Abstract
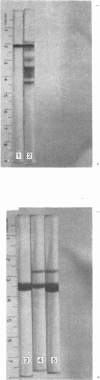
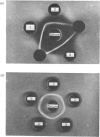
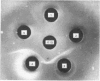
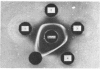
NAD+-specific glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.12) from Escherichia coli was purified to homogeneity by a relatively simple procedure involving affinity chromatography on agarose–hexane–NAD+ and repeated crystallization. Rabbit antiserum directed against this protein produced one precipitin line in double-diffusion studies against the pure enzyme, and two lines against crude extracts of wild-type E. coli strains. Both precipitin lines represent the interaction of antibody with determinants specific for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nine independent mutants of E. coli lacking glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity all possessed some antigenic cross-reacting material to the wild-type enzyme. The mutants could be divided into three groups on the basis of the types and amounts of precipitin lines observed in double-diffusion experiments; one group formed little cross-reacting material. The cross-reacting material in crude cell-free extracts of several of the mutant strains were also tested for alterations in their affinity for NAD+ and their phosphorylative activity. The cumulative data indicate that the protein in several of the mutant strains is severely altered, and thus that glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is unlikely to have an essential, non-catalytic function such as buffering nicotinamide nucleotide or glycolytic-intermediate concentrations. Others of the mutants tested have cross-reacting material which behaved like the wild-type enzyme for the several parameters studied; the proteins from these strains, once purified, might serve as useful analogues of the wild-type enzyme.
Full text
PDF


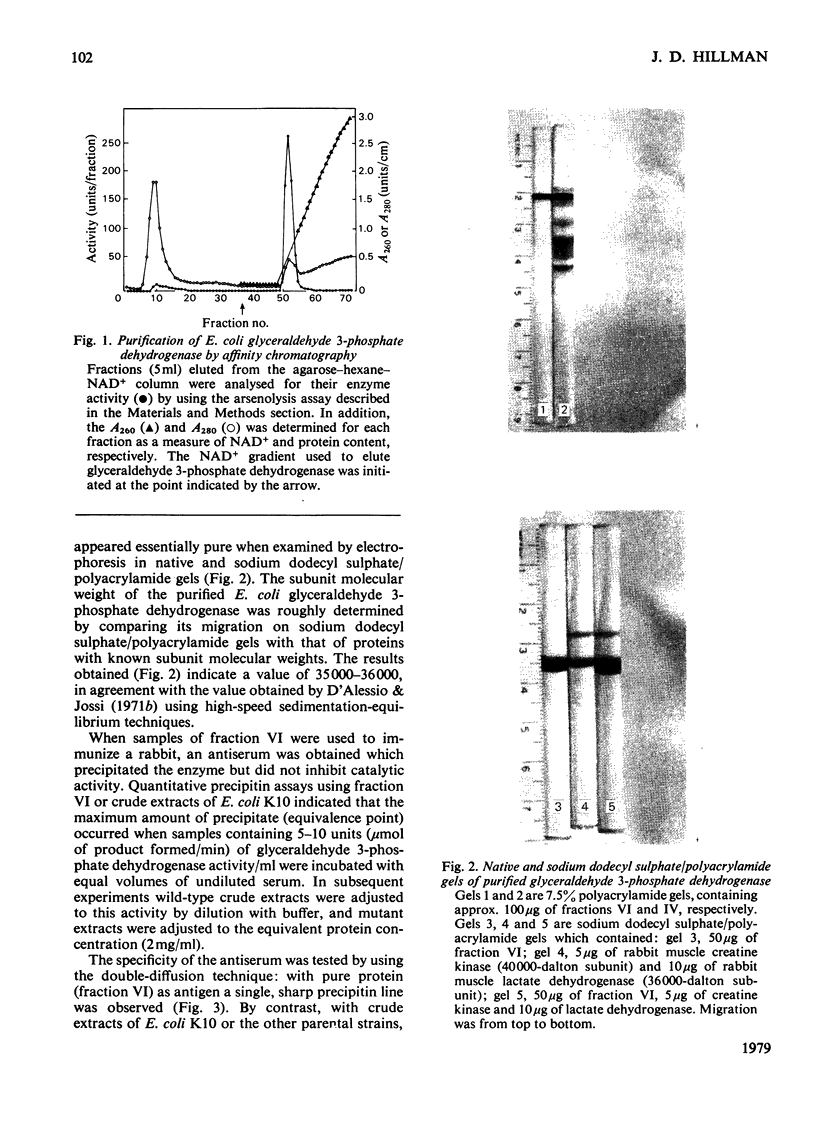
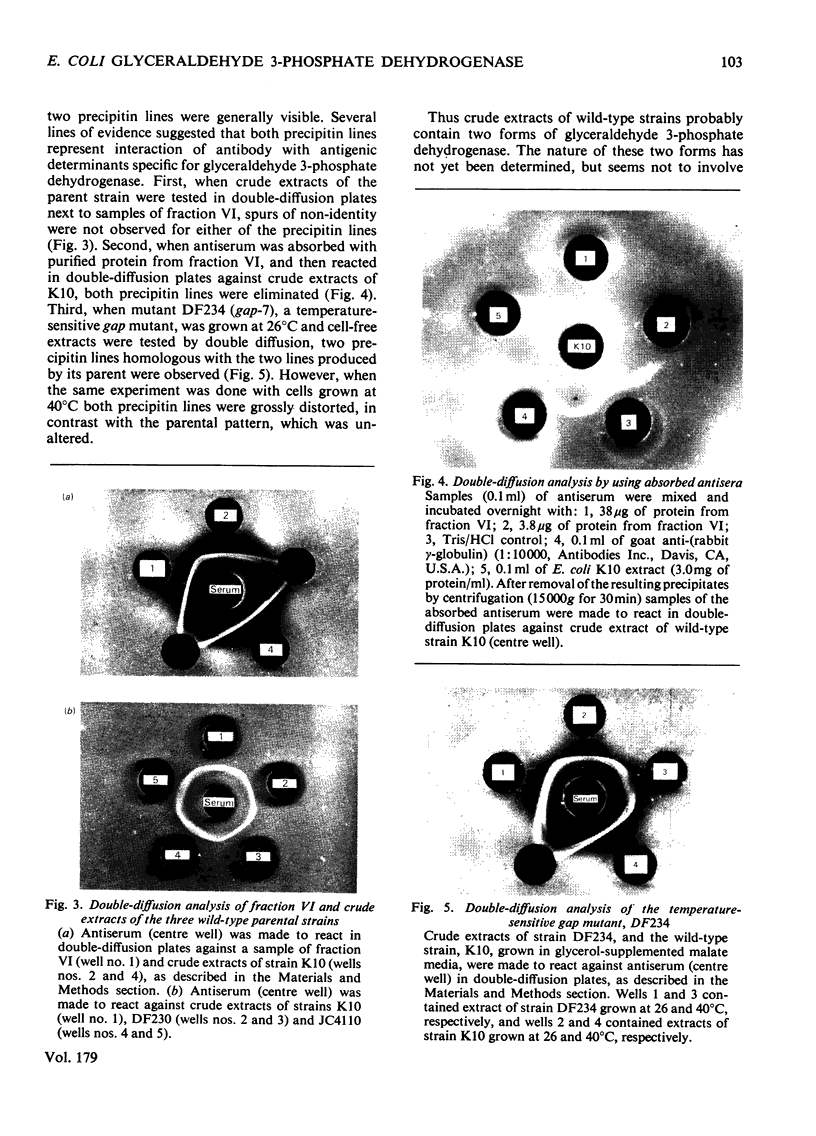


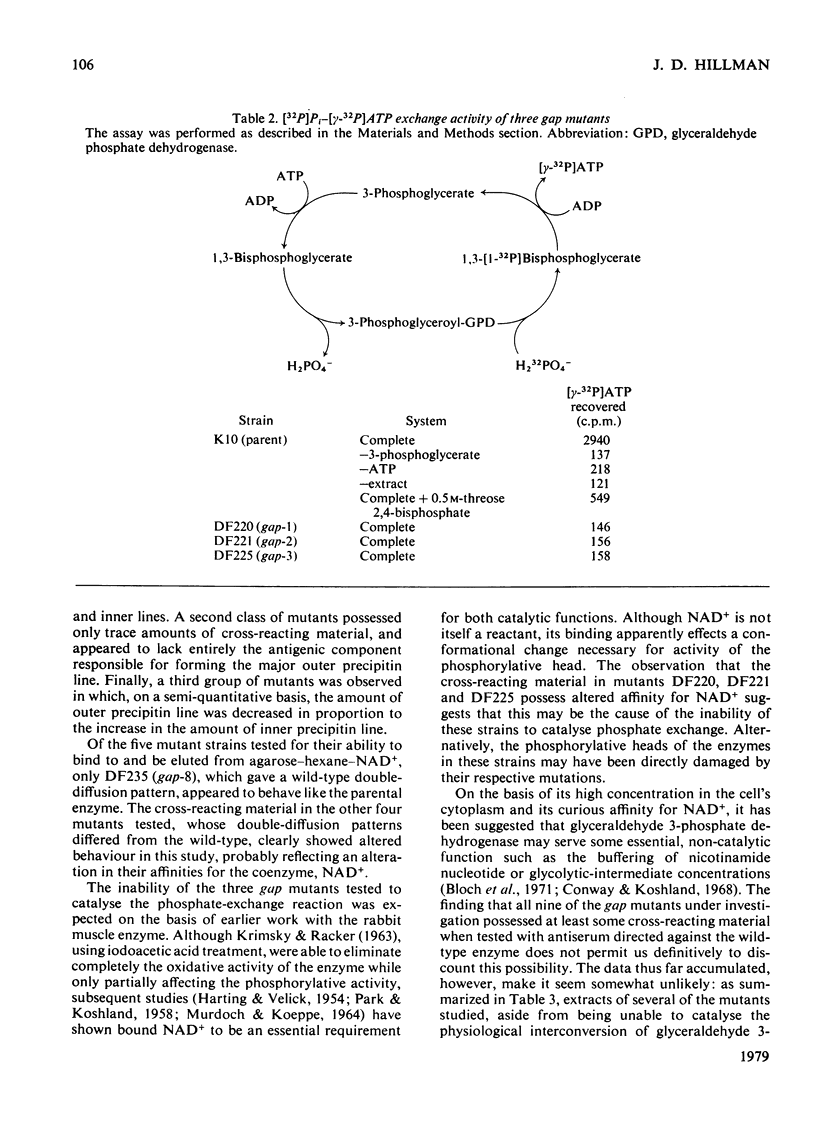

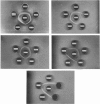
