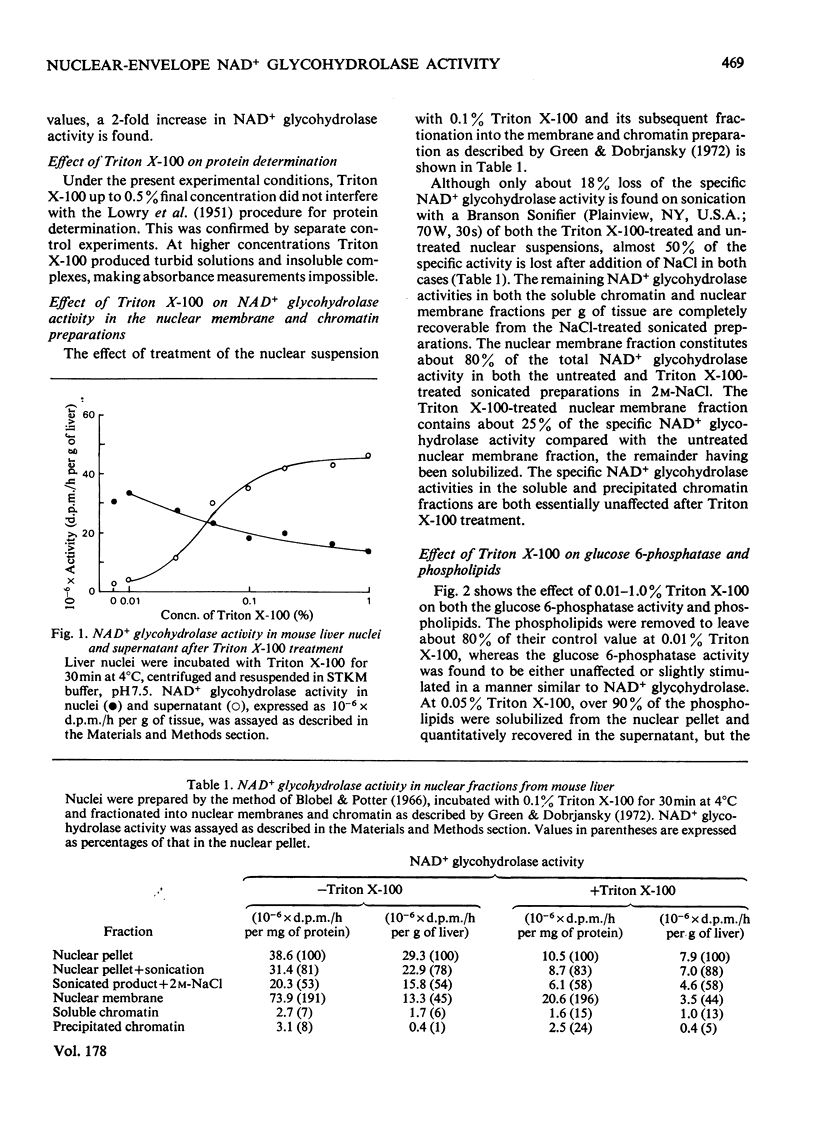
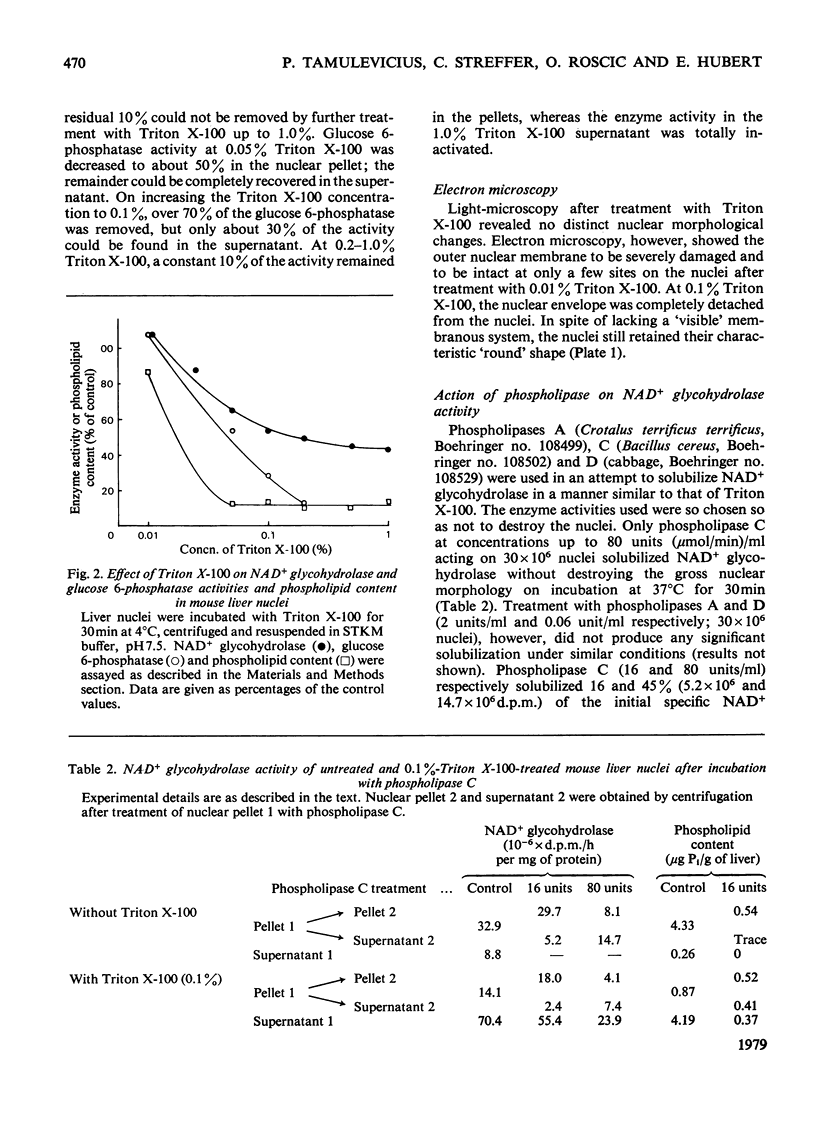
NAD+ glycohydrolase activity located in the nuclear envelope was maximally solubilized by treatment with 0.1--0.2% Triton X-100. The residual activity largely represents the chromatin-associated NAD+ glycohydrolase. Under these conditions the phospholipids were extensively solubilized (over 90%) while leaving the nuclei physically stable, although the nuclear membranes were removed, as shown by electron microscopy. After Triton X-100 treatment, deoxyribonuclease I did not significantly affect the residual NAD+ glycohydrolase activity, although the DNA was completely broken down. This enzyme activity can be released from the nuclear pellet by incubation with phospholipase C. For comparative studies, the glucose 6-phosphatase activity, known to be present in the nuclear envelope, was investigated. Treatment with 0.01% Triton X-100 released 10--20% of the phospholipids, but without solubilizing either glucose 6-phosphatase or NAD+ glycohydrolase. Higher Triton X-100 concentrations (0.1--1.0%) inhibited glucose 6-phosphatase, but not NAD+ glycohydrolase activity. NAD+ glycohydrolase is apparently present in a latent form in the nuclear envelope. Glucose 6-phosphatase, However, shows no such latency.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson R. P., Blobel G. On the attachment of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):746–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. The relation between the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid and the synthesis of protein in the multiplication of bacteriophage T2. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):473–483. doi: 10.1042/bj0610473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee M. L., Spangler M., Morris H. P., Ove P. DNA synthesis in membrane-denuded nuclei and nuclear fractions from host liver and Morris hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1975 Oct;35(10):2752–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W. Structure, biochemistry, and functions of the nuclear envelope. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;Suppl 4:71–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukishima M., Okayama H., Takahashi Y., Hayaishi O. Characterization of the NAD+ glycohydrolase associated with the rat liver nuclear envelope. J Biochem. 1976 Jul;80(1):167–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland R. C., Cori C. F. Separation of phospholipids from glucose-6-phosphatase by gel chromatography. Specificity of phospholipid reactivation. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4712–4718. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Dobrjansky A. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolases from Ehrlich ascites tumor cell nuclei: isolation, partial purification, and properties. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4108–4113. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. Phosphoinositides and protein secretion in pancreas slices. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):805–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilz H., Stone P. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1976;76:1-58, 177. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Jarasch E. D., Franke W. W. Nuclear membranes from mammalian liver. VI. Glucose-6-phosphatase in rat liver, a cytochemical and biochemical study. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Sep;81(1):175–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Riley D. E. Nuclear ghosts: a nonmembranous structural component of mammalian cell nuclei. Science. 