Abstract
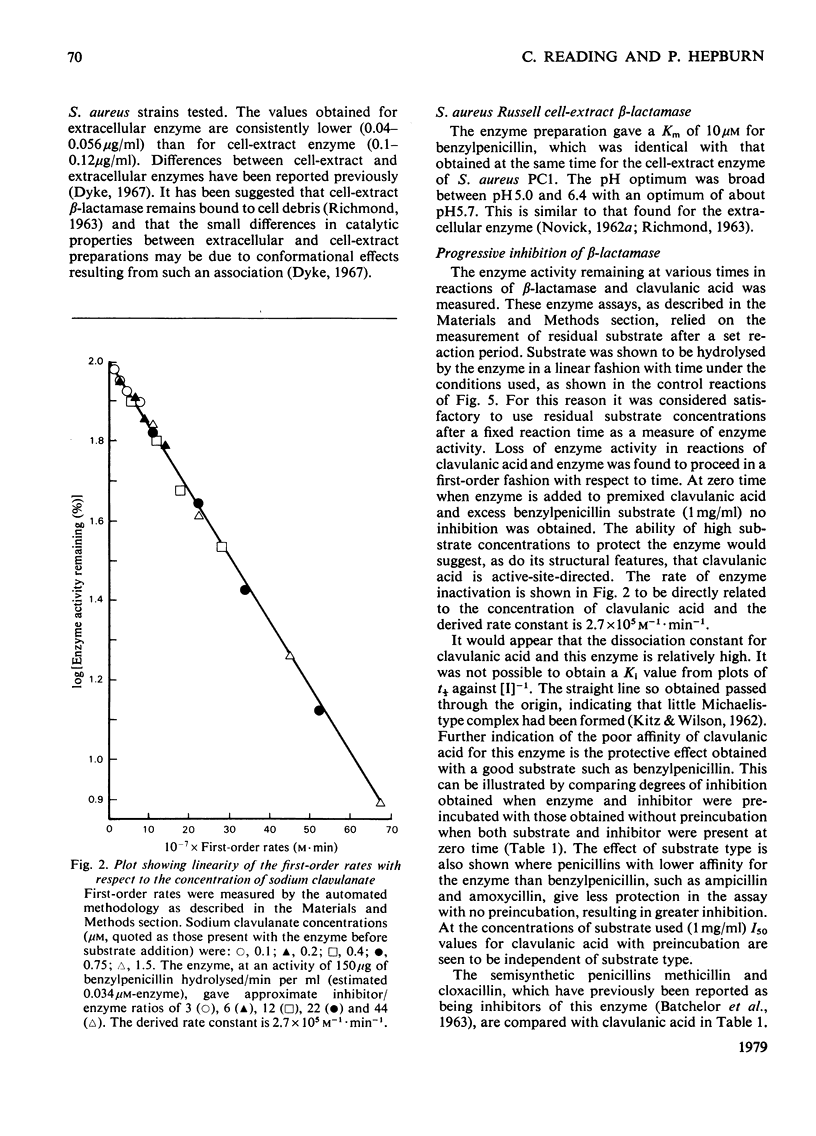
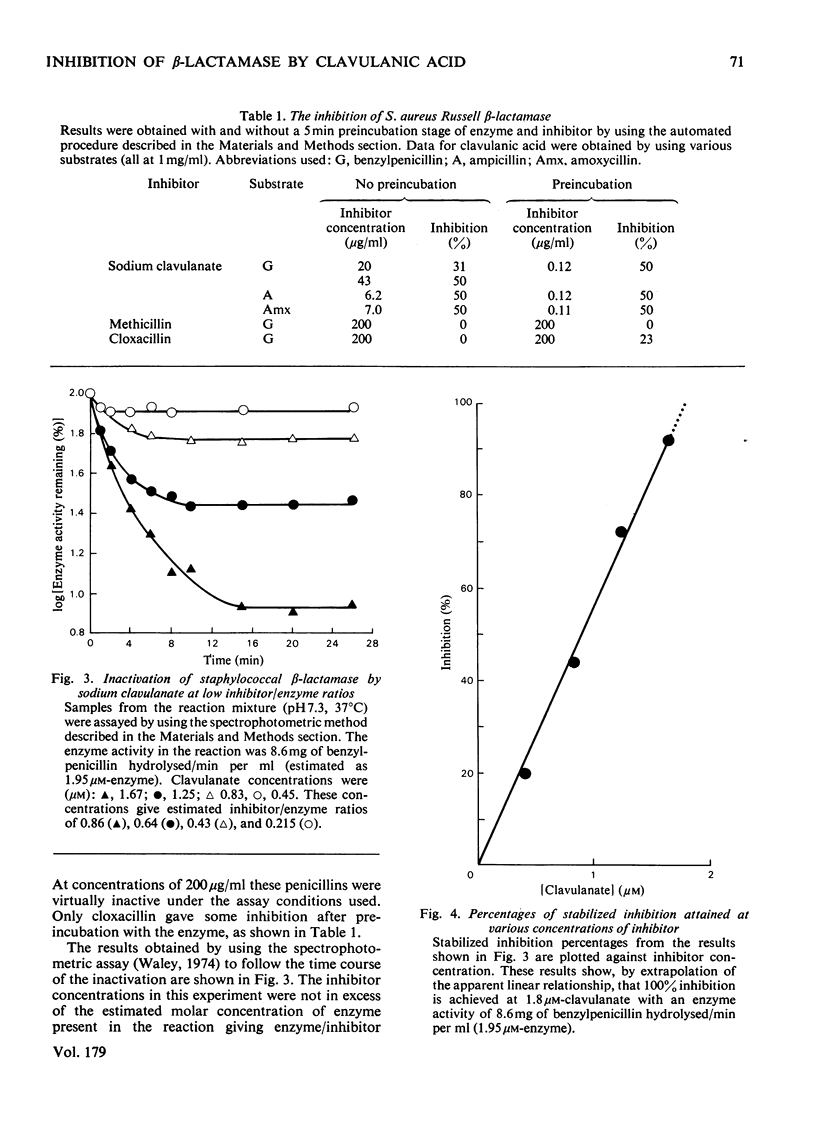
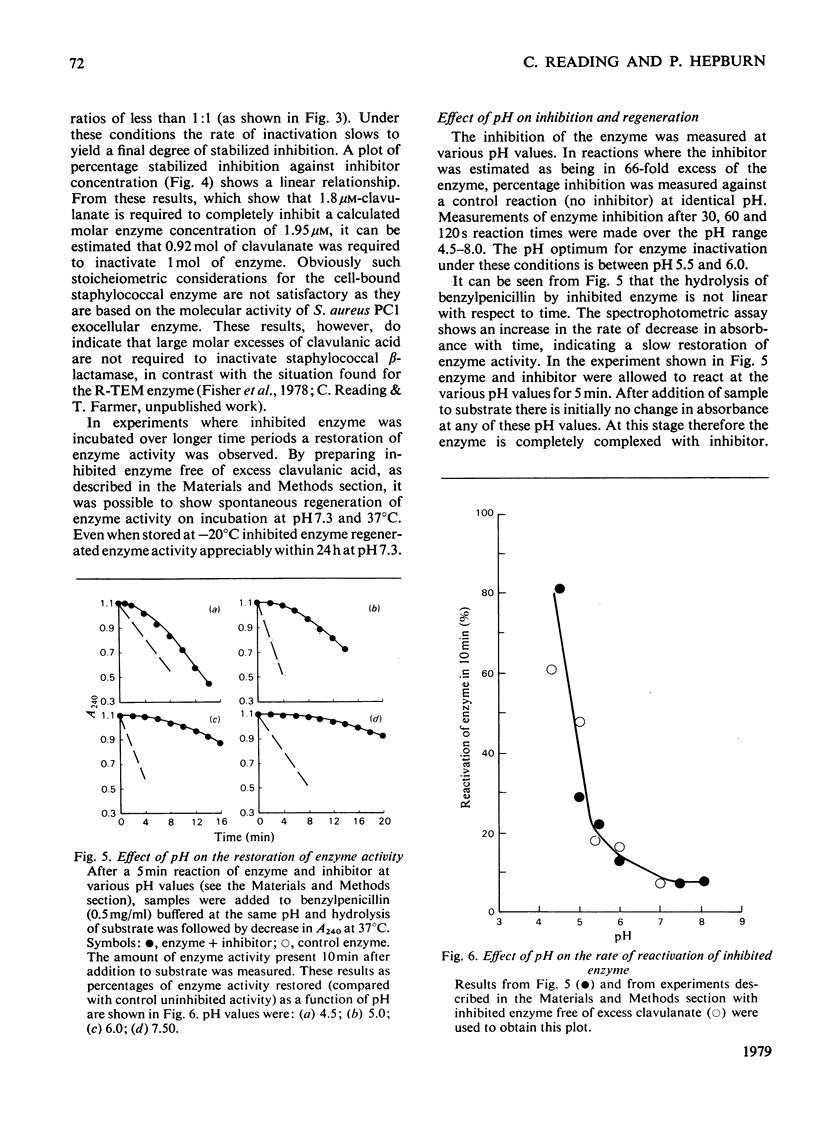
Clavulanic acid inhibited both the extracellular and cell-extract beta-lactamases of the four Staphylococcus aureus strains tested. The inhibition of S. aureus Russell cell-extract enzyme appeared to be active-site-directed and proceeded in a first-order fashion consistent with the formation of a covalent intermediate. Inhibited enzyme free of excess clavulanic acid was shown to regenerate enzyme activity slowly at pH 7.0, but the rate of reactivation increased at acid pH. When the enzyme was incubated with excess clavulanic acid complete inhibition was rapidly obtained, during further incubation clavulanic acid was shown to disappear slowly and complete loss of clavulanic acid from the reaction mixture coincided with the onset of the return of enzyme activity. A reactive enamine resulting from enzymic hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring of clavulanic acid has been proposed as a possible intermediate in the inhibitory mechanism.
