Abstract
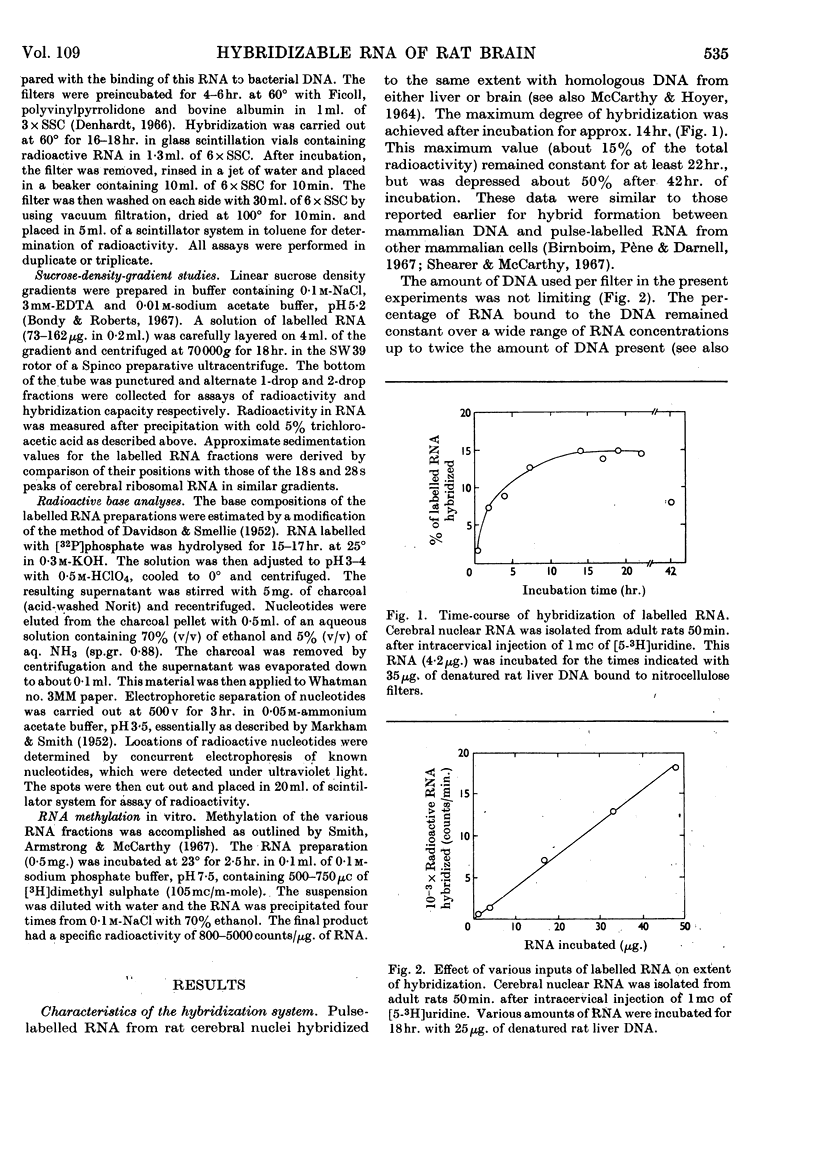
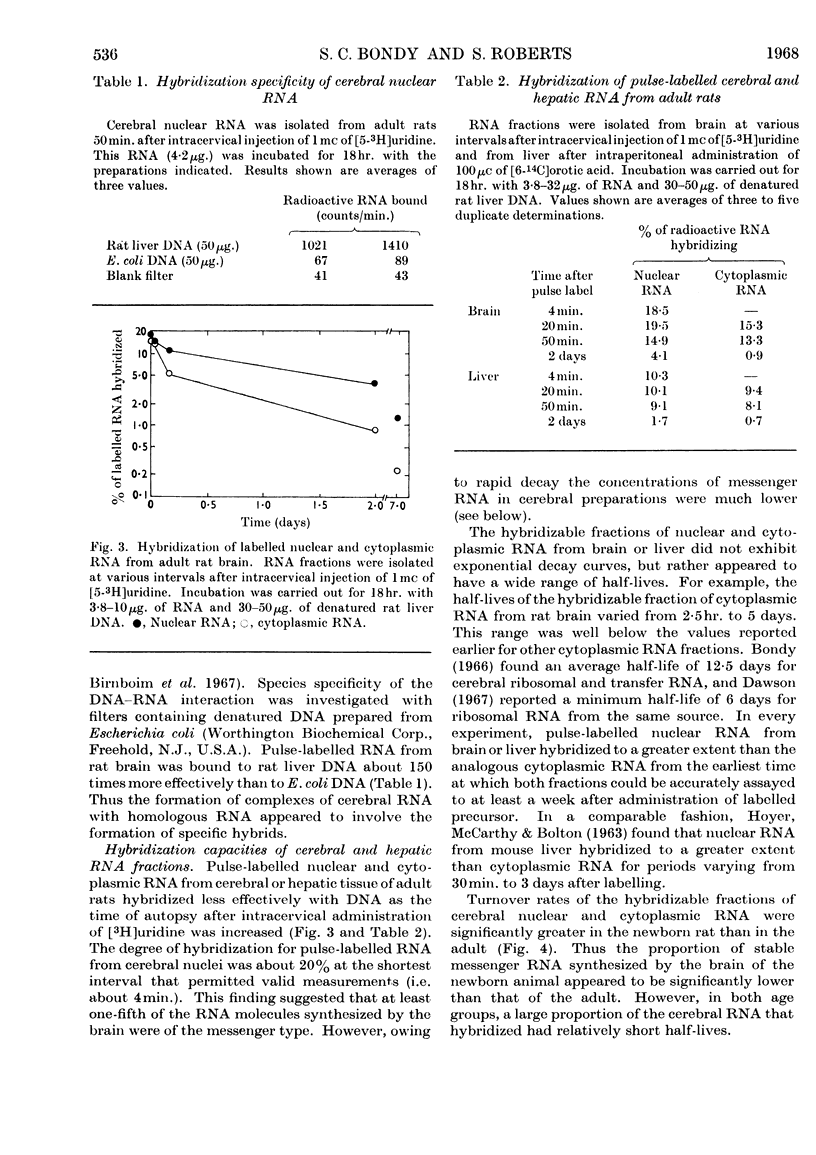
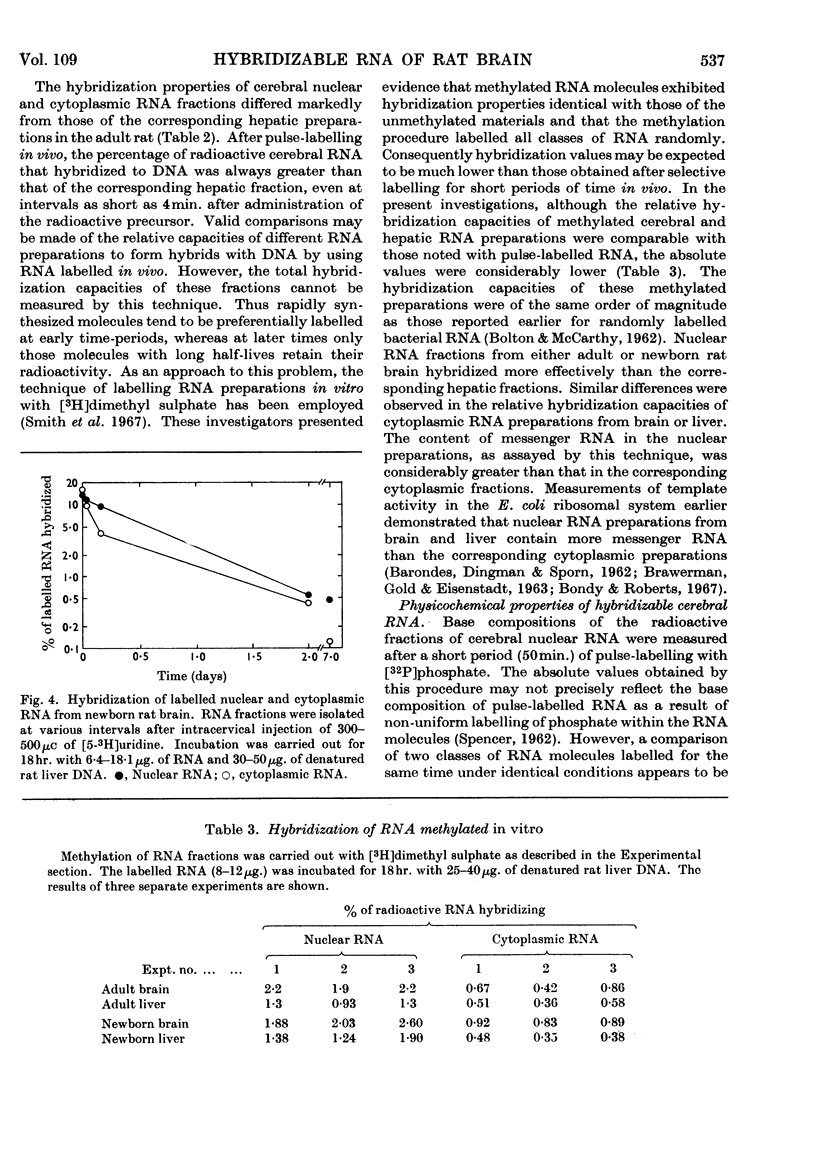
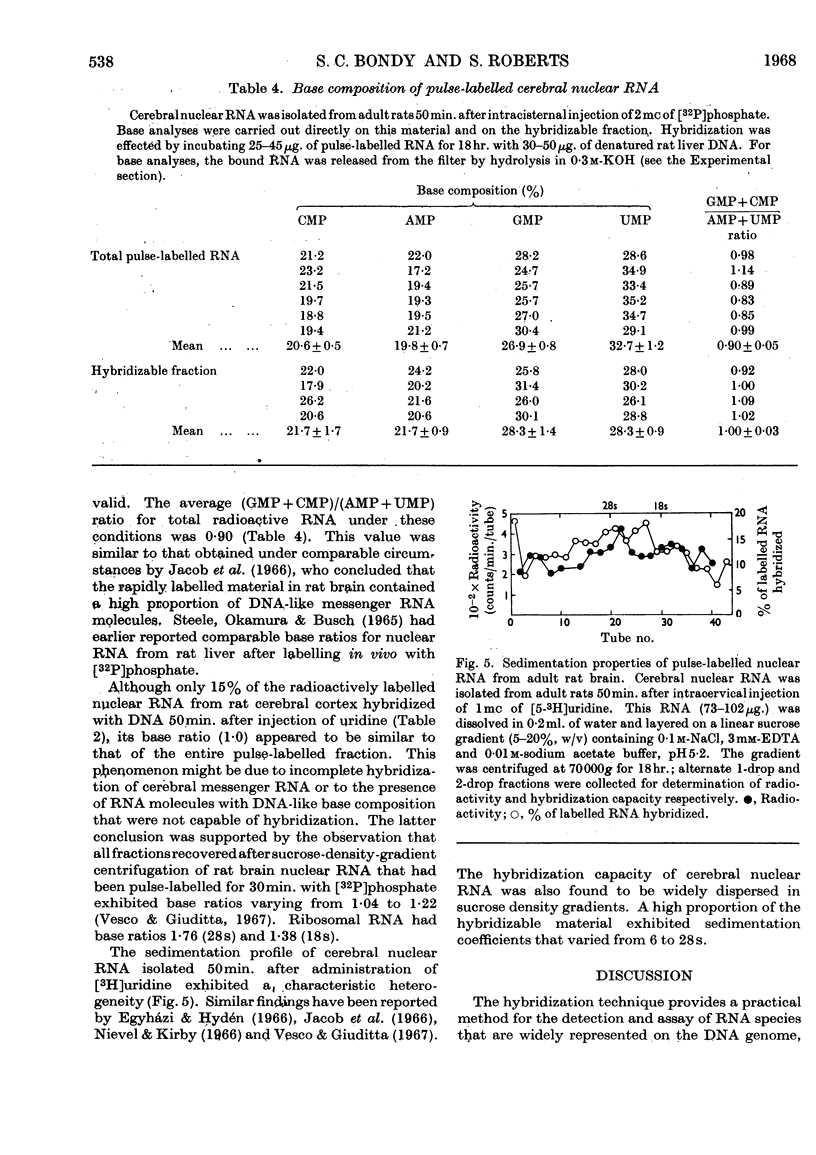
1. Cerebral RNA of adult and newborn rats was labelled in vivo by intracervical injection of [5-3H]uridine or [32P]phosphate. Hepatic RNA of similar animals was labelled by intraperitoneal administration of [6-14C]orotic acid. Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were isolated and purified by procedures involving extraction with phenol and repeated precipitation with ethanol. 2. The fraction of pulse-labelled RNA from cerebral nuclei that hybridized to homologous DNA exhibited a wide range of turnover values and was heterogeneous in sucrose density gradients. 3. Base composition of the hybridizable RNA was similar to that of the total pulse-labelled material; both were DNA-like. 4. Pulse-labelled cerebral nuclear RNA hybridized to a greater extent than cytoplasmic RNA for at least a week after administration of labelled precursor. This finding suggested that cerebral nuclei contained a hybridizable component that was not transferred to cytoplasm. 5. The rates of decay of the hybridizable fractions of cerebral nuclei and cytoplasm were faster in the newborn animal than in the adult. Presumably a larger proportion of labile messenger RNA molecules was present in the immature brain. 6. Cerebral nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA fractions from newborn or adult rats, labelled either in vivo for periods varying from 4min. to 7 days or in vitro by exposure to [3H]-dimethyl sulphate, uniformly hybridized more effectively than the corresponding hepatic preparation. These data suggested that a larger proportion of RNA synthesis was oriented towards messenger RNA formation in brain than in liver.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attardi G., Huang P. C., Kabat S. Recognition of ribosomal RNA sites in DNA. II. The HeLa cell system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):185–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi G., Parnas H., Hwang M. I., Attardi B. Giant-size rapidly labeled nuclear ribonucleic acid and cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleic acid in immature duck erythrocytes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):145–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARONDES S. H., DINGMAN C. W., SPORN M. B. In vitro stimulation of amino-acid incorporation into protein by liver nuclear RNA. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:145–147. doi: 10.1038/196145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLTON E. T., McCARTHY B. J. A general method for the isolation of RNA complementary to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1390–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAWERMAN G., GOLD L., EISENSTADT J. A RIBONUCLEIC ACID FRACTION FROM RAT LIVER WITH TEMPLATE ACTIVITY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:630–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H., Nirenberg M. W. Fate of a Synthetic Polynucleotide Directing Cell-Free Protein Synthesis I. Characteristics of Degradation. Science. 1962 Nov 16;138(3542):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3542.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Pène J. J., Darnell J. E. Studies on HeLa cell nuclear DNA-like RNA by RNA-DNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):320–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Roberts S. Messenger ribonucleic acid of cerebral nuclei. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1111–1118. doi: 10.1042/bj1051111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C. The ribonucleic acid metabolism of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Oct;13(10):955–959. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb10291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J., Widholm J. Molecular complementarity between nuclear DNA and organ-specific chromosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1379–1385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON J. N., SMELLIE R. M. S. Phosphorus compounds in the cell. II. The separation by ionophoresis on paper of the constituent nucleotides of ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):594–599. doi: 10.1042/bj0520594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. M. Turnover of ribosomal RNA in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1967 Oct;14(10):939–946. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews J., Brawerman G., Morris H. P. Nucleotide sequence homologies in nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid from rat liver and hepatomas. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Jan;3(3):284–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb19528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egyházi E., Hydén H. Biosynthesis of rapidly labeled RNA in brain cells. Life Sci. 1966 Jul;5(13):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODWIN B. C., SIZER I. W. HISTONE REGULATION OF LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE IN EMBRYONIC CHICK BRAIN TISSUE. Science. 1965 Apr 9;148(3667):242–244. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3667.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman D. L., Wicks W. D., Kenney F. T. Stimulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis by steroid hormones. II. High molecular weight components. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4420–4426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOYER B. H., McCARTHY B. J., BOLTON E. T. Complementary RNA in nucleus and cytoplasm of mouse liver cells. Science. 1963 Jun 28;140(3574):1408–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3574.1408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriman I. D., Hunter G. D. Cytoplasmic protein synthesis in mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1965 Nov;12(11):937–947. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb11937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssais J. F., Attardi G. High molecular weight nonribosomal-type nuclear RNA and cytoplasmic messenger RNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):616–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Stevenin J., Jund R., Judes C., Mandel P. Rapidly-labelled ribonucleic acids in brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):619–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H. RNA synthesis in mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1967 Jan;14(1):123–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAJTHA A., FURST S., GERSTEIN A., WAELSCH H. Amino acid and protein metabolism of the brain. I. Turnover of free and protein bound lysine in brain and other organs. J Neurochem. 1957;1(3):289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis A. G., Krsmanovic V., Errera M. A rapidly labelled RNA associated with DNA in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):577–595. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKHAM R., SMITH J. D. The structure of ribonucleic acid. I. Cyclic nucleotides produced by ribonuclease and by alkaline hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):552–557. doi: 10.1042/bj0520552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY B. J., HOYER B. H. IDENTITY OF DNA AND DIVERSITY OF MESSENGER RNA MOLECULES IN NORMAL MOUSE TISSUES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:915–922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchis-Mouren G., Cozzone A. Inhibition by actinomycin D of valine incorporation into specific proteins of rat pancreas in vivo. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3684–3690. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie H. R., Zimm B. H. Molecular weight of the DNA in the chromosomes of E. coli and B. subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1636–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Dubin D. T. RNA-DNA hybrid formation with methyl-deficient and mature ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):102–110. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell P., Smith I., Dubnau D., Marmur J. Isolation and characterization of low molecular weight ribonucleic acid species from Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):258–265. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy M. R. Protein synthesis in growing-rat tissues. II. Polyribosome concentration of brain and liver as a function of age. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 22;119(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney R. L., Davis W. W., Garren L. D. Heterogeneity of templae RNA in adrenal glands. Science. 1966 Aug 19;153(3738):896–897. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3738.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego F., Lipmann F. Protein synthesis in brain slices. Effects of electrical stimulation and acidic amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):665–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY R. P., SRINIVASAN P. R., KELLEY D. E. HYBRIDIZATION OF RAPIDLY LABELED NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEIC ACIDS. Science. 1964 Jul 31;145(3631):504–507. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3631.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL M., HIATT H. H. THE STABILITY OF LIVER MESSENGER RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:810–818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITOSSA F. M., SPIEGELMAN S. LOCALIZATION OF DNA COMPLEMENTARY TO RIBOSOMAL RNA IN THE NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGION OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:737–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K. Studies on RNA synthesis in Ehrlich ascites cells extraction and properties of labeled RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 8;108(3):474–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMARINA O. P. THE DISTRIBUTION AND PROPERTIES OF CYTOPLASMIC DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID-LIKE RIBONUCLEIC ACID (MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:688–691. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEED R. W., GOLDBERG I. H. BIOSYNTHESIS OF THYROGLOBULIN: RELATIONSHIP TO RNA-TEMPLATE AND PRECURSOR PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:275–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE W. J., OKAMURA N., BUSCH H. EFFECTS OF THIOACETAMIDE ON THE COMPOSITION AND BIOSYNTHESIS OF NUCLEOLAR AND NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1742–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K., Marcaud L., Zajdela F., London I. M., Gros F. Patterns of RNA metabolism in a differentiated cell: a rapidly labeled, unstable 60S RNA with messenger properties in duck erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1571–1578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer R. W., McCarthy B. J. Evidence for ribonucleic acid molecules restricted to the cell nucleus. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):283–289. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. D., Armstrong J. L., McCarthy B. J. The introduction of radioisotopes into RNA by methylation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 18;142(2):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Birnboim H. C., Darnell J. E. Rapidly labeled HeLa cell nuclear RNA. II. Base composition and cellular localization of a heterogeneous RNA fraction. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):362–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAKATELLIS A. C., AXELROD A. E., MONTJAR M. STUDIES ON LIVER MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4237–4244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thadjivassiliou A., Brawerman G. Template and "DNA-like" ribonucleic acids as distinct entities in a preparation from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 8;103(2):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesco C., Giuditta A. Pattern of RNA synthesis in rabbit brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 18;142(2):385–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Hoagland M. B. Physiology of rat-liver polysomes. The stability of messenger ribonucleic acid and ribosomes. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):556–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1030556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagami S., Fritz R. R., Rappoport D. A. Biochemistry of the developing rat brain. 8. Changes in the ribosomal system and nuclear RNA's. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):532–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomzely C. E., Roberts S., Brown D. M., Provost C. Cerebral protein synthesis. I. Physical properties of cerebral ribosomes and polyribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):455–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