1976 Jul 30;193(4251):399–401. doi: 10.1126/science.935874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings A. W., Brauer W., Streffer C. Letter: Radiosensitivity of NAD glycohydrolase in the nuclear membrane of fast growing mouse liver. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1975 Dec;28(6):589–591. doi: 10.1080/09553007514551451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K. Enzymic synthesis of coenzyme I in relation to chemical control of cell growth. Nature. 1958 Feb 22;181(4608):540–542. doi: 10.1038/181540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Blobel G., Palade G. E. Fractionation of the nucleus by divalent cations. Isolation of nuclear membranes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):104–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ove P., Coetzee M. L., Morris H. P. DNA synthesis and the effect of sucrose in nuclei of host liver and Morris hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1971 Oct;31(10):1389–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuber F., Travo P. Calf-spleen nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase. Solubilization purification and properties of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shall S., Goodwin P., Halldorsson H., Khan G., Skidmore C., Tsopanakis C. Post-synthetic modifications of nuclear macromolecules. Biochem Soc Symp. 1977;(42):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shushevych S. I., Pakyrbaeva L. V., Khalmuradov A. G., Chanysheva I. R. [Effect of detergents and ultrasound on NAD-glycohydrolase activity in rat liver cell nuclei]. Ukr Biokhim Zh. 1975 Jul-Aug;47(4):474–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikstrom R., Lanoix J., Bergeron J. J. An enzymic analysis of a nuclear envelope fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 21;448(1):88–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streffer C., Beisel P. Radiation effects on NAD-and DNA-metabolism in mouse spleen. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streffer C. DNA-synthesis in the spleen of mice after whole-body X-irradiation and its modification by 5-hydroxytryptamine and NADH. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 May;25(5):425–435. doi: 10.1080/09553007414550601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streffer C., Schmiebusch H. Letter: Nuclear enzymes of NAD metabolism in mouse tissues after whole-body-x-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1975 Dec;28(6):581–583. doi: 10.1080/09553007514551431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streffer C., Scholz G. Metabolism of pyridine nucleotides and its relation to DNA synthesis in regenerating mouse liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Dec;353(12):1855–1862. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura T. Poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose). Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:127–151. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhadolnik R. J., Baur R., Lichtenwalner D. M., Uematsu T., Roberts J. H., Sudhakar S., Smulson M. ADP-ribosylation of isolated nuclei from HeLa cells, rat liver, fetal rat liver, and Novikoff hepatoma. Effect of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide analogs on template activity for DNA synthesis, incorporation into nuclear proteins, and a new 1''-3' osidic linkage. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4134–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Fukushima M., Okayama H., Hayaishi O. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase from rat liver nuclei. Isolation and characterization of a new enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7541–7546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]