Abstract
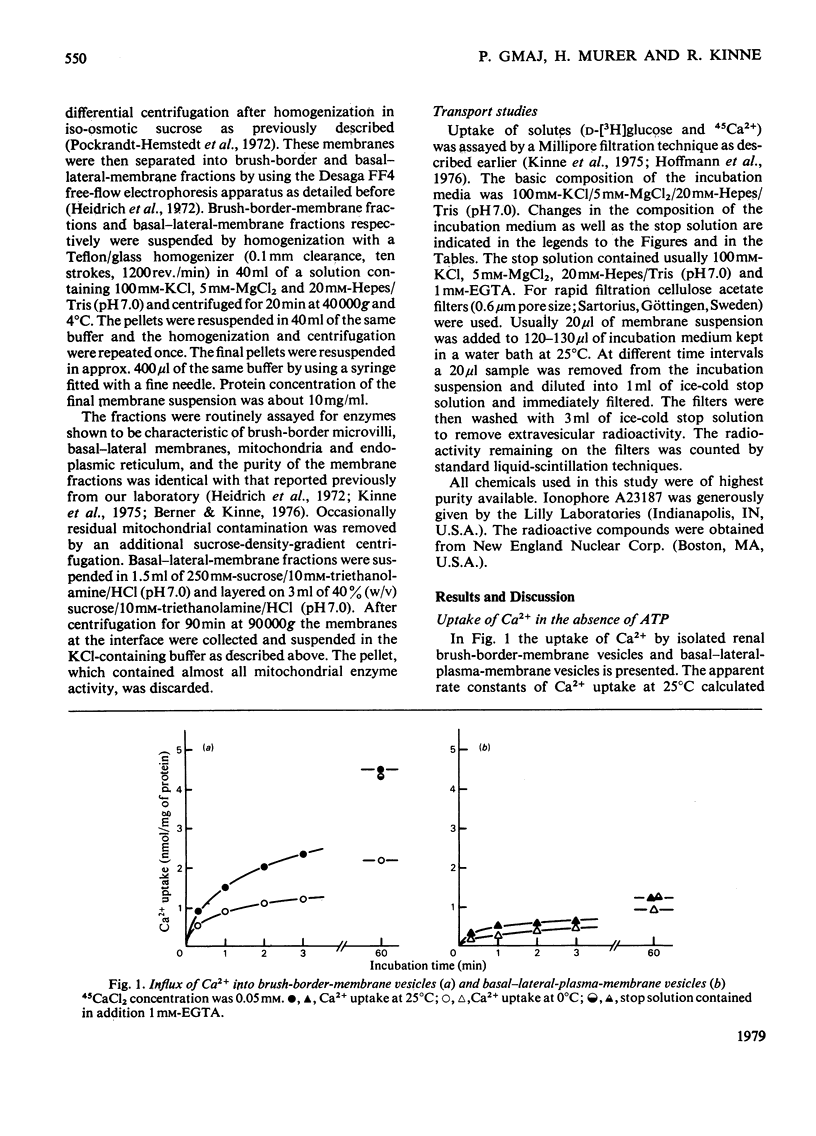
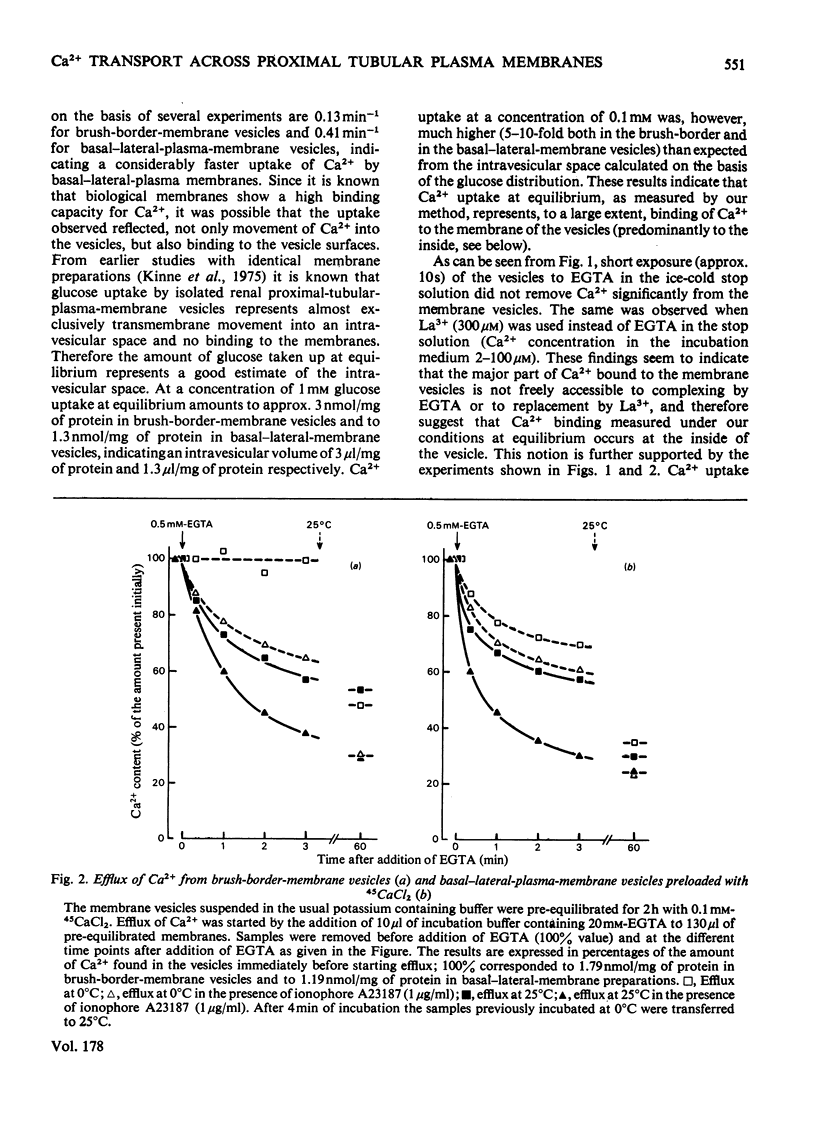
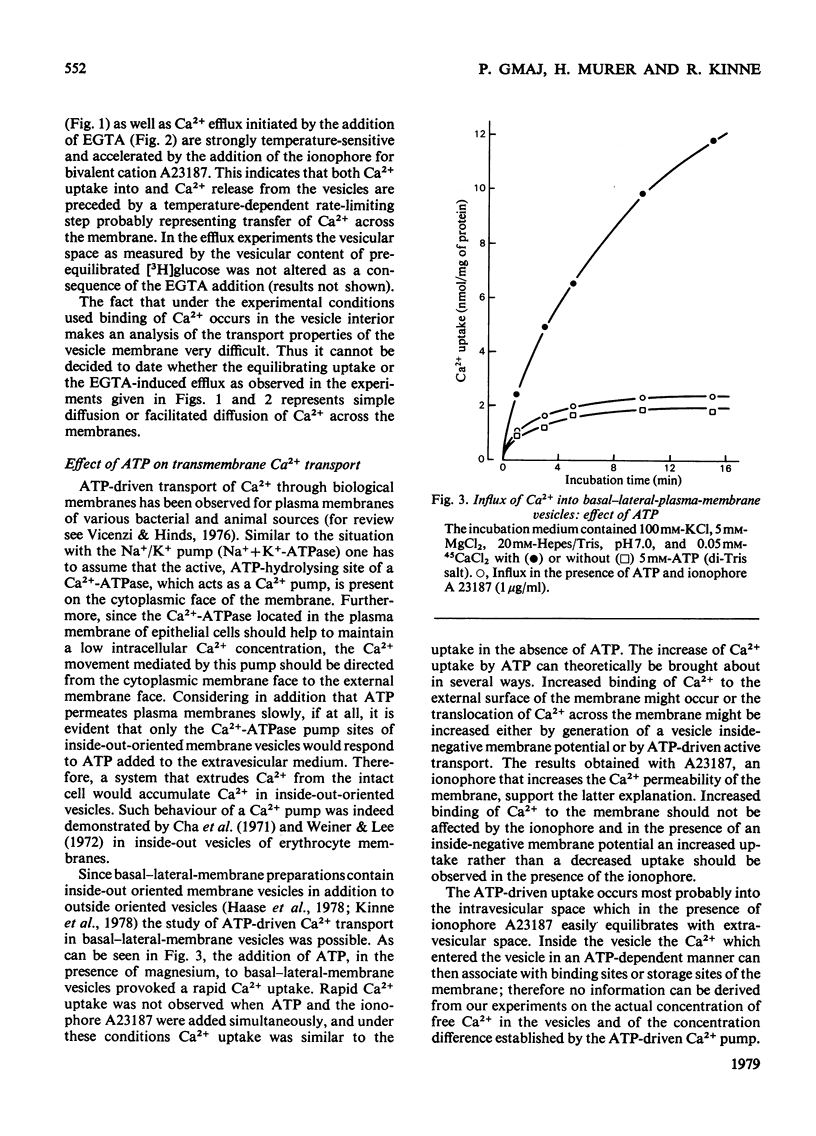
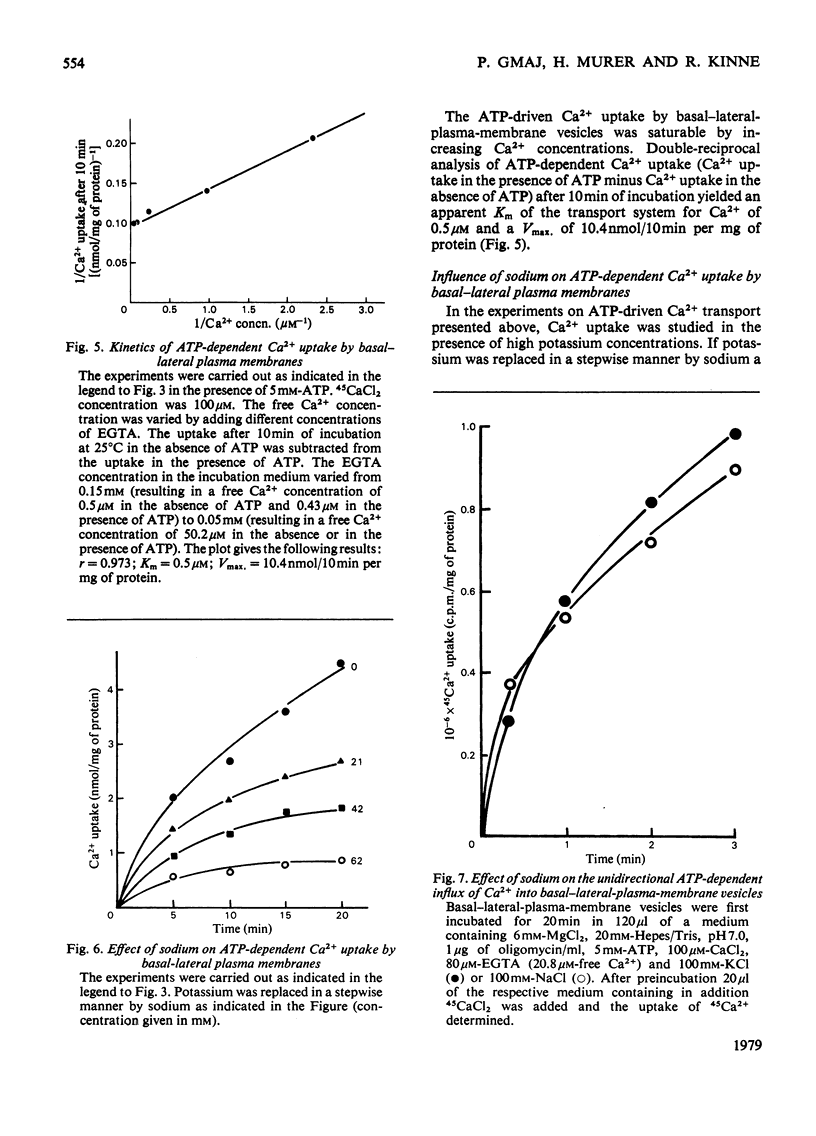
Basal-lateral-plasma-membrane vesicles and brush-border-membrane vesicles were isolated from rat kidney cortex by differential centrifugation followed by free-flow-electrophoresis. Ca2+ uptake into these vesicles was investigated by a rapid filtration method. Both membranes show a considerable binding of Ca2+ to the vesicle interior, making the analysis of passive fluxes in uptake experiments difficult. Only the basal-lateral-plasma-membrane vesicles exhibit an ATP-dependent pump activity which can be distinguished from the activity in mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum by virtue of the different distribution during free-flow electrophoresis and its lack of sensitivity to oligomycin. The basal-lateral plasma membranes contain in addition a Na+/Ca2+-exchange system which mediates a probably rheogenic counter-transport of Ca2+ and Na+ across the basal cell border. The latter system is probably involved in the secondary active Na+-dependent and ouabain-inhibitable Ca2+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule, the ATP-driven system is probably more important for the maintenance of a low concentration of intracellular Ca2+.