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON W. S., KAPLAN N. O. THE COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY OF TRIOSEPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2140–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison W. S. Structure and evolution of triose phosphate and lactate dehydrogenases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 14;151(1):180–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb11888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch W., MacQuarrie R. A., Bernhard S. A. The nucleotide and acyl group content of native rabbit muscle glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):780–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Wittenberger C. L. The occurrence of multiple glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases in cariogenic streptococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 2;43(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway A., Koshland D. E., Jr Negative cooperativity in enzyme action. The binding of diphosphopyridine nucleotide to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4011–4023. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Josse J. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Structural and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4326–4333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Josse J. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate kinase, and phosphoglyceromutase of Escherichia coli. Simultaneous purification and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4319–4325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELODI P. Comparative studies on D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. V. Immune-biological and serological studies. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1958;13(3):219–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTING J., VELICK S. F. Transfer reactions of acetyl phosphate catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):867–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman J. D., Fraenkel D. G. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1175–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1175-1179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIMSKY I., RACKER E. SEPARATION OF OXIDATIVE FROM PHOSPHORYLATIVE ACTIVITY BY PROTEOLYSIS OF GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. Biochemistry. 1963 May-Jun;2:512–518. doi: 10.1021/bi00903a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURDOCK A. L., KOEPPE O. J. THE CONTENT AND ACTION OF DIPHOSPHOPYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE IN TRIOSEPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1983–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQuarrie R. A., Bernhard S. A. Subunit conformation and catalytic function in rabbit-muscle glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 28;55(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra O. P., Bernhard S. A. Spectrophotometric identification of an active site-specific acyl glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The regulation of its kinetic and equilibrium properties by coenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1243–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovãdi J., Telegdi M., Batke J., Keleti T. Functional non-identity of subunits and isolation of active dimers of D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 14;22(3):430–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. H., KOSHLAND D. E., Jr The hydrolytic activity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):986–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E., KLYBAS V., SCHRAMM M. Tetrose diphosphate, a specific inhibitor of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2510–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W. Proteolytic cleavage of bacteriophage lambda repressor in induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vijlder J. J., Slater E. C. The reaction between NAD+ and rabbit-muscle glyceraldehydephosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 27;167(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90274-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]