Full text
PDF

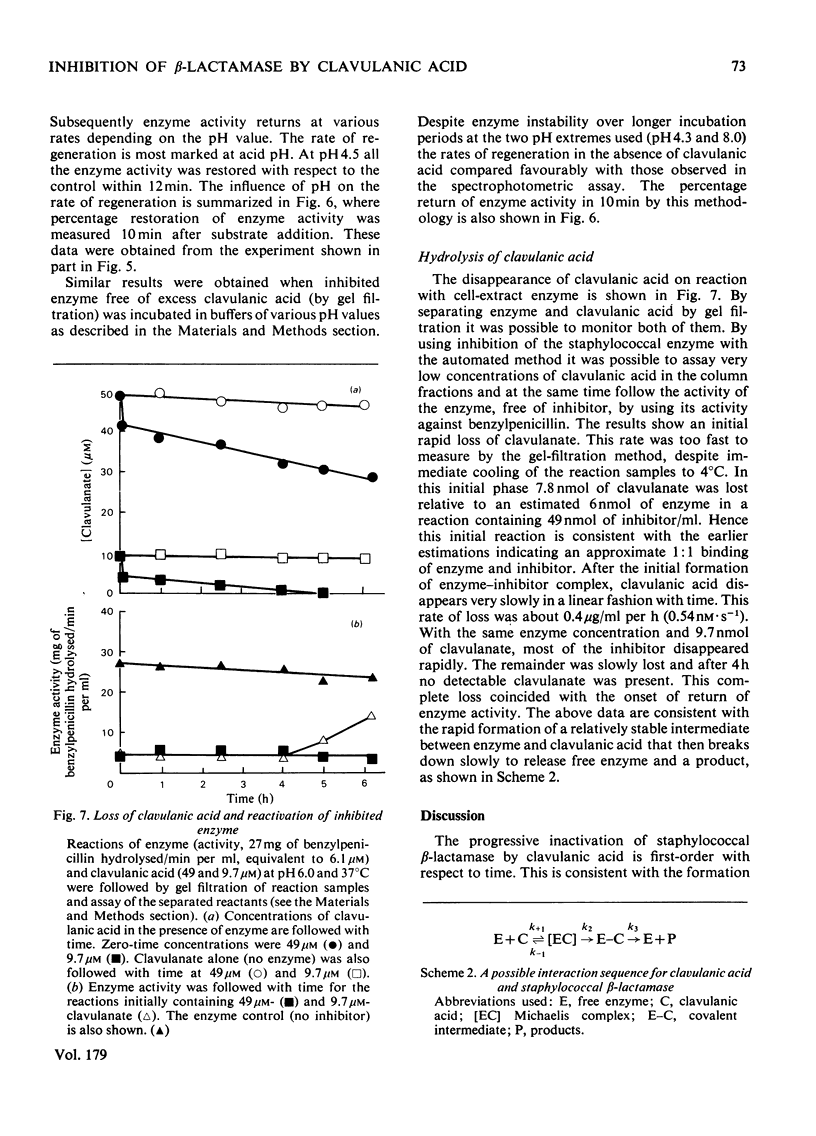
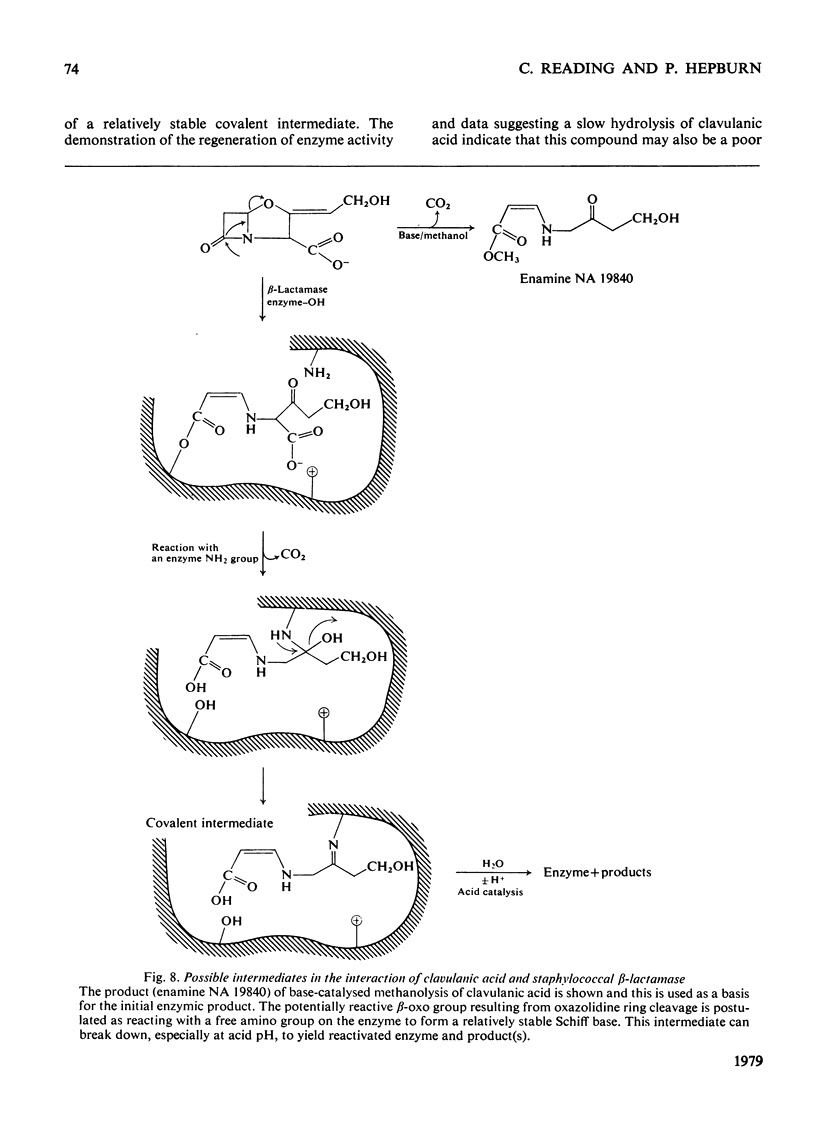


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATCHELOR F. R., CAMERON-WOOD J., CHAIN E. B., ROLINSON G. N. 6-Aminopenicillanic acid. V. 6-Aminopenicillanic acid as a substrate for penicillinase and an inducer of penicillinase formation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1961 Aug 15;154:514–521. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1961.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATCHELOR F. R., CAMERON-WOOD J., CHAIN E. B., ROLINSON G. N. STUDIES ON PENICILLINASE PRODUCED BY A STRAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1963 Oct 22;158:311–328. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1963.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnas R. L., Fisher J., Knowles J. R. Chemical studies on the inactivation of Escherichia coli RTEM beta-lactamase by clavulanic acid. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2185–2189. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke K. G. Substrate-specific inactivation of staphylococcal penicillinase. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):641–646. doi: 10.1042/bj1030641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZ R., WILSON I. B. Esters of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3245–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Staphylococcal penicillinase and the new penicillins. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj0830229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE EXOPENICILLINASE FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:452–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0880452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Chemistry and enzymology of kcat inhibitors. Science. 1974 Jul 26;185(4148):320–324. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4148.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virden R., Bristow A. F., Pain R. H. The active site of penicillinase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1. Isolation of a specific covalent complex with the substrate quinacillin. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):397–401. doi: 10.1042/bj1490397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. The pH-dependence and group modification of beta-lactamase I. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1490547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