Full text
PDF

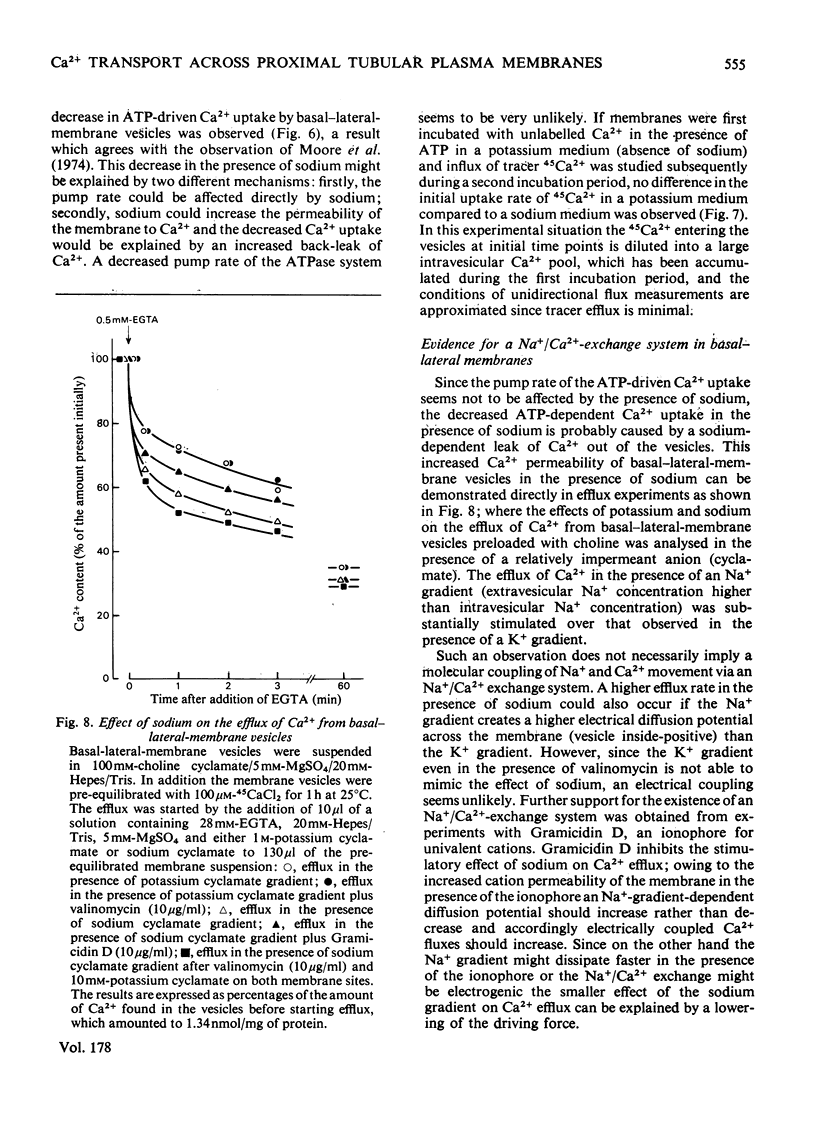
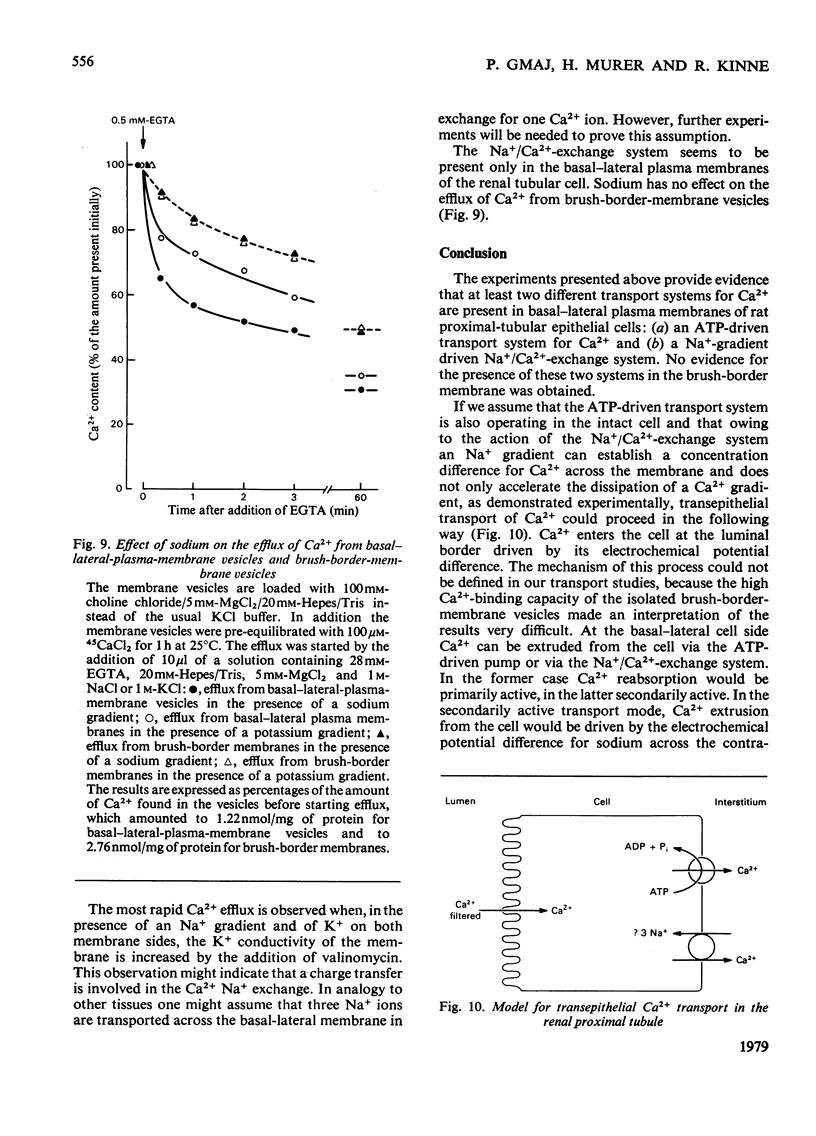

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berner W., Kinne R. Transport of p-aminohippuric acid by plasma membrane vesicles isolated from rat kidney cortex. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Feb 24;361(3):269–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00587292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns D. E., McDonald J. M., Jarett L. Energy-dependent calcium transport in endoplasmic reticulum of adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7191–7197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha Y. N., Shin B. C., Lee K. S. Active uptake of Ca++ and Ca plus,plus-activated Mg++ ATPase in red cell membrane fragments. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Feb;57(2):202–215. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase W., Schäfer A., Murer H., Kinne R. Studies on the orientation of brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):57–62. doi: 10.1042/bj1720057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich H. G., Kinne R., Kinne-Saffran E., Hannig K. The polarity of the proximal tubule cell in rat kidney. Different surface charges for the brush-border microvilli and plasma membranes from the basal infoldings. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):232–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann N., Thees M., Kinne R. Phosphate transport by isolated renal brush border vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 30;362(2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00583641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Localization of a calcium-stimulated ATPase in the basal-lateral plasma membranes of the proximal tubule of rat kidney cortex. J Membr Biol. 1974 Jul 12;17(3):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01870187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. F., Posey V. A. Calcium and adenosine triphosphate binding to renal membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):89–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pockrandt-Hemstedt H., Schmitz J. E., Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Morphologische und biochemische Untersuchungen über die Oberflächenstruktur der Bürstensaummenbran der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch. 1972;333(4):297–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00586210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Capasso G., Rumrich G., Papavassiliou F., Klöss S. Coupling between proximal tubular transport processes. Studies with ouabain, SITS and HCO3-free solutions. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Apr 25;368(3):245–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00585203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Klöss S. Active Ca2+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. Dependence on sodium- and buffer transport. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Aug 24;364(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00581759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. L., Lee K. S. Active calcium ion uptake by inside-out and right side-out vesicles of red blood cell membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):462–475. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


