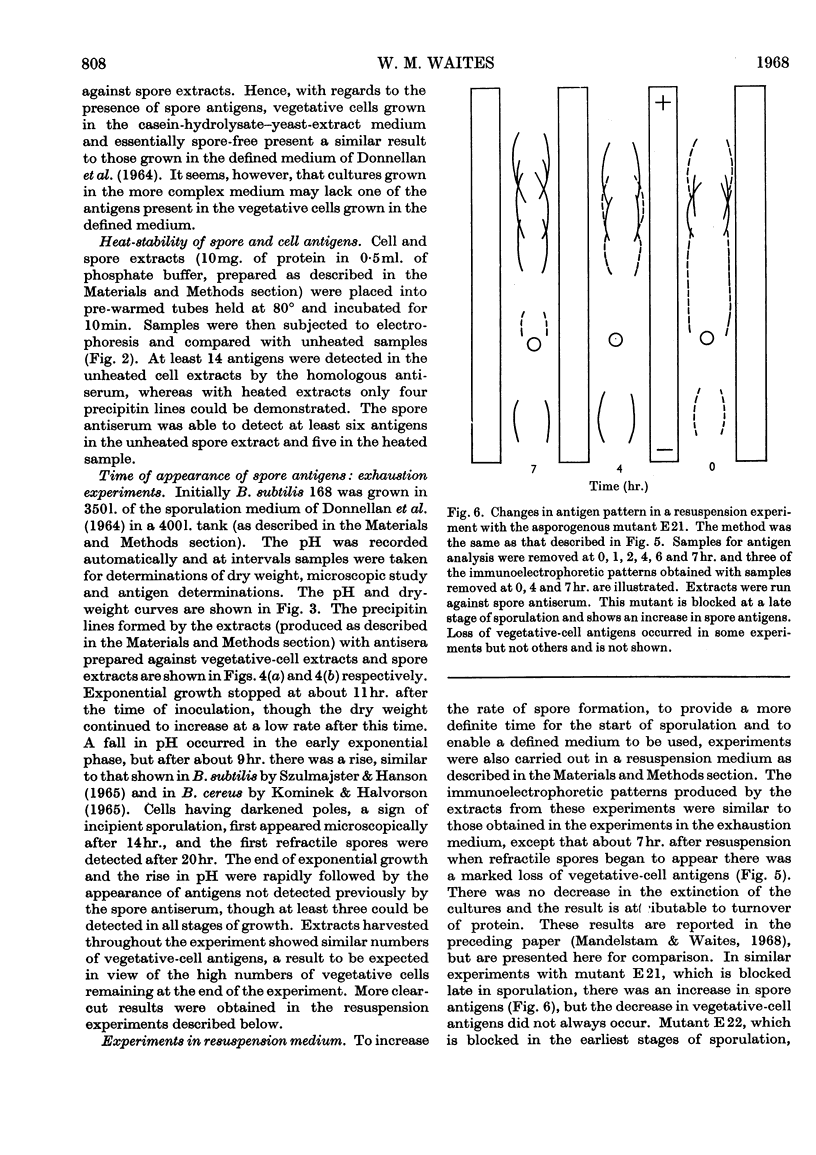
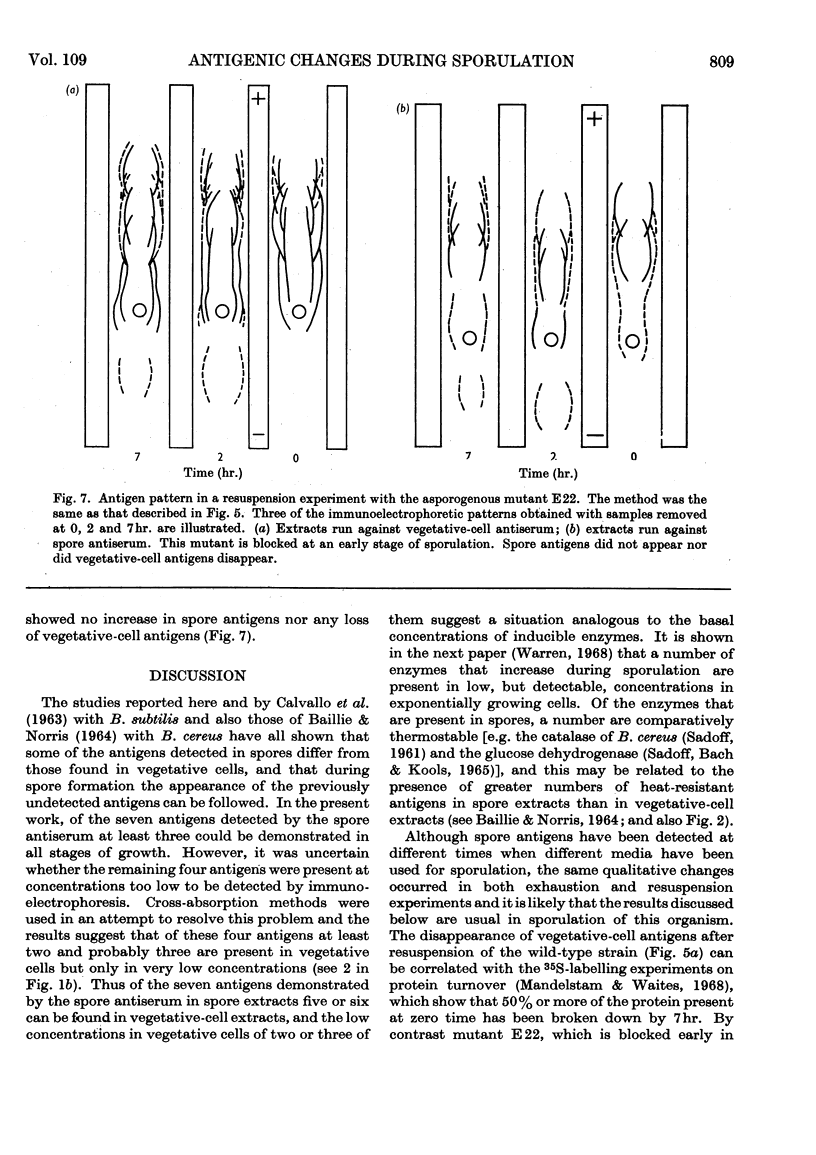
Abstract
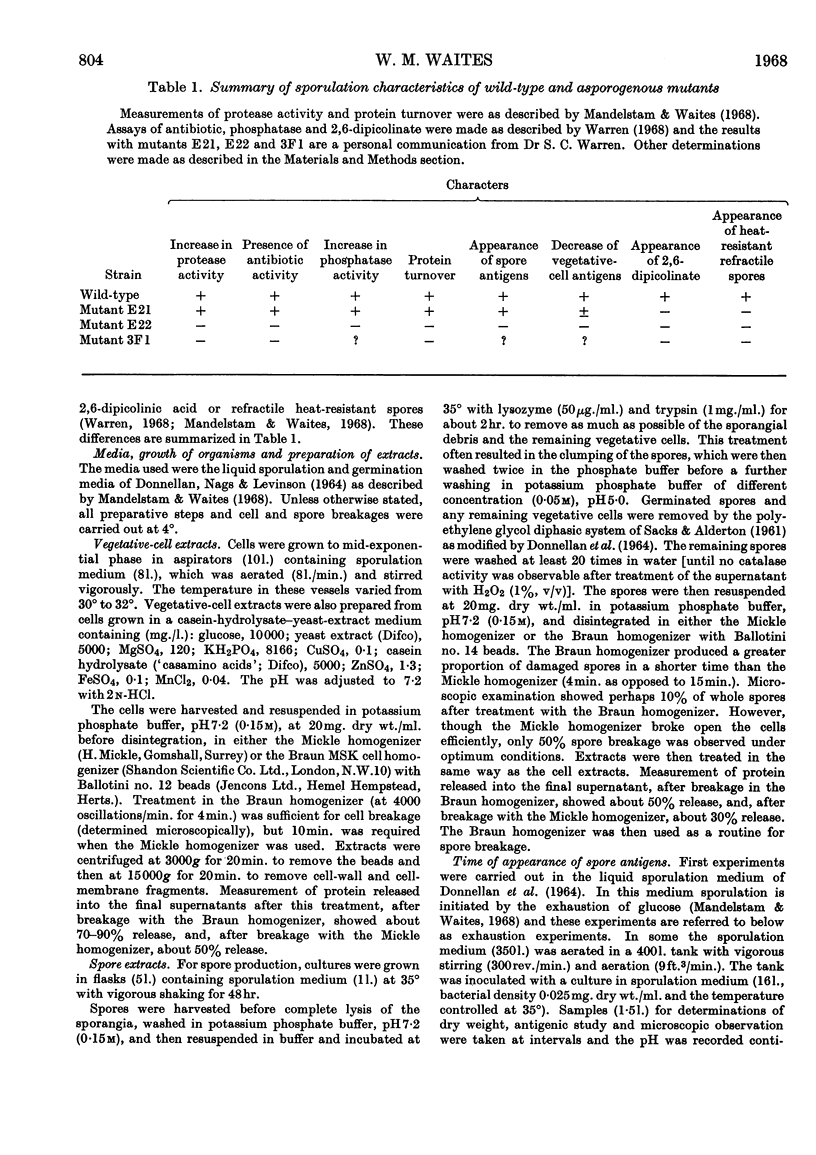
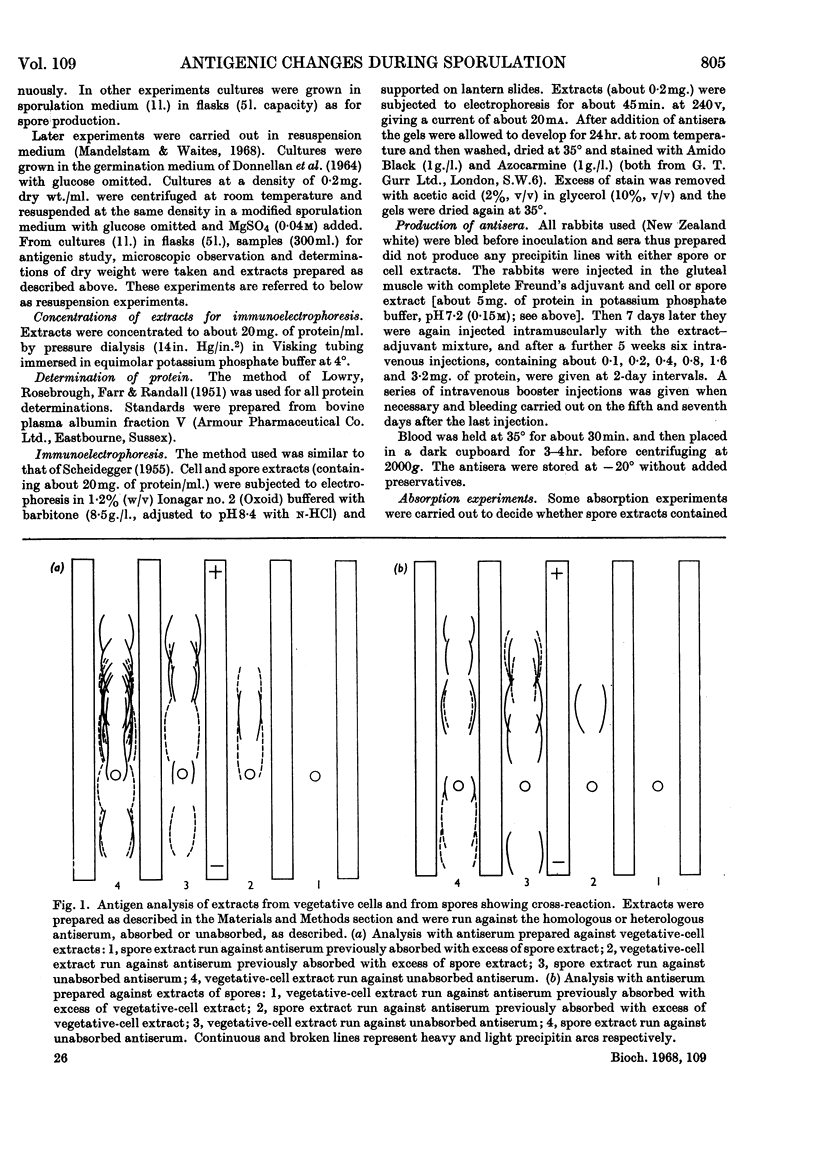
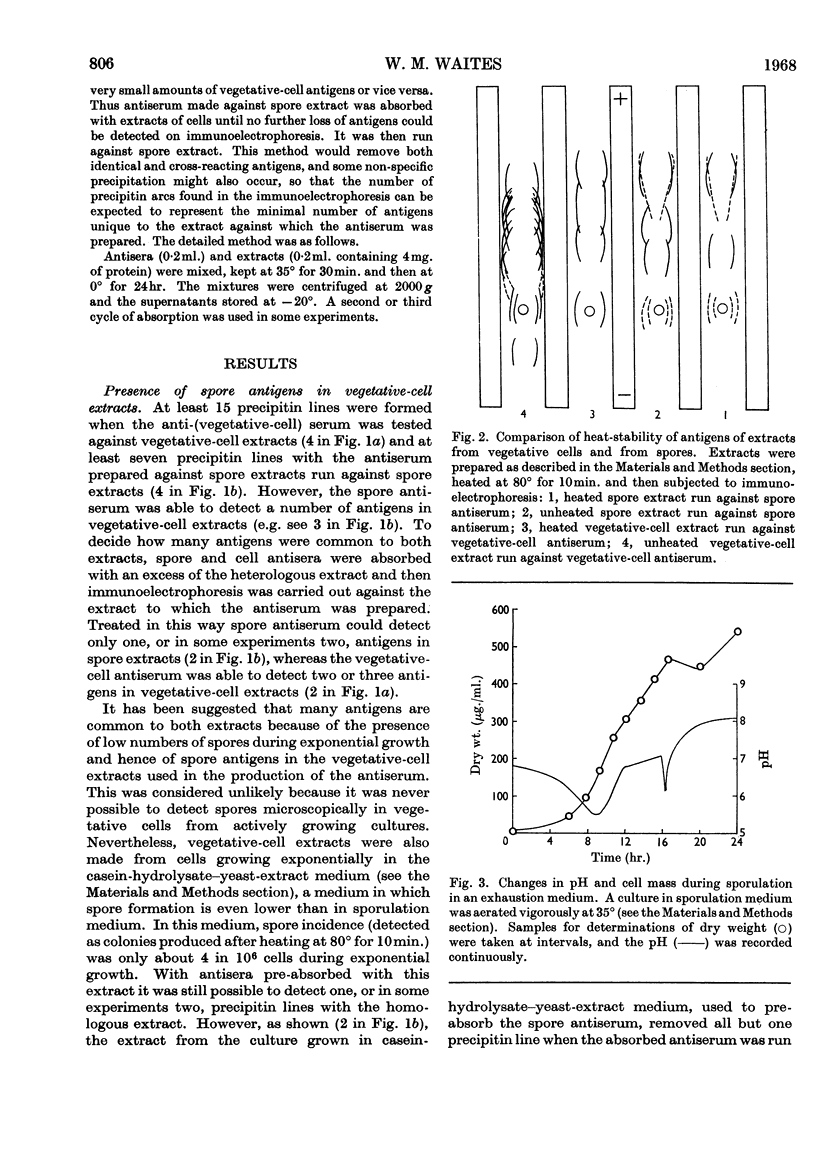
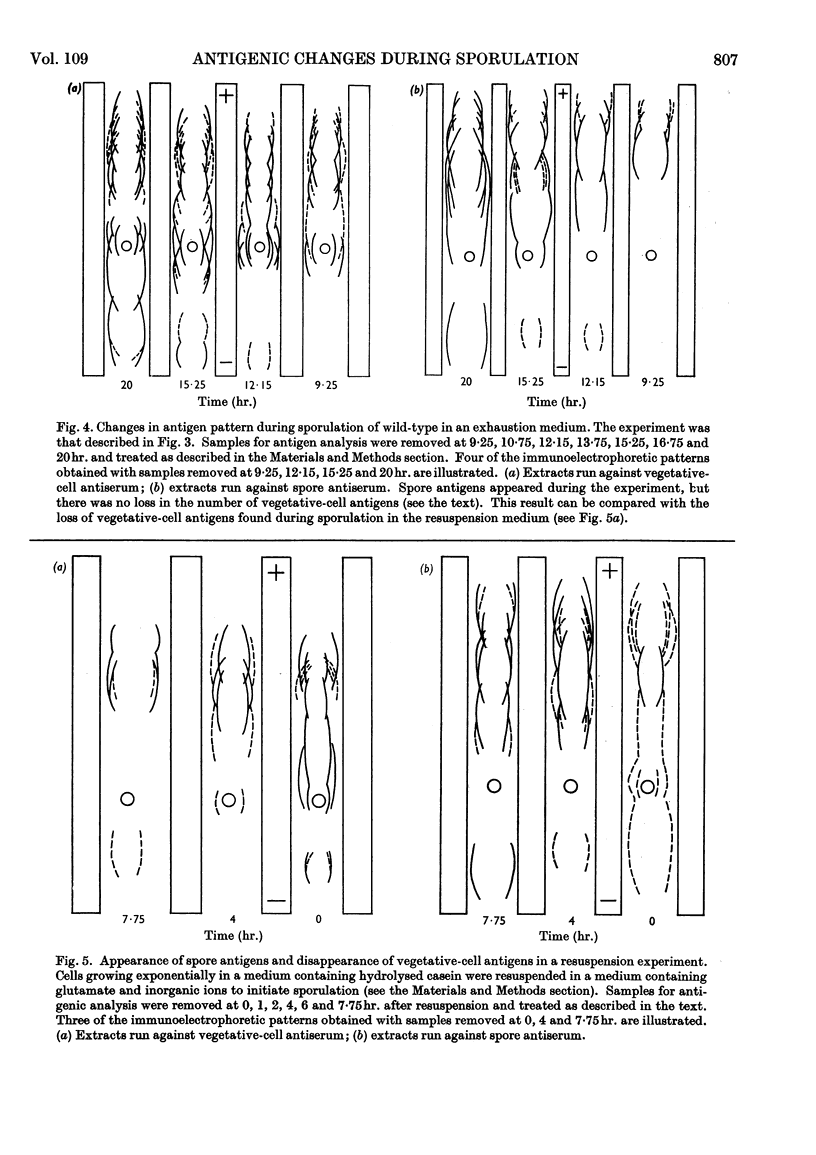
1. Antisera, prepared against extracts of cells and spores of Bacillus subtilis, were used in immunoelectrophoretic studies of the changes occurring in cell extracts during the course of spore formation. 2. At least 15 antigens could be detected in vegetative-cell extracts by the antiserum prepared against cell extracts and at least seven could be demonstrated in spore extracts by the homologous antiserum. 3. Cross-absorption studies showed that two of these antigens were probably completely specific for vegetative-cell extracts and that one was probably completely specific for spore extracts. The remainder were probably present in very small quantities in the heterologous extract. 4. In extracts of cells sporulating in an `exhaustion medium' those antigens characteristic of the spore began to appear about 1hr. after the end of exponential growth. 5. In cells sporulating in a resuspension medium, spore antigens were detected at 4hr., and by 7hr. a decrease in vegetative-cell antigens was observed. 6. In an asporogenous mutant blocked early in sporulation there was neither an increase in spore antigens nor a decrease in vegetative-cell antigens. 7. In an asporogenous mutant blocked later in sporulation, there was an increase in spore antigens similar to that which occurred in the sporogenous strain.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baillie A., Norris J. R. Antigen changes during spore formation in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1221–1226. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1221-1226.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONNELLAN J. E., Jr, NAGS E. H., LEVINSON H. S. CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIA FOR SPORULATION AND FOR GERMINATION AND GROWTH OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:332–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.332-336.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominek L. A., Halvorson H. O. Metabolism of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoin in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1251–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1251-1259.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Waites W. M. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. The role of exoprotease. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):793–801. doi: 10.1042/bj1090793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS J. R., BAILLIE A. IMMUNOLOGICAL SPECIFICITIES OF SPORE AND VEGETATIVE CELL CATALASES OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:264–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.264-265.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS J. R. Bacterial spore antigens: a review. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jul;28:393–408. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-3-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS L. E., ALDERTON G. Behavior of bacterial spores in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. J Bacteriol. 1961 Sep;82:331–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.3.331-341.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochemical changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj1090811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


